Instructions for use IBUPROFEN
Inducers of microsomal oxidation (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, increasing the risk of severe hepatotoxic reactions.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. Reduces the hypotensive activity of vasodilators (including slow calcium channel blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), natriuretic and diuretic activity of furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide. Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs, enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics (increasing the risk of hemorrhagic complications).
When interacting with mineralocorticosteroids. glucocorticosteroids, colchicine, estrogen, ethanol can cause an ulcerogenic effect with bleeding. Enhances the effect of oral hypoglycemic drugs and insulin. Antacids and cholestyramine reduce the absorption of ibuprofen. Increases the blood concentration of digoxin, lithium and methotrexate.
Caffeine enhances the analgesic effect of ibuprofen. When administered simultaneously, ibuprofen reduces the anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet effect of acetylsalicylic acid (an increase in the incidence of acute coronary insufficiency in patients receiving small doses of acetylsalicylic acid as an antiplatelet agent is possible after starting ibuprofen).
When prescribed with anticoagulant and thrombolytic drugs (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase), the risk of bleeding simultaneously increases.
Cefamandole, cefaperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid, plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
Myelotoxic drugs increase the manifestations of hematotoxicity of the drug. Cyclosporine and gold preparations enhance the effect of ibuprofen on the synthesis of Pg in the kidneys, which is manifested by increased nephrotoxicity.
Ibuprofen increases the plasma concentration of cyclosporine and the likelihood of developing its hepatotoxic effects.
Drugs that block tubular secretion reduce excretion and increase plasma concentrations of ibuprofen.
When using ibuprofen simultaneously with potassium-sparing diuretics, there is a risk of developing hyperkalemia; with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - the risk of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract increases.
When is it appointed?
Ibuprofen is to some extent a harmless drug, but if there are contraindications noted in the instructions, you should stop using the medicine. The opposite can lead to dire consequences. In addition, you cannot take an increased dose of medication, as there is a serious danger to life and health.
Benefits for headaches
Ibuprofen will be a good help when you suffer from excruciating headaches. In particular, it is prescribed for migraines, characterized by prolonged pain. In this situation, the drug should be used as soon as possible after the onset of migraine symptoms. If your health does not improve, repeat taking the medicine after 5 hours. This treatment regimen is very effective and most often leads to a positive result.
When nervous tension occurs, “discomfort” occurs; in this situation, an Ibuprofen tablet will help.
Ibuprofen for toothache and menstruation
The medicine is a pathognomonic drug. If there is no way to get an appointment with a dentist, you can take an Ibuprofen tablet to relieve toothache. You should not take more than 6 tablets of the drug per day, the treatment course is a maximum of 5 days.
Ibuprofen will be useful after implant placement and tooth extraction; it will help relieve pain.
During menstruation, many women experience pain; to relieve it, it is advisable to take Ibuprofen. However, you should beware of overdose. The first dosage should be 400 mg; if the discomfort does not go away, after a few hours you will have to repeat the medication.
Treatment in this case should not exceed 3 days; if a positive result is not noted, consult a doctor.
Ibuprofen for colds
Each property of the drug is very effective for various types of colds. After taking Ibuprofen, the fever quickly passes, pain decreases, due to which the patient’s condition quickly returns to normal.
To treat colds, tablets can be prescribed to persons over 12 years of age. The doctor may prescribe a different dosage than indicated in the instructions. Of course, Ibuprofen alone is not enough to get rid of a cold, but its anti-inflammatory properties help enhance the effects of other medications. Thanks to all this, recovery is accelerated.
Ibuprofen for fever
With many illnesses, people's body temperature rises; Ibuprofen will help reduce it. The pharmaceutical is prescribed as part of a complex therapeutic course for various diseases:
- Cold
- Injuries
- ENT diseases
- Viral, bacterial infections
- Joint and muscle pain
What to do in this case?!
The algorithm of actions for patients who do not have stomach problems and those who have a history of peptic ulcers or erosive changes is different. For the first group, when prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for more than 5 days, it is mandatory to prescribe drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Such as omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, etc. (for the entire course of treatment). For the second group, any prescriptions from the NSAID group, regardless of the duration of use, require parallel prescription of proton pump inhibitors. It is also mandatory to take a PPI for patients taking aspirin for a long time.
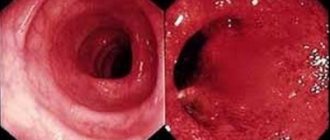
NSAID gastropathy
In the scientific literature, this problem is called “NSAID gastropathy.”
The term was first proposed in 1986 to distinguish specific damage to the gastric mucosa that occurs with long-term use of NSAIDs from classic peptic ulcer disease. The difference between NSAID gastropathy and peptic ulcer disease can also be traced by the affected area. Most often, ulcers can be seen in the stomach, and not in the duodenum. Plus, the changes are more common in older people than in younger people.
How it works?
