pH-metry is a diagnostic procedure, the essence of which is to measure the acidity of the environment in the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. This method is widely used in gastroenterology for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases of the digestive system, the course of which is characterized by changes in pH. Determining the acidity of the stomach at home allows you to identify the causes of a particular pathology, develop adequate tactics and monitor the progress of treatment.
pH-metry - determining the acidity of the stomach at home
Cost: from 1150 rubles
Order service
*Doctor’s visit is paid separately
Symptoms of high stomach acid levels
The main symptom of this pathological condition of the body is late pain in the pit of the stomach. They can be aching, dull, tugging and occur several hours after eating. Because of these pains, many patients have a fear of eating.
In addition, symptoms of high acidity are heartburn, sour belching, which appears after eating. Appetite usually does not change. In some cases, the patient may experience nausea and vomiting some time after eating.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) |
| Removing and deciphering the result obtained during daily pH-metry of the esophagus (within 24 hours or more, without hospitalization) | 1250 |
| Removing and deciphering the results obtained during short-term intragastric pH-metry (within 2-3 hours, without hospitalization) | 1150 |
| Removing and deciphering the result obtained during daily pH-metry of the stomach (within 24 hours or more, without hospitalization) | 1250 |
*The visit of a medical professional is paid separately
Gastritis with increased acidity of gastric juice is also manifested by intestinal colic and chronic constipation. The tongue has a characteristic appearance - it is bright red, covered with a gray-white coating, which is located closer to the center of the organ.
Diagnostics
One of the key methods for determining the acidity of the stomach is to conduct a urease breath test to identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Also, PCR and ELISA studies are performed to identify antibodies to this microorganism. Other mandatory research methods for suspected gastritis with high acidity include:
- Endoscopic examination of the stomach (gastroscopy). Using this method, the condition of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum is assessed. If necessary, during the examination, fragments of the mucous membrane are taken (biopsy).
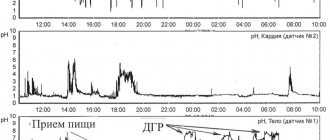
- Intragastric pH-metry. To conduct the study, a pH-metric transnasal probe is used, which is connected to an autonomous recording unit. If the pH of the gastric contents is less than 1.5 units, then the diagnosis of hyperacid gastritis is confirmed.
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs may be prescribed as an auxiliary examination method.
How to determine stomach acidity at home
Conducting esophageal and intragastric pH measurements is the main method for identifying acid-related pathologies of the digestive organs. For diagnosis, a special thin probe is used. It is painlessly inserted through the nose into the esophagus, after which it is carefully pushed into the stomach. The probe does not interfere with food intake and natural breathing. An individual disposable sterile probe is used for each patient.
Research stages:
After insertion, the end of the probe is left in the stomach or moved a little lower, to the duodenum (if indicated).
From the outside, the probe is connected to a special device (recorder), which will collect and record information throughout the day. The recorder is attached to the patient's shoulder or belt.
An electrode is placed on the collarbone, which helps to catch and record signals.
In order for the information obtained during the examination to be as objective as possible, the patient must adhere to his usual lifestyle.
After 24 hours, the probe is painlessly and easily removed, after which the patient can return home and lead a normal lifestyle.
Results are usually ready within 1-2 days. The attending physician deciphers them, makes a diagnosis and prescribes therapy.
Reasons: what causes changes in normal stomach acidity?
Normally, the level of hydrochloric acid in the stomach does not change. A sufficient number of cells producing it are compensated by substances that partially neutralize it. But if this process goes wrong, it causes the pH to change and become either high or low.
What could be causing this?
- poor nutrition;
- irregular meals;
- bad habits;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- long-term treatment with certain medications;
- frequent stress;
- emotional stress.
These factors can lead to either a decrease or an increase in pH. However, the consequences of these processes are different:
| pH level | Consequences |
| Reduced pH | Leads to the growth of bacteria in the stomach, deterioration of digestion and absorption of nutrients, the development of infectious and parasitic processes, and anemia. |
| Increased pH | Causes functional disorders, gastric bleeding, the formation of ulcers and foci of inflammation in the stomach and its vestibules. |
But before you start treating any of these conditions, you need to understand what exactly the acidity of gastric juice is and why it has changed
Cherepenko Lyudmila Vikentievna
doctor - therapist • doctor - cardiologist
The pH of the stomach can be adjusted quite easily with medication. However, you should not self-medicate, as uncontrolled use of medications can aggravate the problems. If you suspect digestive problems, be sure to consult your doctor. Our doctors will remotely help you select diagnostic procedures without making an appointment or queuing.
