Causes of mushy stool in adults
One of the main causes of pathology that occurs most often is IBS, namely irritable bowel syndrome. An adult may develop mushy stool over a long period of time due to poor nutrition, namely the consumption of stale foods of low quality.
Associated with this factor is intolerance to a particular product, which gives such a pronounced reaction. The list of the most likely reasons for changes in stool in an adult is supplemented by:
- a nonspecific form of ulcerative colitis is a chronic pathology associated with ulcerative inflammation of the mucous surface of the large intestine,
- Crohn's disease,
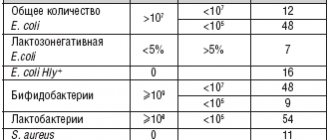
- dysbacteriosis, namely a decrease in the number of lactobacilli - beneficial microorganisms that are present in the intestinal area, improving the process of food digestion.
Another factor in the occurrence of soft stools in adults for a long time is infectious diseases. We are talking about salmonellosis, dysentery, and shigellosis, which may be the root cause of the pathology. In many cases, in order to determine the specific cause of the pathology, it is necessary to understand the symptoms that accompany it.
What symptoms accompany this?
Typically, the patient's condition is associated with systematic and loose stools three or more times a day. There is often an urgent and sometimes uncontrollable urge to have a bowel movement. In addition, the occurrence of liquid or pasty stool is associated with flatulence (a tendency to increased gas production), rumbling and pain in the area.
If unformed stool in adults lasts for three weeks or more, a feverish state is more likely to occur, as well as a general weakening of the body. The condition is characterized by an increase in the mass of unformed stool up to 250-300 g during the day, while the water ratio can reach 60% and even 85%.
Read also: Why is the spleen enlarged and what to do
Briefly about diagnostics
Before starting a rehabilitation course, a complete diagnosis is provided. As a rule, it consists of:
- conducting a general analysis of stool, urine, examining stool for the presence of occult blood,
- performing irrigoscopy and colonoscopy,
- introduction of ultrasound and other informative tactics for studying the digestive system.
Simultaneously with the diagnosis, it is recommended to ensure the replenishment of the water balance, which has become disturbed due to prolonged mushy stools.
It is important to note that after the end of the main therapy, additional diagnostics are carried out to identify the results of treatment and demonstrate the current state of the gastrointestinal tract.
Unstable chair
Almost every patient who has encountered disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract reports the occurrence of various types of stool disorders (unstable stool). Such a disorder is caused by frequent changes in constipation and diarrhea, changes in the color and amount of feces, which significantly depletes the patient’s body and makes it difficult to treat the underlying disease.
It is worth noting that unstable stool is most often associated with intestinal diseases, however, problems with the stomach, liver and pancreas can also cause stool disorders.
Stool instability due to improper functioning of the stomach is associated with the intensity of its secretion of digestive juices. If the stomach produces them in excess (occurs with gastritis, stomach ulcers), then most likely the patient will be bothered by constipation. With gastritis, unstable stool will be pronounced - there may be no stool for 3-4 days (less often - a week), the patient feels pain during bowel movements, but during remission of the underlying disease, there are no problems with stool.
When diagnosed with a gastric ulcer, constipation may be accompanied by significant pain along the large intestine (usually in the lower abdomen, left and/or right). The reason is that the acidic gastric contents from the stomach entering the intestines irritate the walls of the organ, resulting in noticeable spasms. Along with spasms and constipation, the quality of the stool leaves also changes - the amount of exiting masses decreases significantly, taking on the appearance of “sheep feces”.
In cases of stomach diseases with reduced production of gastric juice (chronic gastritis, stomach tumors), stools, on the contrary, become more frequent and the patient regularly experiences diarrhea. This is due to the fact that food is not sufficiently processed by juices and enters the intestines almost in its original form. Diarrhea is an increase in bowel movements up to 2-3 times a day, which is naturally not the norm. With diarrhea associated with a decrease in the secretion of gastric juice, the feces do not change qualitatively - there are no impurities in the masses, and its quantity does not increase.
With unstable secretion of gastric juices (periods of exacerbation and remission of stomach diseases, periods of initiation of treatment for such diseases), unstable stools are most pronounced, constipation and diarrhea very often alternate.
But still, the main reason for the development of unstable stools is intestinal diseases, this is due to the fact that it is this organ that is responsible for the digestion, absorption and final formation of feces.
Among the intestinal diseases that can provoke the development of fecal disorders are the following:
– inflammation of the small intestine – chronic enteritis – (causes frequent bowel movements, 2-3 times a day with unformed feces in the form of a liquid golden-yellow porridge);
– chronic inflammatory processes in the colon – colitis, enterocolitis – (stool is unstable: constipation alternates with diarrhea; during constipation, feces look like sheep’s: it is very dry and is excreted in small portions, sometimes mixed with blood or mucus, with diarrhea: stool can be up to 10-15 times a day; emptying is preceded by rumbling, flatulence and severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen).
– functional disorders in the large intestine – irritable bowel syndrome – (stool is disturbed in the direction of constipation, from minor to persistent and long-lasting, with severe pain and significant discomfort – bowel movements seem incomplete, unsatisfactory).
– disturbances in the functioning of intestinal vessels – hemorrhoids, anal fissures – (stool is disturbed towards constipation: severe pain during defecation forces patients to be forced to restrain the act of bowel movement, which over time leads to chronic constipation: hard stool, sometimes mixed with blood).
