The last weeks of pregnancy are full of excitement and preparation for the birth of your baby. The expectant mother is worried about how the birth will go and what her newborn child will be like. The well-being of a pregnant woman in the later stages worsens against the background of emotional changes and restructuring of the body.
Such a nuisance as constipation often accompanies women while carrying a child. Problems with going to the toilet are explained by the physiological characteristics of the body before childbirth.
Characteristic signs of labor during the first pregnancy week by week
Their list is very large. For some women, it is not enough to know about the warning signs of labor in first-time mothers, so they look for other signs and become overly superstitious and wary. In fact, you need to understand what symptoms may appear in the last weeks of pregnancy and be prepared for this. As a rule, their number increases gradually if labor does not occur. Some primiparous women have no precursors at all, especially multiparous women, while others have one or more. This is influenced by the individual characteristics of the body:
- age of the first-time mother;
- a list of chronic and previously suffered diseases;
- body structure;
- condition of internal organs, reproductive system.
Precursors of labor at 37 weeks of pregnancy
Symptoms:
- This is the week when the belly drops before childbirth in first-time mothers and its shape changes. This is very clearly visible in the photo. The uterus moves into the pelvic area. At the same time, the woman can breathe much easier, and her heartburn finally disappears. Previously, they even tried to determine who would be born: a boy or a girl, by the shape of the belly.
- Pressure on the intestines and bladder increases, so a pregnant woman goes to the toilet more often.
- The body weight of a primigravida decreases. Weight does not increase anymore because a lot of fluid leaves the body.
- The pelvic bones expand, which is accompanied by discomfort and sometimes severe pain.
- The center of gravity is shifted, so the gait changes. People around her note that the woman began to look different.
38 weeks pregnant
At this time, the following precursors of labor may appear in first-time mothers:
- slight increase in the volume of discharge;
- periodically the stomach aches and pulls;
- the mammary glands become even larger, colostrum may be released;
- movements are felt less and less often;
- during this week, a mucus plug may already be released, which indicates the onset of labor in the coming days (this is normal, the fetus is already fully term).
39 weeks pregnant
Characteristic precursors of labor in primiparous women:
- A woman's mood changes frequently and greatly. She feels the nesting instinct. Pregnant women, for example, carefully clean the house and prepare children's things. This change indicates that the first signs of labor in first-time mothers will appear very soon.
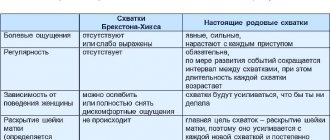
- Training prenatal contractions begin. As a rule, this happens at 39 weeks, but sometimes the warning signs of labor appear earlier. Contractions are irregular. Taking a bath with warm water helps relieve pain. Some, on the advice of a doctor, take No-shpa.
- Vaginal discharge is abundant, it can be either transparent or beige, milky, light brown, sometimes with bloody streaks.
- Constipation stops.
- At this stage, the mucous plug often comes off, which indicates the birth of the baby within two to seven days.
- The weight of the first-time mother becomes less than one and a half kilograms.
40 weeks pregnant
If a woman has reached this period, then she will feel the following harbingers of imminent labor in first-time mothers:
- My appetite suddenly disappears and I almost don’t feel like eating. By this time, the weight decreases by another one or two kilograms.
- The cervix becomes soft and short, however, this symptom is noticeable only to the doctor, the woman will not be able to feel it. Upon examination, a specialist can determine that the fetal head has entered the pelvis.
- The child is already very large. The uterus is cramped for him, so he moves much less. Only occasional jolts and kicks will be felt. Immediately before birth, the baby may become, on the contrary, overly active.
- There may be leakage of amniotic fluid, which should be reported to the doctor.
- The woman has loose stools (diarrhea), and sometimes has bouts of vomiting. This is how the body reacts to the upcoming stress and tries to “bring out” everything unnecessary in order to more easily bear the load. Often these symptoms are a sign that labor will begin within a couple of days.
- The mucus plug should come off completely or in parts. After this, it is not recommended to take a bath or swim in open places to avoid contracting an infection.
- The last symptoms before childbirth are contractions, regular and painful. Gradually they intensify, and the gap between them decreases. Then the amniotic fluid leaves, which indicates the beginning of labor. If this does not happen, the doctor can puncture the amniotic sac, this is quite acceptable.
How does a woman feel during such a period?
Most mothers are concerned about one question at 38 weeks of pregnancy: “When to give birth?” After the 37th week, most expectant mothers are already looking forward to the birth of their baby and dream that this will happen sooner. The fundus of the uterus during this period is approximately 18 cm above the navel and naturally this causes a lot of inconvenience. Poor sleep, extreme fatigue when walking, anxiety, heaviness in the legs - most women experience all this closer to childbirth.
At 38 weeks of pregnancy, children are often born to multiparous women. It is noted that girls are in a hurry to be born at this time. There is nothing terrible or pathological about this; according to statistics, only 5% of pregnant women give birth at exactly 40 weeks.
Most children appear two to three weeks earlier, and a small percentage of babies appear later. After the 37th week of pregnancy, a woman understands that new sensations are joining the old ones.
The fetal head drops down and this leads to the stomach also dropping. Such a change is considered the next stage of preparation for subsequent births; the baby takes the position necessary to move along the birth canal.
- Due to the fact that the fundus of the uterus becomes lower, positive changes in well-being may occur at 38 weeks of pregnancy. We are talking about reducing heartburn and shortness of breath, the enlarged uterus no longer puts so much pressure on the internal organs;
- The downward displacement of the baby's body also causes unpleasant sensations appearing in the pelvic bones. Often during this period pain in the pubic area and hips intensifies;
- Before childbirth, the mammary glands become even larger. During this period, the nipples are very sensitive and yellowish colostrum is released from them;
- Women may experience false contractions, which are expressed in the appearance of cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Unlike real contractions, these contractions are not as intense and pass over time;
- At 38 weeks, the baby’s movements may decrease; this is also due to the baby’s descent downward—the cramped space limits his activity.
