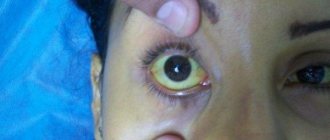
This is a special category of bacterial cultures, many species of which are dangerous to human health. Staphylococci are commonly called opportunistic microbes. Living in the body constantly, they are under the control of the immune system. But when the protection is weakened, they can provoke an inflammatory process. Some bacteria are extremely resistant to antimicrobial agents and often cause superinfections.
About the disease
When grown in a petri dish containing blood agar, Staphylococcus aureus colonies have a characteristic golden yellow color, hence the name. This microorganism is extremely common, colonizing about a quarter of the world's population.
It usually spreads in the nasal cavity, groin area, armpits and other parts of the skin, but in most cases it is a normal part of human skin flora and does not cause any problems.
However, as the number of bacteria on the skin increases, they begin to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through microcracks and can lead to skin infections and abscesses.
Pathological processes can affect not only various internal organs, such as the liver, kidneys, spleen, brain, but also muscles, bones and joints, which leads to extremely disastrous consequences, therefore, if you suspect an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor.
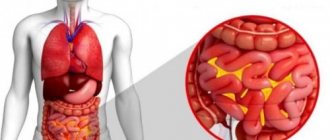
Intestinal diseases
Taking a smear for staphylococcus
Staphylococcus aureus often causes intestinal inflammation. The appearance of such a pathology may be associated with food poisoning or other factors. The disease is called bacterial gastroenteritis.
The effect of bacteria on the intestinal wall can cause fluid retention and interfere with the absorption of nutrients. The patient often experiences acute symptoms, including fever, vomiting, severe abdominal cramps, and diarrhea.
The course of bacterial gastroenteritis can range from mild to very severe. There is always a risk of acute loss of body fluids, which is usually associated with vomiting and diarrhea. This disease can be observed against the background of an improper diet, malabsorption syndrome and other pathologies.
The disease often resolves on its own, but improper treatment of the acute form of the infection can lead to the development of a chronic process. It is also important to stay hydrated, as dehydration can be fatal.
Bacterial gastroenteritis can be the result of poor hygiene. Infection can occur after close contact with animals or consumption of food contaminated with bacteria.
Types of staphylococcal infections
There are several most common types of staphylococci:
● Hemolytic staphylococcus.
Most often, this infection affects the upper respiratory tract, causing purulent sore throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis and other inflammatory diseases. These bacteria are very resistant and difficult to treat.
● Golden.
This microorganism is extremely resistant to almost all types of penicillin antibiotics, antiseptics, high temperatures, and active direct sunlight. It causes various skin lesions, such as eczema, abscess, boils, lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, upper respiratory tract, mucous membranes, and in the worst case leads to toxic shock.
● Epidermal.
This microorganism lives on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of any healthy person and does not cause any harm. But, if this bacterium enters the blood of a person with a weakened immune system, which most often occurs during surgical operations, the use of improperly processed instruments, catheters, blood poisoning occurs, which leads to inflammation of the inner lining of the heart.
● Saprophytic.
Despite the fact that this species is the least dangerous, when infected it leads to general intoxication of the body due to the release of dangerous toxins and enzymes during its life processes. These microorganisms often cause inflammation of the urethra and bladder. This is mainly typical for women due to the anatomical features of the structure of their genitourinary system. If left untreated, cystitis leads to kidney inflammation and problems conceiving a child.
Causes of infection
Among the reasons why Staphylococcus aureus enters the human intestine are the following:
- Eating contaminated foods. Most often, staphylococcus lives in confectionery products with cream, canned food, the manufacturing process of which has been disrupted.
- Direct contact with people carrying Staphylococcus aureus.
- In a hospital setting, during medical examinations.
- During childbirth or breastfeeding, from mother to child.