Online consultation
Methods for determining acidity
Today, there are several main types of acidity determination, with the help of which various diagnostic problems are solved.
1. Endoscopic pH-metry . The fastest method. It is performed during fibrogastroscopy. The procedure takes no more than 5 minutes. The specialist inserts a special probe into the endoscope channel, with the help of which the acidity level is determined at nine points of the duodenum and stomach. The study is carried out under visual control. The doctor interprets the results. It must be remembered that the endoscopy procedure itself stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
2. Express diagnostics . Takes approximately 30-40 minutes. Using this procedure, the acidity level is determined only in the body of the stomach.
3. Intragastric short-term pH-metry . During this procedure, the acidity of the stomach is studied under normal conditions, as well as when it is stimulated with special substances. The doctor analyzes the results and makes a professional conclusion.
4. Daily study . The patient is given a probe, which he wears for 24 hours while leading a normal lifestyle. He takes food in the same mode and in the same quantities as always, and also records his feelings and well-being in his health diary.
The choice of one or another technique is made by the attending physician, individually for each patient, depending on the disease, age, and characteristics of the body.
How the environment is formed in the stomach of a healthy person
The stomach is one of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. It looks like a hollow muscular organ filled with gastric juice. Food enters it from the mouth through the esophagus. The main functions of this body are as follows:
- food accumulation;
- primary digestion;
- absorption of carbohydrates, alcohols, salt and water;
- removal of metabolic products from the body;
- release of substances that promote the absorption of vitamins;
- production of substances that perform endocrine functions;
- protection against bacteria.
Gastric juice contains a variety of substances - pepsin, gastrin, histamine, chymosin, lipase, serotonin and many others. But the main and most famous of them is hydrochloric acid. It regulates many processes, for example, it is responsible for the swelling of proteins and antibacterial protection. It is its content in gastric juice that determines its acidity or pH.
Special cells of the stomach glands are responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. The rate of its production is influenced by the number of these cells, as well as the production of special substances that neutralize the acid. The pH of gastric juice depends on these factors.
Important!
Hydrochloric acid is found in gastric juice and outside the digestive process. But its concentration decreases significantly in those moments when the stomach is empty.
Indications for the study
The decision that the patient needs to check the acidity of the stomach at home is made by a gastroenterologist.
The main indications are:
- ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- Barrett's esophagus;
- various types of chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive system (duodenitis, gastritis);
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome;
- dyspepsia of various etiologies;
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease);
- monitoring the patient's health after gastric resection.
How to restore a normal environment in the stomach?
Treatment depends on which direction the deviation occurred and what reasons it was caused by. Often the pH itself returns to normal after correction of the disease and normalization of nutrition. However, if this does not happen, the patient may be prescribed medication.
In case of low acidity, drugs are prescribed that increase the pH and restore the normal composition of gastric juice. If acid levels are elevated, pH-lowering medications are used. The dosage and regimen should be determined by the doctor based on the clinical picture and tests.
But more important is non-drug help, but correction of lifestyle and diet:
| pH | Nutrition |
| At elevated pH | It is necessary to exclude everything sour, salty, spicy and fried, as well as foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice (for example, strong broths). You also need to drink more and give preference to plain still water or alkaline mineral waters. |
| At low pH | You need to eat foods that increase acidity and stimulate the production of your own hydrochloric acid. Salted mineral water and frequent small meals are recommended. |
In addition, you must give up all alcohol and smoking for the entire duration of treatment. If the change in pH is due to organic reasons, then diet and medications are prescribed for life. Recovery and treatment usually occurs at home and does not require hospitalization.
Important!
If the condition improves, it is necessary to adjust the drug treatment. Be sure to consult your doctor to change your dosage or medication schedule.
Symptoms of increased acidity
There are proven signs that indicate excess hydrochloric acid inside the stomach. If a large amount of this fluid constantly irritates the walls of the organ, the following symptoms are observed:
- a burning sensation is felt in the area of the esophagus, which may not go away for a long time;
- belching has a sour taste;
- after eating, vomiting occurs;
- severe pain periodically occurs in the stomach;
- discomfort in the stomach that occurs on an empty stomach, subsiding after eating;
- stool becomes irregular, constipation predominates;
- there is often a sour or copper taste in the mouth;
- The color of the mucous membrane of the tongue may change to bright red, in addition, a whitish coating may appear in its center.