Since childbirth is not uncommon at 38 weeks, it is advisable for every woman to know how to determine the onset of labor.
Prohibitions and recommendations at 40 weeks of gestation
The main recommendation for expectant mothers during this period is to try to be less nervous and worried, tune in to positive emotions and rest more. Everything is ready for the upcoming birth: the maternity hospital bag is packed, the children's room is equipped, the necessary things are purchased. A woman can only relax and enjoy the last days of pregnancy.
Nutritional Features
Recommendations regarding nutrition remain the same - do not experiment, do not starve or overeat. It is better to give preference to fractional meals, choosing easily digestible dishes. It is impossible to give up meat, fish, eggs and dairy products, as some online sources advise. The fetus still receives essential vitamins and nutrients through the placenta. By excluding the above products from the diet, a woman deprives her baby of beneficial microelements. To compensate for their deficiency, the fetus will begin to take vitamins from the mother’s body. As a result, the expectant mother will be exhausted and weak, which may affect labor.
Taking vitamins
If the expectant mother cannot ensure that her body receives nutrients through a balanced diet, she is prescribed special multivitamin complexes for pregnant women. They can also be taken during breastfeeding. Calcium and vitamin D intake should also be continued.
Sex at 40 weeks pregnant
In the absence of direct contraindications (multiple pregnancy, placenta previa, threat of miscarriage, leakage of amniotic fluid, etc.), normal pregnancy and good health of the expectant mother, intimate relationships may not be limited. Moreover, after childbirth, sexual contact will be prohibited for a long time.
Sexual intercourse in the last weeks of gestation helps soften the uterus with prostaglandins, which are contained in male sperm, and stimulate contractions through orgasm.
After the mucus plug has passed, it is better to stop sexual relations or use barrier contraception to avoid infection of the membranes.
Physical activity
Intense physical activity should be stopped this week. Even specially designed exercises can become overwhelming for the expectant mother. The optimal load that will help keep your body in shape is walking in the air. You can continue doing Kegel exercises. They will strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and speed up postpartum recovery.
Many pregnant women, in order to speed up the onset of labor, begin to walk up the steps, hang curtains and wash the floors. Such actions may bring labor closer, but it is unknown how they will affect the health of the fetus and the expectant mother. Therefore, it is better not to take risks and not do anything like that.
Medical procedures, taking medications
Any procedures and medications should be prescribed only by a doctor after assessing the health status of the pregnant woman and the characteristics of pregnancy. If possible, treatment is delayed until the postpartum period.
Treatment of constipation
Treatment for constipation is determined by your doctor, who will prescribe laxatives, glycerin suppositories or enemas. It is prohibited to take medications on your own, since almost all medications are contraindicated during pregnancy. With the permission of a doctor, you can use folk remedies:
- decoction of prunes or a mixture of dried fruits,
- glass of kefir with 1 tsp. oils,
- a glass of milk with 1 tbsp. l. honey before bed
- herbal infusions of fennel, anise and cumin.
The permitted decoctions are effective and do not harm the unborn baby. However, decoctions of buckthorn bark and senna leaves are prohibited for pregnant women. You also need to be careful with laxatives, they can provoke uterine contractions at 38, 39 or 40 weeks.
Signs of imminent labor in first-time mothers
What are the harbingers of childbirth for first-time women? How can you understand that a baby will soon be born? What happens to a woman’s birth canal, what are the external and psychological changes?
The precursors of labor in first-time mothers are not always obvious. Expectant mothers love to look for them, but often give them too much importance. We will list some of the signs of impending labor that are usually talked about in women's communities.
1. Visually, the stomach becomes lower, and thanks to this, the expectant mother feels better, it is easier for her to breathe, and she suffers less from heartburn. The abdomen droops due to the fact that the baby's head or other presenting part drops lower into the pelvis. A doctor can easily diagnose this when examining the expectant mother’s abdomen. With a cephalic presentation, a stationary or inactive head is found below. Immobile precisely because it is restrained by the mother’s pelvic bones. This is one way to recognize the warning signs of labor in first-time mothers at 36, 38, 39 and 40 weeks, but not the most important one. The baby may become pregnant several weeks before labor begins. But visually the stomach will “fall” already at the beginning of labor, during contractions.
2. When the 36th week of pregnancy begins, precursors of labor appear in first-time mothers in the form of so-called false contractions. In principle, these are the same Braxton Higgs contractions that appear at the beginning of the third trimester and feel like a hardening of the abdomen, but can cause nagging pain in the uterus and lower back. But they are also irregular and do not lead to dilatation of the cervix. If false contractions very often bother the expectant mother, the doctor recommends that she take no-shpa.
3. During the 38th week of pregnancy, the precursors of labor in first-time mothers become more obvious. For some, the mucus plug comes out of the cervix. Visually, it is a fairly large lump of transparent mucus with bloody streaks inside. The cork may take more than one day to go away. Sometimes such signs of the onset of labor in first-time mothers appear already at the beginning of contractions. Other women talk about the plug coming out a few weeks before giving birth. And some people don’t notice her at all. This also happens if the plug comes off during contractions, and the woman lies under a drip.
