Sometimes there is a single diverticulum, but, as a rule, most often people have multiple bulges in one part of the intestine.
Diverticula are divided into “true” and “false”, as well as “congenital” and “acquired”.
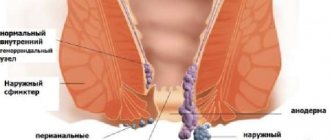
- True diverticula are most often congenital - due to a direct violation of the structure of the intestine. One of the features of a true diverticulum is that the walls of the diverticulum have all the layers characteristic of the intestine. True diverticula, for example, include Meckel's diverticulum: a protrusion of the wall of the small intestine at the junction of the patent embryonic vitelline duct as a developmental anomaly.
- False diverticula are acquired and represent a bulging of the intestinal mucosa outward through thinned places in its muscle layer.
As a rule, acquired diverticula are multiple and rarely occur in single quantities. Diverticulosis is a change in the intestinal wall with the presence of multiple diverticula in it without inflammatory processes occurring in them and not manifesting themselves clinically. If an inflammatory process develops in the diverticulum, they speak of diverticulitis and, as a consequence, the development of diverticular disease.
Incidence of diverticular disease
Of all the diseases of the colon, intestinal diverticula are one of the most common in the modern world. The incidence of diverticular disease averages 20% in European countries; moreover, in older age groups of the population (60–80 years), the incidence increases, reaching 40–50%, and among patients over 80 years of age, the incidence reaches 60–65%. In our country, diverticula of the large intestine are found in approximately 17-28% of gastroenterological patients. The incidence of the disease in men and women is approximately the same.
Classification of diverticular disease
- Uncomplicated.
This form is detected accidentally during an X-ray or endoscopic examination of the intestine. Blood tests usually show no changes. The examination must be carried out to assess the extent of intestinal damage, prognosis of the course of the disease and the choice of a method for preventing complications or treatment. - Complicated
, occurring with an acute inflammatory process (diverticulitis, diverticular infiltrate, diverticulum perforation, abscess, peritonitis), a chronic inflammatory process, as well as bleeding. A chronic process includes situations when inflammation cannot be eliminated within 6 weeks, or it occurs again. In severe cases, an infiltrate, narrowing of the intestine, or a fistula from a destroyed diverticulum may form.
Causes of diverticula
The occurrence of this disease does not have any specific cause. It is caused by a combination of many factors. There is an opinion that some people are predisposed to this disease due to congenital underdevelopment of the muscular layer of the intestinal wall. As a result, diverticula form with age or under the influence of any factors.
Congenital predisposition plays a role in people with hereditary syndromes of connective tissue dysplasia (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, when there is a deficiency of collagen in the human body), and a combination of diverticular disease of the colon with diseases associated with a decrease in the elasticity and strength of connective tissue (hernias) is also often found , varicose veins, visceroptosis, polycystic disease). However, congenital tissue deficiency is not the only cause of pathological changes in the intestinal wall.
The high incidence of diverticular disease in older people is associated with a gradual decrease in the tone of the colon wall as the body ages. Diverticular disease is a chronic disease that occurs due to the formation of a pouch-like protrusion (diverticulum) in the intestinal wall, and, as a consequence of the stagnant process, the development of inflammation in them. The muscle layer of the colon becomes thicker and less elastic. The supporting connective tissue loses elasticity and the intestinal wall becomes less extensible. Therefore, diverticula appear more often in older people than in younger people.
It is also known that diverticula occur significantly more often with a decrease in plant fibers and fiber in the diet. Therefore, diverticular disease occurs 3 times less often in vegetarians than in people who limit their intake of vegetables and fruits. Foods low in fiber do not stimulate intestinal motility well, the movement of contents through the colon slows down, which increases water absorption and, as a result, constipation develops. Retention of feces in the intestine, combined with disruption of the normal intestinal microflora, leads to inflammation and progression of diverticular disease. This can also explain the more frequent appearance of diverticula in the sigmoid colon (constipation plays the role of a resolving factor).