Stomach acid has little or no effect on increased appetite or lack thereof, so such symptoms do not indicate pH imbalance. Factors that provoke and accelerate the violation of gastric acid secretion are the abuse of strong drinks and smoking. Having such bad habits and having discovered the above symptoms of imbalance, you should make an appointment with a gastroenterologist and undergo a full examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
Products of animal origin tend to provoke excessive production of hydrochloric acid. Important: a clear sign of an increase in the secretion of gastric acid is nausea and abdominal pain after taking medications that are part of the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, Diclofenac or Aspirin.
Methodology and preparation for the study
As noted above, the devices used for pH measurement are called acidogastrometers. These are flexible probes equipped with special measuring electrodes, which are inserted through the mouth or nose into certain parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
The probe is inserted exclusively in the morning, on an empty stomach. In this case, at least twelve hours must pass since the last meal. Smoking is also prohibited during this time. Please note that you can drink water for the last time no later than four hours before the procedure - otherwise the risk of complications when inserting the probe increases (the patient will feel nauseated and may vomit). In addition, water can change the acidity of the stomach, which will distort the study data, as a result of which the reliability of the results will decrease.
Before diagnosis, you should inform your doctor about what medications you are taking. Some medications should be stopped at least three days before the procedure, others should be stopped twenty-four hours before the test.
It is recommended that a few days before the procedure, you avoid taking foods that can distort the data by changing the pH of the stomach. So, it is necessary to completely exclude black coffee, strong tea, fruit juices and yoghurts from the diet, or at least reduce the presence of these products on the menu as much as possible. Alcohol and carbonated drinks, as well as mineral water, should be completely excluded.
Express and short-term pH measurements are carried out in a medical office, under the constant supervision of a doctor. The patient is in a sitting position. For these studies, oral pH probes are usually used - in other words, those that are administered through the mouth. Such probes are thicker than transnasal ones, but the risk of them getting wrapped up in the stomach is an order of magnitude less.
The most frightening thing for many patients is the daily diagnosis. Typically, people are concerned about the fact that they will not have a medical professional nearby and the probe will be inside for a long time. A qualified doctor should treat such experiences with understanding and explain to the patient in detail the essence of the procedure and his behavior during the study.
The probe for daily research is inserted through the nasopharynx, so the patient will be able to eat as usual. The recorder is attached to the belt. To make the research data more accurate and complete, the patient is asked to keep notes in a special diary. Most often, it is necessary to note the time of meals and medications, as well as indicate the periods of staying in a horizontal position. It is also necessary to record any negative sensations associated with the gastrointestinal tract - heartburn, nausea, discomfort. It is the daily diagnosis that is considered the most informative and complete and provides the maximum amount of information necessary to analyze the patient’s condition.
Signs of a decrease in pH
A prolonged lack of gastric juice leads to the fact that the vitamins and microelements that make up the food are not fully absorbed. All this leads to a deterioration in the general condition of the body. When the pH deviates downward for a long period, a person experiences the following symptoms:
Read also: Diseases of the operated stomach
- separation of the nail plates and their slow growth;
- acne;
- weight loss;
- dry skin of the face and hands (mainly on the elbows);
- hair fragility;
- decrease in hemoglobin level in the blood;
- fast fatiguability;
- rosacea on the cheeks and nose.
Important: another symptom of insufficient production of hydrochloric acid is poor absorption of iron and, as a result, iron deficiency anemia.
You can assume a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid without gastroscopy by paying attention to the following manifestations of deficiency:
What can you eat if you have high stomach acidity?
- If the pH level is insufficient for comfortable digestion, a person develops an appetite for foods that are high in acid content. Excessively sour lemons or apples do not cause disgust; in addition, heartburn or stomach pain does not occur after eating them;
- Due to poor digestion of food, a person develops bad breath, reminiscent of the smell of a rotten egg;
- The character of the stool changes. Often the patient complains of regular diarrhea. Particles of undigested foods appear in the stool due to a lack of acid;
- After a heavy meal, a dull pain occurs in the epigastric region;
- Bad-smelling belching occurs regularly;
- There is constant fermentation in the intestines. Bloating and flatulence appear;
- There is a feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium.
A person who has reduced secretion of gastric acid drinks sour vegetable and fruit juices with appetite.
