As a rule, in the presence of a pathological process in the digestive system, the patient must take several types of medications, some of which eliminate symptoms, others have a therapeutic effect. For example, in case of inflammation of the stomach tissue, it is necessary to take medications that will protect the organ from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid, agents that normalize the digestive process, as well as medications that will eliminate the cause of inflammation.
Thus, the list of pills that need to be taken daily is impressive. Many of the medications irritate the mucous membrane, therefore, as part of complex therapy or for prevention, enveloping agents for the stomach and intestines are prescribed. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) are manifested by abdominal and dyspeptic syndrome.
To eliminate severe pain, non-narcotic analgesics are used, and after the condition improves, they switch to antispasmodics. Enzyme preparations, antacids, enveloping agents, and antifoam agents help relieve dyspepsia. Medicines to restore gastrointestinal functions should be prescribed by a doctor, since only a specialist can develop the correct treatment regimen, select the best remedy, determine the dosage of the drug and, if necessary, adjust it.
What medications can relieve abdominal pain?
To relieve pain, analgesics or antispasmodics are most often used. Depending on the nature of the pathological process, the use of enzyme preparations, agents that reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, defoamers, sorbents or choleretic agents may be required. Of the analgesics, the most popular drugs are Analgin, Paracetamol and products based on them.
Analgin (metamizole sodium) has an analgesic, antipyretic and slightly anti-inflammatory effect. The active substance inhibits cyclooxygenases, reduces the production of endoperoxides, prostaglandins, bradykinins, free radicals, interferes with the conduction of impulses and reduces the sensitivity of areas of the brain that perceive a painful stimulus.
The drug begins to act 20–40 minutes after administration, the maximum effect appears after 2 hours.
Analgin is used for acute pain after injury or surgery, for colic, and at high temperatures. The drug is prescribed depending on the severity of the pain syndrome and individual sensitivity to it. For children 10–14 years old, a single dose of 8–14 mg/kg is recommended; adults can take up to 1000 mg (2 Analgin tablets) at a time. The maximum simultaneous dose can be taken no more than 4 times a day.
Metamizole sodium is the active ingredient in the following drugs: Analgin-Ultra, Spazdolzin for children, Baralgin M, Spazmalgon, Bral, Bralangin, Spazgan, Plenalgin. Paracetamol is available in syrup, tablets, suppositories, and solution for infusion. It is prescribed to eliminate moderate pain and febrile syndrome in acute infectious and infectious-inflammatory diseases.
Paracetamol tablets are contraindicated in children under 6 years of age.
To take the analgesic, adults, elderly people and adolescents over 12 years of age are prescribed 1-2 tablets if the dosage of the tablet is 500 mg, or 2.5-5 tablets if the dose is 200 mg, with an interval of 4 hours. The maximum daily dose is 4000 mg. Children 6–12 years old are given 1 tablet (200 mg) or half a tablet with a dosage of 500 mg. For children, the daily dose should not exceed 2000 mg.
Paracetamol syrup can be prescribed to children over 2 years of age. Give 5-10 ml of syrup to children aged 2-6 years, children 6-12 years old 10-20 ml of medicine, and adults and adolescents - 20-40 ml. You can take the product once every four hours. If paracetamol is used as an antipyretic, then the maximum duration of therapy is 3 days, and if as an analgesic, then no more than 5 days.
Paracetamol is contained in the following drugs: No-shpalgin, Brustan, Ibuklin, Citramol P, Panoxen, Pentalgin, Rinza, Coldrex, Fervex.
Among antispasmodics, drugs based on drotoverine and papaverine are most often recommended. They have a similar mechanism of action: they relax smooth muscles and dilate blood vessels, which normalizes pressure in the internal organs and clears away stagnant secretions or feces. Antispasmodics are recommended for spasms of the abdominal organs, urinary tract, and spasms of peripheral vessels.
Papaverine is not prescribed to babies under 6 months of age. The product is available in the form of a solution, suppositories and tablets of 40 and 10 mg. Adults are advised to drink 40–60 mg 3 or 4 times a day, children from 6 months to 2 years are given half a tablet (5 mg), children 3–4 years old are recommended to take Papaverine 5–10 mg, and children 5–6 years old A small 10 mg tablet is prescribed.
Contraindication to the use of Drotaverine is children under one year of age. Adults are prescribed 1–2 tablets (dosage 40–80 mg) three times a day, children 1–6 years old, a quarter or half a tablet, children 6–12 years old, half a tablet (20 mg) 2 or 3 times a day.
Myotropic antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa) are used for increased gastric motility and “stomach colic”
List of antispasmodics: No-shpa, Avisan, Spasmocystenal, Bendazole, Duspatalin, Plantex, Spazoverin, Platyfillin. Among the homeopathic remedies, Spascuprel, Nux vomica gomaccord, and Gastrikumel have an antispasmodic effect.
