Local and, less commonly, systemic allergic reactions are more common among children of preschool and primary school age, but signs of allergy can make themselves felt at any age, including adolescence. Any allergic reaction is a systemic process that is activated when chemical compounds and particles enter the child’s body that are perceived by the immune system as foreign. As in adults, complex therapy for allergic reactions in children includes taking medications, as well as following a hypoallergenic diet.
Signs of an allergic reaction in a child
At an early age, children are more likely to experience food allergies, which are associated with adaptation to new dietary habits. The reason for visiting a pediatric allergist and immunologist may be the appearance of the following clinical symptoms in a child:
- a skin rash on the face or all over the body that looks like flat pink spots or papules;
- intense itching of the skin, which prevents the child from sleeping at night and during the day;
- peeling of the skin.
From the gastrointestinal tract, with food allergies in children, symptoms such as loose stools mixed with mucus or blood, increased gas formation in the intestines (flatulence), and frequent episodes of vomiting appear. At an older age, when the child can describe his sensations, he complains of cutting pain in the central part of the abdomen or umbilical region, heaviness in the epigastric region, mainly after eating, as well as unstable bowel movements.
Any allergic reaction, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to the development of complications, which is why it is important to correctly formulate the child’s diet, eliminating foods and ingredients that can provoke allergies.
Before creating a daily menu for a child with signs of an allergic reaction, a consultation with an allergist and immunologist is necessary, followed by a laboratory examination and an allergy panel. This method allows you to accurately identify allergens that provoke a hypersensitivity reaction in the child’s body. The main goal of a hypoallergenic diet is to eliminate factors that would excessively activate the protective function of the immune system.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Regardless of the cause of amilorrhea, the first step in eliminating symptoms is diet therapy. A balanced protein-energy diet with a high content of vitamins is recommended. Preference is given to easily digestible foods that do not cause functional overload of the digestive organs and reduce or completely eliminate amilorrhea. A prerequisite is to quit smoking, since nicotine reduces the synthesis of bicarbonates and promotes acidification of the small intestine.
Conservative therapy
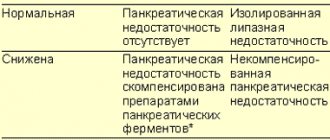
Enzyme preparations are effective in combating amilorrhea. They are dosed according to the amount of lipase, since its secretion is disrupted first. Effective drugs are selected in microgranular form, which are resistant to the action of gastric juice and provide rapid release of enzymes. For amylorhea, in addition to replacement therapy, after confirmation of the diagnosis, a number of drugs are prescribed:
- Probiotics
. The funds are aimed at normalizing the intestinal biocenosis and reducing fermentation processes. They eliminate diarrhea, reduce flatulence, improve digestion, thus reducing amilorrhea. To enhance the effect, probiotics are combined with prebiotics. - Antisecretory drugs
. Used for gastritis with high acidity and amilorrhea. Proton pump inhibitors and H2-histamine blockers are used. Medicines quickly normalize the secretion of hydrochloric acid and slow down gastric and intestinal peristalsis. - Antacids
. Medicines are recommended for the treatment of diarrhea combined with amilorrhea. They have an astringent effect and neutralize the irritating effect of hydrochloric acid on the intestinal wall. When the frequency of stools is about 10 or more times a day, special antidiarrheal drugs are indicated. - Insulin
. Replacement therapy is appropriate for concomitant disorders of the endocrine function of the pancreas. The dosage and frequency of administration are selected individually, taking into account the level of glucose in the blood, glucose tolerance test parameters, and the severity of amilorrhea. - Vitamins
. Injectable vitamin medications are administered for advanced forms of pancreatitis with impaired absorption of all nutrients. To correct the electrolyte composition of the blood during amilorrhea, magnesium, copper, and zinc preparations are prescribed.
For children over 3 years of age, strict dietary restrictions are provided.
The daily diet should replenish the physiological need for calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and other biologically significant components. The diet for food allergies in children over 3 years of age provides the following general rules:
- Meals should be small, medium portions, 3-4 times a day.
- If products require heat treatment, it is recommended to boil, steam or bake them. Frying or deep-frying is strictly unacceptable.
- When preparing fish and meat broths, the water should be changed at least 2 times after boiling.
- Control of drinking regime. Sufficient intake of water in the body allows you to speed up the process of eliminating allergens. The daily fluid intake for a child over 3 years old largely depends on the level of physical activity. At the age of 3-8 years, the norm of fluid intake (in the absence of contraindications) is 1700 ml, taking into account first courses and hot drinks.
- If a child has been diagnosed with an allergy to cow's milk protein, gluten or egg white, then dairy products, chicken, duck and quail eggs, and grocery products containing gluten are excluded from the diet.
The duration of the diet depends on the severity of the allergic reaction. Your doctor may recommend following dietary restrictions for 2-3 weeks.
Causes of amilorrhea
Irritable bowel syndrome
The appearance of a symptom is possible with IBS with a predominance of diarrhea. Amilorrhea is caused by increased intestinal motility, as a result of which digestive enzymes do not have time to act on carbohydrates. It manifests itself as liquid yellow or light brown stool with an unpleasant, pungent odor. Before defecation, spasmodic pain in the abdomen intensifies, after bowel movement it decreases or disappears completely.
Intestinal infections
Amilorrhea in case of poisoning is caused not only by activation of peristalsis, but also by the direct toxic effect of pathogenic microorganisms on the wall of the small intestine. The symptom is more typical at the onset of the disease, when there is a sufficient amount of partially digested food in the stomach and intestines. Diarrhea occurs, the frequency of which depends on the severity of the intestinal infection. The stool is liquid and has a bright yellow, orange or greenish tint.
