Causes of hiccups in children
Physiologically, this phenomenon is caused by irritation of the vagus nerve. The result is a repeated contraction of the diaphragm.
According to doctors, hiccups are an unconscious and persistent powerful inhalation that is repeated for a certain period of time with a sharp narrowing of the glottis.
The reasons that cause this phenomenon in a child include:
- Swallowing air during feeding. The resulting volume puts pressure on the diaphragm, causing it to contract.
- Binge eating. Too much food entering the stomach stretches its walls. As a result, there is also pressure on the diaphragm.
- Long break between feedings or fluids.
- Most often, hiccups in a child occur as a result of a powerful emotional outburst: stress, fear, nervous tension.
- After a lot of laughter. Frequent and sharp breaths during laughter are accompanied by contractions of the diaphragm. The process leads to clamping of the vagus nerve.
- Hypothermia. Hiccups are often a concomitant symptom of severe cold.
The above reasons are episodic, short-lived and should not cause concern to parents. This condition can be easily overcome if you know some techniques.
Hiccups. What to do?
Authors : Vasilenko V.V.
Aw, it hurts! No. 26 (662) September 2009 Category “If suddenly such an illness”
Causes
You finish your meal and suddenly start hiccupping. The hiccups only last a few minutes, and you may be wondering, “Why did this happen?” But it also happens that hiccups last all night, and in the morning the only thing you want to know is how to stop them.
Unfortunately, no one knows exactly why hiccups start, but doctors have come up with an acceptable explanation.
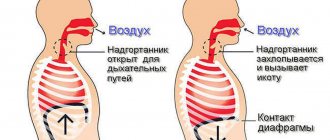
The chest cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by a muscular thoraco-abdominal barrier called the diaphragm. It is located under the lungs and heart directly on the digestive organs. The diaphragm is a muscle involved in breathing; when tense, it allows air to enter the lungs and expels air from the lungs during relaxation.
Control nerves (vagus and sympathetic) pass through the chest, connecting to and branching into the diaphragm. If the nerve endings in the diaphragm are stimulated, the impulse can travel along a reflex arc to the brain. The brain sends a reverse impulse and causes the diaphragm to contract very quickly. During its spasmodic contraction, the lungs suddenly suck in air. When air passes through a closed or sharply narrowed glottis in the larynx, the sound “hic” occurs. The time between the convulsive contraction of the diaphragm and the appearance of sound is only 35 thousandths of a second. When you hiccup, you're not actually breathing because your glottis closes when you make the sound. Rhythmic spasms of the diaphragm cause the phenomenon of hiccups.
Thus, hiccups are an involuntary, usually stereotypically repeated strong and short breath with a closed or sharply narrowed glottis, caused by a sudden convulsive contraction of the diaphragm.
What contributes to its occurrence? The most common cause of irritation of the branches of the phrenic nerve, which causes hiccups, is too hasty absorption of food or liquid, accompanied by additional swallowing of air. Other factors can slow gastric emptying and thus irritate the diaphragm, such as eating large amounts of fatty foods in a short period of time.
Benefit or harm
You may think that hiccups provide some hidden benefit to your body, but doctors know that this is not the case. While vomiting and coughing are useful (sometimes life-saving) reflexes that protect the digestive and respiratory tract, hiccups are of no use.
To be fair, it must be said: there is also an opinion that there is a hiccup center in the brain that causes spasm of the esophagus. And, according to the authors of the hypothesis, this is a mechanism that protects against excessive consumption of food or liquid.
Newborn babies hiccup very often, and this is a normal phenomenon, parents should not worry. They hiccup even before birth! If your child has a similar problem, it will go away with age.
Hiccups are usually harmless. But sometimes it can be a sign of a serious medical problem.
The clinical picture is very clear, expressed in severe shortness of breath with loss of voice during hysterical spasm of the diaphragm (syndrome described by the French doctor P. Briquet).
There are cases when patients with pneumonia develop persistent hiccups. This may be because the infection is irritating the diaphragm or nerves in the chest.
In heavy smokers or those who have smoked for many years, it can be a sign of cancer because a tumor growing in the chest irritates the diaphragm.
Hiccups, accompanied by other unpleasant sensations, including palpitations, are sometimes observed with hiatal hernias (H. Bergmann syndrome).
