In the case where diarrhea is caused by pathogenic microorganisms, the use of antimicrobial drugs is absolutely always necessary to most effectively eliminate the pathology.
Symptoms of diarrhea are associated with various circumstances; taking into account the nature of the malfunction in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, medication is prescribed. Is it possible to take Tetracycline if you have diarrhea?
As a rule, the drug is recommended for use by doctors in this condition. The medication is prescribed by a medical specialist only when the symptoms of an unpleasant condition are caused by the presence of viral microflora.
Taking Tetracycline for diarrhea
The tablets help against diarrhea in adult patients; they help block protein connections that are made by pathogens. During the division process, genetic information can be transmitted in a disrupted form, so the proliferation of bacteria decreases over time.
It must be remembered that Tetracycline is a fairly strong antimicrobial agent, so it should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
This drug is considered an excellent antibiotic, which is able to eliminate any pathological process in the intestines that is accompanied by loose stools. The effect of this medication is based on its ability to inhibit the spread of pathogens in the digestive system.
Along with it, you should take a medicine that is a probiotic, which helps maintain the intestinal microflora in good condition. How to take Tetracycline for diarrhea?
Patients should use the drug orally. It is distinguished by good absorption and penetration into all organs and tissues. The remainder of the drug is excreted from the body through urine or feces.
Indications for antibiotic use
Tablets are prescribed extremely often. A wide range of influences and pronounced accessibility of the drug allow us to work with patients of different age groups suffering from various diseases. Main indications:
- upper respiratory tract infections (except for situations where streptococcal resistance is noted);
- lower respiratory tract infections;
- infections of the dermal tissue and soft tissues;
- pathological processes caused by the activity of rickettsia (the use of antibiotics is also relevant in the case of rare diseases - Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Q fever, rickettsial diseases);
- psittacosis;
- psittacosis;
- chlamydia and uncomplicated urogenital infections;
- inguinal granuloma;
- relapsing fever;
- bartonellosis;
- tularemia;
- plague;
- cholera;
- brucellosis;
- urinary tract infections.
Tetracycline tablets help if the patient is prohibited from taking penicillin drugs. The analogue is relevant for the following forms of pathologies: syphilis, necrotizing gingivitis, anthrax, actinomycosis.
How to take the drug for pathology?
If diarrhea occurs, Tetracycline is used only after meals. The drug must be taken strictly according to the instructions. It is very important to follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that adult patients should take 0.25 grams of tablets three times a day. The main condition is considered to be a one-time intake of a certain amount of water, which helps to optimally and properly absorb the medicine.
According to the instructions for use for the tablets, “Tetracycline” for diarrhea is also used in childhood, but with extreme caution. Such therapy should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Dosage: 25 grams per kilogram of child’s weight per day.
The duration of treatment varies from five to seven days. In this case, it is necessary to focus on the following factors:
- When the least adverse reactions occur, you should stop using the medication.
- Negative effects include itching, as well as burning and rash.
- After the unpleasant symptoms have been eliminated, the tablets are used for one to three days.
It is important to know that “Tetracycline” for diarrhea provokes certain side effects only in cases where the requirements for taking it were not met or the patient did not take into account the restrictions on the use of the medication. Therefore, it is necessary to thoroughly study the instructions for use.
Admission rules
Tetracycline is an active substance that requires compliance with the rules of administration to obtain effective treatment:
- The use of antibiotics in combination with dairy products is unacceptable. Milk contains a substance that neutralizes the effect of the drug.
- The medicine is prescribed only by a medical professional. Not intended for the treatment of diarrhea in children under 8 years of age.
- The period of use of the medicine is determined by the gastroenterologist. The recommendations should be strictly and strictly followed so as not to aggravate the situation.
- The dose of Tetracycline is calculated based on examination data, the patient’s age and health status. Changing the dosage on your own can lead to undesirable consequences. Also, the drug tablet should be taken with a full glass of plain water.
- The stomach must be empty before taking the medicine. It is taken either in the morning on an empty stomach or after a meal 2 hours later.
