- Types of Constipation
- Causes of chronic constipation
- Extraintestinal causes of constipation
- Obstipation and constipation
- Why is constipation dangerous?
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Diet therapy
Constipation is an irregular bowel movement in which the patient has difficulty passing bowel movements.
With constipation, the intervals between bowel movements increase, the intestines are not completely emptied due to a violation of the evacuation function. Feces become dense and rough. Their advancement causes pain to the patient, requires prolonged squeezing, and injures the intestinal mucosa. Adults and children are susceptible to constipation. Most often, this disorder occurs in young children and adults. According to statistics, up to 20% of the population experiences signs of difficult bowel movements. At the age of over 65 years, the frequency of pathology reaches 26% among men and 34% among women.
Constipation is not considered by experts as an independent disease. It is a symptom of disruption in the functioning of various organs and systems. To normalize the evacuation function of the intestine, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the deterioration of its function.
Types of Constipation
Depending on the duration, there are two types of constipation:
- chronic;
- episodic.
In the case of episodic constipation, difficulty in defecation occurs for a short time and is associated with a specific situation. The main reasons for this phenomenon:
- insufficient fluid intake;
- changes in diet and water regime (so-called “travelers’ constipation”);
- insufficient intake of fiber from food;
- taking medications that strengthen the stomach;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- pregnancy;
- menstruation.
Causes of chronic constipation
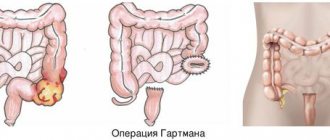
Unlike episodic, chronic constipation becomes permanent. The patient has difficulty defecating for several months. The number of bowel movements is reduced to twice a week, and in many cases the patient is unable to have a bowel movement naturally without the use of laxatives. Chronic stool retention is a symptom of a number of diseases. First of all, these are various gastrointestinal pathologies: pancreatitis, ulcers, colitis, dysbacteriosis. With these diseases, the digestion process is disrupted, which leads to hardening of stool and incomplete bowel emptying. Benign and malignant intestinal tumors create an obstacle to the movement of feces and cause difficulty in defecation.
If the defecation reflex is impaired, the patient experiences functional constipation. Anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and scar changes in the colon can also lead to regular stool retention.
Risk factors
Constipation during menstruation occurs in women in the following cases:
- when drinking too much liquid;
- presence of hormonal imbalances;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the presence of inflammatory foci in the body, especially in the gastrointestinal tract
- if the diet is dominated by foods that contribute to decreased intestinal tone and increased gas formation.
Up to contents
Extraintestinal causes of constipation
Defecation disorders are not necessarily caused by gastrointestinal diseases. There are other reasons why stool retention may occur. This problem is faced by people leading a sedentary lifestyle. Lack of movement leads to stagnation and makes the intestines atonic, that is, “lazy.”
Another possible reason for regular stool retention is endocrine pathologies. Chronic constipation often affects patients with hypothyroidism - reduced thyroid function, people with diabetes, and women with gynecological diseases. Many women regularly experience constipation before and during menstruation. This is caused by the action of the hormone progesterone, which affects intestinal activity. During menstruation, difficult bowel movements may be caused by uterine pressure.
Patients with neurological diseases also often complain of constipation. This problem occurs against the background of stroke, injuries and tumors of the spinal cord, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and vascular diseases of the brain.
Chronic constipation of a psychogenic nature can accompany depression, anorexia nervosa, and hypochondria. If regular stool retention occurs after the start of a course of drug therapy, this may be the cause of difficult bowel movements. Constipation as a side effect can occur with long-term use of diuretics, antidepressants, and medications to lower blood pressure.
Patients with systemic scleroderma, systemic sclerosis, congenital and acquired myopathy experience disorders of colon function, which leads to constant constipation.
Electrolyte imbalances also cause constipation. They occur with a lack of potassium, which may be associated with its increased excretion in pathologies of the kidneys, adrenal glands, and gastrointestinal tract. Hypercalcemia—excess calcium—also contributes to constipation.
