Home>Articles>Hiccups after alcohol: why it occurs and how to solve the problem
quick menu (hide)
- Causes of discomfort
- What is the danger of hiccups from alcohol?
- How to deal with hiccups from alcohol
- Medicines
- Effective Home Methods
- Basic taboos
- Precautionary measures
A hangover - a consequence of alcohol abuse - is fraught with dizziness, weakness throughout the body, nausea, and headaches. Hiccups after alcohol are another “identifying sign” of withdrawal symptoms. It happens that it is not possible to get rid of this symptom for a very long time (from a couple of hours to several days) - the discomfort from hiccups aggravates the already unpleasant clinical picture. Read on to learn why hiccups occur and how to solve this problem at home.
Causes of discomfort
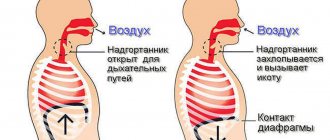
Each of us has been familiar with hiccups since childhood (the first attacks occur during prenatal development). The appearance of hiccups in humans is the result of spontaneous contraction (spasm) of the muscles of the diaphragm and larynx and is associated with many factors . The loud, unpleasant sound that occurs is a reflex that allows you to “push” air out of the stomach.
The so-called physiological hiccups - they appear spontaneously and also disappear imperceptibly.
The cause of the problem is increased gas formation :
- the diaphragm contracts (for example, after quickly eating a large meal), pushing air out of the lungs;
- air masses passing through the larynx slam the epiglottis and cause the appearance of a characteristic “popping” sound.
Physiological hiccups do not cause any particular discomfort and do not require special treatment.
Hiccups from alcohol have a different nature. The “triggers” for discomfort are compounds formed after the breakdown of ethanol (found in all alcoholic drinks). It happens like this:
- toxins, along with the blood flow, “migrate” throughout the human body, the organs of the excretory system are overloaded and cannot cope with the task of their “emergency” removal;
- disruption of the body’s normal functioning is the answer to the question why hiccups after alcohol are a common symptom of a hangover.
Important: liver disease is another factor that causes discomfort after drinking alcohol. As the organ grows, it compresses the diaphragm (muscle-tendon formation), and a spasm occurs.
For a person accustomed to alcohol, hiccups are not something out of the ordinary; most often they do not attach any importance to them. But doctors say that diaphragm spasms that occur during intoxication may indicate serious health problems
Attention! Pathological causes of hiccups from alcohol are alcoholic polyneuritis and microinfarction. In the first case, the unpleasant symptom is associated with dysfunction of the nervous system (toxins kill nerve endings). Hiccups are “complemented” by paresis of the limbs, loss of sensation, and muscle weakness.
Prolonged attacks of hiccups from alcohol can become alarming signals, notifying the patient of a microinfarction. If a spasm of the diaphragm is accompanied by chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances, nausea and other unpleasant symptoms, such “cries for help” cannot be ignored.
Diet
There is no special diet for central hiccups, since it is impossible to influence this process with therapeutic nutrition. For food-related hiccups, it is important to monitor the amount of food you eat and the speed at which you eat it, as both of these factors can trigger hiccups. For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, therapeutic nutrition should be used in accordance with the underlying disease. The general principles are fractional meals, exclusion of fatty, spicy, fried foods, foods that cause bloating (legumes, baked goods, kvass, an abundance of simple carbohydrates).
What is the danger of hiccups from alcohol?
A hangover is a pathological condition that anyone (even a healthy) person can experience after exceeding a reasonable “dosage” of alcohol. It “announces itself”:
- weakness;
- heaviness in the head;
- irritability;
- redness of the mucous membranes and skin of the face;
- nausea.
The list of unpleasant symptoms is completed by hiccups. So, if discomfort bothers the patient for several hours (or even days), this provides additional stress on the body, which is already weakened due to drinking alcohol.
Attention! A drunk person is practically unable to control his own actions - he can fall asleep or lose consciousness. Then hiccups when drinking alcohol often lead to vomiting. The consequences of vomit entering the respiratory tract can be very sad - the “victim” of alcohol will simply suffocate.
How to deal with hiccups from alcohol: useful tips
You can alleviate the condition of a hiccupping person at home using improvised means. The main thing that needs to be done is to cleanse the body of poisonous compounds (toxins), or better yet, to artificially induce vomiting.