The classic stereotype of a drunk who constantly hiccups has some basis in reality: chronic alcoholism can cause toxic hiccups. And in a persistently hiccupping alcoholic, doctors may suspect liver disease, which irritates the diaphragm. “When the liver is inflamed, hiccups are bad,” said Hippocrates.
It even happens that hiccups caused by serious medical problems cause insomnia, exhaustion, exhaustion and even death.
Finally - and, unfortunately, this is exactly how it often happens - hiccups can become a psychological problem if, without obvious causes, they are prolonged or difficult to influence... Long-lasting hiccups are said to exist if they do not disappear within two days. Stable and intractable is a disease that lasts more than a month.
How to stop her?
“In someone who is obsessed with hiccups, the appearance of sneezing stops the hiccups” (Hippocrates).
Here are a number of measures that can be taken if the hiccups persist for too long. They are aimed at opening the neuro-reflex arc. Contrary to popular belief, frightening the sufferer will not help him. Fear is actually another possible cause of hiccups.
Some simple methods almost always work. Their essence is to stimulate the digestive system and oropharynx. Try this:
- drink well-sweetened water or ice water;
- swallow a small amount of finely crushed ice;
- suck half a lemon; slowly eat a slice of stale bread;
- breathe quickly into a paper (but not plastic) bag;
- massage the hard palate (vault of the mouth) with your thumb;
- grab your tongue with your thumb and forefinger and gently pull it forward;
- throw your head back, hold your breath and count to ten, then quickly exhale and drink a glass of water;
- use the so-called vagal Valsalva maneuver (strong straining for 10-15 seconds after a deep breath);
- touch the root of the tongue or the back of the throat (provoking a gag reflex).
There is no shortage of such advice. However, new ones are also appearing. Thus, the study showed that eating a teaspoon of regular granulated sugar in dry form - without drinking water - quickly (immediately) stopped hiccups in 19 out of 20 subjects (some of them suffered from occasional hiccups for more than a month and a half). If the hiccups do not go away immediately, repeat the experiment three times at two-minute intervals.
If these methods do not work and the hiccups do not stop for a very long time, then you can try to stop the hiccups by taking metoclopramide (Perinorm, Raglan, Cerucal).
Sometimes you have to resort to the help of doctors who, naturally making sure that there are no compelling reasons to worry about your health, use more effective medications by injection.
Vasilenko V.V., gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of internal diseases of the Moscow Medical Academy named after I.M. Sechenov, Moscow.
Please note: in January, a new book by Vasilenko V.V. “Secrets of Digestion”, 2009, went on sale.
Does the digestive system have secrets? It turns out there are a lot of them. Why bad breath and loud belching appear, what causes pain in the side and is it associated with a psycho-emotional state, why does the stomach growl after eating and how to stop sudden hiccups - every person encounters such phenomena, but not everyone knows how to deal with them cope with. What is “fishy odor disease” and the zigzag nutrition system, how to get rid of constipation and stop diarrhea without medications, is a low-calorie diet necessary and how diseases of the digestive system were treated 100 years ago - this is only a small part of what you have to learn.
The secrets of digestion are revealed by Vasilenko Vladimir Vladimirovich - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences, doctor, who has devoted 40 years to medicine.
V. Vasilenko, “Secrets of digestion” - ONLINE STORE : https://www.medknigaservis.ru/catalog/popularscientific/6452
published 10/19/2009 00:35 updated 07/07/2013 — Miscellaneous
How to get rid of hiccups in a child
A universal method for most cases is to offer the child a warm drink (water, milk, tea). The method allows you to eliminate the narrowing of the glottis through long, calm sips.
Another most common option is holding your breath.
If air is swallowed, it is recommended to carry the child in an upright position, waiting for a burp. A normal manifestation is regurgitation due to excessive air intake during feeding.
A frozen child must be warmed up with a blanket, warm drinks and rubbing.
If there is mental overstimulation, it is worth distracting the child with a new exciting activity and giving him the opportunity to calm down.
Less popular methods are also used effectively:
- As you inhale, you need to stretch your whole body, and as you exhale, relax;
- chewing one teaspoon of sugar;
- cooling of the earlobe;
- stimulation with acupressure of the middle phalanx of the little finger.
