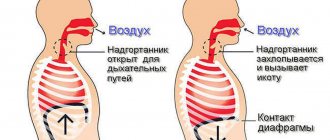
Hiccups are repeated, uncontrollable contractions of the diaphragm muscle, which lies under the lungs and borders the chest and abdomen. The diaphragm regulates breathing. When it contracts, the lungs take in oxygen, and when it relaxes, they release carbon dioxide.
A diaphragm that does not contract in the correct rhythm causes hiccups. With each such spasm, the larynx and vocal cords close sharply, resulting in a sudden rush of air into the lungs. The body, in turn, reacts with a sigh and a specific sound.
Singultus is the medical term for hiccups.
Why do hiccups occur in children?
Numerous causes of hiccups have been identified. However, there is no definitive list of triggers.
Hiccups in children often come and go for no apparent reason.
Possible common causes of short-term hiccups in children (up to 48 hours) include:
- binge eating;
- eating spicy food;
- drinking carbonated drinks;
- eating very hot or very cold food;
- sudden change in air temperature;
- swallowing air while chewing gum;
- excitement or emotional stress;
- aerophagia (swallowing too much air).
The nature of hiccups and the mechanism of its development
Hiccups occur even in babies in the womb
Hiccups are an involuntary contraction of the respiratory diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Various factors can provoke an attack of such a contraction, but in any case they entail a characteristic inhalation of an involuntary nature.
Due to the nature of its occurrence, hiccups are often called an imitation of forced breathing. A “hiccup” attack occurs in both healthy and sick people. There are many reasons for hiccups.
Convulsive and jerky contractions of the muscles of the respiratory system are a natural reflex of the body. From the point of view of human health, such a phenomenon is classified as a characteristic disorder.
Its development occurs reflexively, due to the body’s need to remove excess air from the gastrointestinal tract. Less commonly, the nature of the attack is slightly different, for example, associated with a disruption in the functioning of the musculoskeletal apparatus of the sternum.
All people have encountered hiccups, regardless of age, gender and other physiological characteristics. The feeling of a “hiccup” attack does not bring any pleasure. Any sudden contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles provokes short and unnatural breaths, as well as a pronounced protrusion of the abdomen.
Why do long-term (more than 48 hours) hiccups occur in children?
Hiccups that last more than 48 hours are classified according to the type of irritant that caused them. Most persistent attacks are caused by damage or irritation to the vagus or phrenic nerves, which control the movement of the diaphragm.
These nerves may be affected due to:
- irritation of the eardrum, which may be caused by a foreign object;
- irritation or sore throat;
- goiter (enlarged thyroid gland);
- gastroesophageal reflux (stomach acid retreats into the esophagus);
- esophageal tumor or cyst.
Other causes of prolonged hiccups may be related to the central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord. If the central nervous system is damaged, the body may lose the ability to control hiccups.
Damage to the central nervous system that can lead to persistent hiccups includes:
- hit;
- tumors;
- meningitis and encephalitis (infections that can cause swelling of the brain);
- head injury or traumatic brain injury;
- hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the brain);
- neurosyphilis and other brain infections.
Hiccups that last longer can also be caused by:
- reaction to anesthesia after surgery;
- taking certain classes of medications, including barbiturates, steroids, and tranquilizers;
- diabetes;
- renal failure, etc.
Sometimes long-term hiccups can be caused by a number of medical procedures, including:
- use of catheters to access the heart muscle;
- placement of an esophageal stent to support an open esophagus;
- bronchoscopy (where an instrument is used to look inside the lungs);
- tracheostomy (creating a surgical opening in the neck to allow breathing around an airway obstruction).
Types of baby hiccups
Baby hiccups can be of two types: episodic and continuous. The first type is quite often observed in children in everyday life. It often appears suddenly, for no apparent reason. To successfully get rid of it, you first need to correctly determine the cause of its appearance.
Often, episodic seizures in children occur during severe hypothermia, significant overeating, or due to stress, emotional distress, or nervous excitability. The episodic form is characterized by spontaneous disappearance of symptoms after a short period of time. If they do not stop within half an hour, adults should intervene.
Video from Youtube: Why do people hiccup? — Science
If you are worried about prolonged hiccups - daily attacks that occur for a long time, there is a possibility that it manifests itself as a result of the development of some pathology in the body. You should not try to cope with this type of reflex on your own; a specialist, a pediatrician, should determine the cause and prescribe treatment.
How to stop hiccups in a child?
In most cases, hiccups are nothing to worry about, but they can certainly be uncomfortable.
There are many treatment options for short-term hiccups. Although none of them are backed by scientific evidence, these methods have been proven effective at home in a number of cases.
So, this will help children with hiccups:
- Breathe into a paper bag.
- Eat a teaspoon of granulated sugar.
- Hold the breath.
- Drink a glass of cold water.
- Pull your tongue.