4. When the 39th week of pregnancy begins, even more obvious precursors of labor appear in firstborns; they are seen by the doctor during a gynecological examination. This point includes softening, smoothing and the beginning of dilatation of the cervix. Usually this process starts a few days before the onset of labor. But the cervix may be ready for childbirth even earlier if a woman has isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Sometimes such a gynecological examination leads to the passage of the mucus plug and provokes slight bleeding. All this can be considered normal for a full-term, progressive pregnancy.
5. Weight becomes less. Swelling also decreases. This is what happens about a week before giving birth or even less. The level of the hormone progesterone decreases, and this triggers labor. And the same hormonal changes help ensure that excess fluid stops accumulating in the tissues. Moreover, she leaves them, which is characterized in women by frequent urination. Accordingly, the weight is reduced by at least 1-2 kilograms.
6. Mood changes. In multiparous women, psychological precursors of childbirth are usually always present. A woman, already familiar with life and everyday life with a small child, tries to arrange her home as quickly as possible - she starts general cleaning, repairs, etc.
7. The amount of amniotic fluid becomes less. The baby in the uterus moves a little less often, and often not so clearly. The amount of water and the condition of the fetus must be monitored. This is especially true for women who have been diagnosed with fetoplacental insufficiency, oligohydramnios, if Doppler measurements have shown impaired blood flow to the fetus.
8. Diarrhea, vomiting. Frequent harbingers of imminent labor in first-time mothers at 40 weeks are precisely these unpleasant phenomena. This way the body is cleansed
It is important not to confuse these normal, physiological symptoms with poisoning or intestinal infection.
At what point can softening of the cervix be dangerous?
The softening of the cervix before childbirth begins several weeks and days before the baby arrives. The danger comes from shortening the cervix by less than 2.5 cm and or dilating the cervical canal by 1 cm throughout its entire length before 37 weeks. This condition is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Changes in the cervix are asymptomatic, and the woman does not make any complaints. With the development of this pathology, the risk of miscarriage increases significantly - spontaneous miscarriage (before 22 weeks of pregnancy) or spontaneous premature birth (after 22 weeks of pregnancy). In modern times, ultrasound helps in diagnosing isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
There are many predisposing factors in the development of this pathology - infectious processes of the genital organs, hormonal disorders, cervical scars, shortening of the cervix (for example: congenital or after excision of the cervix), insufficient collagen production, genetic predisposition. To correct isthmic-cervical insufficiency, they resort to suturing the cervix or installing an obstetric pessary (the decision is made individually and depends on a number of factors).
Subsequently, regular monitoring of smears for flora is carried out, and, if necessary, sanitization of the vagina to prevent the development of an infectious and inflammatory process. In most cases, women carry their pregnancies to term at home. But there are a number of contraindications - sexual activity, heavy lifting, it is recommended to avoid stressful situations. In more severe cases, a woman is asked to carry a pregnancy to term in a hospital setting under the strict supervision of doctors. Sutures from the cervix are removed at 37-38 weeks of pregnancy. At the same time, the obstetric pessary is removed. In most cases, it is possible to maintain the pregnancy and make the woman who has become a mother happy.
Recommendations for the prevention of constipation in pregnant women
The best way to combat constipation is to prevent it. Having learned about her pregnancy, a woman should immediately take measures to prevent problems with her stool.
- Rebuild your diet. The diet should include steamed vegetables, soups and other liquid dishes.
- You need to eat often and in small portions, properly distributing the diet. It is better to take protein dishes in the morning, vegetables and dairy products in the evening.
- Normalize fluid intake. You need to drink about 1.5 liters per day. It is better if it is still water, dried fruit compote, fruit drinks.
- In the absence of contraindications to physical activity, it is useful for a woman to walk every day, do yoga, fitball, and swimming.
Signs of pregnancy at 40 weeks
Due to the fact that the stomach sank at the 40th week of pregnancy, the woman’s stomach begins to work more actively, constipation disappears, heartburn decreases, and nausea goes away.
When the fetus descends towards the pelvic ring, the pregnant woman may experience a feeling of pressure, heaviness in the external genitalia and perineum. Pain persists in the back of the thigh and lower back, which is caused by compression of the nerves of the thigh. Increased pressure on the pelvic veins can cause painful hemorrhoids to form, leading to minor bleeding during bowel movements.
Periodically, at the 40th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother's stomach becomes stiff, the tone of the uterus increases, and nagging pain appears in the lower back and lower abdomen. These are Braxton-Hicks training contractions that prepare the body for the upcoming process of childbirth. The cervix becomes soft and short. Its dilation, which is determined by the doctor during examination, indicates the onset of labor.
Physiologically, the breasts are completely ready for the lactation period. The blood supply to the mammary glands increases, colostrum gradually begins to be released, which is replaced by milk a few days after birth. Preparing for breastfeeding should begin in advance: you can take a contrast shower and massage your nipples with a towel. This will make your breasts less sensitive and help avoid the painful sensations that many women experience when breastfeeding.
Most pregnant women experience mood swings during this period. They become irritable and hot-tempered. This is especially true for women who are preparing to become mothers for the first time.
Constipation symptoms
Constipation is the absence, difficulty, or incomplete bowel movement for more than two days. During the act of defecation, a woman feels pain. Symptoms:
- Feeling of fullness in the intestines.
- Abdominal pain of a cramping or aching nature.
- Nausea.
- The need for straining.
- Lack of appetite.
- Irritability.
- Bloating.
With constipation, the consistency of the stool changes, it becomes hard and its volume is small. The act of defecation does not bring relief.
It is important to eliminate constipation; the acute form can become chronic, and after delivery the woman will continue to suffer from an unpleasant symptom.
How a woman feels at 40 weeks
Almost all women are ready to meet the baby and are even worried that the pregnancy has taken so long. All sensations become more acute as the birth gets closer.
