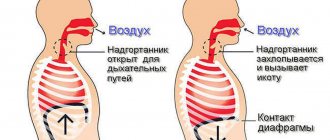
According to the International Classification of Diseases, hiccups are considered under the section “Abnormal breathing”. The mechanism of this involuntary physiological reaction involves the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which, convulsively contracting, initiate a short inhalation, and the sudden closure of the airways by the epiglottis is accompanied by a characteristic sound. This condition does not pose a threat to human life, but it does cause a lot of discomfort. Therefore, people try to find ways to get rid of it. For example, they drink water, do push-ups and do press exercises. Such methods can help when hiccups have a physiological cause. If the appearance of this condition is influenced by a disease, then you can get rid of hiccups only by curing the pathology.
Etiology of the phenomenon
To date, the exact reasons for the appearance of this condition have not been established. However, scientists suggest that short hiccups serve as an evolutionary mechanism aimed at displacing air from the stomach. It is also believed that this is a skill that helped the embryo move fluid in the lungs during puberty. After birth, the manifestation of such a skill subsides, because it is not needed. Although, under the influence of various stimuli, the phenomenon can still occasionally manifest itself.
This condition is associated with increased excitability of the vagus nerve, which stabilizes the functioning of internal organs at the time of compression of the esophagus.
Content:
- Etiology of the phenomenon
- Hiccups in adults
- Hiccups during pregnancy
- Hiccups in men
- Hiccups in a child
- Symptoms and diagnosis of contraction
- Treatment for hiccups
- Treatment of hiccups in infants
- Possible complications and prevention
Is it dangerous?
If the cause is hypoxia, it can be dangerous. This term refers to the lack of oxygen in a child.
There are certain signs of the disease:
- The baby is overly active in the womb. Thus, it replenishes the missing oxygen. At 33 weeks of pregnancy, such activity is normal, but if the baby pushes very rarely, you should start to worry.
- The baby has bradycardia - decreased heart rate.
- Reduction in hiccups, or their duration has increased sharply.
- Baby hiccups occur too often.
Hypoxia is only a consequence of pathologies occurring inside the body of the fetus or mother.
Hypoxia can lead to irreversible consequences. It inhibits the development of the fetus and leads to the formation of various anomalies. Oxygen starvation affects the central nervous system, leading to a decrease in the growth rate of the fetus and its ability to adapt.
Otherwise, if the hiccup process occurs without discomfort, it is completely harmless for both mother and child.
Hiccups in adults
In adults, this condition can be physiological and pathological. Physiological is considered a phenomenon in which contractions occur rarely and go away on their own. They can be triggered by an uncomfortable body position, a full stomach, hasty, dry food, eating cold or hot food, as well as during stress, laughter or hypothermia. In this case, it is episodic and quickly passing.
Prolonged intractable hiccups of central origin can occur with a cerebral stroke in older people or in patients with vascular diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus. In addition, prolonged hiccups can be a symptom of a tumor of the brain and its stem. Cerebellar artery aneurysm can also lead to hiccups. Hiccups may indicate a brain injury, accompanied by the formation of a hematoma.
Hiccups, caused by irritation of peripheral nerves, are a symptom of diseases such as large hiatal hernia (>3 cm), neoplasms of the esophagus, pancreas and stomach. Persistent hiccups can be observed in pathologies of the cardiovascular system: myocardial infarction, heart rhythm disturbances, since they increase the excitability of the endings of the vagus nerve. Respiratory diseases, in particular laryngitis, bronchitis and pneumonia, as well as mediastinal tumors can cause hiccups due to irritation of the phrenic nerve. There is evidence of persistent hiccups in patients with herpes. In these cases, the pathological process is triggered by the herpes virus, which multiplies in the nerve ganglia. The cause of hiccups can also be compression of the spinal root of the fourth cervical vertebra by a hernia, as well as neck tumors. Other factors that cause long-term hiccups include autoimmune diseases (neuromyelitis optica, multiple sclerosis), epilepsy, encephalitis, meningitis, and Parkinson's disease.
