Coprogram is a comprehensive analysis of feces, which allows you to evaluate the functioning of the digestive system as a whole, and the functionality of each organ separately. In order for the research results to be accurate, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules for the preparation, collection and storage of material.
What is a coprogram?
Coprogram is a method of laboratory examination of feces, which is prescribed to identify pathologies of the digestive system. The specialist conducts macroscopic, microscopic, chemical and physical analysis of feces, after which he makes a detailed description of the composition of feces.
What a general stool analysis shows:
- dysfunction of the pancreas, intestines, stomach;
- the presence of foci of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract and their localization;
- disruptions in the process of digestion, movement of feces, and absorption of nutrients;
- dysbacteriosis;
- presence of parasites;
- colitis.
You can make a stool coprogram in a regular clinic for free, but to get a more accurate and detailed result, it is better to contact private laboratories, the average price is 370–420 rubles.
What is the purpose of testing for dysbacteriosis?
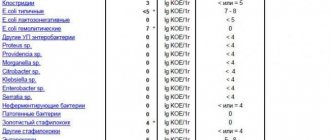
Analysis of stool for the presence of dysbiosis in the child’s body is carried out in order to refute or confirm the corresponding diagnosis. At the same time, by taking this test, you can identify the causes of discomfort in the baby’s body. Based on the data from this analysis, the attending physician makes a specific diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment. As a result, the baby feels much better, and the parents are happy about his recovery. By analyzing a child’s stool to confirm or refute the dysbiosis developing in the body, doctors accurately and practically without errors study the composition of its microflora and determine the concentrations of the following groups of microorganisms:
- Beneficial bacteria, which include microorganisms that improve the processes of digestion and absorption of nutrients for the baby;
- Opportunistic microorganisms contained in the baby’s intestines that can worsen the baby’s health. Typically, this group of microorganisms can be harmful to a child if the number of such bacteria exceeds the number of beneficial ones;
- Pathogenic bacteria that should not be contained in the microflora of a healthy baby at all.
Indications for taking a coprogram
A stool test should be taken as part of an annual preventive examination in order to recognize problems with the digestive tract in time and begin treatment.
When is scatology prescribed:
- inflammation of the digestive system in acute and chronic form;
- hemorrhoids, fissures in the anus, chronic constipation;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract;
- poisoning;
- suspicion of helminthic infestation, amoebic dysentery;
- assessment of the effectiveness of drug treatment;
- before conducting instrumental diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract and surgical interventions.
Children are prescribed a stool test for colic, if there is a suspicion of intestinal infections, inflammatory processes, cystic fibrosis, lactose intolerance, dysbacteriosis, or infection with worms.
What is examined by stool scatology?
There are a number of standard physical indicators that are examined as part of this analysis. These include:
- consistency;
- color;
- smell;
- form;
- presence of impurities.
Table. Indicators studied on the coprogram.
| Index | Decoding |
| Consistency | It is formed depending on the presence of fat, water content and mucus in the stool, indicating pathology. |
| Color | It is formed depending on the food consumed and medications taken, but can also indicate the presence of bleeding and a number of diseases. |
| Smell | May indicate a number of different diseases. |
| Form | It largely depends on the consistency, but indicates pathology. |
| Presence of impurities | It can be observed both in case of incomplete chewing of food (undigested food remains) and in the presence of pathologies. |
How to donate stool correctly
For diagnostic results to be reliable, several simple conditions must be met.
Rules for preparing for coprogram:
- 3-5 days before the examination, stop eating meat, tomatoes, beets, green vegetables, red fish - when testing for occult blood, they can become the culprits of a false positive result.
- The diet should include dairy products, mashed potatoes, lean meat, kazhi, boiled eggs, and porridge.
- A week before the test, you need to stop taking activated carbon, preparations based on bismuth, iron, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs, antacids - they change the color of stool. You cannot take laxatives, use rectal suppositories, or do enemas.
- Sometimes the doctor prescribes a special diet, which details the daily amount of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids - this is necessary in order to maximally load the digestive system, which will help detect even the slightest malfunction in its functioning.
- A coprogram can be performed no earlier than 5–6 days after an X-ray with barium, colonoscopy, or cleansing procedures.