As for the psychological state, it also gets worse, and many women may experience serious shocks.
Possible physical sensations
A woman’s body is already completely ready for childbirth and many women have a baby born this week. There are no significant changes in the body or psychological state:
Uterus. Continues to increase in size and prepare for childbirth. The distance to the pubic symphysis is about 40 cm, and to the navel is about 20 cm. The cervix becomes soft and contracts, so it prepares for future birth. The volume of the uterus increased 100 times relative to its normal size, and its mass increased 20 times.
Stomach. The belly is no longer growing, but the skin is so stretched that the woman may feel itching. This may be a harbinger of the appearance of stretch marks. To avoid this, be sure to use special products that will prevent their occurrence.
Braxton Hicks contractions. They become stronger and more frequent
During training contractions, it is very important to breathe correctly and relax as much as possible in order to improve your condition. Read about how to distinguish training contractions from the onset of labor.
Breast
The mammary glands are already completely ready for breastfeeding. First, they will secrete a thick liquid that is highly nutritious - this is colostrum. It will be released for about 4 days, and after that it will be replaced by milk. It is recommended to prepare nipples for feeding. To prevent cracks from forming, rub your nipples with a hard towel. This will make them much rougher.
Discharge. Continue to monitor your discharge. If you notice the appearance of leucorrhoea that looks like pus, consult a doctor immediately. They need to be disposed of urgently in order to exclude possible infection of the child during its passage through the birth canal. The appearance of blood in the discharge may indicate placental abruption. In this case, urgent hospitalization is necessary, as this may threaten the life of the mother and her child. Watery discharge indicates the release of amniotic fluid, which indicates the onset of labor. Read more about the nature of discharge during pregnancy here.
Movements. The baby is no longer very active, as he is gaining strength before giving birth. Movement is essentially a baby's way of communicating with its mother. For example, if he is hungry, he will push the placenta, thereby causing an increase in the supply of nutrients. The woman clearly feels the baby's movements. They are so strong that you can only sleep when the child is doing this. Continue to monitor the amount of movement, as a sharp decrease in activity may be a sign of fetal freezing. Excessive activity may indicate insufficient oxygen. Read about why it is important to monitor your baby’s movements
Painful sensations. Back and joint pain occurs as the body prepares for childbirth. This week they can occur in absolutely all parts of the body. The stomach becomes hard and nagging pain appears, this is due to the approaching birth. Due to the increased pressure on the perineum, severe and sharp pain in the perineum may appear. Pain in the sacrum occurs due to pinching of the femoral nerve.
Nausea. At this stage of pregnancy, late toxicosis may occur, but it appears very rarely. Nausea is most often felt in the morning, to reduce its manifestation, try not to eat much during the day. If nausea does not go away, consult a doctor immediately.
Possible emotional experiences
In recent weeks, it is very important to remain calm and not give in to panic.
Many women at this time can fall into real depression. And all because of delayed pregnancy.
There is no need to panic, especially since the doctor says that everything is fine. The baby clearly understands your condition, and it negatively affects him. On the contrary, you should be happy so that he understands how good he is outside and how quickly he was born.
To get rid of the fear of the unknown that a huge number of pregnant women experience, read useful literature about childbirth, attend courses for expectant mothers, and be sure to talk with the doctor and close relatives. Helpful advice and communication will help you get rid of anxiety and calm down.
Prevention and treatment of constipation during pregnancy
Constipation is a polyetiological syndrome of prolonged defecation retention. This is the most common intestinal pathology during pregnancy. In addition, it should be noted that constipation affects more women than men. According to the etiology, constipation is: • neurogenic (with organic or functional lesions of the central nervous system, frequent conscious suppression of the defecation reflex, specific living conditions, etc.); • reflex (with organic lesions of various organs and systems, including the digestive organs); • toxic (in case of chronic poisoning with various toxic substances, taking large doses of antispasmodics or anticholinergics); • endocrine (with suppression of the function of the pituitary gland, ovaries, thyroid gland); • nutritional (with insufficient intake of fiber from food); • mechanical (with narrowing of the intestine due to compression, underdevelopment of the nerve plexuses of the colon - megacolon, Hirschsprung's disease); • dis- or hypokinetic (with a sedentary lifestyle, insufficient physical activity, pregnancy). The above reasons can cause intestinal movement disorders, disorders of secretion and absorption, and vasomotor disorders. A.I. Parfenov [2] distinguishes the following pathophysiological types of chronic constipation: nutritional; mechanical (intestinal obstruction); hypo- and dyskinetic type (reduced intestinal transit rate). Constipation can be divided into three groups: primary, secondary and idiopathic. Primary constipation is caused by abnormalities and malformations of the colon. Secondary constipation is a consequence of various diseases and side effects of medications. The idiopathic type includes constipation, which is a consequence of disturbances in the motor function of the colon, the cause of which is unknown (inert bowel, idiopathic megacolon, etc.) [4,10,11]. Constipation that occurs in women during pregnancy can be classified as secondary. The cause of stool retention in the first trimester of pregnancy is increased production of progesterone, and in later stages – compression of the colon by an enlarged uterus. Today, constipation (constipation) is one of the most common gastroenterological problems in pregnant women. Its frequency, according to different authors, varies from 17 to 50%. Most often, constipation occurs between the 17th and 36th weeks of gestation [1,6,9]. The main reasons for the development of constipation during pregnancy are [2,4,7]: 1. An increase in the level of progesterone and its metabolites, which activate the inhibitory gastrointestinal hormone and inhibit substances that stimulate peristalsis (gastrin, cholecystokinin, enkephalins, substance P). 2. Decrease in motilin level in the period from 16 to 36 weeks of gestation (returns to normal a week after birth). 