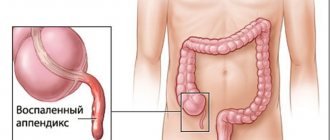
The disease is a common pathology and requires immediate surgical intervention. Surgery to remove the appendix is considered safe and does not affect subsequent health. Surgeons warn that ignoring primary symptoms and prolonged refusal to hospitalize causes the development of complications, including peritonitis. In the latter case, the risk of death increases.
Determining the beginning of the inflammation process
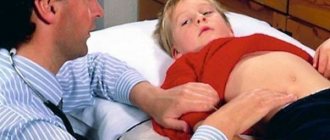
How to determine appendicitis at home without doctors: you don’t need to be a medical professional to make an assumption. The pathological process occurs with various clinical signs, the main of which is pain in the abdomen. Discomfort accompanies not only inflammation of the appendix, but also other diseases; because of this feature, patients are prohibited from taking painkillers.
Anesthetics provide relief, but cause diagnostic problems. Everyone should know the standard symptoms of appendicitis so that they can contact specialists in a timely manner. The list of standard clinical signs includes:
- constant pain syndrome - in the abdominal area;
- Kocher's symptom - pain from the epigastric region gradually moves to the right iliac region;
- Sitkovsky's symptoms - when lying down, on the left side, the unpleasant sensations intensify due to the pressure of the intestines on the inflamed area.
Additionally, patients experience a lack of appetite and a rise in temperature to subfebrile levels of 38 degrees. Attacks of nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and frequent urination may occur.
Why is it needed?
The appendix is important. This is not just a shoot that we received as a gift from evolution. Normally, the appendix performs an immune function. It belongs to the organs of the immune system and therefore is always the first to suffer from inflammatory processes in the abdomen.
In addition to its immune function, this small appendix is a receptacle for intestinal microflora; digested food never enters it. This makes it possible for the entire intestinal microbiota to grow and develop in it, which is involved in the processes of protecting the intestines from pathogenic microorganisms and in the digestion process.
There is evidence that it is from the appendix that the intestinal microflora “comes out” and is restored after intestinal infections. Even 30-40 years ago, sailors who went on long voyages had their appendix removed so that it would not become inflamed at sea, away from medical care. Since then, it has been observed that people with their appendix removed are more likely to suffer from intestinal illnesses, have a reduced immune response, and take longer to recover from intestinal illnesses.
Research is currently underway on the effect of intestinal microflora not only on the immune system, but also on the brain. We have already talked about this.
Appendicitis in women, elderly and children
Clinical manifestations in females resemble certain gynecological pathologies. The anomaly is associated with the close location of the appendages, and pain syndrome is present:
- with ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian rupture;
- apoplexy, etc.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to the presence of gynecological diseases and the menstrual cycle.
Some specific manifestations of appendicitis are present in the elderly, children, pregnant women and with an abnormal location of the appendix.
The following clinical signs are typical for babies:
- diarrhea with frequent vomiting;
- febrile temperature indicators;
- decreased activity - the child loses interest in toys;
- lethargy, moodiness;
- anxiety - with increasing discomfort.
In old age, the symptomatic picture is different:
- temperature rise does not always occur;
- the pulse remains within standard limits - without increasing heart rate;
- there are mild signs of abdominal irritation.
At an older age, the clinical manifestations of appendicitis resemble a neoplasm located in the area of the cecum. During pregnancy, the pain syndrome is localized over the iliac region - due to the upward elevation of the intestines against the background of an enlarged uterus.
Appendicitis - recognize the symptoms and act quickly
22.06.2021
For most, appendicitis occurs suddenly—and it rarely goes away on its own. As a rule, only antibiotics or even surgery . Appendicitis caused by bacteria. If intestinal flora is disrupted, the blockage can cause inflammation of the appendix, a small appendage at the beginning of the large intestine. Sometimes fruit kernels or fecal stones can block the small opening of the appendix and cause inflammation.
Appendicitis can occur at any age, but is more common in teenagers. However, it is quite rare in young children and older people.
Symptoms: how to recognize appendicitis?
Symptoms of appendicitis often come on suddenly, but get worse and become more erratic over time.
Sudden colic pain that initially occurs in the abdomen behind the navel or in the epigastric region.
The pain migrates to the right lower abdomen after 8-12 hours.
When standing, walking, jumping, coughing and laughing, the pain intensifies.
Lying down and pulling your legs up makes the pain a little more bearable.
nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, increased sweating , and rapid heart rate may also occur
Diarrhea or constipation may occur .
Some patients have a coating on their tongue .
In children, older adults and pregnant women, the pain may occur in unusual places, especially at first, and be somewhat milder. In children, attention should be paid if cramping pain in the lower abdomen persists for three hours.
Types of inflammation
Depending on the severity, there are two types of inflammation:
- simple appendicitis (simplex) is easy to treat . The tissue is only inflamed, but not yet destroyed. In the catarrhal stage, the appendix becomes red and swollen. This type of appendicitis may resolve spontaneously. There is no pus here;
- if pus accumulates in the appendix during inflammation, this is called the serous-purulent stage. Destructive or destructive appendicitis is characterized by tissue ruptures occurring during the inflammatory phase.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
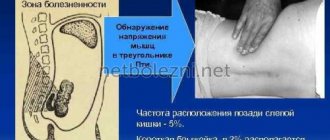
Abdominal pain can have many causes. To check for appendicitis , the doctor palpates what is called McBurney's point. It is located on the outer third of an imaginary line between the upper right iliac crest and the navel . If she is extremely sensitive to pain, this may indicate appendicitis . The diagnosis is completed by ultrasound and blood for markers of inflammation. Depending on the result, the doctor will recommend appropriate treatment. If the inflammation is very severe, surgery is usually inevitable. Otherwise, there is a risk of intestinal . This means that the inflamed appendix ruptures. Germs and pus enter the abdominal cavity and bloodstream. Peritonitis is life-threatening blood poisoning can occur . intestinal obstruction may occur as a complication .