Toxic hiccups occur when metabolic disorders occur due to damage to the nerves by toxins accumulating in the blood. Such hiccups can occur with diabetic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus, intoxication with uremia (the last stage of kidney disease), electrolyte imbalance with hypocalcemia (diseases of the parathyroid and thyroid glands) and hypokalemia (Cushing's syndrome, vomiting, diarrhea, etc.). Toxic hiccups can develop when taking medications: antiparkinsonian drugs, drugs used in psychiatry, azithromycin (an antibiotic), morphine. Chemotherapy drugs used in the treatment of cancer patients, as well as drugs administered during anesthesia and epidural anesthesia, can also cause prolonged hiccups.
To get rid of physiological hiccups, you do not need to carry out any manipulations; they will go away on their own. Although you can use traditional methods, for example, drink water or do exercise. But in order to eliminate pathological hiccups, drug treatment of the root cause of this condition is required.
general characteristics
A sudden attack of hiccups may be preceded by overeating, fast food with poor chewing of hard and dry foods, swallowing air, and drinking highly carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
In young children and sometimes in adults, hiccups are triggered by hypothermia. Some patients begin to hiccup after taking muscle relaxants, barbiturates, benzodiazepines and other medications. Often the symptom appears for no reason and goes away on its own within a few minutes. At the time of an attack, a person experiences jerky muscle contractions in the epigastric region, accompanied by protrusion of the anterior abdominal wall and a strangled sound. Due to the closure of the glottis, breath holding occurs for a short period of time. A special feature of hiccups is the impossibility of conscious control. With intense hiccups, moderate pain is sometimes noted behind the sternum, in the lower parts of the chest. An attack of hiccups is characterized by rhythmic muscle contractions at approximately equal intervals.
Prolonged, especially pathological hiccups often have a debilitating effect and may be accompanied by irritability, emotional instability, increasing asthenia, vegetative manifestations - sweating of the palms, paleness or redness of the skin, a decrease in the temperature of the skin of the distal extremities. For episodes that repeat several times a day or several days a week, last more than an hour and are combined with other disorders (heartburn, pain, shortness of breath, etc.), you should seek medical help.
Hiccups during pregnancy
Hiccups can occur in both the woman and the fetus. The main reasons for this are the following:
- The pressure of the growing uterus on the internal organs, which in turn puts pressure on the diaphragm, because of this it begins to involuntarily contract.
- Experiences of a pregnant woman: in this state, tension occurs in the diaphragm, which irritates the vagus nerve, and it causes its spasms.
- Hypothermia: provoking hiccups occurs in the same way as during experience.
- Overeating or rushing through food: Air and poorly chewed food also irritate the vagus nerve.
- Uncomfortable body position: this is typical for many pregnant women during advanced periods. They cannot get comfortable, which causes pressure on the diaphragm, which causes it to spasm.
There are several ways to get rid of hiccups during pregnancy. Drink a little water, eat something bitter or sweet. You should not experience the cure with fear, so as not to provoke premature birth. To prevent hiccups after eating, you need to eat calmly and slowly.
From about 26 weeks, a woman can feel the baby's hiccups. It arises for the following reasons. The child swallows amniotic fluid, which irritates the diaphragm. There is an opinion that this is a kind of communication between the baby and the mother.
Prolonged or frequent hiccups in a baby indicate oxygen starvation, but neonatologists say that this is an incorrect judgment. On the contrary, it indicates that the nervous system is developing normally and the fetus is developing body muscles. You can find out what exactly is happening to the baby using ultrasound, CTG and counting movements.
Fetal hiccups can be calmed by avoiding sweets before bed, taking an evening walk, or changing body position.
What is hiccups and where does it come from?
Hiccups occur when the diaphragm reacts to certain factors by contracting. Medicine suggests that hiccups are necessary for the fetus in the womb to ensure the movement of amniotic fluid through the respiratory system. Often, a pregnant woman can feel the rhythmic tremors of the unborn baby, which are hiccups.
Medicine knows several cases of prolonged hiccups, the duration of which was more than two decades. Separate studies have identified settlements in which hiccups appear more often than in the rest of the country. The curiosity of scientists forced them to pay special attention to a number of factors that provoke hiccups, which prevail in each specific region.
