Pain in the lower abdomen in women is an unpleasant sensation that often signals a harmful effect on the genital organs, their damage, or the occurrence of a condition dangerous to health. They can occur even in the absence of traumatic factors. However, discomfort affects the psycho-emotional sphere of a person’s life and limits his mobility.
According to the World Health Organization, many diseases are accompanied by this symptom. Therefore, if women experience pain in the lower abdomen, they should make an appointment with a doctor. He will correctly determine the reason for their appearance. To do this, you will undergo an examination and a comprehensive examination, which may include laboratory, visual, endoscopic and other diagnostic methods. Based on the results obtained and medical history, the doctor decides on treatment tactics - conservative and/or surgical.
The nature of pain in the lower abdomen in women
When visiting a doctor, it is important to provide comprehensive information about your health condition. You need to pay attention to the circumstances under which you experienced discomfort, as well as the nature of the manifestations. So, for example, you may experience:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen in women. Sometimes it is called piercing;
- nagging discomfort;
- cutting pain;
- cramping pain. They are accompanied by spasms.
It is also important to consider when exactly you felt discomfort. According to the time of occurrence, there are:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen in women. They appear suddenly and are characterized by high intensity;
- chronic pain. They may be felt for some time, and then subside and reappear after a certain period.
When should you see a doctor for abdominal pain?
Consult your doctor in the following cases:
- the pain gains intensity and intensifies quickly;
- abdominal pain that is prolonged or recurring;
- stomach pain and difficulty swallowing;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss for no reason;
- constant nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain radiating to the chest, shoulder, arm;
- pain and feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowing of the skin;
- difficulty urinating, painful urination;
- too rare or too frequent urge to urinate;
- severe pain during menstruation;
- unusual vaginal discharge, bleeding;
- prolonged (several days) diarrhea;
- prolonged constipation;
- blood in vomit or stool;
- fever;
- increased sweating (cold, sticky sweat).
Causes of lower abdominal pain in women
Discomfort can be caused by physiological conditions, as well as pathologies:
- reproductive organs. In this case, discomfort signals inflammation, neoplasms, etc. Typically, pain in the lower abdomen is not the only symptom in women. It can occur along with increased body temperature, irritation in the genital area and other manifestations;
- urinary system. Pain is caused by infections and viruses that provoke the occurrence of an inflammatory process;
- digestive organs. In this case, neoplasms and inflammation of unknown etiology occur. Gas may occur in the small and large intestines.
Let's take a closer look at the common causes of lower abdominal pain in women.
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system
This symptom may indicate the following pathologies:
- adnexitis. There is a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- endometritis.
With these diseases, intense paroxysmal or constant pain occurs over the pubic bone, as well as discomfort in the lateral abdomen. Their exact localization is a signal of inflammation. However, with acute endometritis, you will not be able to determine exactly where it hurts. You may experience weakness, unusual discharge, and an increase in body temperature.
Chronic adnexitis is accompanied by nagging pain with short-term spasms. Its intensity increases after stress, during hypothermia. It is important to pay attention to the intensity of pain in a woman’s lower abdomen during sexual intercourse. Its rapid intensification is a defining (pathognomonic) sign.
Endometriosis
With this pathology, patients report nagging or aching pain in the pelvic organs. Their intensity increases before the start of the menstrual cycle. Discomfort reaches its peak in its first 2-3 days. You may also notice increased pain during sexual intercourse.
Neoplasms
Depending on the etiology, the following pathologies are distinguished, in which pain in the lower abdomen occurs in women:
- myoma. This disease is accompanied by the formation of a benign tumor. It grows from the muscle and connective tissue of the uterus. With subserous and interstitial forms of pathology, the patient feels dull pain. Submucosal fibroids are accompanied by severe spasms. The nature of the sensations changes on different days of the menstrual cycle;
- oncology. With malignant tumors there is constant discomfort. In this case, the pain “radiates” to the rectum, to the sacrum, to the lower back. With oncology of the uterine body, cramping sensations occur. They appear suddenly. After the attack of pain ends, you can replace the bloody or bloody discharge from the vagina.
Appendicitis
When the appendage of the cecum becomes inflamed, discomfort occurs in the iliac region, as well as above the pubis. The exact location of pain in the lower abdomen in women depends on the location of the appendix in a particular patient.
You will feel intense discomfort with increasing tension in the right iliac fossa. In some cases, problems with bowel movements and vomiting may occur. Do not delay seeking emergency medical help: as acute appendicitis progresses, it can cause peritonitis.
Algomenorrhea
According to WHO data, up to 70% of women aged 15-45 years experience this condition. It is characterized by the onset of pain 12-24 hours before the start of the menstrual cycle. As a rule, women of reproductive age note aching or nagging discomfort. In most clinical cases it is characterized by moderate intensity.
The severity of algomenorrhea (dysmenorrhea) may vary. However, in 15% of cases, women present with severe pain, which leads to disability. They may also be accompanied by dizziness, weakness, and nausea. Spasms intensify with defecation, turning the body, coughing, sneezing. This condition also negatively affects the psycho-emotional background of a woman.
Conditions during pregnancy
Carrying a child is one of the natural states of women. During a normal pregnancy, she may experience discomfort in the lower abdomen for a short time. This is due to the growth of the uterus, the load on the ligaments that support it.
As the fetus gets larger, the uterus begins to put pressure on some other organs. Because of this, pregnant women may experience pain in the lower abdomen in the second or third trimester. This is also when Braxton Hicks contractions begin. They are false, but they cause contractions of the uterus, which can cause discomfort.
