A newly born person seems to us to be very tiny and inept. All actions taken to care for him are aimed at helping him do what he is not able to do on his own. Any independent action on the part of the baby causes emotion in the parents, and sometimes even wariness. There is nothing surprising in the fact that the child breathes, makes sounds, looks for his mother’s breast with his mouth, and knows how to empty himself. But crying, groaning, regurgitation, sneezing are regarded as a reason for worry - is this the norm? The same thing happens with hiccups in a baby. Should you worry about hiccups, we will try to explain below.
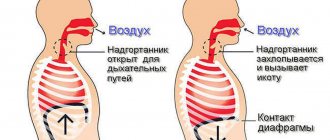
Just like breathing and sneezing, hiccups are a reflex, that is, an involuntary reaction that cannot be controlled: if it occurs, it will only go away when the causes of its occurrence are eliminated.
Causes of hiccups
There are several reasons why a baby hiccups after breastfeeding, which every woman should know. The main reason is the pressure of the increased size due to the feeding of the ventricle on the diaphragm, which can provoke hiccups. However, this is only one of the reasons, and there are several of them. Often, a baby may hiccup because he is cold during a walk or air baths. In this case, it is enough to wrap the baby in a warm blanket or dress him in warm clothes.
Pediatricians note the following reasons why a baby may hiccup:
- filling of the ventricle due to feeding;
- binge eating;
- air entering the digestive tract during feeding;
- hypothermia;
- anxiety or severe fear of the baby;
- insufficient formation and maturity of the digestive tract organs.
Much less often, the reason why a child hiccups after breastfeeding can be a serious illness. Then the hiccups are repeated regularly and continue for a long time, tiring the baby. If the disturbances are serious, regurgitation may also accompany them.
Prevention of regurgitation
When regurgitation in newborns is not associated with pathological processes, parents are advised to follow several recommendations that will help reduce the frequency of this phenomenon.
- After each feeding, hold the baby in a column position for 10-15 minutes.
This will help the air escape easily. In addition, in an upright position, the stomach will throw out less milk. - Ensure proper nipple latching when breastfeeding.
The baby's mouth should deeply grasp the areola. In this case, the entry of gastrointestinal air will be minimal. Feeding position is also important. The child should be in his arms, his tummy pressed against the mother's body. The baby's body is located at an angle of approximately 45°. This position significantly reduces the swallowing of air during feeding. - Don't go overboard with feeding on demand.
Before offering the breast to a crying baby, check whether his diaper is dry, whether his feet are cold, or perhaps the baby is suffering from colic and will calm down in the arms from the warmth of his mother’s body. - After feeding, provide your baby with quiet time.
Do not shake him, do not throw him, do not play outdoor games. Gymnastics, massage and water treatments should also be postponed for an hour and a half. Make sure that the baby is not swaddled too tightly in the abdominal area. Choose clothes that fit, without tight fasteners, elastic bands or belts. Do not over-tighten the diaper's Velcro. - If you are bottle-feeding, carefully read the instructions before preparing the formula.
Accurately observe the dosage of milk powder, the volume of liquid and the interval between feedings. - When choosing a bottle for formula feeding, pay attention to the width of the hole in the nipple.
It should not be wide, otherwise the baby will not be able to suck, and milk will simply pour into his mouth, which will lead to excessive swallowing of air. The bottle and pacifier for it should be selected according to the age of the child. Anti-reflux bottles are now available for sale. - When switching to artificial feeding or changing formula, consult your pediatrician first.
He will help you choose a milk substitute and determine a plan for a gradual transition to a new diet. The smoother this transition is, the lower the risk of digestive upset in the child. - When initially bottle-feeding, choose your formula carefully.
For newborns it must be adapted. Buy food that is appropriate for the child's age. In case of a negative reaction to the mixture (colic, constipation, regurgitation, allergies), contact your pediatrician. The formula may not be suitable for your child and will need to be replaced. An excellent option for comfortable digestion and prevention of regurgitation is Kabrita goat milk infant formula.
In most cases, regurgitation is a temporary physiological phenomenon caused by imperfections in the gastrointestinal tract. It gradually fades away after six months for the majority of babies. And if parents carefully approach the prevention of regurgitation, and if in doubt, consult a competent pediatrician on this topic, then this phenomenon will not cause much inconvenience to either them or the child.
Share on social media networks
What to do
If a situation arises when a child hiccups after breastfeeding, and this repeats regularly and lasts more than half an hour, accompanied by other symptoms, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The baby may need to undergo a medical examination to determine the cause. However, before you consult your pediatrician, make sure that the cause is not due to improper breastfeeding.
If a newborn hiccups after eating or while his mother is feeding him, give him a light tummy massage, lift him upright, gently pressing him to you. This should help the baby, the air will come out, and the hiccups will go away after a while.
