Infectious disease specialist
Sinitsyn
Olga Valentinovna
34 years of experience
Highest qualification category of infectious disease doctor
Make an appointment
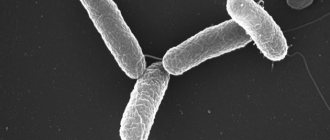
Salmonellosis is damage to the human digestive system by a bacterial infection of the Salmonella genus. Infected patients experience extensive intoxication, severe dehydration, or severe septicemia. The pathogen is often found in chicken eggs, dairy products and ready-to-eat meat products.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The Salmonella bacterium, the causative agent of salmonellosis, is resistant to aggressive environmental conditions. Microorganisms remain viable in water for several months, and can remain in soil for up to 1.5 years. Thermal processing of food is the most reliable way to combat pathogens. Bacteria die at a temperature of 70°C for 10 minutes.
The transmission routes for salmonellosis are typical - the fecal-oral mechanism is involved. In an urban environment, the airborne dust method of infection is added to it. Livestock, poultry, and wild animals remain carriers of pathogens. Bacteria penetrate the victim’s circulatory system and actively multiply in organs and tissues. Human infection occurs when caring for sick individuals or consuming contaminated products.
A person is susceptible to salmonellosis - the symptoms and severity of damage to the digestive system depend on the number of pathogens that have entered the body and the state of the immune system of the child or adult. Bacterial infections are most severely affected by infants and the elderly. Immunity to salmonellosis remains unstable and lasts no more than 12 months.
How to prevent infection
The causes of salmonellosis infection are varied and multivariate. Most outbreaks occur in summer and spring. Bacteria actively multiply in hot weather, which is when food storage rules are violated. Infection is possible under the following conditions:
- insufficient heat treatment of meat;
- improper storage of products, namely dairy and meat;
- consumption of raw milk and products containing raw eggs;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules when in contact with a carrier of the disease.
You can protect yourself and others from acute intestinal infection caused by salmonella by following a number of recommendations. In particular, it is necessary to purchase meat products only from trusted retail outlets. It is important to follow the technology for preparing dishes from those products that most often contain salmonella.
Meat and eggs must be thoroughly cooked. Only in this case can the causative agent of salmonellosis be destroyed. You cannot swim in bodies of water in which birds swim or from which cattle drink water. All rules regarding food storage must be followed. If signs of salmonellosis appear, you should immediately contact a medical facility. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of toxic-infectious shock.
Symptoms
The symptoms of salmonellosis in adults and children are identical. The incubation period lasts from several hours to 2 days. The most common form of infection remains the gastroenteric type. It is characterized by impaired water-salt metabolism and extensive intoxication. The body temperature rises sharply, severe pain, heaviness in the head, and weakness appear.
Stool upset due to salmonellosis is one of the main symptoms. The stool becomes watery, foamy and extremely foul-smelling. Defecation is accompanied by the urge to vomit.
The patient's skin is pale. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue are dried out and covered with a white coating. Children experience bloating. Palpation causes moderate pain. The heart rate is higher than the age norm.
Are you experiencing symptoms of salmonellosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Which form of salmonellosis is the most dangerous?
In 80-90% of cases, the gastrointestinal (gastrointestinal) form occurs. It combines the symptoms of gastrointestinal damage and general intoxication described above. In older children with good immunity, a more smoothed gastric picture occurs, in which chills, nausea and vomiting begin abruptly, but they pass in 2-3 days, and the stool does not change at all. Recovery usually occurs quickly.
Enteritis and gastroenteritis forms more often develop in young children suffering from rickets or anemia. At the same time, the baby's temperature rises, usually within 38 ℃, the stool becomes greenish, liquid and foamy, with an unpleasant odor, lethargy appears, and appetite decreases. Enlargement of the spleen and liver is periodically noted, and jaundice is possible.
The colitis form is accompanied by changes indicating that the large intestine is affected. The stool is frequent, liquid, swamp-green, mixed with mucus or blood. Enterocolitis or gastroenterocolitis is also possible - this means that the pathological process has affected the entire digestive tract. All this is accompanied by infrequent but severe vomiting, and wave-like attacks of fever are observed.
In the typhus-like form, the temperature may drop and rise in waves, thus lasting for 2 weeks or longer. Stools can vary from loose, frequent, green to normal and even constipation. In the first days, the symptoms coincide with the gastrointestinal variety, but later headache, weakness, and sometimes hallucinations come to the fore. The liver and spleen increase in size. Sometimes a rash appears on the skin, most often on the stomach and chest.