– nervous shocks – stress – (severe stress shocks can provoke one-time cases of diarrhea).
Which doctors to contact:
— Gastroenterologist
What to do if an adult has soft stools for a long time?
Having understood the causes and symptoms of mushy stool in adults, you will need to begin a recovery course. You should prepare in advance for the fact that this will be a complex intervention that may take a long time. Gastroenterologists call the main activities:
- The use of medications, the specific list of which depends on the cause of the condition. For example, for IBS, Loperamide and other drugs that regulate intestinal motility are used.
- Drug treatment includes the use of drugs that improve the functioning of the digestive system. They can be considered preventive, but they are used as part of the main course - these are Linex, Smecta, Imodium.
- Replenishment of the water balance, which is carried out not only through the consumption of a significant amount of water, but also subject to the use of Regidron and similar products.
A separate role in the process of treating unformed stool in an adult for a long time should be given to diet. It includes such products and dishes as low-fat broth, rice-based broth, boiled eggs, and all kinds of cereals. It is beneficial to consume tea, jelly, fish and lean steamed meat. Also advisable for use with soft feces are crackers made from bran bread.
The diet should in no case imply the use of spices or, especially, fatty foods. Speaking about proper nutrition, experts point out that:
- To achieve a significant result, you will need to give up a whole list of products. Sweet fruit juices, carbonated drinks, and any dairy products are not allowed. Mushrooms, legumes, as well as marinades, sweets and baked goods are prohibited.
- Literally on the very first day of loose stools, you will need to give up any food. At the same time, it is necessary to provide the body with a sufficient amount of water.
- It is important to stick to the diet for at least one week. It is not recommended to abruptly return to a familiar diet, even if all symptoms cease, including mushy stool in an adult in the morning.
Read also: How to properly use Esmarch's mug for cleansing
The general goals of the recovery course should be considered the elimination of liquid feces, the normalization of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the restoration of water balance and the elimination of the underlying disease, regardless of its cause.
In some cases, an operation is performed for this, but the scale of the intervention (resection of an organ, removal of the inflamed area) can be very different, since it can depend on a significant number of factors.
Disorder of regularity and stool consistency
(constipation, diarrhea; mucus or blood in stool)
Stool disorders are a delicate problem that patients, as a rule, are in no hurry to discuss with a specialist. But in vain. In some cases, such troubles may be the result of severe conditions that require surgical correction (for example, intestinal obstruction). Therefore, the sooner you see a doctor, the lower the risks of dangerous complications.
What can be associated with stool disorders?
- Constipation. They are divided into episodic and chronic. The former occur from time to time due to stress or nutritional disorders and are not considered a disease. The second are regular defecation delays that last for 3 months or more. The development of chronic constipation may be due to decreased intestinal motility (lazy bowel syndrome), helminthic infestations, narrowing of the intestinal lumen, anorectal diseases (in particular hemorrhoids) or neurological disorders. In women, problems with bowel movements often appear during menopause, which is associated with a decrease in the production of estrogen in the body.
- Diarrhea. Like constipation, diarrhea can be acute (lasting less than 3 weeks) or chronic (lasting longer than 3 weeks). Acute is usually caused by pathogenic microorganisms that enter the intestines along with contaminated water or food. In addition to diarrhea, patients with intestinal infections may also experience fever, nausea, and vomiting. Chronic diarrhea can be a symptom of inflammatory bowel diseases (enteritis, colitis), pancreatitis, helminthic infestations, polyps and malignant tumors of the colon.
- Unstable stool (alternating constipation and diarrhea). This symptom is most typical for gastritis, gastroduodenitis, irritable bowel syndrome, dysbacteriosis and biliary dyskinesia.
- The appearance of mucus or blood in the stool. Bloody streaks in the stool indicate damage to the walls of the digestive tract, which is often associated with gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, ulcerative colitis, proctitis, and Crohn's disease. The appearance of mucus is often observed in inflammatory and tumor diseases of the intestine (colitis, enterocolitis, colon cancer, etc.).
Diagnosis and treatment
Mandatory studies for stool disorders include:
- careful collection of anamnesis,
- clinical examination,
- blood and stool tests,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs,
- according to indications - gastro-, colon-, irrigoscopy.
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity with intravenous bolus contrast.
Treatment consists of eliminating the underlying disease and following a certain diet. If necessary, patients may be recommended symptomatic therapy (taking laxatives or laxatives).
In most cases, bowel disorders can be successfully corrected. It is only important not to delay the diagnosis and take timely measures to eliminate the disease. At the Spectra clinic, you can get professional advice and undergo a comprehensive examination, which will allow you to determine the exact cause of the disorder. You can make an appointment both on weekdays and on weekends.
How to prevent the problem
To prevent feces from appearing like plasticine in an adult in the future, it is recommended to ensure proper nutrition and sufficient water intake.
Factors that provoke disruption of bowel movements and the functioning of the body in general should be considered a sedentary lifestyle and the presence of diseases of the endocrine gland. In this regard, the presented factors will also need to be kept under constant control, preventing the aggravation of these problems. Compliance with each of the indicated measures, not only individually, but also together will be an excellent prevention of thick stool.
( 3 ratings, average: 2.33 out of 5)