How to get rid of hiccups after alcohol (popular methods ):
- A simple and affordable option is to slowly drink a glass of water . This is a safe method that allows you to wash away food debris from the larynx and neutralize irritation of the “local” nerve. It is useful to drink water while lying down - the swallowing reflex will turn on, which will help relieve laryngeal spasm.
- Eating sour and bitter foods relieves spasms in the digestive tract. You can eat a slice of lemon , drink a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar - the discomfort should disappear.
- Sugar is a faithful assistant in the fight against hiccups. A small amount of powder is placed on the center of the tongue and slowly dissolved. Alternatively – 1 tsp. Dilute sugar in beer (1/2 cup is enough), drink in one gulp.
- An alternative to sugar is natural honey (do not swallow, but slowly dissolve so that the viscous mass flows down your throat).
- You can “interrupt” the rhythm of hiccups using a reflex method: put your finger in your mouth as if you need to induce vomiting (you shouldn’t let this happen).
The following method also helps to get rid of discomfort: you need to open your mouth, stick out your tongue, hold it between your fingers and lightly pull it forward (2-3 seconds).
Severe hiccups do not go away for a long time: what to do
With prolonged painful hiccups, traditional methods will not help. The patient requires specialized medical care. The simplest option is to go to a drug treatment clinic or call a narcologist to your home. Treatment of hiccups and concomitant alcohol intoxication will include:
- Initial examination. To prescribe optimal treatment, the doctor first examines the patient, clarifies general symptoms and the presence of chronic diseases.
- Selection of therapy method. The list of medications and methods is always selected strictly individually. A good narcologist does not have universal prescriptions.
- Removing alcohol intoxication. A mandatory stage that allows you to both get rid of unpleasant symptoms and relieve stress on the body, and restore overall well-being. Depending on the patient’s condition, drug and non-drug methods can be used. Additionally, antiemetics, sedatives, psychotropic drugs, and antispasmodic drugs are prescribed.
- In particularly severe cases, the patient is hospitalized for the purpose of surgery. To stop the spasms, a special catheter is inserted, which affects the nerve endings of the diaphragm.
- Follow-up therapy. After the attack is over, the patient is sent for a comprehensive examination to detect possible pathologies of the nervous, cardiovascular systems, and digestive tract. Based on laboratory data, the necessary therapy is prescribed.
If hiccups developed during heavy drinking, after initial therapy, such a patient requires further long-term treatment for alcoholism.
Medicines
Prolonged hiccups most often have a neurological basis. If all attempts to cope with discomfort using improvised means are unsuccessful, it is necessary to undergo a full examination and discover the pathological cause of the problem. What drugs are used to combat hiccups:
- Neuroleptics. They neutralize the increased sensitivity of the vagus nerve and have sedative properties.
- Muscle relaxants. Weaken muscle tone (including the diaphragm).
- Enzymes. They have a positive effect on metabolic processes, improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and relieve inflammation.
Attention! Drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor after confirming the diagnosis.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism for the occurrence of hiccups involves a “reflex arc”, consisting of afferent sections, central and efferent sections. Trauma, irritation, inflammation or pathological stimulation can occur at any part of the arch, causing persistent or intractable hiccups. The afferent pathway (branches of the phrenic, vagus nerves and thoracic sympathetic trunk) carries impulses to the hiccup center, where the signal is processed. It is located in the medulla oblongata next to the respiratory center, hypothalamus and reticular formation and in the upper part of the spinal cord (segment C3-C5). The efferent link includes motor fibers of the phrenic nerve, which innervates the diaphragm and the respiratory muscles of the chest (intercostal and scalene). The diaphragm is innervated by two phrenic nerves originating from segments CIII-CIV (neck area).
For any pathology of the abdominal or thoracic cavity, when the phrenic or vagus nerve is stimulated, the “hiccup center” is activated. The hiccup center, which controls the respiratory muscles, especially the diaphragm, is independently activated in brain diseases. In both cases, repeated myoclonic contractions of the diaphragm and respiratory muscles occur. Sometimes hiccups develop when the vagus nerve is stimulated (for example, due to bloating of the stomach and intestines).