The diaphragm is a flat, broad muscle that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity. When it contracts sharply, a spasm of the lungs occurs, which does not go unnoticed by the entire respiratory system. Air passing past the vocal cords may be accompanied by sound.
Hiccups in men
Men suffer from hiccups more often than women. Sometimes the cause of its appearance is the consumption of alcohol, because it poisons the body and irritates the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. In this situation, it can be long-lasting and will stop only after the poisoning is eliminated.
Prolonged hiccups have a negative impact on human health. Because of this, his heart rhythm is disturbed, insomnia, depression and neuroses occur.
If, against the background of prolonged hiccups, a violation of the phrenic nerve is observed, then this condition is life-threatening, since a person can suffocate (the glottis closes and the air supply to the lungs stops). With short-term hiccups, this is not scary, but if it occurs regularly, an attack of suffocation is possible.
Prolonged hiccups must be treated with medications. For this, the doctor prescribes muscle relaxants, tranquilizers, antipsychotics, and antiseptics. You cannot carry out treatment on your own, because if used incorrectly, side effects can be life-threatening. If medications do not help, then surgery is performed to remove the branches of the nerve endings leading to the diaphragm.
What happens to a woman during pregnancy?
24.07.2020
The polite one suddenly becomes aggressive, the calm and reasonable one becomes nervous and whiny.
Being and Consciousness
Metamorphoses are not accidental. The body of pregnant women undergoes complex hormonal changes. The level of progesterone increases: this hormone not only relaxes the uterus , preventing it from contracting excessively, but also affects the emotional background. The woman becomes a little inhibited and more sensitive.
Little things that were not touched at all before are painfully touched; as soon as there are tears.
An increase in estrogen levels awakens hitherto dormant instincts, such as the protection of offspring. The baby has not yet been born, but his mother is already protecting him. Often pregnant women are aggressive, preventing a possible threat from others, experience irritation when touched by strangers, and feel anxiety in the crowd.
The body also produces a new hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin. It changes the psyche in accordance with the upcoming event, making you either fly with happiness or indulge in despondency.
Emotions monthly
The first trimester of pregnancy is the most stressful. Joy and euphoria are interspersed with excitement and even fear. Increased irritability and excitability are observed, emotions become more superficial, laughter or tears are possible for no reason.
In the second trimester, anxiety decreases and a positive mood prevails. The hormonal background, changes in which caused problems in the first months, stabilizes, emotions stop overflowing. Nausea disappear , ailments become less acute. The expectant mother begins to feel her pregnancy more realistically; she feels the first movements and tremors of the baby, during an ultrasound examination she sees his arms, legs, head, and hears his heart beating.
But in the third trimester, anxiety appears again, which is now associated with the upcoming birth . It's not just the fear of pain. A woman is afraid of the changes that will happen in her life after the child is born: a new regime, responsibilities, responsibility for the baby. Questions torment me: What will I do with it? Can I handle it? What if I can’t become a good mother to him?
Baby sensations
Scientists say that a mother's emotions significantly influence the condition of the unborn baby. Observations made during an ultrasound examination show that the baby behaves differently depending on the woman's mood. When she is nervous, he becomes restless and sometimes has hiccups. When the mother is in a good mood, the baby is peaceful, and on a 3D ultrasound you can see his smile.
If we explain the relationship between mother and baby from the point of view of biochemistry, then at the moment of manifestation of strong negative emotions, the level of adrenaline in the blood . vessels narrow , fetoplacental (uterine) blood circulation worsens. The baby in the womb does not have enough oxygen, it becomes cramped and uncomfortable. The mother’s positive emotions, on the contrary, give the baby endorphins, hormones of joy. And even in the perinatal period, the child develops what psychologists call basic trust in the world.
The relationship also occurs at the cellular level: different emotional states correspond to a certain structure of intracellular components. Changes in it are perceived by the child either negatively - as anxiety, threat, lack of resources, or positively - as pleasure, joy, a sense of security.