3. Other possible mechanisms of constipation during gestation are based on the unity of the blood supply system and neurohumoral regulation of the uterus and colon. However, it is difficult to single out any one reason that leads to constipation during pregnancy. As a rule, a combination of various factors operates here [1,6,8]. Firstly, it increases the production of progesterone. Progesterone has a relaxing effect not only on the muscles of the uterus, but also on other smooth muscle organs: the urinary tract, the gastrointestinal tract, which accordingly reduces the motor activity of the intestines. Pregnancy also leads to changes in the topographic and anatomical characteristics of the uterus, which gradually increases in size and compresses the abdominal organs. The causes of constipation in pregnant women can also be changes in the quality of food, the use of various drugs (progesterone, tocolytics). Sometimes a woman is forced to lie down for a long time, and for normal intestinal motor function at least minimal physical activity is required. Prolonged colonic stasis is undesirable and can lead to a number of disorders. In particular, this is the activation of opportunistic microflora, the translocation of microbes and their toxins through the intestinal wall, which, at a minimum, is a risk factor, and in some cases the direct cause of complications during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. Constipation causes disturbances in the biocenosis of the colon, which, in turn, cause disturbances in the biocenosis of the vagina, which can cause ascending infection of the fetus and the development of various complications of the gestational period. The course of pregnancy against the background of colonic stasis is often complicated by the threat of miscarriage, untimely rupture of amniotic fluid, and endometritis. Constipation also causes an increase in the permeability of the intestinal wall and disrupts its barrier function, which is not compensated even in the postpartum period. In the absence of adequate laxative therapy, gestational constipation is ultimately one of the risk factors for purulent-septic complications in the postpartum period [3,9,11]. Therefore, constipation is a pathology that cannot be ignored. She needs to be treated. Clinical picture. With constipation, there is a decrease in the frequency of stools, a change in the consistency of stool, pain and discomfort in the abdomen (usually in the left half), and a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. With atonic constipation, feces are abundant, shaped, and sausage-shaped. Defecation occurs with great difficulty, is very painful, and due to tears in the mucous membrane of the anal canal, there may be streaks of fresh blood on the surface of the stool. With spastic constipation, stool takes the form of sheep feces (fragmented stool). Constipation is often accompanied by flatulence, a feeling of pressure, expansion, and cramping pain in the abdomen. Long-term constipation often causes a feeling of fatigue, lethargy, and decreased performance. Painful sensations can occur for no reason or after excitement or physical activity. Negative emotions, as a rule, cause an attack of acute or exacerbation of constant abdominal pain. Sometimes the pain radiates to the lower back, anus, genitals, and perineum. There are often complaints of nausea, bitterness in the mouth, and difficulty passing gas. The basic principles of prevention and treatment of chronic functional constipation are: dietary recommendations; recommendations for changing the motor mode; prescription of laxatives. Non-drug treatment Lifestyle changes: increasing physical activity, physical therapy, increasing dietary fiber intake, normalizing water balance, correcting neurotic disorders. If constipation is a consequence of other diseases, then achieving compensation for the main type of disease plays an important role in improving intestinal function. Treatment of constipation, especially gestational constipation, begins with non-drug measures. These primarily include diet. The introduction of foods with a high content of ballast substances into the diet is indicated. In terms of nutritional properties, wheat bran is the most acceptable for consumption. Clinical data confirm that the administration of bran for functional constipation is effective in 64–72% of cases. Prunes, dried apricots, and kefir help reduce the symptoms of constipation. Your diet should include fresh cabbage, carrots, cucumbers, tomatoes, beets, and zucchini. You should limit the consumption of strong tea, black coffee, cocoa, chocolate, white bread, flour dishes and slimy soups. The regime of physical activity is reviewed, the types of which are determined by the doctor. And only if all of the above measures are not enough, laxatives are used, which are indicated for constipation during pregnancy. There is a group of expectant mothers who enter pregnancy already experiencing constipation. Women who suffer from constipation outside of pregnancy and abuse certain medications in connection with this problem create a lifestyle for themselves with the problem of constipation. During pregnancy, it is necessary to adjust this style by changing or adding medications that will not affect the course of pregnancy. Feedings that regulate intestinal function • Buckthorn bark – 3, peppermint leaves – 2, nettle leaves – 3, calamus rhizome – 1, valerian root – 1. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 400 ml of boiled water, boil for 10 minutes, strain through gauze. Drink 100 ml of decoction in the morning and evening. • Buckthorn bark – 3, anise fruit – 2, yarrow leaves – 1, licorice root – 3. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over two teaspoons of the mixture, boil for 10 minutes, strain through cheesecloth. Drink 100 ml of decoction in the morning and evening. • Burnet root – 1, bird cherry fruit – 1, gray alder fruit – 1, peppermint herb – 1, caraway fruit – 1, fennel fruit – 1, licorice root – 1, chamomile flowers – 1, St. John’s wort herb – 1. Two tablespoons spoons of the mixture pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for 10 hours in a thermos, strain. Drink 100 ml of infusion 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. • Calamus rhizome – 1, buckthorn bark – 3, peppermint leaves – 2, nettle leaves – 2, dandelion root – 1, calamus rhizome – 1, valerian root – 1. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 3 minutes, strain through cheesecloth. Drink 100 ml of decoction in the morning and evening. Laxative mixtures • Buckthorn bark – 8, licorice root – 1, coriander fruit – 1. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 200 ml of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, strain through cheesecloth. Drink 100–200 ml of infusion at night. • Buckthorn bark – 7, licorice root – 1, caraway fruit – 1. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, leave for 10 hours, strain through cheesecloth. Drink 100–150 ml of infusion at night. • Buckthorn bark – 3, licorice root – 3, fennel fruit – 3, marshmallow root – 5, flax seed (uncrushed) – 6. