Blood discharged from the anus together with feces or separately is a sign of disorders in the body of a pregnant woman. It is important to establish the exact cause of the appearance of such a symptom and select the most effective treatment, otherwise it will not be possible to avoid the development of complications.
Causes and danger of an unpleasant symptom
Basically, blood in the anus appears for the following reasons:
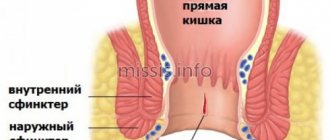
- Haemorrhoids. In most cases, bleeding appears immediately after bowel movement. As a rule, with hemorrhoids, a woman is bothered by constipation, a feeling of heaviness and itching in the anus.
- Proctitis and perirectal abscess. In this case, in addition to blood, mucus and purulent discharge may appear.
- Colon polyps or colorectal polyps are growths that appear on the lining of the colon or rectum. Apart from bleeding, there are no other symptoms that can confirm the presence of polyps, so additional examination (colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy) is required to diagnose them.
- Diverticulosis is a disease in which small protrusions (diverticula) form in the intestinal wall.
- Anal fissure. Usually occurs when the defecation process is disrupted and heals on its own in 50% of cases (after stool normalizes). Cracks make themselves felt not only by severe bleeding, but also by itching, sharp cutting pain in the anus, which stops after bowel movement.
- Blood in the stool may be due to stomach problems.
Blood in stool
The appearance of blood in the stool is an alarming symptom that is the first sign of many dangerous pathologies. Even if a person feels well, but observes regular bloody discharge from the anus, you need to visit a proctologist to find out the reasons for the deviation.
Causes of blood in stool
Bloody impurities in stool are a symptom of diseases in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Blood appears in feces:
- with varicose veins of the esophagus or anal canal;
- hemorrhagic gastritis;
- stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer;
- polyposis;
- cryptite;
- diverticulosis of the large intestine;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- proctitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- mesenteric thrombosis;
- vasculitis;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- hemangiomas;
- terminal ileitis of various etiologies;
- infectious lesions.
Attention: bloody discharge from the anus is one of the early symptoms of intestinal and stomach cancer.
Bloody impurities in the stool can appear as a result of mechanical damage to the anus. For example, during anal sex, improper use of enemas. Sometimes bleeding occurs during a course of taking certain pharmaceutical drugs (anticoagulants, NSAIDs and others). In children, blood in the stool is observed with an allergy to cow's milk proteins or lactase deficiency.
Additional symptoms
Gastrointestinal bleeding can be acute or chronic. In the first case, large-scale blood loss develops rapidly (within a few minutes). The patient has:
- insatiable thirst;
- nausea;
- dry mouth;
- vomiting, the color and consistency of which resembles coffee grounds;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- weakness;
- acute abdominal pain;
- muscle tremors;
- loss of consciousness;
- urinary retention.
Attention: this patient’s condition requires urgent medical attention.
Chronic bleeding can be recognized by the following accompanying signs:
- general malaise;
- brittle nails;
- blanching of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- cardiopalmus;
- noise in ears;
- low blood pressure;
- hair loss;
- fainting;
- heartache.
As the disease develops, its characteristic clinical picture appears. At the initial stages, only a proctologist can determine the cause of the deviation.
Diagnosis of blood in stool
A visit to the clinic begins with a patient interview and palpation. The nature of bloody discharge has a high diagnostic value:
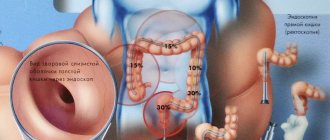
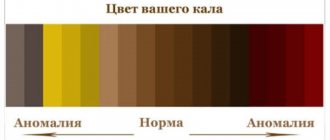
- bright scarlet streams or droplets not mixed with feces, smears on toilet paper - a sign of hemorrhoidal bleeding, anal fissure;
- red streaks are evidence of problems with the sigmoid colon;
- dark brown bloody inclusions, evenly connected with feces, are characteristic of diseases of the initial part of the large intestine;
- black, pasty stools indicate severe bleeding in the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus.
Based on the information received, the doctor establishes a presumptive diagnosis. To confirm (or refute) the patient is sent for additional examinations.
To determine the cause of bleeding and the degree of development of the disease, different methods are used:
- general blood analysis;
- endoscopic colonoscopy with collection of histological material;
- X-ray with contrast agent;
- examination of feces for helminth eggs, occult blood;
- Ultrasound;
- sigmoidoscopy.
The set of diagnostic procedures is selected individually. After receiving the examination results, the doctor prescribes effective therapy for the patient.
Treatment
Therapy for gastrointestinal pathologies, which are characterized by the appearance of blood in the stool, is carried out in two directions: eliminating the cause of the deviation, stopping the bleeding.
In drug treatment, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used, depending on the diagnosis:
- laxatives;
- venotonics;
- antibacterial;
- cytostatics;
- hormonal;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- antiviral and others.
Attention: the use of external or systemic medications without a doctor’s prescription leads to serious complications.
To stop intestinal bleeding, drugs that stimulate thrombus formation are used. When it is not possible to cope with the problem using conservative methods, the patient undergoes surgery.