- Since Tetracycline is taken in doses at certain intervals, it is impossible to skip time. If this happens, you need to take the pill as soon as possible. It is unacceptable to double the dose to catch up.
There may be a case when, after treatment with an antibiotic, a patient requires surgery. It is necessary to warn the surgeon about your recent use of tetracycline.
Adult dosages
In adults, the dosage of tetracycline is prescribed depending on the degree of damage to the body and the results of the examination. Ranges from 250 to 500 mg. The frequency of administration is 6 hours.
Produced in the form of a syrup for adults, the medicine is prescribed in the following dosages: 17 ml no more than 4 times a day. To prepare the solution you need to use 1-2 g of special granules.
Antidiarrhea remedy Tetracycline depot. For adults, as well as for children, this drug is prescribed from the first day of the onset of symptoms of intestinal upset caused by the negative effects of pathogenic microorganisms. On the first day, take 1 tablet every 12 hours. In the following days, until complete recovery, you need to take 1 tablet per day. One adult tablet contains 375 mg of the drug.
Children's dosages
Children from 8 years old receive a dosage of 25-50 mg, with a dosage period of 6 hours. One tablet contains 100 mg of active drug substance, which means it is divided into 4 parts and given to the child.
The suspension medicine is prescribed for the treatment of diarrhea in young patients, taken 4 times a day, every 6 hours. The dosage is calculated: 25 mg per kilogram of weight. One drop of suspension contains 6 mg of medication.
Another form of release of the drug used for diarrhea is Tetracycline depot. The gastroenterologist prescribes this medicine to take from the first days of symptoms. 1 day – 1 tablet, every 12 hours. Days 2,3,4 – 1 tablet per day. The amount of active substance in a children's tablet is 120 mg.
Peculiarities
Initially, medical specialists focus on the impossibility of taking it together with dairy products. In such a situation, the drug loses its beneficial properties.
In addition, you must follow the duration of therapy that was originally prescribed by the doctor. Otherwise, unwanted side effects and complications may occur.
According to the instructions for the tablets, “Tetracycline” for diarrhea is best taken on an empty stomach or two hours after a meal.
Separately, it is necessary to say about the restrictions on the use of the drug, which are important to know before using the medication.
Adverse reactions
When using the drug, certain negative effects may occur:
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing, is a symptom of diseases of the upper stomach, intestines and central nervous system).
- Gastritis (a long-term disease, characterized by dystrophic-inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa, occurs with impaired regeneration).
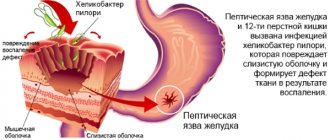
- Stomach ulcer.
- Enterocolitis (a disease of the digestive system that is caused by damage to the intestinal mucosa).
- Itching.
- Hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels of the circulatory system of any organ or area of the body).
- Labored breathing.
- Vertigo (a condition in which a person has the feeling that everything is spinning around him or that he himself is spinning).
- Edema.
- Migraine (a neurological disease, the most common and characteristic symptom of which is episodic or regular severe and painful attacks of headache in one (rarely in both) half of the head).
- Diseases of the organs of vision.
- Fever.
- Vomit.
- Anorexia (a disease based on a neuropsychic disorder, manifested by an obsessive desire to lose weight, fear of obesity).
- Constipation.
DOES PNEUMONIA REALLY FOLLOW COVID-19?
— Recently, an analysis of statistical data shows that the medical community is mistakenly addicted to antibiotics in the treatment of a new coronavirus infection, suggesting that changes in the lungs are immediately associated not only with the virus, but also with a bacterial component. This is not true, says pulmonologist Vladimir Beketov.
According to the expert, to date, a number of reputable medical associations have issued memorandums and open letters calling on colleagues to reduce the use of antibiotics during the treatment of COVID-19, because antibiotics do not provide benefit, but in this case cause harm, including toxic damage to the liver and development of antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
— That is, we seem to be trying to treat pneumonia, which in the doctor’s mind is strongly associated with bacteria, but in fact, at the stage, while there is no secondary pneumonia associated with Covid, we are only dealing with coronavirus lung damage, which is recommended not to be called pneumonia, and call it pneumonitis (inflammation of the vascular walls of the alveoli, as well as the tissue separating the alveoli from the lungs, which is accompanied by scarring - editor's note), says pulmonologist Vladimir Beketov.