- You cannot donate stool during menstruation or bleeding hemorrhoids.
Any deviation from the rules will distort the results of the coprogram.
Decoding coprograms in children and adults
Now let's briefly look at each of the indicators in the table and outline the possible reasons for deviations from the norm. But first, let us once again emphasize that this is the task of a qualified doctor, especially considering the fact that the results of a scatological examination alone, without taking into account symptoms, medical history and data from other tests, mean little and cannot serve as the basis for making a final diagnosis.
Daily volume
The daily volume of feces varies depending on the nature of the diet: it increases from the abundance of raw plant foods, and from the predominance of protein products (meat, fish, eggs) it decreases, but in any case, the amount of feces excreted by a person per day should be within the range norms indicated in the table.
Increased amount of feces - reasons:
- Enterocolitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Fermentative or putrefactive dyspepsia;
- Increased intestinal peristalsis;
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Decreased amount of feces - reasons:
- Malnutrition;
- Constipation.
Consistency
The consistency of feces is influenced primarily by the water content in them. Normally, the stool should be fully formed, cylindrical in shape in children and adults - this happens if the stool is 70-75% liquid. The exception is for infants: if the mother is breastfeeding, the baby’s stool will be mushy, and if the baby is fed artificial milk formula, the stool will take on the appearance of putty, and this is quite normal.
Abnormal consistency of stool - causes:
- Very hard (“sheep”) – constipation, stenosis of the large intestine or spasms of its walls;
- Liquid – diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, increased peristalsis;
- Foamy – fermentative dyspepsia, enterocolitis, dysentery, salmonellosis;
- Ointment-like - pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis.
Color
The stool of a healthy adult and a child over one year old is brown, which is explained by the presence of the bile pigment stercobilin.
Babies who are exclusively breastfed have stool that is light yellow, golden yellow, or greenish yellow. The stool of babies receiving artificial formula differs slightly in color - they are dark yellow, dark orange or yellow-brown.
If we talk about the color of feces of adults, it is greatly influenced by the foods included in the diet, as well as some medications. Therefore, adequate decoding of the coprogram becomes difficult when the patient neglects the rules of preliminary preparation for the study.
Abnormal stool color – causes:
- Black, tarry - bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, varicose veins of the esophagus, ulcer or stomach cancer;
- Dark brown – constipation, excess protein food or disruption of its digestion, colitis, dyspepsia;
- Light brown – excess plant foods, irritable bowel syndrome, increased peristalsis;
- Red-brown – ulcerative colitis;
- Light yellow – pancreatitis;
- Gray-white - hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, blockage of the bile ducts.
Smell
The characteristic smell of feces is caused by the presence of methane, phenol, skatole, indole, hydrogen sulfide and other compounds. Their ratio, in turn, is affected by the composition of the diet. However, in any case, when deciphering a coprogram, a mild, familiar smell is considered the norm for children and adults. The stool of babies up to six months old has a sour smell due to the fact that such young children are fed either mother's milk or an artificial formula. In the second case, the smell will be more pungent.
Abnormal smell of stool – causes:
- Sour – fermentative dyspepsia;
- Putrefactive – enterocolitis, gastric dysfunction, putrefactive dyspepsia;
- Fetid - pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, blockage of the bile ducts;
- Rancid oil – hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, liver cirrhosis.
Undigested food
The feces of a healthy person should normally contain no particles of undigested food. If they are present, especially in large quantities, this is an alarming signal that indicates a serious disruption of the stomach, pancreas or liver.
Slime
In infants, a small amount of mucus may be present in the stool, but it should be transparent and barely noticeable. For older children and adults, the presence of mucus in feces is a deviation from the norm and a sign of trouble.
Mucus in stool - causes:
- Haemorrhoids;
- Intestinal polyposis or diverticulosis;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Celiac disease;
- Malabsorption syndrome;
- Lactase deficiency;
- Acute intestinal infection;
- Parasitic infestation;
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Blood
Neither in adults nor in children, when decoding the coprogram, should blood appear in the stool - this is an extremely undesirable sign, indicating the presence of a serious pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Depending on what type of blood it is, in what volume and when it is released, you can make assumptions about the causes of the problem.
