What happens when body temperature rises
The hypothalamus of the human brain works as a biological “thermostat” that responds to the effects of pyrogens - waste products and decay of pathogenic microorganisms that cause an inflammatory process. The appearance of foreign pyrogens in the human blood is regarded by the hypothalamus as a signal to increase body temperature to combat pathogens. At elevated temperatures, metabolic processes are extremely accelerated, the number and activity of immune cells, which synthesize interferon, a protein that protects the body, increases.
Warming up of the body occurs through the process of thermogenesis, in which muscles and fat layers take part. Involuntary muscle contractions, felt as trembling, are a process of tissue heating; burning fat deposits leads to the release of previously accumulated energy.
Reactive pancreatitis
Reactive pancreatitis is a reaction of the child’s pancreas to some irritants; it is not a separate disease.
Symptoms of reactive pancreatopathy may occur in a child who has recently suffered:
- ARVI
- other inflammatory diseases
- poisoning with poor quality food products,
- it may also be a reaction to a food allergy.
With reactive pancreatitis, spasm of the pancreatic ducts and swelling of the organ itself occurs.
In children under one year of age, the occurrence of reactive pancreatopathy is associated with:
- improper introduction of complementary foods;
- introduction of grape juice;
- introduction of meat products;
- introduction of seasonings before the prescribed age.
These products not only increase gas formation in the intestines, but also disrupt the functioning of the still immature pancreas.
The most common symptoms of reactive pancreatitis are:
- sharp girdling pain above the navel, which decreases in a sitting position with the torso bent forward;
- severe nausea;
- vomiting of gastric contents;
- temperature rise to 37°C, especially in the first few hours from the onset of the disease;
- stool liquefaction;
- dry mouth;
- white coating on the tongue;
- moodiness;
- irritability;
- refusal of games.
If the above symptoms appear, and especially persistent abdominal pain, you should immediately contact a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, or call an ambulance.
In addition to providing first aid, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations (ultrasound of the abdominal organs, tests). Based on the examination results, drug treatment is prescribed.
Temperature in acute pancreatitis
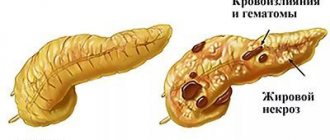
An attack of acute pancreatitis begins with the formation of edema of the pancreatic tissue, disruption of the outflow of pancreatic secretions, resulting in the process of “self-digestion” of the gland. Dead cells become a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms and bacteria. Decay products and toxins, digestive enzymes enter the bloodstream, spreading the infection throughout the body.
Is there high or low body temperature during the development of acute pancreatitis? Along with other symptoms - abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, changes in the condition of the skin, fluctuations in body temperature occur, depending on the phase of the disease and the degree of spread of the infection.
Mild (edematous) pancreatitis
In the phase of edematous pancreatitis, pathological changes have not yet reached such a destructive effect, body temperature is normal or slightly elevated. It stays at this level for one to three days. The general condition of the patient is satisfactory.
Moderate pancreatitis
At this stage of the disease, there is an active process of “self-digestion” and death of pancreatic tissue with the formation of foci of necrosis. In this phase, the patient’s condition is unsatisfactory: severe pain, debilitating vomiting, and increased heart rate. The sclera acquires a yellowish tint, the skin turns pale.
Due to the entry of digestive hormones and toxins into the blood, intoxication of the body occurs. The temperature during pancreatitis in the described phase rises to 38-39 degrees, remains for five to ten days, periodically decreasing and increasing. If complications do not begin, the patient recovers in 10-14 days.
Severe pancreatitis and complications
At this stage of the disease, total-subtotal pancreatic necrosis and purulent abscess develop, affecting parts of the pancreas, spreading to neighboring tissues and organs. Cysts, fistulas, and internal bleeding occur. Toxins, bacteria and enzymes enter the blood. Vessels are destroyed, and in advanced cases, pancreatic tissue becomes infected with intestinal microflora.
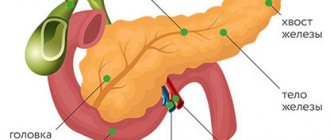
Pancreas
The described leads to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, body temperature reaches 40 degrees. There is a disorder of the body systems: renal, nervous, respiratory, cardiovascular. Spider veins and bruising appear on the skin, and symptoms of peritonitis are observed.
Reduced temperature in acute pancreatitis
Severe intoxication of the body, dehydration or excessive internal bleeding often leads to a state of vascular collapse or coma. Characteristic signs of the condition are considered to be low body temperature, a drop in blood pressure, pale skin, weak pulse, and loss of consciousness.
At this stage, delay in providing medical care leads to death.
Temperature in acute pancreatitis signals purulent-inflammatory processes occurring in the body and becomes an indicator of the severity of the disease.