The very phenomenon of secondary bacterial pneumonia due to coronavirus is overestimated, the expert continues. Such processes develop mainly in patients with heart failure, and for them there are increased precautions, restrictions on movement, recommendations for self-isolation and treatment at home.
- Smokers are also at risk for developing bacterial pneumonia. However, if smokers with COPD receive proper inhalation treatment and are vaccinated against pneumococcus, then their risks of secondary bacterial pneumonia are also minimized, says Vladimir Beketov.
Additional negative effects
According to the instructions, “Tetracycline” for diarrhea can provoke the following unpleasant conditions:
- Glossitis (an inflammatory process in the tissues of the tongue, accompanied by a change in its structure and color).
- Esophagitis (a disease of the esophagus, which is accompanied by damage to its mucous cavity).
- Thrombocytopenia (a condition characterized by a decrease in platelet count below 150·109/l, which is accompanied by increased bleeding and problems stopping bleeding).
- Neutropenia (reduced level of neutrophil granulocytes in the general cellular composition of the blood to a level less than standard).
- Photosensitivity (a condition in which a person develops an acute allergic reaction to exposure to ultraviolet rays).
- Candidiasis (an infectious disease affecting the skin, mucous membranes and/or internal organs, caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida).
- Urticaria (an allergic disease that is manifested by the formation of blisters on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes).
When, after a certain amount of time has passed after taking Tetracycline, the following symptoms appear for diarrhea, you should consult a doctor.
Side effects
How much to take the drug is decided solely by the attending physician, focusing on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the specifics of the problems that need to be dealt with. It is important to choose the minimum dose of the drug at which the maximum effect would be observed.
Such a clear calculation of the dose is important, since there is always a risk of side effects. And they usually arise against the background of an ill-chosen regimen for taking medicinal products. For long-term therapy, tetracycline lect is recommended to be supplemented with antifungal agents (for example, taken with nystatin). Main side effects:
- digestive system (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea);
- Central nervous system (cephalgia, dizziness);
- skin (photosensitivity, rashes);
- local reactions (vaginitis, dysbacteriosis).
By the way, tetracycline antibiotics are widely used in veterinary practice. They can be prescribed to a cat or dog when various infectious processes develop. The issue is resolved exclusively by the veterinarian.
Tetracycline with nystatin
Tetracycline with nystatin should be considered as a separate drug in demand in the modern pharmacological market. This is a combination product that has both antimicrobial and antifungal effects.
The main active ingredients are presented in almost the same amount, which makes the product more versatile and effective.
Pharmacological form: tablets. The medicinal product is relevant for diseases of the ENT organs, acne, pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis, cholecystitis. It is advisable to prescribe a new remedy for sexually transmitted diseases, intestinal infections, infectious processes localized in bones and joints.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of Tetracycline for diarrhea has a number of pros and cons. The main advantages of treatment with this drug are the following:
- The drug effectively eliminates the problem.
- The ability to use Tetracycline simultaneously with other medications that restore intestinal microflora. Prebiotics should be used only after completion of treatment with Tetracycline, otherwise the medication will begin to “fight” bacteria beneficial to the body.
- The main advantage of using Tetracycline for diarrhea is its low cost.
The drug also has certain disadvantages:
- According to the instructions, children under eight years of age should not take Tetracycline, since such therapy can cause destruction of tooth enamel.
- An antibiotic can stop the spread of pathogens, as well as beneficial bacteria that are necessary for digestive processes; dysbacteriosis may occur.
What are the limitations of the medicine?
"Tetracycline" for diarrhea in adult patients is not recommended for use in the presence of the following pathological processes in the body and conditions:
- Pregnancy.
- Breast-feeding.
- Liver and kidney diseases.
- Children's age up to eight years.
- Mycoses (fungal skin disease caused by microorganisms).
- Leukopenia (decrease in the number of leukocytes per unit volume of blood).