Blood in stool - causes:
- Scarlet blood on toilet paper or on top of feces - hemorrhoids, anal fissure;
- Blood streaks - ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, colon cancer;
- Blood in loose stools – dysentery and other intestinal infections;
- Mucus with blood - paraproctitis, ulcerative colitis, polyposis, diverticulosis;
- Blood stains on underwear – rectal cancer;
- Heavy bleeding from the anus – ischemic colitis, damage to the hemorrhoid.
Pus
The presence of purulent inclusions in the feces of infants, older children or adults is a gross deviation from the norms of coprogram and, most often, indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, further examination is necessary, aimed at establishing the cause and exact localization of inflammation, as well as the specific type of pathogen.
Parasites, cysts
The stool of a healthy adult or child should be free of protozoa, worms and their eggs. If, when deciphering the results of scatology, they are detected, it is necessary to carry out specific antiparasitic therapy, which should be prescribed by a doctor. Remember that most anthelmintic drugs are toxic, and you need to select the appropriate medicine taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s health condition, especially if it is a small child.
Acidity, pH
Infants have a slightly acidic or acidic stool reaction due to the fact that the basis of their diet is mother's milk or artificial milk formula. Older children and adults have a neutral stool reaction. This indicator can be shifted to the acidic side by an excess of carbohydrate foods or poor digestion, and to the alkaline side by protein foods.
Stool acidity disorders - causes:
- Alkaline (pH 8.0-8.5) – pancreatitis, colitis, constipation;
- Slightly alkaline (pH 7.5-8.0) – disruption of the small intestine;
- Strongly alkaline (pH above 8.5) – putrefactive dyspepsia;
- Strongly acidic (pH below 5.5) – fermentative dyspepsia.
hidden blood
The fecal occult blood reaction should be negative. If this is not the case, then perhaps the person has erosive gastritis, a stomach ulcer, ulcerative colitis, diverticulosis, hemorrhoids, or even a malignant tumor of the gastrointestinal tract - the list of diagnoses can be very long and varied. Therefore, a positive result of a stool test for occult blood when deciphering a coprogram becomes the reason for an in-depth examination of the patient.
Bilirubin
Normally, intestinal microflora processes the bile pigment bilirubin and converts it into stercobilin. However, in babies under 6 months of age, the body is only colonized by bacteria, and a healthy balance is formed between them. Therefore, the presence of a small amount of bilirubin in the feces of infants is a variant of the norm, while for adults this is already a serious deviation.
Bilirubin in stool – reasons:
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Enhanced peristalsis and accelerated evacuation of feces;
- Intestinal dysbiosis as a result of long-term antibacterial therapy.
Stercobilin
This substance is the result of the processing of bilirubin by intestinal bacteria and causes the characteristic brown color of stool. A person secretes from 75 to 350 mg of stercobilin per day. The infant's coprogram may show lower values. But in an adult, this indicator should be within the established norm.
Stercobilin in feces is increased - reasons:
- Hypersecretion of bile;
- Hemolytic anemia.
How to collect stool
It is better to collect stool from an adult and a child in the morning, immediately after the morning toilet, and try to deliver it to the laboratory as quickly as possible. You need to collect material from different parts of the feces, put them in sterile containers, or special disposable plastic containers, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. Evacuation should be natural; the use of laxatives, much less enemas, is prohibited.
In infants, it is not recommended to collect feces from the diaper; it is better to use a disposable diaper or medical oilcloth if the child has loose stools.
An older child needs to prepare a potty; first wash it with laundry soap or soda.
Important! When collecting material, you need to ensure that there is no urine in the stool.
How much feces do you need?
To carry out the analysis, you need to bring 15–20 g of material to the laboratory, which is approximately equal to 1 tsp. – this amount is quite enough to identify all the main indicators.
Is it possible to collect stool samples in the evening?
It is better to use a morning portion of feces for analysis, but if you are not sure that defecation will occur after waking up, you can collect the material in the evening; it should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 10–12 hours, the container should be hermetically sealed.
Associated symptoms
Often the color of stool is caused by taking medications, eating fruits, vegetables, and drinks. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor specific signs of intestinal ailments.