How to normalize the acidity of gastric juice
Hydrochloric acid promotes digestion, has a bacterial effect, triggers the synthesis of hormones that stimulate the secretion of bile, intestinal and pancreatic juice. If too much hydrochloric acid is produced, the walls of the stomach become inflamed, heartburn, sour belching, and digestive disorders appear.
It is also necessary to reduce the acidity of gastric juice to ensure functional rest of the pancreas or gall bladder. To neutralize hydrochloric acid, you need to take antacids. Drugs from this group are divided into absorbable and non-absorbable.
The former penetrate the bloodstream and begin to act within 3-5 minutes, the latter are not absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract and reduce the acid level after half an hour. Both of them last no more than 4 hours. A representative of absorbable antacids is Rennie. It contains calcium and magnesium carbonate, which contribute to the rapid neutralization of hydrochloric acid and thereby have a protective effect.
Indications for use are heartburn, belching, periodic stomach pain, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen, flatulence, and dyspepsia. The medication is prescribed for adults and adolescents over 12 years of age, 1–2 tablets (they need to be chewed). You can take a maximum of 16 tablets per day.
What to do if your stomach hurts from antibiotics?
Absorbable antacids also include Vikalin and Vikair. Non-absorbable antacids are considered safer because they do not penetrate the bloodstream and do not affect internal organs.
Names of drugs from this group: Maalox, Almagel, Gastal, Phosphalugel, Gastratsid, Relzer. Some antacids contain additional components that are designed to protect the gastric mucosa, relieve pain, or remove air bubbles.
For example, Almagel Neo contains aluminum hydroskid, magnesium hydroxide, simethicone. The drug is prescribed for diseases that occur with increased or normal acidity of gastric juice and with excessive gas formation in the intestines.
Depending on the type of pathology, 1 or 2 sachets of the drug are prescribed four times a day, an hour after meals. The daily dosage is up to 6 sachets, in this quantity you can take the product for no more than a month. In the complex therapy of acid-related diseases, longer-acting agents are used than antacids. These are H2-histamine receptor inhibitors and proton pump inhibitors.
After taking Almagel Neo, it is not advisable to drink or eat for half an hour
Histamine H2 receptor blockers are divided into 3 generations. The first includes Cimetidine (Histodil, Tagamet), which needs to be taken 3-4 times a day, but it has antiandrogenic activity (suppresses the level of male sex hormones).
Ranitidine (Gistac, Zantac, Zantin, Ranisan) belongs to the second generation; it should be taken 1-2 times a day. It has fewer contraindications and side effects. The most advanced drugs from this group are based on famotidine (Kvamatel, Famocid, Famo, Ulfamid).
Famotidine is available in tablets of 20 and 40 mg. It suppresses the basal production of hydrochloric acid and does not allow histamine, gastrin and acetylcholine to stimulate the production of a new portion of acid. The drug increases the stability of the gastric mucosa, as it increases the formation of protective mucus, the secretion of bicarbonates, and indirectly the drug accelerates tissue regeneration.
After using the medication, the effect is noticeable within an hour and reaches a maximum after three hours. Depending on the severity of the pathology, 1–2 tablets are prescribed 1 or 2 times a day. Proton pump inhibitors suppress the production of hydrochloric acid for a long time. This group of drugs includes capsules Omeprazole (Omez, Zerotsid, Losek, Omegast), Lansoprazole (Lansocap, Lancerol), Rabeprazole (Pariet). They need to be taken once a day.
How to determine the need for treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers
Destruction of the integrity of the mucous membrane is an ulcer
An ulcer is a destruction of the mucous membrane, exposing the underlying layers of the wall of the stomach or intestines. Since the history of the appearance of such pathology in the stomach and intestines has much in common, the same medications are used for stomach and duodenal ulcers.
With the development of a peptic ulcer, a sharp pain is felt “in the pit of the stomach”; these pains can be acute, or similar to “hunger pains”. They appear 2-3 hours after eating, accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region. Bloating, belching, flatulence, and complete lack of appetite are constant companions of this disease.
With such symptoms, you should urgently consult a gastroenterologist, surgeon, or therapist. The specialist will conduct a gastroscopy, laboratory tests to clarify the diagnosis, and prescribe medications for stomach and duodenal ulcers.
It is extremely dangerous to self-medicate, following information received from friends and acquaintances, as well as rely entirely only on traditional medicine methods. A gastroenterologist currently has more than 500 modern medications in his arsenal, which can be selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
How to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa
Enveloping drugs, interacting with water, form colloidal solutions that protect the mucous tissues of the esophagus, stomach and intestines from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid and enzymes. These funds participate in the normalization of the gastrointestinal tract, as they allow the mucous membrane to recover. For the symptomatic treatment of heartburn and pain due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, the following medications may be prescribed.