Acute pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment
The symptoms of acute pancreatitis are easily confused with food poisoning, so patients do not immediately call an ambulance. But remember that if an acute attack develops, it is important to seek help as soon as possible, otherwise irreversible changes may occur in the pancreas.
What to pay attention to
:
- Cutting pain in the left hypochondrium or girdle pain
- Temperature rises to 38–39*C
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
- Chills
- Dizziness and general deterioration of health
Most often, an attack develops after alcohol abuse or after a stormy feast, heavy intake of fatty or spicy food. Acute pancreatitis cannot be treated at home! Call an ambulance, describe your symptoms and get help from specialists. In some cases, the patient is indicated for hospitalization.
A therapeutic fast is recommended for 3 days after an attack. In the future, the patient is prescribed a gentle diet, which we will discuss below.
Temperature in chronic pancreatitis
In chronic pancreatitis, degenerative processes in the pancreas continue in the absence of symptoms of the disease. Damaged tissues are not restored; the process of replacing healthy tissues with fibrous ones occurs gradually.
Chronic pancreatitis
Reasons for changes in temperature during remission
During the period of remission, a person feels practically healthy, body temperatures are normal. When exacerbations associated with the disease occur, symptoms characteristic of pancreatitis occur - pain, nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, flatulence, and body temperature rises. This indicates the appearance of inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
This situation is associated with a violation of the diet and nutrition necessary for chronic pancreatitis. Taking small doses of alcohol, eating an abundance of fatty foods, overeating, and taking medications incorrectly can cause an attack of acute pancreatitis.
What to do if signs of fever occur in chronic pancreatitis
If the thermometer reaches 38-39 degrees in the presence of other symptoms of exacerbation of the disease - sharp unbearable pain, severe bouts of vomiting, diarrhea - a dangerous situation arises, which can become the beginning of pancreatic necrosis and subsequent severe complications.
The problem cannot be ignored; urgent intervention by qualified medical personnel is required. Delay can cost the patient his life; hurry to seek emergency medical help.
Is the prolonged presence of low-grade fever dangerous?
If the temperature during pancreatitis remains at a subfebrile level for months, this becomes a warning about the occurrence of pathological inflammatory processes in the body and the development of oncology - pancreatic cancer. In such a case, you will need to undergo an examination to identify the problem in order to urgently begin treatment.
Who is at risk?
As we age, some changes occur in everyone's pancreas, but this does not necessarily lead to pancreatitis.
Among the main causes of pancreatitis it is worth noting
:
1. Alcoholism 2. Smoking 3. Frequent consumption of alcohol in large quantities (for example, weekend alcoholism) 4. Abuse of fried and fatty foods 5. Constant overeating 6. Hereditary diseases of the gastrointestinal tract 7. Abdominal injuries 8. Taking a number of medications ( be sure to check with your doctor about such risks when prescribing medications) 9. Gallstones and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (reactive pancreatitis may develop against their background) 10. Experiencing severe stress (the pancreas is one of the first to respond to stress factors) 11. Hormonal disorders in the body
Pancreatitis develops in 80% of alcoholics and smokers. Giving up bad habits can save the organ from severe forms of the disease.
What to do if your temperature rises due to pancreatitis
Temperature during pancreatitis signals a dangerous situation and worsening symptoms of the disease. An increase in temperature accompanying other symptoms of pancreatitis indicates the occurrence of an infected phase of pancreatic necrosis and other serious complications. Fever, chills, weakness, muscle pain - all these are signs of severe intoxication.
In this case, the patient should receive immediate medical assistance. He needs hospitalization and surgery. Simply bringing down the temperature is an unforgivable waste of time, and the use of painkillers before the ambulance arrives can “blur” the clinical picture. Only a doctor can prescribe medications correctly, both painkillers and antipyretics, for pancreatitis, so first aid for fever is to call an ambulance. Treatment of this disease should be under the supervision of a gastroenterologist.
Chronic pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment
Chronic pancreatitis develops somewhat differently. It does not have such striking manifestations as in the case of an acute attack - changes in the pancreas occur gradually. However, this is not a reason to ignore the symptoms:
- Heaviness in the left side, a feeling of bloating or spasm in the hypochondrium
- The appearance of a yellowish dense coating on the tongue
- Pain in the left hypochondrium 40–50 minutes after eating fried, fatty or spicy foods
- Loss of appetite
- Unreasonable weight loss
- Abnormal bowel movements - diarrhea or constipation
- Changes in stool - the appearance of an unpleasant odor, fat droplets in the composition
Any type of pancreatitis is treated by a gastroenterologist. It is important to contact a professional as soon as you notice symptoms, because the further development of the disease depends on this.
First of all, the disease is treated with a gentle diet (table No. 5), cessation of smoking and alcohol, the prescription of omeprazole, reducing drugs and enzymes that compensate for their insufficient production by the pancreas. Often in patients, periods of remission are followed by relapses, but this can be avoided if you listen to your doctor and try not to violate the rules of nutrition for pancreatitis.