The first year of a baby’s life is a wonderful time, full of love, tenderness and unexpected discoveries. But even during this joyful period, alarming situations arise. For example, many parents are concerned about the fact that their infant hiccups frequently. Let's figure out why this happens and what to do.
Physiological phenomenon
Hiccups are an absolutely normal phenomenon that accompanies a person throughout his life. Why does it occur? The mechanism is simple: under the influence of certain factors, the diaphragm contracts with a simultaneous sharp closure of the airways. A condition occurs that resembles short-term suffocation and is accompanied by a characteristic strangled sound. Such painless but unpleasant convulsive tremors are repeated several times in a row.
Babies experience hiccups much more often than adults, because all their organs and systems are in the process of maturation. Normally, attacks can occur several times a day and last 10-30 minutes.
Why does the baby hiccup? The reasons are:
- errors in the feeding process, leading to overeating, swallowing air (aerophagia) and flatulence
- hypothermia
- stress
Let's look at each factor in detail and find out what to do to help the baby.
Binge eating
In infancy, hiccups often occur after meals: the stomach becomes full of milk or formula, puts pressure on the diaphragm, and it begins to contract. There is only one way to prevent this situation - to control the amount of food your baby eats.
When breastfeeding, pediatricians advise maintaining intervals between meals of 1.5-2 hours and interrupting sucking if the baby eats for longer than 15-20 minutes. When using artificial nutrition, you should strictly observe the dosage of the mixture and the intervals between meals.
It is important not to go to the other extreme - taking too long breaks. In this case, the baby will greedily swallow milk during the long-awaited feeding and will definitely overeat. In addition, hunger and thirst can provoke hiccups as a result of reflex irritation of the walls of the stomach and diaphragm. In an infant older than 6 months who is already eating solid foods, cramping may result from eating too quickly or eating dry foods.
Excess air
If during the sucking process the baby swallows a lot of air, a bubble forms in the stomach, which gradually moves upward and affects the respiratory muscles. To prevent aerophagia it is recommended:
- Apply correctly to the breast. It is necessary that the baby grasps the entire areola of the nipple with his mouth. If milk is released abundantly, you can express it a little before feeding. The baby's position during meals should be almost vertical
- Choose your pacifier and bottle wisely. Swallowing air when feeding with formula is possible if the hole in the nipple is too wide. Ideally, turning the bottle over should release a few drops of milk per second. During feeding, you need to hold it so that the nipple is constantly filled with liquid. It is advisable to use an anti-colic bottle
- After a meal, the baby should be held vertically for 5-10 minutes, pressing his tummy to your chest. Excess air bubbles will come out naturally. The same must be done during an attack of hiccups.
Flatulence
Gases that accumulate in the upper intestines put pressure on the stomach and displace the diaphragm. To prevent flatulence in a baby, the nursing mother follows a diet. Increased gas formation can be caused by whole milk, corn, legumes, brown bread, fresh baked goods, carbonated drinks, fresh vegetables and fruits. If your tummy becomes bloated after the formula, you should change it after consulting your pediatrician.
Abdominal massage and herbal-based carminatives (with fennel, anise, dill, caraway) or with simethicone help with flatulence.
Hypothermia and stress
Why does a baby still hiccup? Other reasons are related to the functioning of the nervous system. We are talking about hypothermia and stress. In these situations, irritation of the vagus nerve, passing from the thoracic to the abdominal region, and spasm of the diaphragm occurs.
A baby can freeze while walking or in a cold room. You need to dress him warmly, cover him with another blanket, or pick him up and warm him up.
Sharp sounds, bright lights, strangers, a sudden change of environment, and so on can cause stress in a baby. What to do in this case? Remove the irritating factor, hug the child, stroke him, sing a song, put him to the chest. A grown-up baby can be occupied with an interesting game or fairy tale.
Watch a short video about hiccups and how to deal with them. Don't forget to read the article to the end
To drink or not?
Drinking is an effective help during hiccups. But until 6 months, many breastfed babies receive only milk. It is believed that they do not need additional fluid. If your baby hiccups, you can break this rule and give him some warm water from a spoon. This is true if the attack occurs after feeding, because in this case, additional breastfeeding will only worsen the problem.
