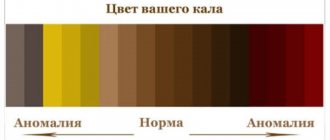
General analysis (coprogram)
- 2 days before collecting biomaterial, discard tomatoes, tomato juice, pasta, beets, blueberries, pomegranates and other vegetables and fruits containing dyes.
- For 3 days, stop taking antibiotics, laxatives, and drugs that cause changes in intestinal motor function. Do not use rectal suppositories, ointments, or oils.
- Do not eat exotic fruits, vegetables and foods that are not typical for your diet as a whole. Do not overeat, exclude fatty, spicy, pickled foods.
- If you are taking medications containing iron and bismuth, they must be discontinued 2 days before stool collection.
Attention. After radiography with a contrast agent (barium), collect feces for coprogram no earlier than 7–10 days after the examination. Women are not recommended to take the test during menstruation.
Procedure for collecting stool:
Collect stool for examination in the morning, on an empty stomach. If this is difficult, you can prepare the sample in advance, but no more than 8 hours before submitting it to the laboratory. In this case, store the sample in the refrigerator (do not freeze!).
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver the sample to the laboratory on the day of collection. Before delivering the sample to the laboratory, the container with stool should be kept in the refrigerator at 2–4 °C. Storage at 2-8 °C is allowed - up to 72 hours.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
Examination of stool for blood hidden in it is prescribed for the following patient complaints:
- Constant/recurrent abdominal pain;
- frequent symptoms of dyspeptic disorder - nausea, vomiting, heartburn;
- regular diarrhea;
- unexplained weight loss.
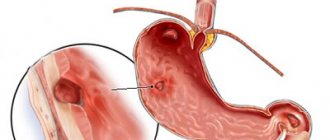
Testing stool for blood present in its composition is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis, for example, peptic ulcer or erosive gastritis. The overall goal of the analysis is to identify hidden damage to the mucous membranes of the stomach or intestinal tract.
Dysbacteriosis, intestinal group
To obtain the correct result, material for research is taken before the start of antibacterial therapy or in the intervals between courses of treatment, but not earlier than 2 weeks after its completion.
Attention Do not collect feces from diapers. For infants, collect material from a sterile diaper or pre-ironed onesies. If liquid feces are collected, it can be collected by placing an oilcloth under the baby.
Collection rules
- Feces should be collected in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection.
The sample can be stored for no more than 2 hours at room temperature; no more than 6 hours at 2-8 °C, more than 6 hours - frozen.
Who is a stool occult blood test indicated for?
This type of research is prescribed in the following cases:
- Persistent periodic pain in any part of the abdomen, as well as in the right or left hypochondrium;
- Discomfort and pain during or after defecation;
- Sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the rectum;
- Any stool abnormalities: constipation, diarrhea, pathological increase or decrease in the volume of feces, changes in their color, consistency or smell, the presence of suspicious inclusions (foam, mucus, blood, pus, parasites or their eggs);
- Loss of appetite, sudden loss of body weight for no apparent reason;
- Nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn, unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- Unexplained increase in body temperature;
- Diagnosed gastrointestinal pathologies: Crohn's disease, intestinal polyposis, ulcerative colitis, diverticulosis, esophageal varicose veins, helminthiasis, and so on - the study is performed to determine the stage of the disease or monitor the progress of treatment;
- Alarming results of other previously conducted examinations, for example, coprogram, general or biochemical blood test;
- Prevention of intestinal cancer over the age of 40-50 years in patients with unfavorable heredity.
Protozoa and helminth eggs
To obtain the most reliable results, three stool examinations are recommended with an interval of 3–7 days.
Attention You cannot collect stool earlier than 3 days after an enema, an X-ray examination of the stomach and intestines, or a colonoscopy. The day before, do not take laxatives and drugs that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine), activated carbon, iron, copper, bismuth, barium sulfate, use fat-based rectal suppositories. Women should not collect stool during menstruation.
Collection rules
- Feces should be collected in the morning, on an empty stomach. If this is difficult, you can prepare the sample in advance, but no more than 8 hours before submitting it to the laboratory. In this case, the sample should be stored in the refrigerator (do not freeze!).
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine, water and pieces of undigested food;
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection.
Types of tests
If there are bleeding areas of the mucosa, blood may be present in a person's excrement. If the site of bleeding is the stomach or duodenum, then the stool becomes dark red in color. When the surface of the large intestine is damaged, they become scarlet. But it is not always possible to see blood impurities in a person’s stool. Very often, small ulcers bleed only periodically.