The hiccup mechanism can be triggered by the vagus nerve when it is exposed to general irritating factors and local ones (when it is compressed along the path). The vagus nerve passes from the thoracic cavity into the abdominal cavity through an opening in the diaphragm, innervating the organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavity. Therefore, inhaled exhaust fumes and chemical gases, cigarette smoke, alcohol, spicy foods or cold drinks that irritate the gastric mucosa provoke an attack. Irritation of the vagus nerve occurs when a person eats hastily, overeats, and is in an uncomfortable position.
Effective Home Hacks
You can stop hiccups by drinking a large amount of water, and then by pressing on the root of the tongue. The settings of the nervous system will “reset” to vomiting - diaphragm spasms will disappear.
Breathing also help to cope with discomfort . You need to take a deep breath (take as much air into your lungs as possible), then hold your breath . This technique is more effective for physiological hiccups, but can also help with alcoholic hiccups.
A cup of soothing mint tea will have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, relieve spasms, and help cope with hiccups. It is better to drink the drink slowly, in small sips.
Hiccups from alcohol: how to get rid of it using improvised means:
- suck a piece of ice ;
- chew black bread or crackers (without drinking);
- warm heating pad to the diaphragm (relieves spasms, removes hiccups). Session duration is up to 25 minutes.
Important: there are many more techniques for fighting hiccups at home. But they will only help if the problem arose as a result of alcohol intoxication, and is not caused by one or another disease.
Classification
By duration:
- Episodic or short-term (duration up to 10 minutes).
- Persistent, persistent (duration more than 48 hours).
- Intractable, persistent, intractable (duration more than 1-2 months).
According to the location of the outbreak:
- Central. It occurs when the brain and spinal cord are damaged - trauma, encephalitis , tumors , vascular disorders.
- Peripheral. Caused by processes that involve the phrenic nerve ( hiatal hernia , pancreatic tumors compressing the nerve, respiratory diseases).
- Toxic. Occurs due to toxic effects ( uremia , the effects of medications, alcohol), and metabolic disorders.
The main “taboo” in the fight against post-alcoholic hiccups
Such a popular technique among people far from medicine should not be used a scare For a drunk person, it can result in serious stress. The thing is that under the influence of alcohol , the work of internal organs and systems already malfunctions; the body functions in “emergency survival” mode, so it can react to fear in a very unexpected way.
Not only useless, but also a dangerous way to combat hiccups is to drink soda . There is an opinion that soda relieves diaphragm spasm. In practice, the situation is different - when carbon dioxide enters the stomach, it only stimulates additional muscle contractions, and the hiccups get worse. The same effect occurs when a person drinks a large amount of food - this not only additionally burdens the body, but can also provoke spasms of the diaphragm.
And the main idea that should be abandoned is the fight against a hangover and the accompanying hiccups with the help of alcohol (for example, beer). This can only prolong the binge and worsen your own condition.
What not to do if the hiccupping person is drunk
To get rid of hiccups in a drunk person, you should never scare him: the nervous reactions of a drunk are unpredictable, and sudden fear can cause fainting, a heart attack, or even a micro-infarction.
There are often tips to perform physical exercises: bend over and drink liquid in this position. But even for a slightly drunk person, such an exercise is unsafe: if coordination of movements is impaired, it is easy to break a glass or even fall. Therefore, it is better to postpone all physical exercises, except for a regular walk, until the next day, when the hops have worn off.
Precautionary measures
You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- bouts of hiccups last longer than an hour;
- spasms of the diaphragm spontaneously “roll up” several times a day or during the week;
- hiccups were accompanied by accompanying symptoms: chest pain, problems with swallowing, heartburn, deterioration in general health.
So, hiccups that arise as a result of alcohol abuse are the body’s physiological reaction to toxins (decomposition products of ethyl alcohol). A spasm of the diaphragm complements the clinical picture of a hangover and causes physical and moral discomfort in the “victim” of intoxication. Short-term hiccups can be dealt with at home, but if the abnormal condition does not go away, you need to seek help from a doctor.
Literature:
- Principles of providing outpatient care to patients with limited mobility: an interdisciplinary training manual / [Larina Vera Nikolaevna, Bart Boris Yakovlevich, Golovko Milada Gennadievna, etc.]; Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education “Russian National Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov”. – Moscow: Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogova Ministry of Health of Russia, 2022. – 179 p.
- Apchhi. To your health!: sneezing, hiccups, yawning: secrets, superstitions, useful tips / L. R. Cheremukhina. – Moscow: Eksmo, 2010. – 125 p.