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 3 minutes, leave for 10 hours, strain through cheesecloth. Drink 100–150 ml of decoction in the evening. Only if these measures are ineffective should one resort to drug treatment with laxatives. Drug treatment Classification of laxatives: • Drugs that increase the volume of intestinal contents, which leads to increased intraluminal pressure and stimulates intestinal motility • Stimulant laxatives • Drugs that soften feces (mineral oils). When prescribing laxatives to pregnant women, the highest safety standards must be observed to ensure normal fetal development. The choice of laxative during pregnancy should be approached with extreme caution. For the treatment of pregnant women, it is necessary to choose drugs with a mild laxative effect, causing stools close in consistency to normal. Irritating laxatives (castor oil, Carlsbad salt, senna preparations) can cause reflex contractions of the uterus. There are drugs that require taking a large amount of liquid, which is also undesirable, since the load on the kidneys increases, which leads to an imbalance in water balance and the development of edema. The choice of a suitable laxative drug should in no case be left to the patients themselves - self-medication with laxative drugs during pregnancy is especially undesirable. It is also necessary to take into account various side effects, for example, the teratogenic effect of senna drugs (senade, senadexin) is known. Thus, it becomes obvious that the range of laxatives that can be used during pregnancy is significantly narrowed, since they must be safe for the woman and the fetus, as well as for the normal development of pregnancy. Currently, one of the most widely used laxatives is the drug Dulcolax, the active ingredient of which is the prodrug - bisacodyl. When taken orally or rectally in an alkaline environment, hydrolysis occurs with the formation of an active metabolite - biphenol, which has an irritating effect on the colon mucosa. The action of Dulcolax is due to direct stimulation of nerve endings in the mucous membrane of the large intestine; this drug stimulates the excretion of water and electrolytes into the intestinal lumen, which results in softening of the stool, acceleration of peristalsis, reduction of evacuation time and defecation. Dulcolax is absorbed to a minimal extent (up to 5%) from the gastrointestinal tract. After conjugation in the liver, the drug is included in the enterohepatic blood circulation and is partially excreted by the kidneys. Dulcolax is a laxative that is used for hypotonic dyskinesia of the colon - constipation, including chronic constipation; for regulating stool in case of hemorrhoids, proctitis, anal fissures; for bowel cleansing in terms of preoperative preparation; to prepare the colon for instrumental and radiological examination methods; for emptying the colon in severe cardiovascular diseases. Contraindications for taking the drug are: individual intolerance (including a history of hypersensitivity) to the active substance, intestinal obstruction, obstructive bowel diseases, acute inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, including appendicitis, acute inflammatory bowel diseases, acute abdomen syndrome, abdominal pain unknown origin, severe dehydration, children under 4 years of age. There are 2 forms of the drug: tablets and suppositories. Dulcolax is prescribed orally for adults and children over 10 years old: 5–10 mg (1–2 tablets), for children aged 4 to 10 years: 5 mg (1 tablet). The drug is taken 1 time per day at night, regardless of meal time. If necessary, take an additional 5 mg in the morning 30 minutes before breakfast. When this laxative is taken orally during the day, the laxative effect occurs after approximately 6 hours, and when taken before bed, after 8–12 hours. One of the advantages of Dulcolax tablets is their enteric coating. The active substance - bisacodyl - is enclosed in a specially designed pH-sensitive shell, which ensures the release of the active substance in the initial part of the colon, thereby minimizing the likelihood of adverse events (spasm, flatulence, abdominal discomfort) that often occur when taking regular bisacodyl. The tablets should be swallowed without chewing. Swallowing a chewed tablet causes irritation of the gastric mucosa and abdominal pain. The drug should not be taken together with products that reduce acidity in the upper gastrointestinal tract (milk, antacids or proton pump inhibitors) to avoid premature dissolution of the enteric coating, which may lead to ineffectiveness of the drug and/or the occurrence of adverse reactions. Dulcolax suppositories are administered rectally at 10 mg (1 suppository) per day. The action of the suppositories occurs after about 30 minutes. Long-term experience with use has not revealed a negative effect of the drug on pregnancy. Dulcolax is practically not absorbed from the intestines, it does not have embryotoxic or uterine stimulating effects, and does not pass into mother’s milk. However, as with any medicine, this drug should be used with caution during pregnancy. Thus, based on the results of numerous foreign and domestic clinical studies and long-term experience (more than 50 years) in using the drug Dulcolax, it has been established that it is highly safe and effective in the treatment of constipation in both adults and children, as well as in pregnant women. Moreover, Dulcolax belongs to group “B” laxatives according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classification and is one of the few laxatives that is approved for use in pregnant women. Literature 1. Obstetrics: national guide / ed. E.K. Ailamazyan, V.I. Kulakova, V.E. Radzinsky, G.M. Savelyeva. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. – 1200 p. 2. Parfenov A.I. Prevention and treatment of constipation in pregnant women. Gynecology. 2002; T.4, No. 3: 14–17. 3. Podzolkova N.M., Nazarova S.V. Tranzipeg: new possibilities for the treatment of colonic stasis in pregnant women. Gynecology. 2004; T.6, No. 6; 22–27. 4. Emergency care in obstetrics and gynecology: A quick guide. / ed. V.N. Serova. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. – 256 p. 5. Guide to outpatient care in obstetrics and gynecology. / ed. V.I. Kulakova, V.N. Prilepskoy, V.E. Radzinsky. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2006.– 1056 p. 6. Yakunina N.A., Zaidieva Z.S. Prevention and treatment of constipation during pregnancy. Russian medical journal. – 2006. – T. 14, No. 1 (253). – P. 6–8. 7. Dukas L., Willett W., Giovannucci E. Association between physical activity, fiber intake, and other lifestyle variables and consipation in a study of women. Am. J. Gastroenterol., 2003, 98, 1790–1796. 8. Lembo A., Camilleri M. Chronic constipation. N.Engl. J. Med., 2003, 349, 1360–1368. 9. Talley N. Definitions, epidemiology, and impact of chronic constipation. Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord., 2004, 4 (suppl. 2), S3–S10. 10. Tytgat G., Heading R., Muller-Lissner M. et al. Contemporary understanding and management of reflux and constipation in the general population and pregnancy: a consensus meeting. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 2003, 18, 291–301. 11. Voskuijl W., de Lorijn F., Verwijs W. et al. PEG 3350 (Transipeg) versus lactulose in the treatment of childhood functional constipation: a double blind, randomized, controlled, multicentre trial. Gut, 2004, 53 (11), 1590–1594.