Since spotting is accompanied by anemia, the patient is advised to take iron supplements to correct hemoglobin levels. In severe cases, the patient is given a transfusion of blood plasma or its components.
During the rehabilitation period, a person is recommended a special gentle diet with the exclusion of foods that injure the intestinal mucosa.
Prevention of blood in stool
There is no specific prevention of intestinal bleeding, but the risks of developing gastrointestinal pathologies can be reduced.
To do this you need:
- eat small portions, 4–6 times a day;
- add fiber to your diet, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive tract;
- avoid stress;
- minimize the consumption of semi-finished products, fast food, fatty, fried foods;
- drink 1.5–2 liters of fluid per day (if there are no kidney diseases);
- avoid hypothermia;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- do exercises regularly.
To notice abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract in the early stages, it is necessary to undergo annual preventive examinations. This is especially important for people with a hereditary predisposition to diseases of the digestive system.
The causes of blood in the stool are varied, and it is not possible to determine them on your own. The answer to the question of why a violation occurred can only be given by a qualified specialist. Most pathologies accompanied by bloody discharge are benign and respond well to treatment in the early stages of development.
Author
Zagirov Fizuli Abumuslimovich
phlebologist, surgeon, proctologist
18 years of experience
+7
When and which specialist should I contact?
Medical assistance is required in cases where:
- weakness, malaise, fatigue, nausea and vomiting appear;
- body temperature rises;
- sharp cutting pain occurs in the abdominal area;
- bleeding becomes very heavy and does not stop after bowel movement.
It must be remembered that in the early and late stages of pregnancy, any bleeding is dangerous for both the mother and the fetus. That is why, if at least one of the mentioned symptoms is present, an immediate visit to the proctologist is required.
Treatment of anal bleeding during pregnancy
The following methods can be used in treatment:
- drug therapy with antihemorrhagic drugs and other hemostatic agents, mainly plant-based;
- detoxification therapy aimed at restoring water balance in the body, cleansing the intestines of harmful substances and improving stool;
- surgical intervention performed in the most extreme cases.
In addition, the woman is prescribed a special diet. Products that negatively affect the intestinal microflora are excluded from the diet.
What tests are performed to identify the cause of bloody impurities in the stool?
After examination, the doctor may prescribe the following studies:
- Fecal occult blood test. Allows you to detect small blood impurities that are invisible to the naked eye.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum. In this case, the doctor can directly examine the mucous membrane and detect the source of bleeding.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the entire colon.
- Irrigography (irrigoscopy). This is an X-ray examination of the colon with a contrast agent. Before the pictures are taken, the patient is given a barium sulfate enema.
Today you can visit a specialist and undergo an examination if blood appears in the stool at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. After all the necessary research has been carried out, the specialist will give recommendations on treatment. If surgical intervention is required, it can be performed in the modern proctology department of the multidisciplinary clinic CELT.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Prevention measures
To avoid such an unpleasant problem as blood from the anus during pregnancy, a woman is recommended to:
- increase the volume of fluid consumed to 1.5–2 liters per day;
- avoid disruption of the digestive process;
- adhere to a balanced diet or a special diet recommended by a doctor;
- do not forget about personal hygiene;
- spend more time outdoors.
During pregnancy, a woman needs to be attentive to her health, promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases and avoid complications. If you notice blood coming out of the anus, you should consult a doctor.
Possible causes of bloody impurities in stool
Possible causes of blood in stool
Hemorrhoids and anal fissures
Bloody impurities in the stool are a characteristic sign of anal fissures and hemorrhoids. There may be varying amounts of blood in the stool.
With hemorrhoids and anal fissures, fresh blood of a bright scarlet color is found in the stool. Also, with these diseases, there is pain during and after defecation, and constipation. With hemorrhoids, the nodes may fall out of the anus.
Rectal tumors
Bloody discharge from rectal tumors resembles that from hemorrhoids. Bleeding is usually accompanied by disintegrating malignant tumors. Therefore, during the examination, the proctologist should be especially attentive, and if suspicion arises, a biopsy for histology should be prescribed - examination of a fragment of a tumor formation under a microscope.
Inflammatory diseases of the colon (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease)
The cause of bleeding in this case is severe inflammation of the intestinal mucosa with damage to the integrity of its structure and the walls of blood vessels. The amount of blood during bowel movements may vary, mixed with mucus. The clinical picture may be accompanied by abdominal pain, symptoms of general intoxication (weakness, fever, etc.).
Bleeding in the stomach and upper small intestine
Most often, bleeding in the stomach and duodenum is caused by a peptic ulcer or the presence of a disintegrating malignant tumor. While the blood reaches the rectum, it has time to be exposed to enzymes and partially destroyed. Therefore, there is no scarlet blood in the stool, the stool is black and tarry.
Intestinal infection
For example, with dysentery, an admixture of dark-colored blood, pus, and mucus appears in the stool. Bloody impurities may appear in the stool and with other intestinal infections. An infectious disease specialist treats these diseases.
Rectal fistulas
With this disease, blood is not released with feces, but through the external opening of the fistula, which is located in the anus. During an exacerbation, pus and blood are released from the fistula. In this case, the general condition of the patient is disturbed and the body temperature rises.