The clinical picture in approximately two out of three cases is not accompanied by any complaints (asymptomatic diverticulosis); the pathology is discovered by chance during endoscopic or x-ray examinations. Most often, the first signs of diverticular disease are pain and functional impairment in the form of constipation or diarrhea. There are complaints of regularly recurring pain in the abdomen, often in the left iliac region or lower sections, which disappear after defecation. Pain of varying intensity can exist for a long time - from several weeks to months. Increased pain is sometimes accompanied by an increase in temperature, and signs of intoxication may appear (dry mouth, nausea, tachycardia). Also often noted is bloating and excessive gases, various dyspeptic disorders, which are sometimes hidden under the guise of irritable bowel syndrome.
In order for the doctor to help you as much as possible, help him and prepare for the examination:
- Do not eat solid food the day before the examination and consultation.
- Write down your symptoms, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which the appointment is planned.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins and supplements.
- Record key medical information, including other conditions and comorbidities.
- Write down key personal information, including any recent changes or stresses in your life.
- Ask a relative or friend to accompany you to help you remember what the doctor says.
- Write down questions to ask your doctor.
Complications of diverticular disease of the colon
- Diverticulitis.
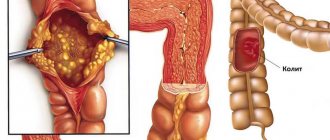
This is an acute inflammation that occurs in the diverticula in a quarter of patients with diverticulosis. Signs of the development of inflammation may include the appearance of pain and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall, increased body temperature, chills, bloating, and bowel problems such as diarrhea or constipation.
- Diverticulum perforation.
Against the background of the inflammatory process in the diverticulum, part of its wall may collapse, and the contents of the intestine enter the abdominal cavity. In this case, local or diffuse peritonitis develops. When perforation (rupture of the wall) of the diverticulum into the retroperitoneal tissue or the space between the layers of the mesentery, infiltrates or abscesses appear.
- Bleeding.
Occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diverticular disease. For many people, it may be the first and only manifestation of the disease. Typically, bleeding is associated with ulceration of the diverticulum wall as a result of chronic inflammation. Also, at the site of the fecal stone, a bedsore may form with damage to the blood vessel. The intensity of bleeding can vary: from a slight admixture of blood in the stool (sometimes there is hidden bleeding, which is manifested by a gradual increase in anemia), to massive profuse bleeding, accompanied by collapse and even leading to death.
- Intestinal obstruction.
The cause of intestinal obstruction can be an inflammatory process around the diverticulum or an adhesive process, leading to deformation of the intestine and disruption of the movement of feces through it. In rare cases, intussusception (rolling in) of part of the intestine with a diverticulum or spasm of smooth muscles may occur.
- Intestinal fistulas.
They can occur when a diverticulum is perforated and an abscess breaks through into a nearby organ (the so-called “internal fistulas”). Men more often develop fistulas with the bladder, and women with the vagina. When an intestinal-vesical fistula forms, air or an admixture of feces may appear in the urine.
Diverticulosis. Diverticulitis. Symptoms and treatment
What is diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis or diverticular disease is a pathological process of the colon in which numerous diverticula (pouch-like protrusions) form in the wall of the colon.
Diverticula can vary in size from pea-sized to much larger. Diverticula are formed due to increased pressure from gas, waste or liquid on weakened areas of the intestinal wall. In addition, diverticula can form during times of straining during bowel movements, such as constipation. Diverticula most often form in the lower part of the colon (called the sigmoid colon). Complications may occur in about 20 percent of people with diverticulosis (diverticular disease). Such complications may be:
Bleeding from the rectum, called diverticular bleeding. Diverticular bleeding occurs when there is chronic damage to the small blood vessels that adjoin the diverticula;
Diverticuli etc. Diverticulitis is an inflammatory process that occurs due to infection in one or more diverticula. Typically, diverticulitis occurs when stool accumulates in a diverticulum, allowing bacteria to multiply, causing an infection.
Diverticulosis is a common disease, affecting 10 percent of people over 40 and 50 percent of people over 60. The incidence of diverticulosis increases with age and reaches almost 100 percent in people over 80 years of age.