Precursors and their absence
Most of all, women who are 41 weeks pregnant are frightened by the situation when there are no precursors of labor. From a physiological point of view, such a situation is completely impossible. The pregnant woman’s body is actively preparing for this period, but sometimes this preparation goes unnoticed, especially if the woman is not highly sensitive.
Pregnant women do not always pay attention to the body’s signals, and sometimes they simply cannot imagine what they should be, so they conclude that the signs and symptoms of an early labor simply do not occur.
Indeed, some women have such low sensitivity of the nervous system that specific markers of well-being before childbirth can be perceived by them as somewhat smoothed out, almost imperceptibly. In addition, it is possible that there really are reasons for the absence of external manifestations of the body’s great internal preparation for childbirth.
Below are the main warning signs and the reasons why they may not be observed.
Abdominal prolapse
The abdomen changes shape and location somewhat, the height of the fundus of the uterus decreases due to the fact that at a certain moment in its development, the baby, anticipating an imminent birth, moves to the lower part of the uterus and props up the internal pharynx with its head. This pressure has a stimulating effect on the cervix - it begins to shorten and smooth out faster, and open slightly.
After the abdomen drops, a woman may feel some relief - there is no longer pressure on the diaphragm, some internal organs are freed, as a result of which it becomes much easier and easier to breathe, and heartburn decreases. However, this increases pressure on the bladder - there is a frequent need to empty it. A woman begins to visit the toilet for “minor needs” very often.
In most cases, in first-time mothers, the belly drops 3-4 weeks before birth, in women giving birth again - a week, or even a few days. It is possible that during repeated births the baby will take the “low start” position only with the onset of labor pains.
At 40-41 weeks, most women have this sign, but there are exceptions. For example, with the pelvic position of the fetus or its oblique position in the uterine cavity, prolapse does not occur, since the presenting part is not the head. The abdomen does not change shape and standing height in women bearing pregnancy, in women with polyhydramnios, as well as with certain structural features of the pelvis.
Weight loss
Two weeks before giving birth, women usually notice that they weigh 2-3 kg less. Many people associate this with excitement and worries on the eve of the birth process, and some are sure that the problem is a loss of appetite and less food consumption.
In fact, such weight loss is a real harbinger, which indicates that there is less intercellular fluid in the body. Its reserves disappear as progesterone levels decrease. The lower the level of this hormone, the faster labor will begin. Also, weight loss is due to a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid.
Mucus plug
The release of a milky or yellowish mucous clot (sometimes streaked with blood) from the cervical canal of the cervix is a sure sign of imminent labor. The cervix expands and softens. The mucus, which served as a barrier against germs and viruses, cannot be retained inside and leaves the thin cervical canal. Normally, the passage occurs either completely or in parts two weeks before the birth of the first pregnancy and a few days before the second birth (jelly-like clots will be present).
It is possible that it will not come out until the very moment of active contractions and then will go outside along with the amniotic fluid. For this reason, the absence of characteristic signs should not be considered the absence of a sign of approaching labor as such.
Cervical maturity
Doctors will pay special attention to this sign at 40-41 weeks. The cervix, the length of which at this stage is about one or less than one centimeter, is considered mature.
It should be soft along its entire length, its location should be central.
Other symptoms
Precursors, which include a decrease in the baby’s activity, insomnia, diarrhea and other rather subjective signs, cannot directly indicate the approach of labor, so their absence should not worry the pregnant woman.
Sensations such as belt pull, tingling inside, back pain, which women mention on thematic forums on the Internet, also cannot be considered direct signs of imminent labor. They are more associated with fatigue and heaviness, because 41 weeks is a very impressive period during which it is very difficult for a pregnant woman to walk.
Causes of constipation before childbirth
The closer the date of birth, the more factors affecting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and contributing to the development of constipation. The functioning of the intestines is mainly influenced by the hormone progesterone, which is designed to reduce the tone of the uterus. Increased progesterone affects nearby organs, in particular the large intestine, and reduces peristalsis, leading to intestinal atony.
There are several other factors that can upset the digestive system of a pregnant woman:
- As it grows, the uterus begins to put pressure on the intestines and even displaces them. Pressure from the uterus physically blocks the movement of stool.
- The natural decrease in physical activity by the 9th month has a strong effect on the tone of the intestinal muscles.
- Stress, depression, fears, panic and anxiety often accompany a woman as she approaches her due date. Disorders of the nervous system disrupt its connection with many organs, including the intestines.
- The drooping head of the baby at 39-40 weeks puts pressure on the colon, creating constipation.
- Due to increased swelling, many mothers reduce fluid intake. Low fluid levels in the intestines cause stool to harden, making it difficult to pass.