How do these drugs work in our stomachs? Everything is very simple, the negative impact is realized due to the imbalance of defensive and aggressive forces. We have a number of defense mechanisms in our stomach that allow us to withstand the onslaught of aggressors. Among the latest:
- An acid whose pH balance is close to that of battery acid
- Bile and pancreatic juice, which can be thrown into the stomach.
- A number of medications.
- Alcohol and nicotine.
- Irritating food components (spices, spicy foods, etc.)
- Helicobacter pylori infection and so on.
The stomach is protected due to a thick layer of mucus and bicarbonates that neutralize acid, adequate blood supply, and the ability to regenerate very quickly. When we use NSAID drugs, the balance of forces changes towards aggressive mechanisms and damage occurs to the mucous and submucosal layer of the stomach and duodenum.
How to take Ibuprofen
Pills
Adults and children over 14 years of age can be given no more than 4 tablets per day. Depending on the condition, the dose can be adjusted and increased to 6 tablets (the dose is divided into several doses). When improvement is noted, the dose should be reduced to the original. The first tablet should be taken in the morning before meals with a glass of water. Then take 1 tablet after meals.
Without consulting a doctor, tablets can be used for no more than 5 days.
Candles
The suppositories are placed rectally. For pain and fever, the dose is determined taking into account the age and body weight of the baby. You can use no more than 10 mg per 1 kg at a time. Candles can be lit up to 4 times per day. The optimal duration of use is 3 days. If suppositories are used as an analgesic, they can be administered for 5 days.
If after the allotted time the fever has not disappeared, then you should consult your pediatrician.
Gel
You can use a 5-9 cm strip of gel at a time. Using smooth, light movements, rub the gel into the problem area until the composition is completely absorbed. It is allowed to use the gel no more than 4 times per day, with repeated use no earlier than after 4 hours.
The duration of the treatment course can be 15-20 days.
Ointment
The scheme for using the ointment is in all respects similar to applying the gel. The drug is rubbed into the problem area of the skin 3-4 times a day. Can be used within 15-20 days.
Children's suspension
Ibuprofen in the form of a suspension can be given to a child no more than 3 times a day. If your child is under one year old, you should definitely consult a specialist before use. If the fever appears as a result of vaccination, then the suspension is given 2 times a day. There should be a break of at least 6 hours between doses.
Some numbers
Some statistics. In the UK, approximately 24 million NSAIDs are prescribed per year. 70% of people over 70 years of age take NSAIDs once a week, and 34% daily. In the United States, up to 6 billion worth of NSAIDs are sold annually. As a result, the risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) increases 3–5 times, perforation by 6 times, and the risk of death from complications by up to 8 times. Up to 40–50% of all cases of acute gastrointestinal tract infections are associated with NSAIDs.
This problem is also relevant in our country, for example, according to the Scientific Center for Cardiovascular Surgery named after. A.N. Bakulev, out of 240 patients taking aspirin daily, even in small doses, gastroscopy revealed lesions of the stomach and 12 p.c. in 30% (of which ulcers - in 23.6%, erosions - in 76.4%). A similar picture was observed among colleagues from the All-Russian Research Institute of Rheumatology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences - in 2126 patients taking NSAIDs without “covering” (protection) of the stomach, erosions and ulcers of the gastroduodenal zone were found in 33.8% of cases. These are very impressive and dramatic numbers of complications from taking NSAIDs, considering the number of people using these drugs in developed countries.
When to take medicine
The medicine in tablet form is effective for the following conditions:
- inflammatory processes in the spine and joints;
- moderate pain of various origins (menstrual, headache, toothache, pain after surgery);
- fever caused by a cold infection.
Gel and ointment should be used in the following cases: osteoarthritis, arthritis, gout and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Suppositories and syrup are usually prescribed to children to reduce body temperature, for various childhood infections and to reduce pain (in the head, throat, ear).
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
It is not advisable to take ibuprofen and certain medications while pregnant. Although fever and pain pose a threat, the corresponding signs require quick elimination.
Ibuprofen, as recommended by your doctor, can be taken in the 2nd trimester; you should not be treated with it if there are contraindications. The medicine is contraindicated in the first or third trimester of pregnancy.
When breastfeeding, the medicine also quickly eliminates fever and eliminates pain. However, it can pass into breast milk and cause some harm to the baby, although there will be no serious health hazard. If there is an urgent need to take medication, the tablet should be taken after feeding. The concentration of the active substance in milk reaches a large amount 2 hours after administration, and then begins to rapidly decrease.
How to choose a medicine
In fact, the most important point is which medications we take. In the figure you can see the scale of aggressiveness of various drugs from the NSAID group in relation to the stomach.
The most aggressive drugs are Aspirin, Ketorolac, Piroxicam, Indomethacin. If possible, it is recommended to use selective drugs that have minimal gastrointestinal risks. Their use is always more desirable, these include Celecoxib and Rofecoxib. But despite their relative safety, they should be prescribed strictly according to indications by the attending doctor, do not forget about this.