What are the symptoms of diverticulosis?
Typically, diverticulosis does not cause any symptoms. Some people may feel discomfort or abdominal cramps.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis
Given that diverticulosis usually does not cause symptoms, the diagnosis is made by chance during diagnostic tests performed for another reason.
How to treat diverticulosis?
If there are no symptoms or complications, treatment for diverticulosis is not required. However, it is important for patients with diverticular disease to eat a high-fiber diet. In addition, such patients should avoid taking laxatives and enemas.
How to prevent diverticulosis?
The most important thing to prevent diverticulosis or reduce its complications is normal intestinal motility, in other words, the absence of constipation. To maintain normal intestinal motility and regular bowel movements, it is recommended:
- Physical exercises that involve the abdominal muscles;
- Adequate amount of fiber consumed in food. The American Dietetic Association recommends consuming 20 to 35 grams of fiber per day. Every person, regardless of the presence of diverticula, should try to consume this amount of fiber daily. Foods rich in fiber include whole grain bread, cereals and crackers, berries, fruits, vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, spinach, carrots, asparagus, zucchini, beans), brown rice, bran, as well as peas and beans. High-fiber foods help prevent constipation and provide a number of other health benefits. It lowers blood pressure, blood cholesterol, increases blood sugar, and also reduces the risk of developing certain intestinal disorders;
- Drinking enough fluid (at least 8 glasses a day, in the absence of contraindications);
- Sufficient hours for sleep and rest.
What are the symptoms of diverticulitis?
One of the complications of diverticular disease is diverticulitis, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Painful cramping or tenderness in the lower abdomen;
- Chills or fever.
Diagnosis of diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is a serious complication and requires immediate medical attention for a correct diagnosis. Some symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and stomach ulcers may be similar to diverticulitis. Your doctor will ask you questions about your medical history (such as how the illness started, the symptoms you are experiencing, your diet, and any medications you are taking). He will also perform an examination, including a digital rectal examination. One or more diagnostic tests may be done to help diagnose your condition. It could be:
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Sigmoidoscopy;
- Colonoscopy;
- Irrigoscopy;
- Blood tests to find out signs of infection or the extent of bleeding.
Treatment of diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis sometimes resolves without treatment, but often requires antibiotics. In some cases, diverticulitis is so severe that it requires hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and other supportive care. In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove the affected part of the intestine. Emergency care, including surgery, may be necessary if antibiotic therapy does not respond to a large abscess, perforation, peritonitis, or ongoing bleeding from the rectum. During an exacerbation (diverticulitis), it is recommended to eat foods low in fiber and drink plenty of fluids. A month after the exacerbation resolves, fiber must be returned to the diet.
What are the complications of diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis can cause serious complications. Most are the result of rupture or perforation of the intestinal wall. If this happens, stool can leak from the intestines into the abdominal cavity, leading to the following complications:
- Peritonitis. If the infection spreads into the abdomen (peritonitis), surgery is necessary to clean out the abdominal cavity and remove damaged parts of the colon. Without proper treatment, peritonitis can be fatal;
- Abscess. If an abscess occurs, a puncture may be performed or surgery may be required to remove the affected part of the intestine;
- Intestinal obstruction. Infection can lead to scarring of the colon, and scar tissue can lead to partial or complete bowel obstruction. Complete obstruction requires emergency surgery;
- Fistula. Another complication of diverticulitis is the formation of a fistula. A fistula is an abnormal connection between two organs, or between an organ and the skin. The most common type of fistula for diverticulitis is a fistula between the bladder and colon. This requires surgery to remove the fistula and the affected part of the colon.
Diagnosis of diverticular disease
- Irrigoscopy
is an X-ray examination in which the lumen of the colon is filled with a contrast suspension and its condition is assessed during filling and after bowel movement. - Colonoscopy
can detect the presence of multiple diverticula, signs of inflammation or intestinal bleeding, and may also be useful in detecting associated lesions such as polyps and cancer. - MSCT
(multispiral computed tomography). Suitable for differential diagnosis of diverticulitis and tumor lesions of the colon.