What to do
It may take many months of recovery for intestinal motility to improve. Following a diet from time to time is not always sufficient to get rid of stool retention. Other areas of life also need to be improved:
- walk more in the fresh air;
- play your favorite sports;
- prefer active recreation, dancing;
- avoid stress;
- give up alcohol and tobacco.
To help your stomach relax, it is useful to massage. Simple yoga exercises will also improve the tone of internal organs and help fecal matter pass out.
If defecation continues to be delayed after menstruation, this may be a symptom of colitis or other pathology in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, self-medication can aggravate the woman’s condition. She needs to be examined by a number of specialists: an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, gynecologist, neurologist and others. The cause of the pathology may be hidden in the most unexpected place.
Why is constipation dangerous?
Regular bowel movements are a necessary condition for health and comfortable well-being. Normally, healthy people have bowel movements once a day. A deviation of plus or minus four hours is considered normal. About 10% of people have bowel movements 3-4 times within two days. This indicator is influenced by diet, level of physical activity and other factors.
In most cases, bowel movement occurs in the morning, after waking up. If the intestines cope with their task normally, emptying them does not cause discomfort and does not require strong pushing. There are no foreign impurities in the stool: mucus, blood.
Even a one-time stool retention negatively affects your well-being. A person experiences heaviness in the stomach and a decrease in appetite. Constipation leads to a deterioration in the quality of life. Patients suffering from a chronic disorder of intestinal evacuation function complain of headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
Due to irregular bowel movements, the entire body suffers as toxins accumulate in it. This has a bad effect on appearance and over time leads to serious illnesses. Constipation increases the risk of developing hemorrhoids, proctitis, and tumors of the rectum and colon.
How to distinguish PMS from pregnancy?
To distinguish PMS from pregnancy, you need to visit a gynecologist. Premenstrual syndrome, the symptoms of which vary from woman to woman, can resemble signs of early pregnancy and cause pain in the chest, frequent mood swings (attacks of sadness and apathy, tearfulness), and other ailments.
Pregnancy and PMS are caused by hormonal changes, so it's easy to confuse the two. If your bad mood persists for two weeks or more, seek medical help. According to the World Health Organization, doctors diagnosed mental disorders, in particular depression, in 10% of pregnant women.
Hormonal fluctuations are often the cause of female constipation, which can be aggravated by excessive consumption of confectionery, fatty foods, smoked foods and sweet soda. Research shows that constipation affects up to 38% of women, not only before menstruation, but also during pregnancy. In the first case, constipation most often appears against the background of intestinal diseases, the aggravation of which occurs under the influence of PMS, in the second - due to significant changes in the body due to the natural formation of the fetus, which is most often characteristic of the first two trimesters.
Common signs of PMS and pregnancy also include:
- changes in the breast, which may include pain, swelling, tenderness. With PMS, they are felt before the menstrual period, and disappear after it begins or ends. In the first months of pregnancy and before childbirth, the breasts become heavier, touching the area around the nipple can cause pain, and the veins located in the chest become more pronounced;
- fatigue. In some pregnant women, it is observed only during the first trimester, in others it persists throughout the entire 9 months until the onset of labor. Along with fatigue, a woman preparing to become a mother may periodically experience “menstrual” ailments, however, as a rule, they disappear within 1-2 days;
- bleeding. In early pregnancy, small blood stains may appear on your underwear. This is called implantation bleeding, which most often occurs 10 to 14 days after fertilization. Many women do not notice such discharge or confuse it with menstruation. You need to understand that menstrual bleeding lasts at least 4-7 days and causes significant blood loss, which is difficult to miss;
- spasms. In early pregnancy, they are similar to menstrual cramps and mostly occur in the lower stomach. In a pregnant woman, cramps may persist for several weeks or months (the reason is the development of the fetus in the womb).