Warning signs
Debilitating hiccups in an infant that do not subside within several hours or days may indicate pathology, especially if it is accompanied by:
- frequent and profuse regurgitation
- hyperthermia
- nervousness, fussiness
- we're crying
- persistent cough
Such symptoms are a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Why might they occur? There are a lot of serious diseases that cause abnormal hiccups. Among them:
- infections that can provoke inflammation of the brain - measles, rubella, toxoplasmosis and others
- traumatic brain injuries
- brain and lung tumors
- pneumonia
- gastroesophageal reflux
- neuritis - damage to the diaphragm and so on
Algorithm of actions
What should parents do if their infant hiccups? Don't panic and try to help him. Here are some tips:
- After feeding, hold the baby in your arms in an upright position
- Give him some warm water
- Attach your baby to your breast if the cause of hiccups is not overeating
- Warm him up in case of hypothermia
- Provide a calm environment, entertain with a game or book
- Contact a doctor if the attack does not go away for more than an hour and other signs of trouble are observed.
Hiccups in a baby after a meal or as a result of fright are a physiological reflex. In the first months of life, the baby’s body actively develops, which is why it reacts so violently to external stimuli. With age, the frequency of attacks decreases markedly. Parents should protect the baby’s peace, monitor his nutrition and respond in time to weather changes. The main thing during hiccups is not to create unnecessary fuss, because in fact, diaphragm spasms do not cause much discomfort to the child.
Hiccups as a symptom of pathology
Constant and prolonged hiccups (every day or throughout the day) may be a sign of a serious illness. If your child's condition is of concern, you should immediately contact a specialist. It may be a symptom:
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- infections;
- inflammation;
- birth trauma;
- spinal cord injuries;
- deviations in the functioning of the nervous system.
Parents need to be vigilant so as not to miss the danger signal. After all, it is always easier to solve a problem at its initial stage.
Survey
A diagnostic search aimed at clarifying the causes of hiccups is carried out when it is combined with other symptoms, occurs frequently, and attacks last more than 60 minutes. The examination plan is drawn up taking into account the medical history and accompanying symptoms. Most often, primary diagnosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist, who, according to indications, involves other specialists in examining the patient. Depending on the suspected cause of the symptom, the following are used for express diagnostic purposes:
- Endoscopic studies
. Gastroscopy is the most informative method that allows you to quickly objectify pathological changes in the esophagus and stomach. If space-occupying formations, erosions and ulcers are detected during endoscopy, a biopsy is performed for histological analysis of the material. - X-ray methods
. X-ray of the abdominal cavity, X-ray examination of the chest are carried out to detect gastrointestinal pathology, relaxation of the diaphragm, pleurisy, mediastinal tumors and other possible causes of hiccups. Next, RCP and other X-ray contrast techniques are used. - Ultrasound research .
Sonography of the abdominal cavity is performed to assess the echostructure of the main parenchymal organs and identify free fluid; according to indications, it is supplemented by ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver. If pleurisy or mediastinal tumors are suspected, ultrasound of the pleural cavity and mediastinum is indicated. - Tomography
. If radiography and sonography are insufficiently informative, CT, MSCT and MRI of the abdominal or thoracic cavities and individual organs are performed. MRI of the head and spine are highly accurate in diagnosing cerebral and spinal pathologies. In difficult cases, an MRI of the whole body is performed. - Electrofunctional Research
. After excluding abdominal and thoracic causes of hiccups, electroencephalography is recommended. The method identifies foci of pathological activity in the brain. To clarify the level of damage to the nervous system, electroneurography and electromyography are also performed. - General blood analysis
. With high leukocytosis, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, and an increased ESR, further diagnostic search is aimed at identifying inflammatory and neoplastic processes. The analysis is often supplemented with the study of enzymes (ALT, AST) and determination of the level of C-reactive protein.
Upon receipt of preliminary information about a possible disease that provoked hiccups, further examination is carried out according to the appropriate protocol and may include a wide range of laboratory and instrumental methods. Differential diagnosis is carried out between various pathological processes in which hiccups may develop.
If you have hiccups, it is recommended to drink water in small sips.
Symptoms
With episodic, that is, hiccups that do not have a pathological basis, there will be no associated symptoms.
The attack itself will be characterized as follows:
- involuntary contraction of the diaphragm occurs with transmission to the intercostal muscles;
- At the same time, a violation of the respiratory function occurs, in other words, breathing stops for a split second;
- The glottis closes, which provokes the appearance of a characteristic sound.