Published in Pregnancy and pregnancy management Premium Clinic
Hiccups in a child
In most cases, this condition is physiological in nature. It does not pose a threat to the health and life of the baby. In infants, this condition indicates overeating, hunger, fear, or swallowing excess air. In this case, hiccups can be eliminated by getting rid of the initial cause.
In very rare cases, it is a symptom of a pathology of the nervous system or anatomy. If the cause of hiccups is not clear, you should consult a doctor, because this condition can be caused by quite serious illnesses. The doctor will help you figure this out.
Causes of hiccups
Hiccups can occur for several reasons:
- with hypothermia;
- due to stress;
- when overeating or consuming food quickly;
- due to dry food.
There are also neurological disorders that provoke reflex contraction of the diaphragm. For example, if the vagus nerve, which transmits a signal from the lungs to the brain that a breathing movement needs to be made to inhale or inhale, begins to send false commands to contract the diaphragm.
A nerve irritated by external factors sends false impulses not only to the brain, but also to the spinal cord. As a result, the central nervous system causes the muscles of the respiratory system to contract. These movements can be compared to convulsions. The respiratory center of the brain loses its ability to control the process. The epiglottis occupies a position in the trachea that is characteristic of the swallowing reflex. The vocal cords close together.
This contraction of the respiratory system can occur both during inhalation and exhalation. It is impossible to stop the process with one effort of will. Rare episodes of hiccups do not pose any health hazard. However, regularly occurring spasms should be a reason to seek help from a specialist.
Symptoms and diagnosis of contraction
During hiccups, a sharp contraction and relaxation of the muscles occurs, which begin to twitch quickly. The symptoms of this condition are:
- causeless sharp contraction of the diaphragm with a parallel short inhalation (in this case protrusion of the abdomen occurs);
- a specific sound “hic” (a person makes it due to the closing of the glottis and epiglottis);
- spontaneous termination of physiological hiccups after a short time.
Pathological hiccups can be quite long-lasting, sometimes up to several days. To begin treatment for this condition, it is necessary to diagnose the causes of its occurrence. To do this, the doctor does:
- Collecting an anamnesis of the disease: in this way, it will be established what the patient suffered from before. These can be pathologies such as diabetes, diseases of the digestive tract, pericarditis, alcoholism, neoplasms of various types, stroke, injuries and much more. You also need to clarify with the patient what medications he is taking, because they can also cause hiccups.
- Physical diagnostic methods include visual examination of the patient, palpation, tapping and auscultation. During such an examination, the doctor must examine the abdomen, sternum, nasopharynx, eardrums, esophagus and stomach.
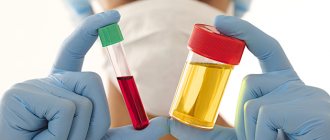
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- Chest X-ray.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
Radiation diagnostics will help to establish why hiccups cannot be eliminated by simple methods, and what triggered its appearance. For example, this way you can recognize tumors pressing on the diaphragm. If necessary, a consultation with other specialized specialists, such as a surgeon, psychiatrist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, is scheduled.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Treatment for hiccups
As soon as hiccups appear, you immediately want to stop them. Moreover, when this phenomenon happens surrounded by strangers (they will definitely pay attention to specific sounds). Therefore, the question: “How to get rid of hiccups?” quite relevant at this moment. Many are beginning to advise drinking water, taking a deep breath and even doing push-ups. But such methods can help if the cause is physiological. In this case, the hiccups will go away on their own in a short time. If the appearance is affected by a serious pathology, then the help of a qualified specialist is necessary. Then treatment will be aimed at eliminating the pathology and its symptoms.
The doctor prescribes medications when: the patient complains of frequent hiccups; the attack lasts more than two days; Along with hiccups, chest pain and heartburn occur.
To eliminate such symptoms, the following are used: antispasmodics (will help relieve spasms and excitability of the diaphragm); neuroleptics (reduces spontaneous activity and response to stimuli, and also reduces skeletal muscle tone); medications to stimulate contractile movements of the gastrointestinal tract (in addition, they promote rapid bowel movements); inhibitors; prokinetics.
In addition to drug treatment, carbon dioxide inhalations and vagus nerve stimulation are prescribed.