Diagnostics
To clarify the cause of constipation, a comprehensive examination is required. The patient must make an appointment with a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, and other specialized specialists. To assess the state of health, general clinical tests are prescribed, an analysis of thyroid hormones, an endoscopic examination of the intestines, and an ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract. To clarify the diagnosis, CT or MRI may be prescribed.
In case of a family history that is associated with severe intestinal diseases in relatives (polyposis, cancer), the patient is advised to have a colonoscopy. This diagnostic procedure should be performed by all people over 50 years of age for prevention purposes.
According to statistics, up to 80% of patients with chronic constipation do not have organic disorders, that is, difficulty in defecation is due to poor diet and lifestyle.
Treatment
When stool retention occurs, many patients self-medicate by taking laxatives and doing enemas. Laxatives can be natural (herbal preparations) and synthetic. The most commonly used are senna leaves, buckthorn bark, castor oil, preparations based on phenolphthalein, magnesium sulfate.
This gives temporary relief, but leads to negative consequences. Systematic use of laxatives leads to atony of the large intestine. The body loses the ability to carry out bowel movements without external help, that is, the person is forced to constantly take medications. Addiction develops, due to which the effectiveness of the drug decreases, and the patient is forced to increase the dosage.
In addition to addiction, uncontrolled use of laxatives causes other negative effects:
- dyskinesia;
- electrolyte imbalance;
- deterioration of nutrient absorption;
- dysbacteriosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
When prescribing laxatives, your doctor will determine how long you should take them, and these guidelines should be followed.
If constipation occurs due to endocrine pathology or another serious disease, in order to normalize bowel movements it is necessary to influence the cause of the disorder. The doctor will first prescribe medications and procedures that will help compensate for the negative consequences of the disease, thereby helping to get rid of its symptoms, including constipation.
How to treat PMS?
Contact your gynecologist to relieve your PMS symptoms. The doctor will tell you how to deal with unpleasant sensations before menstruation and not harm women’s health after collecting an anamnesis and gynecological examination of the patient. Based on the examination results, the doctor makes a diagnosis of PMS. The gynecologist gives an explanation of the regimen for taking prescribed medications. Do not self-medicate so as not to worsen the situation.
To treat PMS use:
- medications (painkillers, antidepressants, diuretics);
- hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches);
- aerobic physical activity (cardio exercise), in which oxygen serves as the source of energy to maintain muscle function;
- diet (gradual transition to a healthy menu, avoiding excessive consumption of caffeine, salt and sugar two weeks before the start of menstruation).
Anecdotal research suggests that certain vitamins and minerals may help relieve menstrual discomfort. These include calcium, magnesium, vitamin B6, polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega). However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not recommend unauthorized use of vitamin complexes and supplements, as this can cause menstrual dysfunction. Before taking them, you should consult your doctor.
You also need to give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), avoid stressful situations, yoga and meditation, massage are recommended. According to the study, women who smoke reported more PMS symptoms than non-smokers. Problems in the family and at work, lack of sleep, and restless sleep can aggravate the situation. Women's periods should be regular and not cause significant harm to women's well-being and health. A gynecologist will help solve problems with the menstrual cycle and prevent dysfunction of the ovaries and other female genital organs.
1
1
6
Article rating:
4.11 out of 5 based on 9 ratings
Author: Filatova Tatyana Sergeevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist. First category. Work experience over 18 years.
Diet therapy
For sustainable normalization of stool, the patient needs to review his menu. It should contain:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products with live lacto- and bifidobacteria;
- bran, wholemeal bread, products with fiber and dietary fiber;
- vegetable oil.
The amount of food for an adult should be at least a kilogram per day. Be sure to drink up to two liters of liquid.
Foods that harden the stomach should be avoided. First of all, these are cheese, eggs, rice dishes, and foods high in pectin. It is worth limiting the consumption of chocolate, sweets, pasta (especially made from soft wheat flour), wheat bread, fresh milk, and legume dishes. These products contribute to increased gas formation and impair intestinal motility.
It is important to avoid a sedentary lifestyle in the treatment of constipation. Spend 30-50 minutes walking or other physical activity every day.