General information
The stomach is the main organ involved in the digestion process. Inside it, food entering the body accumulates and is broken down. Its normal processing is ensured by gastric juice. An indicator that the stomach is functioning normally is its acidity level. This indicator refers to the concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. Its level is constant and amounts to 160 mmol/l.
If the ratio between the alkaline component and the acid changes, then we speak of a decrease or increase in acidity. When the concentration is too high, acidity increases, and, accordingly, a decrease in concentration below normal indicates low acidity. Any shift leads to a disruption in the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and causes diseases of the organs of this system.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
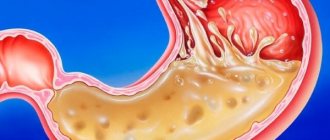
A classic companion to high acidity is a specific baking, burning sensation in the esophagus, which we call heartburn. Heartburn can be so intense that the attack ends in vomiting. Most often, heartburn is caused by the so-called. reflux, i.e. reverse reflux of stomach contents up the esophagus, which should not happen under any circumstances with normal peristalsis, secretory activity and sphincter function: the walls of the esophagus do not have the same mucous-alkaline protection against acid that the stomach is equipped with.
In addition to heartburn, almost all patients complain of heaviness, abdominal pain of various types (dull, aching, pulling, “twisting”) and with various irradiations. Painful discomfort is usually associated with eating: when the stomach is full, the acid, so to speak, finds a new field of activity, but after 1-2 hours the pain returns.
It should be understood that a violation of the acid-base balance is a guarantee of complex, multifactorial digestive disorders (dyspepsia inevitably develops: constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, appetite disorders) and, therefore, metabolism. The walls of the stomach and the duodenum closest to it, from constant contact with an aggressive acidic environment, are covered first with superficial erosions, and then with ulcers that corrode the submucosal, deeper and therefore unprotected cell layers. A special “ulcerative type” of a patient suffering from gastroduodenitis or peptic ulcer disease itself is a thin, emaciated person with unhealthy skin and problem hair, a sallow complexion, dull and ever-tired eyes, a sarcastic, doomed mood (though many of them do not consider necessary to make at least some adjustments to your lifestyle). However, if the syndrome of high acidity and the associated erosive gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, peptic ulcer continue to remain, as they say in medicine, untreated, the situation can quickly become life-threatening: massive bleeding can begin at any moment or a perforation of the walls of the stomach or intestines can occur. , which leads to peritonitis, sepsis and other deadly complications.
The diagnostic standard in modern gastroenterology is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) - examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract from the inside. For this purpose, today we use not the ever-memorable “hoses” or “rubber tubes”, which served as a nightmare for many generations of patients, but high-tech, thin, flexible and very “smart” endoscopes, interfaced with a computer, equipped with a backlit video camera and the necessary manipulators (which allows “on the spot” to select material for biopsy, deliver the necessary treatment solutions, measure the pH level in various zones, etc.). The discomfort from such a procedure today is, perhaps, more of a psychological nature than physiological: the sensitivity of the pharynx and the gag reflex are suppressed by reliable irrigating anesthetics, and the procedure itself lasts only a few minutes - but the whole “picture” from the upper parts of the esophagus to the internal space of the duodenum is displayed in high resolution, stored on disk and provides invaluable information about the real state of affairs.
If necessary, radiography, tomographic and ultrasound examinations, and a set of laboratory tests are also prescribed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
What test determines stomach acidity?
Normally, the pH in the stomach area is 1-2; the acid concentration varies in different parts of the stomach. In a hospital setting, a test is usually prescribed, during which gastric juice is collected by inserting a probe into the esophagus. Using this probe, a portion of the liquid is taken and examined. The resulting value is an average, since the acidity is measured in a specific location. It is not necessary to carry out an analysis at home to determine acidity.
One of the optimal diagnostic methods is videogastroscopy, videocolonoscopy. Videogastroscopy involves inserting a thin probe into the stomach area with a camera at the end. As a result, it will be possible to completely monitor the condition of the mucous membrane, diagnose ulcers, gastritis, or other serious pathologies.
What test determines stomach acidity:
- With this probe, it is possible to collect biological material for analysis, determine acidity and prescribe medications. It is best to contact specialists for a full examination and diagnosis if gastrointestinal diseases occur.
- After all, sometimes certain methods do not give accurate results. They do not allow us to find out why specific ailments occur.
- Videogastroscopy is a visualization method that is as accurate and informative as possible. Additionally, they may prescribe an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to identify tumors, cysts, or neoplasms.
Indicator strips