Diet
Since diverticular disease occurs much more often in people who limit their intake of vegetables and fruits, all patients with diverticulosis need to use foods high in plant fiber and pectin. Wheat bran (especially coarse bran) is very useful, which significantly reduces the pressure inside the intestine and accelerates the rate of movement of contents through the intestines.
It is imperative to exclude all foods that cause increased gas formation (legumes, lentils, grapes, sauerkraut, butter and yeast dough, onions) and constipation (blueberries, rice). It is also advisable to exclude seeds, fruits with a large number of grains and excessively coarse fiber (persimmons, pineapples, turnips, radishes, radishes).
Folk remedies for treatment
Treatment of intestinal diverticulosis with folk remedies must be agreed with the doctor, since there is a risk of complications of the situation due to incorrect use of prescriptions. Doctors quite often comply with such methods and record data on traditional treatment and the use of diets in official protocols.
Diet as a treatment method
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the task is to reduce the load on the intestines, up to fasting and intravenous nutrition. If extreme measures are not necessary, the diet is determined according to table No. 4. This menu involves reducing the level of fats and carbohydrates while maintaining the amount of proteins. The amount of salt and liquid consumed is also monitored. Boiled foods and steamed dishes are used as food. Anything fried, smoked, spicy, as well as canned food and pickles is excluded. You should eat the diet in small portions - 5 or 6 times a day, keeping the food puree or liquid in consistency.
In the absence of exacerbations of diverticulitis, with the asymptomatic course of the disease, it is recommended to follow a diet, limiting:
- Fried, spicy, salty.
- Consumption of flour products.
- Dishes with viscous consistency.
- Fatty meats.
- Products rich in tannins.
- Vegetables and mushrooms containing essential oils and coarse fiber.
- Alcohol.
Instead, you should increase the percentage of fiber consumed (except for coarse fiber), and replace some animal fats with vegetable fats.
Bran for treatment
In folk medicine, in addition to excluding foods from the diet, special nutrition can be used. One effective method is to use a bran-based recipe. This will allow:
- Reduce the amount of gases produced during the day;
- Relieve pain and spasms;
- Normalize bowel movements.
For preparation you will need bran, as well as natural yogurt or kefir. They must be mixed and allowed to brew for 30 minutes. Then you can eat it. The initial dosage is one tablespoon per day, and over time it is allowed to increase the dosage. The maximum allowed dosage is 50g of bran per day.
Tinctures with herbs and berries
To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, elderberry tincture is used. It must be brewed like tea – by pouring boiling water over it. In the decoction for one serving, use up to one tablespoon of berries.
Another option is a mixture of herbs based on chamomile, calendula, and nettle. Dill seeds and dried rose hips are added to them. All ingredients are mixed in equal proportions and poured with boiling water. The mixture must be brought to a boil, cooled and taken 1/2 cup in the morning and evening. This remedy is used to reduce inflammation.
Another recipe is thorn tincture with alcohol. The composition includes alcohol, sloe plums and sugar.
To prepare the fruits, you need to pour alcohol and leave to infuse in a room with a temperature of up to 20 degrees. The mixture is taken out and mixed with sugar at a rate of 100 g per liter after four months of storage. After this procedure, the liqueur is infused for another six months. Use for diverticulosis - the medicine is taken one or two teaspoons per day and helps relieve pressure in the intestines.
Cleansing the gastrointestinal tract
In case of diverticulosis, the use of means that help the functioning and cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract has a beneficial effect.
Green apples and sprouted wheat grains help improve peristalsis and eliminate fecal retention in the gastrointestinal tract. The ingredients are pureed and mixed. The mixture should be consumed as the first meal, 250 or 300 grams at a time. The duration of the course is 20 days or a month.
Boiled beets can serve as a natural laxative and prevent constipation. Beets should be consumed grated with the addition of linseed or olive oil. The frequency of administration is 1 or 2 times per day.
Seed-based medicines
The seeds can be used to replenish fiber in the body, the lack of which becomes one of the causes of disease. A high content of this substance is observed in plantain seeds.