It is acceptable to suspect a pathological process, but without examination even a doctor will not make a diagnosis.
Signs include gas formation, flatulence, belching with a pungent odor and taste. Digestion and absorption of eaten food is accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting. Any intestinal or stomach disorders, coupled with changes in feces, indicate an unfavorable process in the body.
Conventionally, accompanying symptoms are divided into intestinal and extraintestinal. Disorders actively manifest in the last stages of pathology development. At first, it is difficult to detect the disease on your own. Various manifestations from delayed evacuation to abdominal pain are a serious reason to consult a specialist.
Decoding the results of scatological research
When the results are ready, the person will receive a form indicating normal indicators and the results obtained from the study of the material. It is better to consult a doctor for a decoding, since even a deviation from the norm of several indicators does not always indicate the presence of pathologies.
Normally, an adult's feces should be uniformly brown in color, dense, and have a characteristic odor.
The feces of a healthy person are free of foreign impurities, food debris, protozoa and parasite eggs. The presence of undigested fiber in the stool indicates low acidity of gastric juice, the presence of blood and pus indicates serious gastrointestinal pathologies.
Norm of stool coprogram in the table
| Index | Patient age and diet type | |||
| Infants | Artificials | Children | Adults | |
| Macroscopic parameters | ||||
| Daily volume | 40-50 g | 30-40 g | 100-250 g | 100-400 g |
| Consistency | gruel | putty | decorated | decorated |
| Color | yellow, golden, greenish | orange, light brown | brown, dark brown | brown, dark brown |
| Smell | sourish, unsharp | sour, sharp | characteristic, blurry | characteristic, blurry |
| Undigested food | — | — | indigestible plant fiber may be present | indigestible plant fiber may be present |
| Slime | may be present, transparent | may be present, transparent | absent | absent |
| Blood | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Pus | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Parasites, cysts | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Chemical parameters | ||||
| Acidity, pH | 4,8-5,8 | 6,8-7,5 | 7,0-7,5 | 7,0-7,5 |
| hidden blood | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Bilirubin | up to 3 months may be present | up to 3 months may be present | absent | absent |
| Stercobilin | present | present | present | present |
| Soluble protein | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Microscopic parameters | ||||
| Detritus | present in different quantities | present in different quantities | present in different quantities | present in different quantities |
| Ammonia | absent | absent | 20-40 mmol/kg | 20-40 mmol/kg |
| Starch | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Neutral fats | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities | none | none |
| Fatty acid | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities | none | none |
| Soap | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities |
| Digestible plant fiber | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Muscle and connective tissue fibers | none | none | may be present in small quantities | may be present in small quantities |
| Leukocytes | units in view | units in view | units in view | units in view |
| Yeasts | none | none | none | none |
| Pathogenic flora | absent | absent | absent | absent |
Dark thread-like inclusions after surgery
If a child has undergone surgery on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to especially carefully monitor his well-being and the appearance of feces, since it is the change in the color of feces that is the first symptom of hidden (internal) bleeding in the intestines or stomach. If the bleeding is intense, the blood accumulates in the stomach, coagulates and in this form enters the intestines, from where it is excreted as a black, sticky, tarry mass, which some people mistake for excrement.
Small threads and veins of bright black color can be a signal of bleeding at a very early stage, so if such signs are detected, parents should immediately inform their doctor. Dark threads in the stool during gastrointestinal bleeding usually appear without any other symptoms, but the child’s condition deteriorates very quickly, and the clinical signs of the pathology rapidly progress.
Symptoms of internal bleeding in the active phase may include:
- increasing weakness syndrome;
- bloody vomiting;
- temperature rise to febrile levels (above 38.5 ° C);
- severe cramping pain in the abdomen.
A laboratory test of blood and urine can detect an increase in ESR and platelets, as well as an increase in urea levels against the background of normal creatinine levels.
To treat mild forms of gastrointestinal bleeding, hemostatic agents (Vikasol, Dicynon) are prescribed, as well as a gentle diet for faster healing of the mucous membranes. In more severe cases, endoscopy, surgical treatment and blood transfusion (in emergency cases) are indicated.