Should I remove my appendix or not?
If previously a scalpel was quickly used for appendicitis , today this is usually only in the acute stage. The operation itself is routine, often performed in a minimally invasive way, such as laparoscopy (keyhole method) and does not take much time. With this surgical method, wound healing is much better.
After surgery, victims usually must remain in the hospital for several days so that bowel . Solid foods should be avoided on the day of surgery Walking may also be difficult in the first few days.
The appendix is not a useless appendage, as was believed a few years ago. It is considered a reservoir of beneficial bacteria and is therefore important for the immune system .
It is assumed that gut bacteria that have settled there recolonize the intestines after diarrhea . When in doubt, surgery is the lesser of two evils.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic
Appendicitis in men
The primary signs of developing pathology include:
- pain syndrome;
- elevated temperature;
- one-time vomiting;
- white coating on the tongue;
- state of general weakness;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- rapid heartbeat, diarrhea;
- refusal to eat.
The intensity and nature of the manifestations are different for each patient. Age and individual characteristics of the body are of great importance. Sharp and diffuse abdominal pain becomes the reason for an urgent visit to the local clinic.
Treatment of acute appendicitis
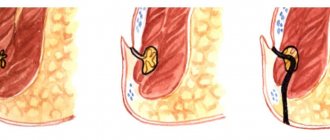
- surgical only. The operation is performed immediately after the diagnosis of acute appendicitis is made. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Performing an appendectomy under local anesthesia, although technically possible, is quite painful. The intervention is performed from a small incision in the right iliac region or videolaparoscopically. Now surgeons in Moscow are increasingly performing laparoscopic operations. For appendicitis complicated by diffuse peritonitis, surgery is performed through a large midline incision.
After surgery, during the normal course of the postoperative period, patients are usually discharged on days 7–10 (after removal of the sutures). After discharge, being on a certificate of incapacity for work is 10-15 days, limiting heavy lifting to 5 kg is 1-4 months (depending on the method of intervention).
General information
Appendicitis can even occur in infants
Appendicitis is an inflammatory process in the area of the appendix of the cecum. The term was proposed in 1886 by the American professor R. Fitz in an article in which he indicated the exact symptoms of the pathology and the most effective method of its treatment - surgery.
In 1887, the first appendectomy was performed in the United States - an operation to remove the appendix. In 1890, A.A. received his first experience in appendicitis surgery. Troyanov. But only after the Congress of Surgeons in 1909 did this practice begin to gain momentum.
The appendix is relatively small in size - up to 1.2 cm in diameter and up to 10 cm in length. Its location relative to the cecum may vary between patients.
The most difficult case for surgery is when the appendix is located behind the peritoneum. In addition, it can fuse with the posterior abdominal wall.
All these factors influence the degree of accuracy of the diagnosis and the complexity of the operation, as well as the development of subsequent complications. There are 4 types of location of the process:
- descending - down from the cecum;
- lateral - to the side;
- medial – along the medial intestinal wall;
- ascending - upward from the intestine.
The descending type is the most common, occurring in 50% of cases. The next most common type is the lateral type (25%), medial – 20%, ascending – 13%.
Features of chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis: Ultrasound diagnosis
A chronic course is extremely uncharacteristic of appendicitis, since inflammation of the appendix usually has an explosive nature due to the abundance of lymphoid tissue in the appendix.
However, there are cases of a mild course of the inflammatory process. In this case, appendicitis remains undiagnosed until a sudden exacerbation.
Chronic appendicitis has the same symptoms and causes as acute appendicitis. However, symptoms of the chronic form may be less pronounced or absent altogether.
The most common manifestation of the chronic form of the pathology is rare aching abdominal pain.
Surgery for appendicitis
Surgery is the main treatment for appendicitis. The procedure is called an appendectomy and is performed under general anesthesia.
Modern medicine makes it possible to remove appendicitis with minimal consequences for the body. During the operation, small punctures are made in the abdominal wall using a special instrument, through which the inflamed organ is removed, then the punctures are sutured. This operation is considered the least invasive compared to interventions that were practiced several decades ago.
Removing the appendix using conventional abdominal surgery is considered an outdated method of treatment. It is used quite rarely, usually in clinics that do not have modern surgical equipment.
The operation is preceded by a fairly long recovery period, when the patient is prohibited from engaging in physical activity and eating “junk food.”
Causes of the disease
Chronic appendicitis can have different causes
The etiology of chronic appendicitis is no different from the causes of the acute form of the disease. The main cause of inflammation of the appendix is obstruction of the lumen of the appendix.
In most cases, obstruction of the appendix occurs due to the proliferation of internal lymphoid tissue.
The lymphoid tissue of the appendix, in turn, grows due to primary infectious and inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease, gastroenteritis and amebiasis.
Another common cause of appendicitis is obstruction of the appendix by fecal matter. Parasites and foreign bodies can also enter the appendix.