The septic form is the most rare, but it is also the most dangerous - it is diagnosed when the pathogen spreads through the bloodstream to all organs and secondary foci of inflammation arise. As a rule, newborns and weakened children are susceptible to it. It is characterized by sudden changes in temperature, the patient's liver and spleen increase in size, a decreased heart rate is noted, and thrombohemorrhagic syndrome develops. Metastatic purulent foci appear in different organs of the body. General intoxication is very pronounced, the skin is pale.
The subclinical, or latent form, when symptoms are absent or mild, is diagnosed mainly in children over 5 years of age. As a rule, it is detected by chance, when taking tests from contact persons of a patient with more severe symptoms.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures involve collection and microscopy of vomit and feces after bacterial culture. Laboratory tests can detect the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the patient’s biological materials. If a generalized form of salmonellosis is suspected, a blood test is performed.
Laboratory tests allow doctors to determine the degree of dehydration of the patient’s body, blood viscosity, and electrolyte balance. These data are necessary to formulate an effective strategy for the treatment of salmonellosis. In case of complicated infection, consultation with a cardiologist, nephrologist, urologist and doctors of other specializations may be required.
List of sources
- Kilesso, V.A. Salmonellosis / V.A. Kilesso // Guide to the epidemiology of infectious diseases. M., 1993. T. 2 - P. 14 - 28.
- Rakhmanin, S.P. Epizootic condition and measures to combat salmonellosis / S.P. Rakhmanin, AB Kulikovsky // Veterinary medicine. -1990.-No. 7.-S. 40-44.
- Salmonellosis / V. I. Pokrovsky, N. D. Yushchuk // Great Soviet Encyclopedia: [in 30 volumes] / ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978.
- Solodovnikov, Yu.P. Modern methodology of sanitary and epidemiological surveillance of intestinal infections / Yu.P. Solodovnikov, TH Berglezova, AA Temkina, etc. // Journal. microbiol., epidemiol. and immunobiol. 2002. - No. 4. - P. 103 - 108.
Therapeutic measures
Patients suffering from severe salmonellosis or complications must be hospitalized. Adults and children experiencing mild infection are treated at home.
The basic procedure is washing the stomach and intestines of an infected person, the so-called. "siphon enemas". The next stage of treatment for salmonellosis is restoring the balance of electrolytes in the patient’s body and correcting the water-salt balance. Dehydration is eliminated by frequent (but not copious) ingestion of saline solution orally. For severe dehydration, intravenous infusion therapy is performed, which includes polyionic solutions.
Antibacterial therapy is indicated for patients with a generalized form of salmonellosis. Doctors prescribe drugs from the fluoroquinolone group. Gastrointestinal forms of infection require the use of antibiotics if the pathogen is not susceptible to other drugs. With the standard treatment regimen, patients are prescribed enzymes (pancreatin, dry bile). During acute attacks of salmonellosis, clinical recommendations provide for diet No. 4. After eliminating the intestinal manifestations of the infection, the patient can switch to diet No. 13.
Treatment with folk remedies
Almost every thematic forum contains recommendations on the treatment of salmonellosis using folk remedies. But every patient must understand that such methods can only be used as aids for mild salmonellosis. But even in this case, the use of any folk remedy must be agreed with a doctor. The following methods can be used:
- Calendula and chamomile . You can make an infusion from these flowers separately or use them together. To prepare it you need 1 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw material, leave for about half an hour and drink half a glass of the product before meals.
- Walnut . The product made from walnut partitions has an astringent effect. To prepare it, partitions of 200 g of nuts need to be poured with 1 glass of alcohol and left for 3 days. Take 3 times a day, dropping 10 drops onto water.
- Burnet . A decoction is prepared from the crushed roots of this plant. 1 tbsp. l. raw materials need to be poured with 1 glass of boiling water, then boil for another half hour. After straining, drink 1 tbsp. l. during the day.
- Plantain . 1 tsp. crushed dry leaves should be poured with boiling water (1 cup). After 10 minutes, strain and drink in small sips over an hour.
- Oak bark . 1 tsp. means pour 1 tbsp. water and boil for a few minutes. Drink a third of a glass three times a day.
- First collection of herbs . To prepare it, take three parts each of burnet and marshmallow roots, bird cherry fruits and knotweed grass, four parts of oak bark, one eucalyptus leaf, two coltsfoot and calendula flowers. Grind all components thoroughly and mix. 2 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of water into the mixture. Boil for 10 minutes, leave for a few more hours and strain and drink in 4 doses throughout the day.