You can consume the seeds by pouring one tablespoon of yogurt, water or juice and stirring well. Drink the mixture immediately, in small sips. Then wait half an hour and drink half a glass of water.
Flax seeds have the same effect when consumed. They are washed down with a sufficient amount of liquid and taken one tablespoon per day. Flaxseed oil also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the intestines and stomach.
All seeds used in the treatment of diverticulosis are effective due to the fact that they swell when they enter the gastrointestinal tract and stimulate its activity.
Drug treatment
- In uncomplicated cases, the disease does not require the use of medications. The need to take medications depends on the clinical manifestations.
- For abdominal pain, antispasmodics are used.
- If dysbiosis is detected, drugs are used that help restore normal intestinal microflora.
- For persistent constipation, take medications to enhance gastric and intestinal motility: lactulose preparations, petroleum jelly or olive oil orally or in microenemas.
- For diverticulosis with clinical manifestations of inflammation, it is necessary to use the entire range of therapeutic measures: a laxative diet, antispasmodics; drugs that regulate intestinal motor function, and agents that normalize the composition of the intestinal bacterial flora.
Treatment
How to treat diverticulosis is determined individually in each case. If the symptoms are not pronounced, no treatment is required - just adjust your diet.
Treatment of diverticulosis without complications includes:
- Use of antimicrobials and enzymes to improve digestion;
- Laxatives;
- Antispasmodics.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. In case of acute and complicated course of the disease, if the effectiveness of treatment is insufficient in the first 3-4 days, hospitalization and the following treatment regimen are carried out:
- Antibiotics are prescribed for 7-10 days;
- The stomach is washed, the intestines are cleansed;
- Fresh frozen plasma is used;
- Blood substitutes are administered to normalize blood functions, as well as saline and electrolyte solutions to obtain a detoxification effect.
For life-threatening complications, surgical intervention is performed.
The operation is performed if the patient:
- Severe intestinal obstruction;
- Prolonged internal bleeding;
- Perforation with peritonitis;
- An intestinal fistula has formed.
After surgery, you should undergo annual examinations and routine examinations.
Surgery
The need for surgical treatment for diverticular disease can arise both urgently and routinely. This happens when complications occur that can threaten a person’s life (bleeding, perforation, peritonitis). Planned surgical treatment is always aimed at eliminating the threat of such complications. The choice of surgical method in each specific case depends on the extent of the process, inflammatory changes in the diverticula, the condition of the intestinal wall and surrounding tissues, the presence of inflammation outside the intestinal lumen or peritonitis. It is important to consider comorbidities that are often observed in older people. As a rule, resection (removal) of the affected part of the colon is performed in a planned manner with simultaneous anastomosis. Surgical treatment in our Clinic is performed laparoscopically, which allows patients to quickly return to active life. Planned surgery is always performed during the period of remission, 2-3 months after the acute attack of the disease has passed. Fistulas of the colon are an indication for planned surgical treatment, since it is not possible to achieve their independent healing, and chronic inflammation leads to the development of rough scars that impair the movement of intestinal contents, as well as to the development of chronic intoxication and decreased immunity. When intestinal-vesical fistulas form, there is a threat of developing an ascending urinary tract infection and kidney damage.
- Surgical removal of fistulas
is a complex surgical intervention requiring the participation of highly qualified specialists. In our clinic, when planning such interventions, related specialists (urologists, gynecologists, endoscopists) are involved as necessary. For intestinal bleeding, conservative treatment (hemostatic therapy) or endoscopic bleeding control is most often prescribed. The operation is performed only if conservative treatment methods are ineffective. - Surgical treatment for diverticulum perforation.
If surgery is performed for urgent reasons, a colostomy may be performed to reduce the risk of postoperative complications. Reconstructive surgery with closure of the colostomy and restoration of intestinal continuity is performed after the inflammatory process has subsided (after approximately 3 months).
Treatment of intestinal diverticulosis
Since it is necessary to treat diverticulosis taking into account the causes of its occurrence, the patient must be prepared to change his lifestyle, first of all, to a significant change in his diet. A special diet is the basis for the treatment of this disease, regardless of its form, since the causes of divertriculus lie mainly in poor nutrition. Additionally, medications are used, and in difficult cases, surgery.