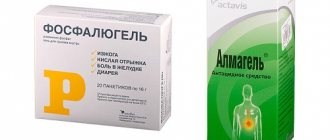
Phosphalugel
Reduces the level of hydrochloric acid, has enveloping and adsorbing properties, reduces the aggressiveness of pepsin, binds bile acids. The active substance captures only excess acid, which is due to its buffering properties, while maintaining conditions for normal digestion.
Hydrochloric acid levels change within 30 minutes after taking the product. By stimulating the synthesis of prostaglandins, they increase the secretion of mucus and bicarbonates, which protect the stomach tissue. The medicine is not prescribed to children under 12 years of age. It is recommended to use 1-2 sachets of Phosphalugel 2 or 3 times a day after meals or when heartburn or pain occurs.
Almagel
Contains aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide. It has an antacid, enveloping, adsorbing effect. Protects stomach tissues, protects them from inflammatory and erosive lesions. The effect after administration appears within 3–5 minutes. The action lasts for three hours (until the stomach is empty).
The drug is prescribed as part of complex therapy for acid-related diseases, as well as to reduce stomach irritation during drug treatment. To prevent the inflammatory process, 5–15 ml of suspension is prescribed 15 minutes before taking medications.
For therapeutic purposes, adults and adolescents over 15 years of age take the medicine 5–10 ml of liquid 3 or 4 times a day 60 minutes before meals or at night; children 10–15 years old are prescribed 5 ml. After achieving the desired effect, the dosage is reduced, but use continues for 15–20 days.
Vikair
This is a combined drug that has an antacid, antispasmodic, enveloping effect. The bismuth nitrate included in its composition forms a protective film on the gastric mucosa, thereby providing anti-inflammatory, bactericidal and reparative effects.
The medicine also contains calamus (relaxes the muscles) and buckthorn (provides a laxative effect), therefore the passage of feces through the intestines improves. The drug is taken 1–1.5 hours after a meal, 1–2 tablets, frequency of administration – 3 times a day, duration – 30–60 days.
Venter
Contains sucralfate, which has an antiulcer effect. By interacting with the proteins of the affected tissue at the site of erosion or ulcer, the product forms a protective layer that for a long time protects the necrotic area from the aggressive effects of acid and enzymes. The medicine inhibits the activity of pepsin. For the prevention of peptic ulcers, 1 tablet is prescribed twice a day; in case of exacerbation of an ulcer, 1 tablet is prescribed four times a day, half an hour to an hour before meals.
Duration of treatment with Venter – 4–6 weeks
Aluminum hydroxide
It is an antacid and has adsorbing and enveloping properties. Neutralizes free hydrochloric acid without causing its secondary hypersecretion. Raises the pH of gastric juice to 3.5–4.5 and maintains it at this level for several hours.
For prophylactic purposes, take 5–10 ml of the suspension before taking aggressive drugs (medicines, alcohol). The drug is prescribed 0.6–1.2 g (in the form of chewable tablets) or 5–10 ml of suspension 1–2 hours after meals. Duration of therapy – from 6 weeks.
De-Nol
The active ingredient is bismuth. After taking the drug, a film forms on the walls of the stomach, which protects the tissues from aggressive substances. In addition, the medicine increases the synthesis of prostaglandin and stimulates the production of mucus and bicarbonates. De-Nol also has a bactericidal effect against Helicobacter.
It is recommended to take 1 tablet 4 times a day half an hour before meals or at night for 4-8 weeks. Folk remedies can also be used to restore the mucosa. Decoctions and infusions are made from medicinal plants (oats, comfrey, licorice root, flaxseeds), white clay, and starch.
Medicines for the stomach and intestines have a number of contraindications and, with long-term use, can cause unwanted side effects. Therefore, before treating the digestive tract with medications, you need to consult a specialist and find out the cause of the pathological process.
Antibacterial agents against Helicobacter pylori
One of the tests prescribed by your doctor may be a blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. And this is not accidental, since according to data from various sources, it is this bacterium that is resistant to hydrochloric acid that in the vast majority of cases is the cause of peptic ulcer disease.
Medicines for stomach and duodenal ulcers: De-Nol
If this bacterium is not eliminated, regardless of the effectiveness of the drugs used to treat the ulcer, the risk of relapse of the disease and a decrease in periods of remission are very high. There are several treatment regimens for such bacterial infection, the main drugs in which are antibiotics of the nitroimiazoline group - Tinidazole, Metronidazole, Tetracycline.
Since these drugs have been on the drug market for a long time, their effectiveness is increasingly being questioned. This is due to the increased resistance of bacterial strains to this group of antibiotics. They were replaced by more modern antibiotics from the macrolide group. They have many advantages, and significantly fewer side effects and contraindications.
We must not forget about the extremely aggressive environment in which antibiotics have to “work” in the gastrointestinal tract. They must resist the effects of hydrochloric acid, the production of which increases significantly during peptic ulcer disease. The most stable antibiotic in this group is Clarithromycin. It is used in combination with other drugs in a dosage of 0.5 g twice a day.