Functional disorders of the hepatobiliary system - everything you wanted to know, but were afraid to ask
Functional disorders of the gallbladder are disorders of its tone and motility, in the absence of organic changes (deformations, stones, polyps). Basically, there are 2 types of disorders - the hyperkinetic type, when the outflow of bile is too fast, and the hypokinetic type, when the bile is not evacuated in time and stagnates in the gallbladder.
There are many reasons for the disorder:
- Disturbance in the regulatory system of bile outflow when the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are unbalanced (for example, with neurosis)
- Endocrine system disorders (obesity, diabetes, women taking oral contraceptives)
- occupational hazards
- taking medications
- various diets,
- alcohol and tobacco
The modern classification of functional disorders according to the Rome IV criteria includes:
E. Gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi disorders
E1. Biliary pain
E1a. Functional biliary bladder disorder
E1b. Functional disorder of the biliary sphincter of Oddi
E2.Functional disorder of the pancreatic sphincter of Oddi
General manifestations of functional disorders of the biliary tract, according to the Rome criteria, should include attacks of pain in the right hypochondrium and/or epigastric region in combination with all of the following symptoms:
• the duration of pain episodes is at least 30 minutes; • repetition of attacks at different intervals (not daily); • pain increases and becomes persistent; • the pain is of sufficient intensity to interfere with the patient's activities or force him to seek urgent medical attention; • defecation, taking antacids, or changing body position do not relieve pain; • other pathological processes that could explain the appearance of these symptoms are excluded.
Additional, clarifying signs:
• pain is combined with nausea and vomiting; • pain radiates to the back or right subscapular region; • pain awakens the patient from a night's sleep.
1. Gallbladder dysfunction is a violation of the contractile activity of the gallbladder, caused either by initially existing metabolic disorders (for example, oversaturation of bile with cholesterol), or by primary functional disorders. The prevalence of this condition, according to some data, reaches 7.6% among men and 20.7% among women. In addition to those listed, criteria for gallbladder dyskinesia include the presence of a gallbladder and normal levels of liver transaminases, direct bilirubin and amylase/lipase.
Ultrasound examination helps:
- eliminate biliary sludge
- cholelithiasis
- determine the contractility of the gallbladder.
Transabdominal ultrasound or dynamic hepatobilis scintigraphy (DHS) can be used to assess gallbladder contractile function after challenge with a test breakfast or intravenous administration of cholecystokinin. Normally, after stimulation with cholecystokinin, the volume of the gallbladder decreases by 40% or more . In this case, it is necessary to carefully evaluate the medical history regarding the use of drugs that affect the contractility of smooth muscle fibers.
If the presence of small stones (<3 mm) is suspected, endoscopic ultrasonography is advisable. In some cases, to exclude microcholelithiasis, it is advisable to evaluate bile taken by duodenal intubation.
According to the recommendations of the Rome criteria, when gallbladder contractility decreases to less than 40%, according to GBSG with cholecystokinin, and the ineffectiveness of other treatment methods, the issue of cholecystectomy can be discussed.
2. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction . This term refers to disorders of the motor activity of the sphincter with impaired excretion of bile and/or pancreatic secretions.
Dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi is a violation of its contractile activity, expressed in increased basal pressure and/or paradoxical contractions of smooth muscle fibers.
Factors predisposing to the development of dyskinesia include: female gender
- changes in hormonal levels (during the premenstrual period, during pregnancy, taking hormonal contraceptives)
- diabetes
- stress
- diseases of organs functionally associated with biliary excretion (liver, pancreas, duodenum), operations on the stomach and biliary tract, accompanied by impaired innervation and changes in secretion.
According to accumulated data, dysfunction (in the form of dyskinesia or stenosis) of the sphincter of Oddi is one of the most common forms of so-called postcholecystectomy disorders, developing in 20% of patients who have undergone surgery. This may be explained by the fact that in the absence of a gallbladder, the common bile duct partly takes over the function of storing bile. Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi among patients undergoing cholecystectomy occurs with a frequency of at least 1.5%.
Clinical manifestations of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction:
- The pain is usually paroxysmal (cramping or gradually subsiding) lasting up to several hours, but sometimes it persists for a long time.
- Attacks of pain can develop 2-3 hours after eating fatty, fried foods, in some cases they are provoked by emotional stress.
- One of the clinical manifestations of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction may be recurrent idiopathic pancreatitis. Among such patients, an excessive increase in pressure in the sphincter is recorded in 15-72% of cases.
- According to a biochemical blood test, soon after an attack a more than twofold increase in the activity of liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin can be recorded.
Non-invasive research methods in the diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction:
- Ultrasound stimulation with a high-fat meal or administration of cholecystokinin or secretin can be considered as a screening test for signs of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. The diameter of the bile ducts is measured at intervals of 15 minutes for 1 hour. Dilation of the bile duct by 2 mm or more after consuming fatty foods (administration of cholecystokinin) indicates a violation of the evacuation of bile; a transient dilation of the pancreatic duct after the administration of secretin indicates a violation of the excretion of pancreatic juice.