Diet
Diet forms the basis of treatment for uncomplicated and asymptomatic diverticulosis. It is recommended to include more fiber products in the diet of patients. They increase the volume of stool and help reduce pressure in the intestines, which promotes faster and easier bowel movements. Fiber prevents further progression of diverticula, and in some cases leads to their regression.
The menu includes the following sources of fiber:
- bran bread or wholemeal bread;
- cereal porridge (wheat and buckwheat) with the addition of vegetable oil;
- vegetable casseroles or vegetables baked on a wire rack as a side dish;
- soups with meat or chicken broth and vegetables;
- dairy products.
In addition to vegetables and fruits, it is useful to include wheat bran in the menu. This should be done gradually so as not to provoke intestinal irritation. The initial daily intake is from 5 to 10 g of bran, then it is increased to 30 g.
To prevent the bran from damaging the intestinal walls, it is recommended to pour boiling water over it for half an hour and drain. You can add steamed bran to vegetable dishes, cereals, yogurt and soups.
Pasta and baked goods, semolina and rice porridge, jelly, strong coffee and tea, wine (red), and cocoa products should be excluded from the diet.
Drug therapy
With colonic diverticulosis, symptoms and drug treatment are directly related. The list of medications that are recommended for patients with this diagnosis includes:
- antispasmodics - Mebeverine, No-Shpa, Meteospasmil, Bucopan - are often used at the initial stage of therapy;
- sources of dietary fiber - Mukofalk, Solgar, Ispagol - replace bran, as they do not cause flatulence and cramps, stimulate the restoration of intestinal microflora;
- probiotics - Linex and its analogues - to restore microflora;
- prebiotics for loosening stool based on lactulose - Duphalac, Normaze and others;
- enzyme preparations are prescribed for severe digestive disorders, as well as in the presence of an inflammatory process;
- stimulants of intestinal motility - Motilium, Motilak, Domperidone;
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed for inflammation of diverticula.
If treatment with medications does not lead to improvement, the patient is hospitalized and given infusion therapy. At the same time, additional research is being carried out and the issue of surgical intervention is being considered.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is used if diverticulosis of the descending section (or any other) worsens more than 2 times. In such situations, it is important to prevent intestinal perforation and the development of peritonitis, which often occurs with repeated attacks. For patients over the age of 40 years, elective surgical intervention is prescribed after the first exacerbation.
Also indications for the operation are:
- intestinal bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- intestinal perforation;
- suppuration of the diverticulum with threatening or ruptured abscess.
During surgery, part of the intestine affected by diverticula is removed; the volume of intervention is determined individually.
The prognosis for timely diagnosed disease is favorable. More than 80% of operations are completed without subsequent complications, the risk of relapse is no more than 25%.
Forecast
The prognosis is usually favorable if the disease is detected in a timely manner and the necessary preventive and therapeutic measures are started, provided that the patient follows all the necessary recommendations. However, if the need for prevention is ignored, diverticular disease can lead to the development of severe complications that threaten the life and health of the patient. Moreover, the disease is more common among older people who have a variety of concomitant diseases and lower body resistance.
Prevention
Among preventive measures, a varied and balanced diet is of primary importance. Due to the fact that a diet low in plant fiber predisposes to the formation of diverticula, in order to reduce the risk of developing the disease, it is necessary to include large quantities of plant-based products. Since timely detection of diverticula plays an important role, it is extremely important to undergo preventive examination and regularly perform endoscopic examination of the intestine.
Reasons for development
If there is not enough fiber in a person's diet, physical activity slows down. Constipation and bloating occur, and intraintestinal pressure increases. As a result, protrusions (diverticula) form in the walls. The disease is promoted by muscle weakness, which can result from inflammation or injury. Often weak muscles provoke congenital diverticulosis of the large intestine. Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon can occur due to impaired intestinal motility.
Risk factors for developing pathology
- Frequent constipation;
- Incorrectly formulated diet with excess amounts of refined foods;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Poor circulation;
- Advanced age.