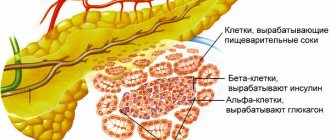
The pancreas interacts quite closely with other organs, and a malfunction in its functioning affects the functioning of the entire body. For diagnosis, various methods are used, including palpation. Pain during the inflammatory process in the pancreas, in the Shoffard area, is characteristic of pancreatitis. In an acute process, this manipulation is difficult, since the abdominal muscles are very tense; in a chronic process, the organ can be palpated in half of the individuals; in healthy people, in isolated cases.
Principles of palpation
The palpation method began to be used for diagnostic purposes at the end of the twentieth century. At that time, there was no special equipment (MRI, ultrasound) to help detect the causes of pathology and pain in an individual. Therefore, during the examination, doctors used their fingers. The advantage of this method is that with its help you can quickly suspect pancreatitis in the acute stage and begin therapy. If there is no malfunction of the gland, then it is impossible to palpate it.
Pain in the Choffard area with pancreatitis is considered a characteristic clinical sign. In acute and chronic course of the disease, pain is localized in other areas and points.
Therapeutic measures
It is not possible to get rid of specific symptoms, including Mayo-Robson syndrome, individually. Complex treatment of pancreatitis is required. First of all, it is necessary to begin therapy for the acute form of the disease with conservative therapy. It is usually used for mild cases of the disease, when the patient has an edematous form of pancreatitis. Also, such therapy helps with the sterile type of pancreatic necrosis.
From the first days, in severe cases of pancreatitis, antibiotics are prescribed. It is necessary to choose a group of drugs with a wide spectrum of action. In addition, they are also used to prevent septic and purulent processes. Contrical is administered to inhibit proteolytic enzymes that circulate in the blood. If the intoxication of the body is pronounced, then hemosorption and plasmapheresis are required - these are methods of purifying the blood outside the kidneys. To prevent the occurrence of disseminated blood coagulation inside the vessels, Heparin is prescribed. It is better to choose its analogues with a low molecular structure. Infusion therapy plays an important role. It replenishes the lack of blood, and also removes harmful substances from the body and improves blood circulation at the micro level. All medications and procedures are prescribed only by a doctor.
Under no circumstances should you try to eliminate the manifestations of the Mayo-Robson symptom and other signs of pancreatitis on your own.
Surgery is required when serious complications develop. For example, septic and purulent, hemorrhagic and arrosive, mechanical jaundice. The same applies to cholecystitis of a destructive nature, various necrosis of an uninfected type. It is necessary to take into account the presence of cysts of a false nature.
You definitely need to stick to your diet. It is very tough, but effective. Thanks to the constant implementation of her rules, pain, including the author’s symptoms, will not appear. Nutrition should be gentle to reduce the load on the stomach and pancreas. It is best to eat vegetables stewed and boiled. Baked apples are useful fruits. Jam and honey are allowed, but no more than 1-2 spoons per day. Vegetarian vegetable and milk-cereal soups are very healthy. Milk porridge is also allowed. You can eat poultry, fish and meat, but they should not be fatty. Cottage cheese casseroles and steamed omelettes are healthy. For sweets, marmalade, biscuits, and marshmallows are allowed, but not much.
You will have to give up sour-tasting vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries. All spices and seasonings are prohibited. You cannot eat nuts, legumes and mushrooms. Coffee, chocolate, cocoa, baked goods, brown bread, kvass and carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited. You will have to give up sausages, smoked meats, marinades, sausages, and pickles. You should not eat foods that are spicy or sour to taste, as well as anything fatty or fried.
Pancreatitis is a serious inflammatory disease of the pancreas. It can occur in both acute and chronic forms. When the disease occurs, various symptoms appear, some of which have become named in medicine. The most common symptom in patients with this disease is Mayo-Robson syndrome, when a certain point is felt with severe pain. Treatment is the same as for pancreatitis: medications, procedures, diet and surgery in severe cases. Be healthy!
Physical methods for studying the pancreas
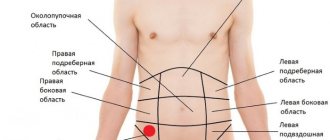
Palpation, according to doctors, is successful only in cases where the gland is compacted and enlarged. And palpation examination using the method of Obraztsov V.P. possible only in thin individuals with a flaccid abdominal wall. It is possible to verify that the palpable formation is the pancreas only if its relationship to the surrounding organs is established. The projection of the head of the gland onto the anterior surface of the abdomen corresponds to the Choffard-Rivet zone, or, as it is also called, pancreatic-choledochal.
It is located in the upper right part of the abdomen, on the bisector of a right angle, which is formed by horizontal and vertical lines passing through the navel. The upper border of this area is located at a distance of approximately five or six centimeters from the navel. When an organ enlarges and hardens, palpation has diagnostic value.