- dynamic hepatobiliscintigraphy
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreaticography with secretin stimulation. This study is significantly safer than invasive methods and can reliably detect type II dysfunction.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography (ERCP) allows for targeted examination of the papilla of Vater and contrasting of the ducts, however, this diagnostic procedure is associated with a high risk of complications (acute pancreatitis develops with a frequency of up to 24%) and in itself is not sufficiently informative.
- The “gold standard” for diagnosing sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is direct endoscopic manometry, which allows you to determine the basal pressure in the sphincter (normally does not exceed 40 mm Hg) and register periodic contractions (normally at this time the pressure in the sphincter should not exceed 240 mm Hg Art., and the frequency of contractions should not be more than 10 per minute).
For these types of pathology, there are many treatment options, both medical and surgical methods, incl. minimally invasive, they even use botulinum toxin injections.
Materials used when writing this article:
Sheptulin A.A., Kurbatova A.A. New Rome criteria for functional dyspepsia IV revision // RZHGGK. – 2016. – No. 26(4). pp. 124-128.
Upnitsky A.A. Functional disorders of the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi: general principles of diagnosis and treatment // Consilium Medicum. Gastroenterology. – 2010. – No. 1. – pp. 30–34.
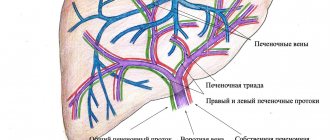
Ultrasound of the GBS organs (hepatobiliary system)
The hepatobiliary system (HBS) is a complex of internal organs that includes the liver, gallbladder, intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts, spleen, and pancreas. Many metabolic processes take place in this zone, toxins are neutralized, biologically active substances are produced that promote the absorption of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Stable operation of the hepatobiliary system ensures the normal functioning of the small intestine and the entire digestive tract as a whole. The slightest violations in the zone affect the general health of a person and can pose a threat to life. Ultrasound of the GBS organs helps to detect pathology at the very beginning of development. The sooner a patient sees a doctor, the more effective the treatment and the lower the risk of complications.
At the MedEx clinic you can undergo an ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system using modern digital equipment. A highly sensitive scanner allows you to obtain an accurate, informative image. If necessary, we will schedule you for a consultation with a general practitioner to interpret the results of the GBS ultrasound.
Indications for examination
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is prescribed for the following indications:
- Heaviness, pain, discomfort in the right hypochondrium.
- Bitter, unpleasant taste in the mouth, not associated with food consumption.
- Disorders of the stomach, intestines, increased gas formation.
- Deviations from the norm in the parameters of a biochemical blood test (for example, a high level of bilirubin, indicating GBS dysfunction).
- Pale or icteric tint of the mucous membranes of the mouth, eye sclera, and skin.
- Mechanical injuries of the abdomen in the area of the GBS.
- Long-term use of potent medications.
- Acute poisoning with toxic substances.
- Preparation for surgical treatment.
- Postoperative observation of the patient.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed medications, etc.
Preventive ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is recommended for patients with cancer, with a hereditary predisposition to liver cancer (carried out as part of oncological screening). People whose work is associated with exposure to harmful production factors need to check the health of the GBS annually.
Preparing for an ultrasound: 8 hours before the examination you need to stop eating and drinking water, so it is better to carry out the procedure in the morning.
Ultrasound standards
Average ultrasound indicators of the hepatobiliary system of a healthy adult:
- Liver: smooth, clear contours, homogeneous structure. There are no areas with pathological echogenic activity. The length of the right lobe of the organ is up to 140 mm, thickness – up to 120 mm, oblique-vertical dimension – up to 150 mm.
- Gallbladder: oval or pear-shaped, uniform density of contents. Wall thickness is up to 3 mm with a volume of 35-70 cm3.
- Intrahepatic ducts: smooth contours, no deformations. Diameter – up to 2 mm.
- Bile ducts: common diameter – up to 5-7 mm, lobar – up to 2-3 mm.
What does a GBS examination show?
During an ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system, the doctor evaluates the structure, density, size of internal organs, tissues, and vessels. The scanner allows you to analyze data in real time, which is important for monitoring blood flow. The results of ultrasound examination of the GBS are recorded in the protocol. When deciphering the conclusion, the doctor takes into account the gender and age of the patient.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system helps in the diagnosis of pathologies such as cholelithiasis, viral and reactive hepatitis, liver failure and coma, cholecystitis, polycystic HD. An experienced doctor will examine the smallest neoplasms, foci of fibrosis, and impaired blood flow on the monitor. When scanning, the abnormal structure of the zone is determined with high accuracy, for example, duplication of the gallbladder or left-sided location of the liver.
Other possible diagnoses:
- cholangitis – infection of the bile ducts;
- dyskinesia of the excretory tract;
- hepatosis – degeneration of functional liver cells;
- cirrhosis;
- hepatic decompensation;
- cholecystopancreatitis – simultaneous inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas;
- abscesses, tumors, cancerous formations in the GBS, etc.
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor can make a diagnosis and determine the stage of development of the pathology. This is important for choosing the right treatment tactics.
Sign up for an ultrasound of the GBS organs in Moscow
In our clinic, examinations are carried out by appointment. There are no queues; our offices are always comfortable and calm. Sign up for a GBS study by phone or online. Our clients appreciate affordable prices and high level of service.