Laboratory testing of stool for occult blood can determine even the minimal amount of hemoglobin contained in it.
The study is performed in two ways:
- Gregersen method (benzidine test);
- immunochemical test.
The Gregersen test is quite informative, but only if the patient has thoroughly prepared
Gregersen's technique allows you to detect even the minimum concentration of hemoglobin. This is both an advantage and a disadvantage of the method. Benzodine colors iron molecules blue, but it reacts with both human and foreign hemoglobin (present in meat).
The immunochemical method is more accurate. Its significant drawback is that it takes quite a long time. Test results will be received only two weeks after submitting the material for research. Therefore, in most cases, stool testing is prescribed using the Gregersen method.
Bacteriology
To obtain a reliable result, material for research is taken before the start of antibacterial therapy or in the intervals between courses of treatment, but not earlier than 2 weeks after its completion.
- 3-4 days before the study, it is necessary to stop taking laxatives, castor and petroleum jelly and stop administering rectal suppositories.
Attention: Feces obtained after an enema, as well as after taking barium (during an X-ray examination), are not suitable for research.
Collection rules
- Feces should be collected in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection.
False results
Failure to follow the preparation rules before donating stool may result in erroneous results. They can be either false positive or false negative.
The main reason for false-positive tests indicating the presence of internal bleeding is improper preparation.
False positive results are quite common. The reason is a person’s disdainful attitude towards the preparatory stage. In this case, the test shows a high hemoglobin content in the absence of internal bleeding. Just one apple eaten a day before the delivery of biological material can distort the final results.
Proper preparation for examining stool for occult blood in many cases allows you to avoid a very unpleasant colonoscopy procedure. The technique involves examining the intestines by inserting equipment through the anus.
PCR studies
Collection rules
- Feces should be collected in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection.
Rules for submitting stool for analysis
After the appointment, the doctor must explain to the patient how to correctly collect biological material.
- Immediately before defecation, you need to urinate. Trapped urine may distort the results.
- Pre-washing is not always recommended. If a person has parasite eggs on the sphinketer, they can be easily washed off with water. The result will be false negative.
- It is better not to collect feces directly from the toilet. The flora located on the walls can end up in feces. You should urinate in a clean bag or pot.
- It is recommended to collect feces in a container specially purchased for this purpose. It is sold at the pharmacy and is equipped with a small spatula for ease of use.
- For regular constipation, you can first perform a light intestinal massage. If this is not effective, you will need to do an enema and then collect the fecal pieces from the water.
- For one analysis, 10-15 g of feces is enough.
When sending for analysis, the doctor also indicates what kind of research is needed (coprogram, identification of pathogenic flora, identification of protozoa, etc.). Each option has distinctive features of material collection.
Culture for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics
3-4 days before the study, it is necessary to stop taking laxatives, castor and vaseline oil, and stop administering rectal suppositories. Feces obtained after an enema, as well as after taking barium (during X-ray examination) are not accepted for examination!
Attention: Feces are collected before starting treatment with antibacterial and chemotherapy drugs.
Collection rules
- First urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver to the laboratory on the day of collection. If it is impossible to quickly deliver the sample to the laboratory, you can store it in the refrigerator for no more than 4 hours at 2-8 °C.
How are the results interpreted?
The test gives a false negative answer if there is no free hemoglobin in the submitted stool sample, or if only undestructed red blood cells are present, for example, if there is external bleeding from an anal fissure.
The physiological loss of red blood cells in feces forms the limit for a normal result level of 14 ng/ml. Diagnostic thresholds are set depending on the objectives of the study. For example, to detect cancer in a risk group, 50 ng/ml is considered the normal concentration of free hemoglobin.
For carbohydrates
- Carry out hygiene procedures and first urinate in the toilet and flush.
- Place sterile paper (or an ironed sheet) or a disposable plastic plate in the bowl or bottom of the toilet and perform a bowel movement.
- Collect feces immediately after defecation from different places in a single portion with a special spoon mounted in the lid of a plastic container in a volume of 1–2 g (no more than 1/3 of the container’s volume). Avoid contact with urine and pieces of undigested food.
- Deliver the sample to the laboratory within 4 hours.
Attention Storing a stool sample for more than 4 hours, including in the refrigerator, is not allowed.