The fact that air enters the digestive tract along with milk is one of the reasons why a baby hiccups after breastfeeding. However, other factors that are no less important can provoke this manifestation. As already mentioned, hypothermia can be easily eliminated with a warm blanket. If hiccups are accompanied by regurgitation, elevated body temperature, restlessness, persistent cough and increased activity, as well as crying and other signs of irritability, you should immediately visit a children's hospital and have your baby examined.
Why does a newborn baby hiccup?
Hiccups are very common in newborns and are involuntary contractions of the large diaphragm muscle. While the child is still too small, his diaphragm is very sensitive to various influences. Because the nervous system responsible for muscle contraction, including the diaphragm, is still immature. Therefore, hiccups will occur more often the smaller the baby.
Causes contributing to the occurrence of hiccups:
Mom's food
According to a number of pediatricians, hiccups occur more often in infants whose mothers eat large quantities of vegetables and fruits with coarse fiber, soy, citrus fruits, chocolate, peanuts and drink coffee or carbonated drinks. This may be due to increased gas formation and bloating in the child.
Swallowing air
Incorrect attachment to the breast, inverted nipples that make it difficult to fully latch on, an inappropriate bottle, a nipple with a large hole, or intense crying before feeding - all these reasons lead to the baby swallowing air during feeding.
Cold
Babies have imperfect thermoregulation, so they easily and quickly become hypothermic, which is often accompanied by an attack of hiccups.
Binge eating
If a baby eats a lot and quickly, his stomach becomes full and puts pressure on the diaphragm, which can cause hiccups.
Strong aromas, gas pollution, dust in the air
. They provoke coughing and vibration of the diaphragm, causing hiccups.
Prevention of hiccups
Having figured out why a child hiccups after breastfeeding, it is also worth noting methods for preventing this condition in the baby. As a rule, preventive measures are:
- take breaks during feeding;
- feed at an angle of at least 45 degrees;
- raise the baby to an upright position after feeding;
- do not force the child to eat if he does not want to;
- Don’t let your baby get too hungry;
- make sure the hole in the nipple is not too large;
- adjust your diet. Legumes and other foods can often cause a similar condition in a baby.
Why does a child hiccup after breastfeeding? Your pediatrician will tell you what to do. Consult your doctor, ask him all the necessary questions, make sure you understand everything and follow the basic rules of prevention, and then your child will feel good. Remember that the baby’s body is very delicate and requires mother’s attention and care. Watch his diet and your diet, since everything that the mother eats goes to the baby with milk.
How to prevent hiccups?
In many cases, it is easier to prevent something than to eliminate its consequences later. This is true in the case of hiccups.
- Limit strong emotional shocks for a sensitive baby - prolonged crying without consolation from adults, forced awakening, communication with a person who allows harsh actions with the child (for example, at a doctor's appointment), sudden changes in ambient sound levels (hello neighbors) and lighting.
- Feed the baby only after he has calmed down a little after crying, sucks measuredly and does not swallow air when sobbing.
- If point 2 is not feasible (because many children calm down only from the breast or from food), feeding should be carried out in fractions: the baby sucked, overexcited - calmed down a little - they interrupted him, rocked him, as an option, helped him burp the air, applied him again - sucks until satiated.
- Avoid large volumes of each meal and long breaks between them. Most newborns are characterized by frequent and short feedings, which do not fill the stomach entirely, but provide a state of satiety and satisfaction.
- If it is necessary to offer supplementary feeding, try to choose a means of supplying it that ensures a smooth flow. At the same time, make sure that there is no air suction.
- Place the baby in a comfortable position that does not squeeze his insides, both during feeding and immediately after it. If the baby hiccups very often after being moved from the arms to the crib, then feeding in a lying position and leaving the sleeping child in the place where the feeding took place helps. In some cases, a relaxed feeding posture can curb the occurrence of hiccups.
- Provide a comfortable temperature. Avoiding hypothermia after swimming, when changing clothes, in cool air in the room, while walking. The child's thermoregulation is still imperfect; the requirements for a comfortable temperature are determined by the child's condition.
It is worth noting that in rare cases, very frequent and prolonged hiccups, the causes of which cannot be traced, should be a reason to consult a doctor, especially if it is accompanied by the following conditions:
- occurs after each feeding, accompanied by excessive regurgitation or vomiting, accompanied by a lack of weight gain;
- difficulty breathing (excluding pathology in the lungs);
- hiccups are accompanied by constant restlessness, crying, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, and the general appearance of the child with marbling of the skin;
- constant bloating and unstable bowel movements (too frequent, or rare, or sharply changed stools - to exclude inflammation in the intestines).
In conclusion, I would like to note that most often hiccups cause more distress for parents than for the child - his mood or condition does not deteriorate. Even if hiccups have been your baby’s companion from the first day of life, it is quite possible that by the end of the first month of life the baby will mature, get stronger, his rhythm of life will become more orderly, so there will be no place for hiccups.
Yulia Chistova, lactation consultant