In addition, the bacteria can begin to actively multiply against the background of a decline in immunity. This happens even if it simply existed in the human intestines for several years without causing inflammation.
Symptoms and forms of staphylococcus in adults and children
The symptoms experienced by the patient vary greatly depending on the method and location of infection and the state of the immune system. But a number of the most characteristic features can be identified:
● elevated temperature;
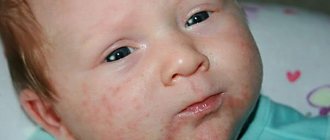
● suppuration of cuts, swelling, purulent rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, itching and redness of the eyes;
● lack of sense of smell and nasal breathing;
● sore throat, pain when swallowing, dry cough;
● nausea, vomiting, general weakened state;
● severe headaches, epileptic attacks, severe shortness of breath;
● painful sensations in the joints.
One of the most common forms of staphylococcus in adults is its asymptomatic carriage. A healthy person does not feel any signs of the disease until a provoking factor appears that gives impetus to the development of the disease.
For women, the most dangerous form is the saprophytic form, which can lead to cystitis. This is due to the fact that the women’s urethra is located very close to the vagina, which is why there is a high probability of pathogenic microflora, including staphylococcus bacilli, entering the urethral canal, and then into the bladder, causing its inflammation.
Since young children do not have a strong immune system, the risk of developing an infection in a child is quite high. Moreover, even those types of staphylococcus that cause practically no problems in adults can lead to serious complications in children. Staphylococcus is especially dangerous in children under one year of age, as it can easily spread throughout the body in the shortest possible time and lead to serious consequences, including death.
Symptoms
Bacterial gastroenteritis is a fairly aggressive disease characterized by acute symptoms. Violations of intestinal functions make themselves felt already on the first day of the development of the disease. The following symptoms may appear:
- Nausea and profuse vomiting.
- Prolonged diarrhea.
- Cramping abdominal pain and abdominal muscle cramps.
- Presence of blood in the stool.
- Fever.
- Dizziness and impaired consciousness.
- Weakness and loss of appetite.
- Headache.
- Reduced blood pressure.
The appearance of fever and abnormal blood pressure may require urgent hospitalization. The most dangerous symptoms of bacterial gastroenteritis are associated with dehydration, which can cause death in the patient. In addition, you should consult a doctor if symptoms do not go away within five days.
Causes
Most often, the bacterium enters the human body through wounds and microcracks in the skin. The infection, having penetrated through the wound, begins to multiply in the blood, spreading throughout the body and affecting the lungs, heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and joints.
With staphylococcus, diseases can be very different, such as pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, sepsis and many others.
Staphylococcus infection can occur in the following ways:
● Through contact and household use when using the patient’s personal items;
● Airborne droplets during close contact with an infected person;
● Fecal-oral on dirty fruits, vegetables and other food products, dirty dishes and hands;
● Vertical when a child passes through the birth canal of an infected mother during childbirth.
● Infection often occurs during surgery through medical instruments and during various manipulations.
Symptoms of staphylococcus in the intestines
Once in the body, the bacterium quickly causes the first symptoms of poisoning, most often this time is about half an hour. In some cases, the incubation period can last up to 6 hours.
Among the symptoms, a person notes the following:
- Stool disorder. At the same time, the urge to have a bowel movement is regular and may occur every hour.
- The nature of feces changes. They become liquid and slimy. In some cases, blood may be present.
- The patient complains of acute pain, localized in the epigastric region and lower abdomen.
- Poisoning is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- The skin around the anus is irritated, and diaper rash can form, even despite sufficient hygiene.
- Body temperature rises, but, as a rule, to low values and remains within 37.5 °C.
- General signs of intoxication are observed - fatigue, loss of appetite, dizziness, headaches.
As for children, at an early age, infection with this type of bacteria is more acute. A rash appears on the skin, the baby often spits up in gushing masses, the stool is foamy, copious and frequent, it may contain mucus and blood. Sometimes an increase in body temperature to high values is observed in cases where infection with intestinal staphylococcus occurs as a toxoinfection.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can diagnose the presence of infection based on the results of a staphylococcus test.
