From this article you will learn:
- 2 types of digestive disorders
- 2 main causes of indigestion
- 9 foods that normalize digestion
- 4 Bonuses of Drinking Water to Improve Digestion
- 9 Exercises to Improve Digestion
- 4 groups of medications to normalize digestion
- 4 final tips for normalizing digestion in the body
Many people today are forced to both normalize digestion using certain methods and completely switch to proper nutrition. And there’s nothing you can do about it: often the presence of certain ailments is dictated by lifestyle. Well, and the environment, how could we live without it?
In fact, there are quite a lot of ways to solve the problem. But if you give preference to only one, there is a high probability that a positive result will not follow. It would be better to use several methods in combination.
Abdominal pain after eating - what to do?
30.04.2021
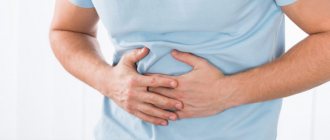
Stomach pain after eating can affect anyone. It is important to accurately diagnose and determine which part of the abdomen hurts the most.
One of the reasons may be celiac disease, that is, gluten intolerance, so do not underestimate abdominal pain after eating.
Abdominal pain after eating is most often the result of poor diet, food poisoning, or indigestion .
If the pain is accompanied by symptoms such as flatulence, nausea or other alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor who, after consultation and tests, will recommend treatment.
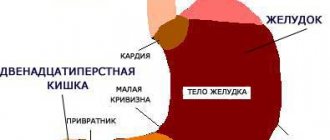
Causes of abdominal pain
Abdominal pain after eating can be one of the symptoms of various diseases, such as:
- Indigestion dyspepsia ) is a condition for which the digestive system is responsible. It is divided into organic and functional. The source of its occurrence is not completely known, but there are factors such as poor diet, stress or increased stomach ;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease involves the reflux of food contents and gastric juice into the esophagus , which gives a number of unpleasant symptoms, namely: heartburn chest pain , bad breath ;
- ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Main symptoms include: pain under the breasts or just above the navel , nausea , gas and belching , symptoms worsening about 45 minutes after eating;
- Irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic intestinal manifested by abdominal and impaired bowel ( diarrhea and constipation );
- Celiac disease primarily affects children, but also affects adults. Avoid products that contain wheat, barley or rye;
- poisoning is one of the most common causes of abdominal . It occurs as a result of eating stale or expired foods. Poisoning should not be underestimated, as it leads to dehydration.
Types of pain
To correctly diagnose the cause of dysfunction, you need to accurately describe where the greatest pain occurs. This is often not an easy task because it spreads throughout the entire abdominal cavity:
- stomach pain after eating is caused by indigestion or poisoning, as well as diseases such as reflux , pancreatitis , stomach cancer , peptic ulcers or inflammation of the bile ducts;
- pain on the left under the ribs after eating indicates damage to the spleen, diseases of the digestive system and reproductive system;
- pancreatic pain after eating is one of the symptoms of cholelithiasis , pancreatitis , and in the worst case, even cancer . But most often it is a symptom of excessive alcohol consumption or the result of overeating;
- liver pain after eating is actually a gallbladder ;
- pain in the intestines after eating. Crohn's disease is one example of a disease that is characterized by pain in the intestines after eating, as well as ulcerative colitis and chronic intestinal .
Abdominal pain in a child after eating
In many cases, you can help your child on your own, without medical intervention.
Abdominal pain is associated with infant colic, which is irritating intestinal spasms. The discomfort may last for several hours, usually in the evening.
The main causes of colic:
- the intestines are not fully developed;
- swallowing air while eating;
- stress;
- intolerance to certain nutrients.
However, unpleasant ailments after eating can have other causes, for example:
- food poisoning;
- constipation;
- presence of parasites.
If the pain is chronic, very severe, or accompanied by other troubling ailments, you should consult a doctor .
Treatment of abdominal pain
Only based on an accurate diagnosis the doctor choose the appropriate form of treatment for each patient.
In the case of gastroesophageal reflux disease, treatment is largely based on a proper diet , as well as regular medication to reduce acid secretion.
Regarding peptic ulcers , patients should stop taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and also take acid neutralizing medications.
People suffering from irritable bowel syndrome take medications with diastolic and antidiarrheal effects. You should avoid coffee and remember to eat properly.
Home Remedies
Abdominal pain immediately after eating often requires the introduction of an easily digestible diet . If constipation , you need to drink a lot of water.
You should also avoid exercising immediately after a full meal and limit the consumption of alcohol, spicy and fatty foods, and smoking. It is important not to overeat and eat easily digestible foods.
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
When does the body need help?
Digestion is a complex and long process that involves all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The leading role in this process is played by enzymes - substances with the help of which food is broken down and absorbed, saturating the body with useful substances. Digestion occurs in several stages, and at each of them, food and drinks encounter enzymes:
1. Once in the mouth - with salivary enzymes.
2. In the stomach - with gastric enzymes.
3. In the small intestine - with pancreatic enzymes.
4. Enzymes from intestinal juice complete the digestion process.
Sometimes at one of the stages a failure occurs due to a lack of enzymes. This is where enzyme preparations come to the rescue. If the digestion process fails, a person may be bothered by:
- heaviness and pain in the abdomen;
- flatulence;
- nausea, heartburn, belching;
- diarrhea, remains of undigested food in the stool.
Such symptoms can accompany many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.