Additional symptoms
In addition to what is written above, we can identify other specific characteristics that bear the names of doctors. Mondor's sign is detected during the acute course of the disease. It is caused by changes in the patient’s skin. Blue spots appear on the patient's body. The etiology is based on the penetration of toxins that are produced by the gland.
Grotta's sign. This symptom is characterized by pain at certain points, each of which has its own name, and appears to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process in a certain part of the internal organ.
Desjardins' sign is caused by pain in the area, which is located four centimeters above the navel along a line connecting to the armpit on the right side. In the acute form of the disease, it is diagnosed in 70% of cases.
The characteristic signs of acute pancreatitis develop suddenly. Typically, the inflammatory process is provoked by the consumption of fatty and heavy foods, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. Under the influence of these factors, the patient experiences the following clinical manifestations:
- Intense excruciating pain in the epigastric region.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Yellowness of the skin (not in all cases).
- Attack of nausea, vomiting.
- The abdomen increases in volume.
- The functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted.
There are often signs of shock. These include lethargy, low blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, pale skin, etc. These symptoms do not always indicate inflammation of the pancreas, as they may indicate other diseases. However, their appearance is a reason to call a medical team. Often, along with pancreatitis, cholecystitis is diagnosed.
For treatment, medications are used and a special diet is prescribed. In some cases, surgical treatment is required. Surgery is resorted to in the presence of complications of the disease, to eliminate painful sensations.
An expert will tell you what Voskresensky’s symptom is in the video in this article.
The author's symptoms of pancreatitis are syndromes of pancreatic disease that are so common and unique that they were named after their discoverers: Voskresensky, Mayo-Robson, Kerte, Razdolsky, Kach, Mondor.
Identifying pain points
In case of disease, their determination is carried out by pinpoint palpation, which is important in diagnosis. In pathologies of the pancreas, weakness is detected in the areas:
- Shoffara;
- Gubergritsa - Skulsky, which is located symmetrically to the previous zone, on the left.
Discomfort when pressing on the Mayo-Robson point is present in individuals with inflammation in the tail of the pancreas. This place is located at the junction of the lower and middle third of the straight line, which connects the middle of the left costal arch with the navel.
In 1984, doctors Tuzhilin S.A. and Gubergrits A.Ya. a method was proposed for detecting organ pain when examining a patient in an upright position. The doctor presses with his fingers into the area of the projection of the gland, after this action the patient feels pain or its intensification and must bend down. He experiences a similar condition when he is in a horizontal position and tries to rise during a palpation examination.
Symptoms of Voskresensky
The symptom of the author Voskresensky has another name - a clinical manifestation of false insensitivity. The etiology of its development is due to inflammation of the infiltration of the retroperitoneal space.
During palpation, the medical specialist does not feel the pulsation of the abdominal aorta in the area where this blood vessel intersects with the pancreas. Normally, there should be a pulsation five centimeters above the navel and four centimeters to the left of its axis.
This clinical picture is based on the fact that the internal organ is swollen and has significantly increased in size, thereby blocking a large vessel.
You can feel the pulsation yourself. To do this, the patient lies on his back and stirs his fingers as indicated above. If everything is in order, then he feels a pulsation; in the acute form of pancreatitis it is absent.
You cannot rely entirely on this clinical sign. In some cases, this symptom indicates other pathological conditions:
- Tumors of the pancreas.
- Increased size of lymph nodes.
- Severe gas formation.
The symptom according to the authors, in particular according to Voskresensky, may not give an idea of the clinical picture in obese patients. The correct diagnosis is made after instrumental and laboratory tests; a physical examination is not enough.
If acute appendicitis is suspected, this symptom is most indicative. However, verification occurs using a different method. In medical practice, the symptom has another name - shirt symptom. During palpation, the patient’s shirt, which is located on the back, is lowered and pulled over the body, and through a sliding movement, the ribs of the palm are drawn along the abdomen from top to bottom. This action is repeated on both sides. In acute appendicitis, the patient experiences pain in the right iliac region.
This manifestation is explained by irritation of the peritoneum, which occurs as a result of inflammatory processes in the appendix.
How to determine chronic pancreatitis?
In an individual with a chronic form of pancreatitis, during a medical examination, hemorrhagic rashes ranging in size from one to four millimeters are clearly visible on the dermis. They are presented in the form of convex droplets. They are otherwise called “point angiomas,” which are formed as a result of the destructive effects of pancreatic enzymes on the capillaries. After examination, objective signs of pathology are revealed, which have their own names:
- Mayo-Robson - pain is observed in this place, as well as in the left costovertebral angle.
- Grotta – reduction of subcutaneous tissue from the navel on the left in the projection of the pancreas.
- Gubergritsa - Skulsky - painful area between the tail and head of the gland.
- Kacha is a pain syndrome in the area of the left TVIII-TIX and right T1X-TX1 thoracic vertebrae.
- Voskresensky - pulsation of the abdominal aorta is not detected.