It is worth remembering that testing is recommended only if symptoms of the disease are present. The presence of bacteria in biological material may mean that a person is its carrier, which in itself is the norm.
For analysis, material is taken from the area where the infection is believed to be developing. To detect a pathological process, several tests are carried out to track the dynamics of bacterial growth. If their number increases rapidly, the presence of a staphylococcal infection can be diagnosed. Also, additional analysis will determine the specific type of infection so that the doctor can choose a personal treatment regimen.
Treatment
Staphylococcus can be treated surgically if there is a purulent lesion in the area of infection. It may also be necessary to remove an infected implant, catheter, etc.
As a conservative treatment for staphylococcus, antibiotics and antibacterial agents are used in combination with immunomodulatory therapy. The drugs are selected taking into account the resistance of staphylococcus to a wide range of medications. The use of brilliant green solution for treating infected wounds has shown greater effectiveness.
What tests need to be taken
First of all, to determine the presence of infection, a staphylococcus test is taken.
For diseases of the respiratory tract, a swab is taken from the nasopharynx and oropharynx, for cystitis - urine, for gastrointestinal disorders - feces, for skin lesions - a scraping from the skin, and if there is a suspicion of extensive infection, they donate blood.
Also, before starting treatment with antibiotics, it is required to be tested for resistance to these medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
Advanced cases of the disease are dealt with by an infectious disease specialist.
But if you just have suspicions and want to get an accurate diagnosis, first you should consult a therapist, or with children, a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and, based on the results obtained, will write you a referral to the necessary doctor.
How and when to get tested for staphylococci
Symptoms of staphylococcus A persistent runny nose or constant inflammation on the skin may indicate the activity of staphylococci in the body. Where can I get tested for staphylococcus?
Important! Staphylococcus aureus can infect any organ of the human body, causing inflammatory diseases. Go through diagnostics
Tests at home You can take the necessary tests without leaving your home. Call a specialist to your home
Cause of allergy Staphylococcal enterotoxin A can act as an allergen and cause COPD, bronchial asthma, and allergic dermatitis. More details
Diagnosis of diseases Regular preventive examination allows for timely detection of diseases and reduces the risk of complications. Where can I get tested?
Promotions and special offers Special offers and discounts on diagnostic laboratory services allow you to save on medical examinations. View current promotions
Staphylococcus is a genus of bacteria that can cause various diseases. For example, a cold or constant inflammation of the skin may be a consequence of the activity of Staphylococcus aureus, a dangerous and fairly common representative of the Staphylococcaceae family. What are the dangers of infection with staphylococcus, what tests can be done to identify the bacterium, and when is it necessary to take a sample for the microorganism? The answers to these questions, as well as tips on choosing a clinic for research, are in the article.
Types of tests for the detection of staphylococci
Staphylococcal bacteria are spherical in shape and are gram-positive. There are about 30 species in total[1]. Some representatives of the genus are present in the body, on human mucous membranes and skin, without causing harm. But golden, saprophytic, hemolytic and epidermal staphylococci under certain conditions can cause serious harm to health. In some cases, bacteria cause inflammatory processes[2]. The action of dangerous representatives of staphylococci is to damage the body with toxins that they produce in the process of life, as well as to reduce immunity.
Saprophytic staphylococcus is localized mainly in the urinary and genital organs, is more common in women than in men, and can cause cystitis. Staphylococcus epidermidis lives on the surface of our skin, but if, when the integument is damaged, it enters the blood, then in case of weakened immunity it can cause infection. Hemolytic staphylococcus most often affects the upper respiratory tract, causing purulent sore throat, pharyngitis, bronchitis and other diseases[3].