- Lift the uvula (the tissue at the back of the throat) with a spoon.
- Try to intentionally gasp.
- Pull your knees to your chest and sit in this position for a while.
- Close your mouth and nose and exhale forcefully.
- Relax and breathe slowly and restrainedly.
Ways to get rid of hiccups
Every parent should know what to do if their child hiccups frequently. The main thing you must always remember is that you cannot use the old way of scaring. In fact, this method has no scientific basis, but the worst thing is that you can harm the child and traumatize his psyche. Therefore, you should not resort to such, as they say, barbaric methods.
There is a very simple way that allows you to quickly get rid of hiccups. To do this, you should ask your child to do light breathing therapy. He should inhale slowly but very deeply, and then also exhale; after a short period of time, the hiccups will disappear and your child will return to his previous activity. If you notice that your child is hiccupping in the morning, as in the photo, you should take it seriously.
The best ways to get rid of hiccups
It often happens that hiccups are caused in newborns by the structure of their body. This is a manifestation of the so-called reflux. This is caused by the characteristics of the gastric valve. In a baby, the stomach does not close completely; this often manifests itself in regurgitation and hiccups. Perhaps the hiccups are caused by temporary hypothermia; in order to get rid of the hiccups in this case, you need to dress him warmer. Basic warm socks can save the situation.
Understand that hiccups are not always a funny behavior for your baby, sometimes it is a serious condition that requires medical attention. In the morning the child hiccups in the photo you see, this is a real symptom of a serious illness such as diabetes. In order not to risk the health of your child, we advise you to visit a pediatrician. This specialist will be able to determine exactly what is causing persistent hiccups and prescribe effective treatment.
What to do if a child’s hiccups do not go away?
If hiccups persist for more than 48 hours, you should consult a doctor. He may do gastric lavage or carotid sinus massage (rubbing the main carotid artery in the neck).
If the cause of hiccups is unclear, your doctor may order additional tests:
- blood tests to look for signs of infection, diabetes, or kidney disease;
- liver function tests;
- visualization of the diaphragm using chest x-ray, computed tomography, or MRI;
- echocardiogram to assess heart function;
- endoscopy;
- bronchoscopy.
Treating any causes of hiccups will usually make them go away. If this condition does not go away, your doctor may prescribe anti-hiccup medications.
When to see a doctor?
If a child experiences spasms for a very long time, sometimes every day or many times without an obvious underlying cause, contact a doctor who will prescribe the necessary set of examinations for the baby. Very often, the cause of spasms may indicate the presence of worms in the body.
In this case, the doctor will prescribe special medications for the child. If no worms are found, then you will need to be examined by a neurologist.
If the child is one year old or younger, the cause may be an immature nervous system. In this case, you need to wait until the baby grows up. Don't let him get overexcited, play calm games, rest. You can do a relaxing massage once or twice a day.
Older children may also suffer from spasms due to overstimulation. It happens that a child cannot calm down all day, and in the evening he has an attack of spasms, which can continue on the second day. Monitor the baby's condition. The doctor may prescribe sedatives or herbal infusions.
If inflammatory processes or elevated blood sugar levels are detected in the body, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment that will relieve the child of the disease and stop its consequence - hiccups.
Every mother has repeatedly had to deal with hiccups in her child. Moreover, the first manifestations of the reflex can be observed before its birth - almost all children hiccup while in the womb. This is not always a harmless phenomenon, especially when it often bothers the baby. To explain why this happens, it is necessary to find out the causes of this phenomenon.
Consequences of laughter
Many people are interested in why a child sometimes hiccups after loud, prolonged laughter. When he laughs, sharp and intermittent breaths compress the vagus nerve with air pressure. It sends a response signal to the diaphragm to contract to release it. To stop the attack, it is necessary to release and relax the vagus nerve.
To stop your baby from hiccupping, you can give him water to drink, and swallowing will help the diaphragm return to normal. You can also stretch while standing, taking the deepest possible exhalations and inhalations.
Consequences of overeating
Too much food and liquid entering the stomach causes the walls to stretch, causing the diaphragm to contract, resulting in hiccups. Overeating is often the cause of its appearance and the answer to the question of many mothers, why does the child hiccup after eating.
To stop this attack, you need to give the baby water at room temperature, and then ask him to hold his breath as much as possible. If the initial attempt does not produce results and the baby continues to hiccup, you can repeat the procedure several times to achieve the desired effect.
Severe nervous shock
Emotional excitement, nervous stress or fear are the reasons that often cause bouts of hiccups in children. To eliminate it in the event of a nervous shock, parents need to calm the baby down and, if possible, try to figure out what exactly is the cause of the child’s worries and fears.
If, due to these reasons, the attack lasts a long time and the baby cannot calm down, you should try to distract him with an interesting activity. Captivated by his favorite game, he will soon and unnoticed stop hiccups. If attacks due to stress recur periodically, you should urgently consult a psychologist.