- Calcium and iron are consumed by the body in very large quantities during pregnancy. To replenish these elements, doctors prescribe special medications. Some substances in these drugs and the remains of undissolved iron can cause constipation.
Position of the baby in the womb in late pregnancy
If problems with bowel movement were observed throughout the entire period of gestation, the risk of complications in the final stages increases significantly
In such a situation, you should pay special attention to the delicate problem and prepare in advance for possible difficulties with bowel movements in the fortieth week
The danger of late bowel retention
Diarrhea and frequent training contractions are harbingers of labor. Rare stool before childbirth can also indicate the end of pregnancy. The reason is simple: the baby’s head has dropped and puts pressure on the intestines, preventing feces from moving normally. But constipation is dangerous due to complications and therefore requires treatment.
Constipation before childbirth negatively affects the health of the mother. Due to the difficult process of defecation, the contents of the intestine, and along with it, harmful substances, stagnate. They are absorbed through the intestinal walls into the blood.
Consequences of constipation in the late term:
- Intoxication.
- Long-term constipation provokes the appearance of cracks in the anus and inflammatory processes in the intestines.
- Varicose venous plexuses of the rectum.
- The beginning of labor.
Due to a crowded intestine, the general condition of a pregnant woman worsens. She feels nausea, abdominal pain, heaviness in the abdominal cavity.
Intoxication
Through the intestinal mucosa, fluid and nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Prolonged fecal retention promotes the absorption of toxic substances, which causes:
- Feeling of lack of energy.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Lack of appetite.
Intoxication is dangerous for a woman and an unborn baby: toxins can penetrate the placental barrier.
Haemorrhoids
In late pregnancy, an enlarged uterus and a crowded intestine place serious pressure on the pelvic vessels, which leads to difficulty in the outflow of blood. The intestinal veins dilate. Signs of hemorrhoids include:
- Prolonged absence of bowel movements.
- Itching sensation in the anus.
- Painful sensations.
- Blood from the anus.
Symptoms of the disease worsen a woman’s quality of life and negatively affect her emotional state. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Early treatment will help prevent complications.
Start of labor
The intestine, which is crowded with feces, puts strong pressure on the uterus, which can cause contraction of the organ. Childbirth is a relatively safe consequence of constipation, since a baby born at 39-40 weeks is considered full-term. But pathogenic microflora, which has developed due to stagnation of feces, can enter the vagina and infect the baby during passage through the birth canal.
Doctors agreed that pushing at any stage of pregnancy is dangerous, but delayed bowel movements also pose a real threat to a woman’s health. For this reason, it is important to prevent constipation.
Treatment
Physical activity, necessary for the proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, is almost impossible in late pregnancy. Exercises are replaced by light walking in the fresh air.
If your health allows, it is permissible to do special gymnastics, the exercises of which are designed for pregnant women.
Drug therapy
If physical activity is strictly contraindicated, and the diet does not bring the desired result, medication will be required. Most medications are contraindicated during pregnancy; medications can harm the health of the unborn child.
It is important to consult a gynecologist before starting drug therapy
Glycerin or sea buckthorn suppositories are relatively safe means in the fight against the disease. Glycerin-based suppositories are often prescribed by a gynecologist to a pregnant woman for quick emptying. Glycerin is not absorbed by the intestines and does not cause harm to the fetus. Sea buckthorn suppositories are a medicine containing the active substance in the form of sea buckthorn oil. The drug will help get rid of constipation, heal microcracks, and relieve pain.
Enema
An enema will help cope with stool retention. It is permissible to install it only with the permission of a doctor in case of urgent need. Stimulation of the intestines can trigger the onset of labor, which may be slightly premature for 37-38 weeks. At the onset of labor, if a woman cannot empty her bowels, an enema will be required, since the accumulated lump of feces will make it difficult for the baby to pass through the birth canal.
Folk recipes
The folk method of eliminating defecation retention using decoctions of medicinal herbs can be effective, but unsafe for the health of mother and baby. Before using traditional medicine, you should consult your doctor.
Home recipes to combat constipation:
- Dill is a safe plant for pregnant women and newborn children. To get rid of the symptom, you need to brew a tablespoon of plant seeds in a glass of boiling water and leave. Consume before meals.
- A drink made from milk and honey normalizes peristalsis.
- Beetroot decoction will effectively relieve constipation if you drink it before bed. Add prunes and oatmeal to the grated root vegetable, add water to the ingredients and cook over low heat for an hour. Next, the drink is filtered and stored in the refrigerator.
- Herbal decoctions: mint, chamomile, plantain, motherwort are safe for pregnant women and effectively combat stool retention.
Prevention
Treating constipation during pregnancy with modern medications is prohibited. Therefore, doctors advise paying more attention to prevention. Pregnant girls are advised to avoid emotional stress and stress, which often cause deterioration of intestinal motility.
Also, if you are prone to constipation, you should carefully monitor the amount of fluid you consume. Doctors advise drinking at least 2 liters of clean water a day. Constipation is often caused by improper food intake. Large pieces take a long time to digest; food must be chewed thoroughly.
To avoid unpleasant symptoms in the later stages, you need to carefully monitor your diet. It is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- Causing flatulence - cabbage, legumes.
- Dishes with viscous consistency.
- Products containing essential oils.
- Products containing tannin.
It is extremely difficult to treat the disease for a pregnant woman. It is easier to prevent symptoms by following simple recommendations.
Constipation at any stage of pregnancy is a dangerous symptom for mother and baby. It is important to quickly eliminate it using available means without causing harm to the fetus. To do this, you need to tell your doctor about the delicate problem, who will help you cope with the phenomenon.