The most common one, which causes more than 60% of staphylococcal infections, is Staphylococcus aureus[4], it can harm absolutely any organ. It equally easily affects women and men, the elderly and children. It mainly causes purulent processes on the skin or in internal organs (such as the brain, heart and others), and can also cause food poisoning, pneumonia, meningitis and other diseases. At the same time, Staphylococcus aureus is quite difficult to defeat; it is not afraid of high temperatures, and is resistant to many antibiotics and antiseptics[5]. Despite the fact that the bacterium has been studied in some detail for a long time, a completely effective treatment does not yet exist. How is staphylococcus transmitted?
You can become infected with Staphylococcus aureus through airborne droplets, through indirect contact (dust, surfaces of things, clothing), through blood, and unsterile medical instruments. The pathological activity of staphylococci can be provoked by severe hypothermia of the body, constant consumption of nicotine and alcohol, permanent stress and lack of sleep.
By the way
You can catch Staphylococcus aureus by eating expired food. This is especially true for dairy and fermented milk products: cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt and even ultra-pasteurized milk. It is necessary to check the expiration date and throw away the expired product, even if it does not have an unpleasant odor and its taste has not changed.
Since staphylococcus can be localized in almost any part of the body, only a qualified doctor can decide what kind of biomaterial is needed to confirm or deny the presence of the bacterium. To test for staphylococcus, a swab is most often taken from the nose, throat or other mucous membranes. They also donate blood, urine or feces, and breast milk[6].
The pathological activity of staphylococci is not asymptomatic. There are a number of signs that may indicate the presence of an infestation. If these appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When should you get tested for staphylococcal infection?
If a person notices rashes on the skin (especially pustular ones), frequent and seemingly causeless inflammation of the sebaceous or sweat glands, or hair follicles, this is a reason to consult a specialist. A constant runny nose that cannot be cured, constant nasal congestion or excessive discharge may also indicate the activity of staphylococci. Sore throat, dry or wet cough, fever - these “cold” symptoms can be caused by staphylococcus. The probability, of course, is small, but getting tested will not hurt.
There are people who become more easily infected by these bacteria. Thus, those at risk are those suffering from cancer, diabetes mellitus or HIV, and patients on hemodialysis. Also, the likelihood of getting an infection is higher in people with skin injuries (cuts, burns), medical workers or agricultural workers. The elderly and newborns, breastfeeding mothers and people with weakened immune systems are also among those at increased risk of contracting staph.
A staphylococcus test is taken not only when symptoms appear. It can be prescribed to pregnant women to reduce the likelihood of transmission of staphylococcus from mother to child during pregnancy and (or) childbirth, to hospitalized patients for preventive purposes, to catering staff and medical personnel. A referral for analysis can be given by a therapist or pediatrician, ENT specialist, infectious disease specialist, urologist, mammologist, dermatologist and even a gastroenterologist. If a person has received such a referral, he must fulfill a number of instructions that affect the degree of reliability of the result.
How to prepare for a test for Staphylococcus aureus
Before being tested for Staphylococcus aureus, you should not take antibiotics for two months. If the patient has been treated with antibacterial drugs, he needs to inform the doctor about this [7]. The material is taken on an empty stomach, usually in the morning. It is best to refrain from smoking for several hours before visiting the laboratory.
A patient taking sputum from the nose or throat for analysis needs to drink plenty of fluid 10–12 hours before the test. This will make the discharge less thick, and it will be easier for the doctor to take the material. Eight hours before the test you should not drink, eat or brush your teeth, so the test is usually scheduled for the morning.
Two days before donating urine, the patient needs to stop taking diuretics, and three days before donating stool, stop using laxatives or other drugs that affect bowel function (including suppositories and ointments)[8]. If a genital smear is taken, men are advised not to visit the toilet three hours before the procedure, and women are advised to come for testing before menstruation or two days after it ends.