Hyperacid gastritis
The appearance of amilorrhea is due to two mechanisms: inactivation of salivary amylase in the acidic environment of the stomach and accelerated movement of chyme due to the irritating effect of acid on the small intestine. Stool disorders are associated with errors in diet - consuming large amounts of complex carbohydrates. One- or two-time diarrhea with the release of liquid, foul-smelling feces is observed. Amilorrhea is accompanied by abdominal cramps and epigastric pain.
Chronic pancreatitis
With inflammation of the pancreas, signs of amilorrhea are relatively rare, which is explained by the high enzymatic activity of intestinal amylase. The condition is more often observed in advanced forms of the disease. Amilorrhea occurs when the diet consists primarily of carbohydrate foods. A person is worried about severe flatulence and pain in the epigastric region. Then unformed, foul-smelling stool appears, which may contain particles of undigested food.
When following a diet, amilorrhea disappears. Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by a sequence of changes in the composition of feces. First, steatorrhea occurs, as evidenced by grayish soft feces with a greasy sheen. Later, creative rhea occurs; in the later stages of the disease, amilorrhea develops. The symptom is also typical of a complication of pancreatitis - pancreatic fibrosis.
Pancreatic enzyme deficiency
Violation of the exocrine function of the organ is accompanied by a decrease in the production and release of pancreatic amylase into the small intestine. In the initial stages, the condition is compensated by intestinal enzymes, but in advanced stages of the disease, amilorrhea may begin. It has typical clinical manifestations specific to the chronic form of pancreatitis. The main causes of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency:
- Congenital pathologies
: genetic enzyme deficiency, agenesis or hypoplasia of the pancreas, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. - Space-occupying formations
: congestive, tumor and parasitic cysts, pancreatic cancer. - Postoperative complications
: during operations on the stomach, small intestine, pancreatic gland.
Chronic enteritis
With inflammatory damage to the wall of the small intestine, the secretion of enzymes is disrupted, and the processes of cavity and parietal digestion are inhibited. Undigested carbohydrates in the form of starch move into the large intestine, increase peristalsis and increase the wateriness of stool. Therefore, with amilorrhea, repeated diarrhea occurs. The stool has a liquid consistency or is released in separate soft lumps.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Amilorrhea is provoked by an overdose of laxatives, which affect intestinal motility. As a result, a person develops diarrhea. Food quickly passes through the gastrointestinal tract and does not have time to be completely broken down. Feces are abundant, liquid, and have a strong, unpleasant odor. Amilorrhea is combined with cramps and discomfort in the abdomen, flatulence. After 12-24 hours, the effect of the medications ends and the condition returns to normal.
List of approved products
A nonspecific diet for food allergies in children over 3 years of age allows the consumption of the following foods:
- Vegetable and cereal soups, as well as first courses cooked in secondary meat or fish broth.
- Natural fermented milk products with low fat content.
- Dietary meats (poultry, veal, beef, rabbit) boiled.
- Seasonal green vegetables and fruits.
- Wholemeal bread.
- Porridge made from buckwheat, oatmeal and rice.
- Boiled potatoes.
- Natural butter.
- Vegetable oils (sunflower, olive).
- Dried fruit compotes, weak black tea, apples, currants, plums.
The list of products is generalized, and the menu for each day for the child is compiled individually, taking into account the results of laboratory allergy tests.
Associated symptoms
There are no specific clinical signs of amilorrhea. The patient can pay attention to the well-known symptoms of ill health of the digestive canal, namely:
- bloating, passing gas;
- feeling of discomfort, diffuse diffuse pain of moderate intensity;
- rarely nausea and vomiting;
- several (2-3) acts of bowel movement per day;
- abundant feces with an unpleasant fetid odor, areas of undigested food are visually visible;
- with long-term pathology - loss of body weight due to poor absorption of nutrients.
If any of the above signs appear once, then there is no need to worry. If such symptoms appear regularly or persist over a long period of time, the help of a specialist is necessary.
What is forbidden to include in the diet
A general hypoallergenic diet excludes the consumption of the following food ingredients:
- chicken, quail, duck eggs in any form;
- any types of nuts (in particular peanuts and almonds);
- mushrooms;
- red, yellow and orange bell peppers, tomatoes, radishes, eggplants, red apples;
- fatty meats and fish, smoked meats;
- any types of canned food;
- citrus fruits, strawberry, pineapple, melon
- products containing cocoa (in particular chocolate), honey;
- any products containing dyes, flavors, stabilizers, preservatives.
At the entire stage of compliance with dietary recommendations, the child’s condition is monitored.
From permitted food products, parents can independently create a menu that will be physiologically complete. It is important to take care of preventing the development of food allergies in a child even before birth by creating the right diet for a pregnant woman.
If there are cases of intolerance to certain foods in the family, then the child automatically falls into the risk group. Such children, as a rule, are registered with an allergist and undergo an annual laboratory examination.
Diagnostics
In the complex diagnosis of amilorrhea syndrome, the following are used:
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- biochemical tests (blood amylase, urine diastase, glucose, bilirubin and its fractions, total blood protein and its fractions);
- repeated coprogram (micro- and macroscopy of feces);
- Ultrasound of organs inside the abdominal cavity;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy with assessment of gastric acidity;
- X-ray of the digestive canal with a contrast agent to assess the motor-evacuation function of the intestine.
As a result of the information received, the doctor will be able to draw a conclusion about damage to one or another part of the digestive canal.
Diagnosis of hereditary enzymopathies is very complex and expensive, and is carried out only in large medical centers. Complex immunochemical and molecular genetic techniques are used.