- Mussi-Georgievsky - upon palpation, discomfort in the right supraclavicular zone, between the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Desjardins - pain during palpation is felt at the so-called pancreatic point of Desjardins.
- In the Choffard area, which is located six centimeters above the navel on the right side of the body, soreness is also detected.
Further laboratory types of research are carried out:
- general and biochemical blood test, amylase and lipase test;
- general urine analysis;
- coagulogram;
- coprogram;
- elastase test;
- identification of tumor cell growth marker;
- glucose tolerance.
Of the instrumental methods, the following must be performed:
- radiography of the abdominal organs;
- Ultrasound;
- ERCP – endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Additional types of studies are prescribed if necessary - these are spiral CT, FGDS, plain chest radiography, laparoscopy, angiography, radionuclide cholecystography.
What are the symptoms of pancreatitis?
Given the symptoms, ambulance workers often confuse pancreatitis with poisoning, gastritis and appendicitis. After delivering the patient to the hospital, taking a more thorough history and conducting tests, the doctor determines pancreatitis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following methods of examining the patient are carried out:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor finds out where, how, when the pain began, and whether there is a disturbance in general health.
- Visual inspection. The condition of the skin is assessed and the patient's tongue is examined.
- Analysis of the patient’s general condition: measurement of body temperature and blood pressure, palpation, auscultation and percussion. In this case, various methods are used - symptoms. Mayo-Robson, Razdolsky, etc.).
- Laboratory - general and biochemical blood tests, assessment of water and electrolyte balance in the blood, general urine analysis.
- Instrumental - ultrasound, X-ray examination, computed tomography, FGDS, laparoscopy.
Palpation: area of Choffard, Mayo-Robson and Desjardins
The areas for palpation examination are the areas of the greater gyrus of the transverse colon and the stomach. The medical professional determines in advance the places that will be palpated so as not to mistake them for a gland. Usually the most common methods of palpation of the pancreas are used: the usual method according to Groth, as well as according to Obraztsov - Strazhesk.
Palpation begins from the head of the organ, due to the fact that it has a more pronounced configuration compared to other parts. During this procedure, the doctor examines the condition of the organ at certain points:
- Desjardins - if an individual feels some discomfort when pressing on this area, then it indicates an inflammatory process in the head of the gland.
- Mayo-Robson - pain indicates damage to the tail of the organ.
- Shoffara - pain syndrome indicates damage to the head of the pancreas.
Characteristic signs of pathology
Inflammatory processes in the pancreas lead to a pancreatic attack. The acute syndrome, in its symptomatic picture, resembles poisoning: vomiting and diarrhea appear. But with the release of the masses there is no relief - the person still feels very sick.
Other characteristic signs of pathology include the following:
- severe pain in the upper abdomen;
- increased body temperature;
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes;
- grayish complexion, circles under the eyes and sharpened facial features;
- tachycardia;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- shortness of breath;
- putrid smell of feces;
- taste of bile and dry mouth.
In chronic pancreatitis, the symptoms are not so intense. Body temperature is usually normal. Dyspeptic symptoms may include only frequent nausea in the morning, bowel irregularities, and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after minor snacks.
Chronic inflammation of the pancreas is more difficult to diagnose than acute pancreatitis. If the patient complains of lack of appetite in the morning, significant weight loss and frequent aching pain in the epigastric region, he is referred to a gastroenterologist for consultation and confirmation (or denial) of suspicions of pancreatitis.
Examination of a patient for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis
When diagnosing a disease, in addition to objective and subjective signs of the disease, as well as test data, special research methods are used. In order to implement them, the individual takes the following poses:
- lies on the back, under which a cushion is placed;
- rolls over onto the right side and tilts the body forward 45 degrees;
- stands up and bends the body to the left and forward.
By palpation, the doctor detects pain in the Shoffar area and other points and areas. For example, discomfort caused by pain in this place is characteristic of the inflammatory process in the head of the organ. And in case of damage to the organ body - in the Gubergritsa-Skulsky area. At the Desjardins point - with inflammation of the head part, at the Mayo-Robson point - characteristic of damage to the tail section of the pancreas. Thus, with pancreatitis, pain is noted in such points as Desjardins and Mayo-Robson, as well as the Shoffar and Gubergrits-Skulsky zones.
Diagnosis of the disease
Based on general signs of malaise, it is impossible to immediately make a diagnosis and say that pancreatitis is certainly present. In addition to the form of the disease, several types of pancreatitis with various complications are known. A thorough examination is carried out to make a diagnosis. It will be necessary to take tests, conduct an ultrasound examination and a full examination of the patient.
The examination is carried out by palpation according to the established methodology. The method is based on a person’s feeling of pain in certain places during palpation and percussion of the area under study; each case is characterized by special symptoms. Symptoms of pancreatitis are named after the authors, named after the doctors who studied these symptoms: Kerte's symptom, Mayo-Robson, Voskresensky, Kach, Razdolsky, Mondor.