How to submit biomaterial for analysis correctly
If the patient collects biomaterial independently, he is responsible for the correctness of the procedure. It must be remembered that feces or urine must be collected in a sterile container, which can be purchased at any pharmacy or obtained from a private laboratory.
The collection of material in a medical institution occurs as follows. A swab from the nasal and oropharyngeal mucosa is taken with a small cotton swab - the procedure is absolutely painless. Then the doctor places the sample in a special nutrient medium, where bacteria, if any, will rapidly multiply.
Collecting discharge from a wound or any other affected area is also done using a cotton swab - the doctor only needs a small amount of biomaterial. Whether this manipulation will be painful depends on the nature of the damage, but, as a rule, the pain is tolerable.
Staphylococcus test results
You can get the result of a blood test after 24 hours, and a stool or urine test a little later. In the latter case, the timing depends on the specifics of the medical institution; usually the study takes from one and a half to three days.
If the result is negative, then there is no Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in the area being tested. If the result is positive, this means that the person is either sick or a carrier of the infection. It is necessary to undergo a course of treatment as prescribed by a doctor.
A person who does not have medical knowledge cannot independently determine the fact of infection with a staphylococcal infection. No symptoms can clearly indicate the presence of bacteria in the body. Therefore, in case of frequent respiratory diseases, in case of periodic poisoning, recurrent skin infections, it is worth contacting specialists and getting tested for Staphylococcus aureus. Prompt results and timely treatment can save the patient from many complications, some of which sometimes develop into chronic diseases.
Where can I get tested for staphylococcus?
A person who is concerned about his health and decides to undergo testing to determine staphylococcus can use the services of a public medical institution or contact a private laboratory.
In the first case, you may encounter long queues and mediocre service. In this sense, private medical centers are becoming a more attractive option. You can get tested for staphylococcus at the Gemotest Laboratory: the company has more than 1,250 laboratory departments throughout Russia. So patients will certainly find “their” Hemotest department, for example, near home or closer to work.
The company offers medical services such as determination of Staphylococcus aureus toxins in fecal samples, microbiological examination of breast milk and nasopharyngeal smears for Staphylococcus aureus, and so on[9]. It is also possible to detect Staphylococcus aureus in urine, scrapings from the conjunctiva, rectal scrapings, sputum discharged from the ear, and in venous blood. The results will be ready within one to seven days.
If necessary, you can take the test without leaving your home. To do this, you need to leave a request for a Hemotest specialist to visit you by phone or on the company’s website. You can get the results in any laboratory department or in your personal account on the Hemotest website. Also, indicators can be sent to the patient by email.
High accuracy of results, the shortest possible time for conducting research, low probability of error - all this is possible thanks to the modern equipment of the Hemotest Laboratory. Automation of the production process and multi-level quality control also help to avoid errors.
PS The Hemotest laboratory conducts more than 2,500 studies. The results are recognized by all medical institutions in the country.
* License to carry out medical activities No. LO-50-01-011414 issued on November 1, 2022 by the Ministry of Health of the Moscow Region.
** License to carry out medical activities No. LO-23-01-014424 issued on March 13, 2022 by the Ministry of Health of the Krasnodar Territory.
Sources:
- 1 https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococci
- 2 https://minzdrav.gospmr.org/press-tsentr/arhiv/o-stafilokokke-i-stafilokokkovoy-infektsii1434.html
- 3 https://doctor-anna.ru/publikatsii/stafilokokk/
- 4 https://09.rospotrebnadzor.ru/content/k-voprosu-o-stafillokokkah
- 5 https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aureus_staphylococcus#Antibiotic resistance
- 6 https://studfile.net/preview/5778985/
- 7 https://invitro.by/analizes/for-doctors/583/2408/
- 8 https://clck.ru/Vo5Bq
- 9 https://gemotest.ru/search/?q=golden+staphylococcus
All information related to health and medicine is presented for informational purposes only and is not a reason for self-diagnosis or self-medication.