- Second collection of herbs . It is necessary to mix two parts each of lingonberry and mint leaves, clover flowers, horsetail grass, three parts each of plantain and snakeweed, five parts St. John's wort. Grind everything thoroughly and 2 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Boil for 10 minutes, leave. Drink a third of a glass three times a day.
Preventive measures
Prevention of salmonellosis is based on compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards. Owners of livestock and poultry should carefully monitor the storage conditions of their products and the timeliness of their heat treatment. Remember the importance of washing your hands before eating and after returning home.
When preparing homemade dishes, you need to monitor the temperature. Products with expiring dates should be disposed of promptly. Adults should conduct preventive conversations with children of preschool and primary school age.
Specific measures to prevent salmonellosis - in the form of vaccination - are not used due to low effectiveness. The pathogen is heterogeneous, and acquired immunity has low resistance.
Prevention
To prevent infection with salmonellosis, it is necessary to follow the following important prevention rules:
- Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap, doing this after visiting public places, the toilet, and before eating.
- Never buy animal products from places where there is uncontrolled trade.
- When purchasing eggs, be sure to check the date of sorting of the products. Eggs cannot be sold longer than 25 days from the day of sorting.
- The widespread belief that quail eggs cannot be infected with salmonellosis is a misconception, since quails, although they do not suffer from this disease, can be carriers of salmonella. Therefore, heat treatment of such eggs is also necessary.
- When purchasing products, you need to keep track of where they are stored. Raw and prepared food should be kept in separate display cases. Food should be stored at home in the same way.
- It is important to regularly clean the refrigerator, including the container for raw eggs.
- Use different cutting boards for raw and prepared foods.
- Wash the dishes thoroughly and scald them with hot water.
- Do not eat raw animal products: do not drink raw eggs and milk, or try minced meat.
- Fruits, vegetables and herbs should be washed under running water.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling raw foods.
- Cook food of animal origin for a sufficient amount of time.
- Strengthen your immune system , lead a healthy lifestyle, get rid of bad habits.
Questions and answers
How to avoid getting infected from an infected relative with whom you live in the same apartment?
The main precaution will be consistent adherence to personal hygiene rules. Each family member must use an individual set of utensils during the period of outpatient treatment of a relative. The toilet and bathroom need daily cleaning.
Is it possible to find out about the presence of the bacteria that causes salmonellosis in food?
Only laboratory staff can confirm the presence of pathogenic microflora in food products after conducting appropriate research. Customers of popular retail chains should choose products with a valid expiration date and individually packaged in sealed containers or bags.
Diet
Diet Table No. 4
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 7-10 days
- Time frame: 21 days
- Cost of products: 1120-1150 rubles. in Week
Diet No. 4b
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 10 days
- Duration: 2 weeks - 1 month
- Cost of products: 1300-1400 rubles per week
Diet Table No. 2
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 3 weeks
- Terms: 1 month or more
- Cost of products: 1550-1600 rubles. in Week
When developing a diet for a patient with salmonellosis, it is necessary to take into account the severity of intoxication, the form of the disease, and the individual characteristics of the course of the disease.
If the illness is severe, you should drink only semi-sweet tea on the first day. Next, slimy soups, rosehip decoction, and fresh juices of vegetables and fruits are added to the menu.
Next, the patient is shown following Diet table No. 4 , and after the stool partially returns to normal - Table No. 4b . After complete normalization of stool, you should switch to diet Table No. 2 .
Immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to ensure that the patient is properly hydrated to prevent dehydration. You should consume at least 2 liters of fluid per day. You need to drink it in small sips, making even intervals between drinks. If your doctor allows it, you can drink herbal decoctions or rehydration solutions in the first days.
Adult patients, after reducing the severity of acute symptoms, should consume fermented milk products, berries, and vegetables in order to quickly restore normal microflora . It is better to prepare fruit drinks and compotes from fruits and berries. Recommended puree of carrots, apples, bananas. You can cook mashed potatoes using water.
You can also gradually introduce the following dishes into the menu:
- white bread crackers;
- porridge on water - semolina, rice, buckwheat;
- steam cutlets from lean meat or fish.
You should completely avoid the following products:
- marinades;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- semi-finished products;
- spices;
- sweets;
- legumes;
- citrus.
The diet must be followed for at least a month after the acute symptoms disappear.