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (a serious disease in which the body’s own immune system perceives the human body’s cells as foreign).
- Hematuria (a medical term that refers to the presence of blood in the urine above the physiological norm).
Oral tablets Tetracycline hydrochloride (Tetracyclini hydrochloridum)
Instructions for medical use of the drug
Description of pharmacological action
A broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic of the tetracycline group.
Indications for use
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug: bronchitis, pneumonia, purulent pleurisy, subacute septic endocarditis, bacterial and amoebic dysentery, whooping cough, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, gonorrhea, brucellosis, tularemia, typhus and relapsing fever, psittacosis, ornithosis, infectious diseases urinary tract, chronic cholecystitis, purulent meningitis, purulent infections of the skin and soft tissues, cholera. Prevention of postoperative infections.
Release form
Film-coated tablets. 20 tablets in a blister pack.
Pharmacodynamics
A broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic of the tetracycline group. It acts by inhibiting protein synthesis due to blocking the binding of aminoacyl transfer RNA (tRNA) to the messenger RNA (mRNA)-ribosome complex. Active against gram-positive (Staphylococcus spp., including those producing penicillinase; Streptococcus spp., including Streptococcus pneumoniae); Haemophilus influenzae, Listeria spp., Bacillus anthracis) and gram-negative microorganisms (Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp.), as well as Ricketsia spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., Treponema spp. Resistant to the action of the drug: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., Serratia spp., most strains of Bacteroides spp. and mushrooms, small viruses.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, 75–80% of the drug is absorbed, 55–65% is bound to plasma proteins, the maximum concentration in the blood is reached after 2–3 hours and is 1.5–3.5 mg/l. Over the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. It is distributed unevenly in the body: the maximum concentration is found in the liver, kidneys, lungs and organs containing many elements of the RES (spleen, lymph nodes). The concentration of Tetracycline in bile is 5–10 times higher than in blood serum. In the tissues of the thyroid and prostate glands, the content of the drug is the same as in the blood plasma. In pleural and ascitic fluid, saliva, and breast milk, the concentration of the drug is 60–100% of its concentration in blood plasma. It accumulates in large quantities in bone tissue. Penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. Penetrates the placental barrier and enters the fetal blood. 30–50% is metabolized in the liver. It is determined in urine in high concentration 2 hours after administration and persists for 6–12 hours; During the first 12 hours, 10–20% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys. 5–10% of the total dose is excreted with bile into the intestine, where partial reabsorption occurs (enterohepatic circulation), which promotes long-term circulation of the active substance in the body. Excretion through the intestines when taken orally is 20–50%. The half-life is 8 hours.
Use during pregnancy
Contraindicated during pregnancy. During treatment it is necessary to stop breastfeeding.
Contraindications for use
Hypersensitivity to the drug and related antibiotics, fungal diseases, liver dysfunction, kidney disease, leukopenia, pregnancy, lactation (stop breastfeeding during treatment), children under 8 years of age.
Side effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, glossitis, discoloration of the tongue, staining of teeth, esophagitis, transient increase in blood levels of hepatic transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine. From the central nervous system: fainting, headache. From the hematopoietic system: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia. Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, eosinophilia, Quincke's edema. Dermatological reactions: photosensitivity. With prolonged use of the drug, complications may arise due to the development of candidiasis (damage to the skin and mucous membranes, as well as septicemia caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans). Antifungal antibiotics (nystatin, levorin) are used to treat candidiasis.
Directions for use and doses
Tetracycline is taken orally, during or immediately after meals, with water. A single dose for adults is 250 mg every 6 hours. The highest daily dose is 2 g. Children from 8 to 12 years old – 10 – 15 (up to 25) mg/kg per day in 3 – 4 doses; over 12 years old - adult doses, that is, 250 mg 3 - 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 5 – 7 days. After normalization of body temperature and disappearance of clinical signs of the disease, the drug is taken for another 1 to 3 days.
Overdose
The manifestations of the described side effects may increase. Treatment is symptomatic therapy.