If the manifestation of hiccups is not caused by a pathological process, then the duration of the attack does not exceed 15 minutes.
But if the provoking factor is a gastroenterological disease, the following symptoms may appear:
- heartburn, belching with an unpleasant odor;
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea;
- poor appetite, the baby may even refuse his favorite foods;
- weakness, lethargy, apathetic mood of the baby;
- increased flatulence;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- pallor of the skin.
An increase in temperature will indicate the beginning of the inflammatory process. If the cause of the symptoms is infection with helminths, then there will additionally be itching in the anus and discomfort during bowel movements.
It should be noted that similar symptoms can be present in any gastroenterological disease and even ARVI, so it is impossible to carry out treatment on your own, without a diagnosis. In addition to the fact that the drugs may not provide the desired therapeutic effect, this can also lead to serious complications, since the baby may be allergic to some components of the drug.
Etiology
If a child often hiccups, this may indicate the following pathological processes in his body:
- gastritis;
- esophagitis;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach;
- parasitic infections;
- helminth infection;
- intoxication of the body with medications, poisons, toxic and other chemicals;
- pathological processes of the nervous system;
- diseases of the upper respiratory system.
In addition, it is necessary to highlight the physiological reasons that a child hiccups all day:
- binge eating;
- eating food quickly, on the go, chewing poorly;
- habit of drinking carbonated drinks with food;
- stress, nervous tension;
- fright
It should be noted that in a child under 5 years of age, frequent hiccups are normal, since the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract has not yet been established.
In any case, if hiccups are constantly present in a baby (of any age), you should consult a doctor, and not treat yourself or ignore the symptoms altogether.
Causes of hiccups in children
How to stop causing hiccups
Don't overfeed your baby. Keep in mind that breast milk is digested within 2.5-3 hours, formula - 3-4.
Maintain intervals between feedings and at the same time do not make them too long. A hungry baby will begin to worry and rush while eating, and this can cause hiccups.
If you give a mixture, follow the dosage according to age. With natural feeding, there is no need to tear the baby off the breast before he does it himself. But when there is a lot of milk, and there is a suspicion that the baby is overeating, pumping before feeding will help.
Avoid situations in which the baby swallows air along with food. When breastfeeding, make sure your baby latches onto the entire areola of the nipple. Express a little before feeding if your baby is constantly choking and cannot cope with the flow of milk.
When bottle-feeding, hold the bottle at an angle so that the nipple is filled with the mixture. Use a bottle with a small hole. A simple test will help you make the right choice: fill the bottle with liquid and turn it upside down - the contents should drip slowly. Immediately after eating, hold the baby in a column for 5-10 minutes - this will help him burp and get rid of excess air.
Monitor the microclimate. In a newborn's room, it is usually recommended to keep the temperature within 22 degrees. Dr. Komarovsky considers 18-19 degrees ideal. And this seems to be true.
The child should breathe clean, cool, moist air. And if he is cold, which he can signal by hiccups, just dress him a little warmer. And do not forget to humidify the air to the optimal 50-70%. If you don’t have a humidifier, place a container of water near the radiator, hang a wet towel, spray water from a spray bottle, and do wet cleaning more often.
A newborn may hiccup both when he is hypothermic and when he is overheated. It is important not to allow either one or the other. The indicators are the back, bends of the arms and legs. Touch them, if they are wet, then the baby is hot, if they are cold, he is freezing. Cold hands, feet and nose are not indicators that the child is cold. Focusing only on hiccups is also wrong - the reason may be different.
Pay attention to your baby's emotional well-being during a hiccup attack. Perhaps the reason was fear. Take the baby in your arms, stroke him, dim the lights, ensure silence, hold him to your breast for a while so that he calms down.
Massage for colic
It is recommended to massage your baby's tummy before each feeding. For best results, massage after using a heating pad for five minutes. You can heat the diaper with an iron or hold it on a warm radiator, then put it on the baby’s stomach, cover it with your hands and hold it for a while. There is no need to lubricate your hands with oil or cream.
- Lightly stroke your belly in a clockwise direction. Make about 10 turns.
- Then alternately bend and unbend his legs, pressing them to his stomach. Do this for 6–8 repetitions with each leg.
- Turn the baby over onto his tummy and make several stroking movements from the sides and over the pelvic bones in the direction from the stomach to the lower back.