Interactions with other drugs
Preparations containing metal ions (antacids, iron, magnesium, calcium preparations) form inactive chelates with Tetracycline, and therefore their simultaneous administration should be avoided. Combination with penicillins and cephalosporins, which have a bactericidal effect and are antagonists of bacteriostatic antibiotics (including tetracycline), should be avoided. When used simultaneously with retinol, intracranial hypertension may develop. When used simultaneously with cholestyramine, the absorption of Tetracycline is impaired. The combination of Tetracycline with oleandomycin and erythromycin is considered synergistic. Due to the inhibition of intestinal microflora, the prothrombin index decreases, which necessitates dose adjustment of indirect anticoagulants. Chymotrypsin increases the concentration and duration of circulation of Tetracycline.
Special instructions for use
If renal function is impaired, accumulation and development of side effects are possible. Tetracycline is prescribed with caution for leukopenia. Tetracycline is not prescribed to children under 8 years of age, as it causes long-term discoloration of teeth, enamel hypoplasia, and slower longitudinal growth of skeletal bones. Tetracycline should not be taken simultaneously with milk and other dairy products, since this interferes with the absorption of the drug. During treatment with Tetracycline, it is necessary to carefully monitor the patient's condition. If signs of hypersensitivity to the drug and side effects appear, take a break from treatment and, if necessary, prescribe another antibiotic (not the tetracycline group); If symptoms of candidiasis appear, antifungal antibiotics and vitamins are prescribed. It is not advisable to prescribe the drug to adults in doses less than 800 mg per day, since in addition to the insufficient therapeutic effect, the development of persistent forms of microorganisms is possible. Due to the possible development of photosensitivity, limiting insolation is required. In case of long-term use, it is necessary to periodically monitor the function of the kidneys, liver, and hematopoietic organs. It may mask signs of syphilis, and therefore it is necessary to conduct a serological test monthly for 4 months. To prevent hypovitaminosis, it is necessary to prescribe vitamins B and K, and brewer's yeast. This medicine contains ponceau 4R dye, which may cause allergic reactions, including asthma. Allergies most often occur in patients who are allergic to acetylsalicylic acid.
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light and out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Best before date
36 months
ATX classification:
J Antimicrobials for systemic use
J01 Antimicrobials for systemic use
J01A Tetracyclines
J01AA Tetracyclines
J01AA07 Tetracycline
When else should the drug not be used?
The drug "Tetracycline" is not recommended for use in conjunction with drugs that contain metal ions or penicillin.
An infectious disease is always considered a dangerous pathological process, since the virus has the ability to multiply, and therefore it is necessary to act immediately and effectively.
According to the instructions for use, “Tetracycline” for diarrhea is considered a good option for quickly eliminating the unpleasant signs of diarrhea.
This drug effectively eliminates pathogenic microorganisms and creates obstacles to their further spread.
Analogues of the drug
Tetracycline antibiotics are a whole range of various lyophysilates, capsules, ointments, suspensions for the total and local elimination of pathogenic microorganisms. The table shows analogues of drugs that can replace the popular tetracycline.
| Active substance | Names of pharmacological product | Manufacturer | Price |
| doxycycline | Vidoccin | ABOLmed LLC, Russia | From 250 rubles |
| oleandromycin | Olethetrin | Biosynthesis JSC (Russia) | From 180 rubles |
| tetracycline with nystatin | Tetracycline with Nystataine tablets | JSC "Biosintez", Russia | From 65 rubles |
| minocycline | Minocycline | AVVV RUS (Russia) | From 500 rubles |
The listed funds can be an alternative replacement. You cannot change the drug product yourself or make changes to the dosage regimen (including the dosage of the drug). This issue is dealt with exclusively by the attending physician.
How to properly store the drug?
According to the instructions for use, it is known that the shelf life of Tetracycline is twenty-four months. It should be kept in a dark, dry place, away from children, at a temperature of no more than 25 degrees.
In pharmacies, the drug is dispensed strictly according to a prescription from a medical specialist. You cannot take the drug yourself without a doctor’s prescription, as this can lead to various complications. The cost of Tetracycline varies from 40 to 100 rubles.