However, intense pain in the lower abdomen in women carrying a fetus is often a signal of the development of complications. For example, a sign of an ectopic pregnancy is considered to be aching discomfort on the left side of the groin area or on the right side. In this case, the patient notes a delay in menstruation, swelling of the mammary glands, and a change in appetite.
During a miscarriage, acute pain occurs in the sacrum and above the pubis, as well as bleeding. This can be triggered by stress, heavy lifting, or a blow to the stomach.
Another complication may be placental abruption. It can be recognized by acute paroxysmal intense or aching pain in the lower abdomen in women during pregnancy. It is accompanied by bleeding. The abdomen becomes hard on palpation.
Pain in the lower abdomen after intercourse
In most cases, after sexual intercourse, women may experience discomfort in the lower abdomen due to contraction of the uterus. If its intensity is low, then do not worry.
However, systematic intense pain in the lower abdomen in women after sex can occur with the development of the following pathologies:
- endometriosis;
- fibroma;
- cystitis.
Hernias
When organs protrude in the groin area, as well as spigelian or white lines, pain in the lower abdomen is observed in women. They clearly appear when this area is compressed with a belt, straining when going to the toilet, or wearing uncomfortable clothes. With significant protrusion of the hernia, the discomfort becomes constant.
Intestinal infections
Pain in the lower abdomen occurs in women and men with the following infectious pathologies:
- yersiniosis;
- Escherichiosis;
- shigellosis;
- campylobacteriosis.
The patient experiences severe cutting discomfort. It occurs against the background of a painful urge to defecate. Diarrhea develops with urges 10 times a day.
Pathologies of the urinary system
- Bladder polyps. When they occur, dull pain appears in the pubic area. Their intensity increases at the end of urination.
- Urethritis, pyelonephritis. With these pathologies of the excretory system, pain occurs in the lower back. When urinating, a woman may feel pain in the suprapubic area.
- Cystitis. Inflammation of the bladder is characterized by severe pain. It is provoked by E. coli or staphylococcus. Women experience aching pain in the lower abdomen and a frequent urge to urinate. Going to the toilet is accompanied by cramps and pain. As cystitis progresses, the urge to urinate becomes false. In the acute form of the disease, blood may appear in the urine.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome
These manifestations are not associated with menstruation and last for 6 months or more. The patient may notice discomfort in the pelvic organs, sacrum, perineum, and suprapubic region.
You may feel the pain “radiating” to the buttocks and joints. It intensifies with hypothermia, physical exertion, sexual contact, and gynecological examination.
Rare causes of lower abdominal pain in women
The symptom occurs most rarely with the following pathologies:
- inferior vena cava syndrome, varicose veins;
- genital prolapse. In this case, nagging pain occurs;
- Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
Spasm in the intestines: why does this happen?
The rhythm of life of a modern person can affect the functioning of the intestines, leading to unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of spasms in the intestines
The intestine is a muscular organ that consists of smooth muscle cells. Like any muscle, these cells must contract and relax so that the intestines can move and digest food. When a smooth muscle cell contracts and cannot relax for a long time, this means that it is in spasm.
Cramping pain in the intestines may be accompanied by additional symptoms such as diarrhea or constipation, as well as bloating. A spasm can provoke either a retention of contents in the body or its excessively rapid movement. With constipation, the contents remain in the body for a long time, causing fermentation processes and increased gas formation1. With diarrhea, on the contrary, the contents are removed from the body too quickly. As a result, the intestines cannot perform their functions because their functioning is impaired.
Thus, pain and spasm may be accompanied by other unpleasant intestinal symptoms: stool disturbances and bloating. All these symptoms may indicate that the functioning of the intestines is disrupted, that is, it is irritated.2
How to treat intestinal spasms
For any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is important to provide a light diet: establish regular meals, eliminate the consumption of junk food (fast food), reduce the amount of spicy, fatty, smoked and fried foods. It is better to completely exclude from the diet foods that lead to fermentation: baked goods, low-alcohol drinks (beer and wine), sauerkraut, legumes, etc.2
In addition, medications for intestinal spasms (antispasmodics) are used. At the same time, it may seem that to solve the problem it is enough to relieve the spasm once, and the intestines will work like clockwork. But it is not so. To effectively get rid of unpleasant symptoms, it is important to restore the disrupted functioning of the irritable intestine. How to do it? This requires that the cramped smooth muscle cells return to a healthy state and provide the intestines with the ability to move food.
To work at full capacity, you need to be in good shape. The situation is the same with the intestines. And it is important to understand that not every drug can help with this.
Most antispasmodics (for example: drotaverine, hyoscine butyl bromide) relax intestinal cells, which means they cannot restore its motor activity. Moreover, they have a number of side effects because they affect the functioning of other organs and systems, and as a result, they have limitations on the duration of independent use3.
To get rid of irritable bowel symptoms, a comprehensive approach is needed to restore proper bowel function. Duspatalin® 135 mg tablets cope with this task: they relieve spasms and abdominal pain3. But unlike conventional antispasmodics, Duspatalin® 135 mg does not just relax the intestines, but allows it to return to a healthy state, i.e., restores its function3. As a result, bowel irregularities and bloating disappear.
Duspatalin® 135 mg can be used long-term5.
Diagnosis of lower abdominal pain in women
Various doctors can identify the cause that accompanies such an unpleasant symptom: gastroenterologists, gynecologists and other specialists. The patient is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination. It includes:
- gynecological examination. It is carried out in a chair. The gynecologist pays attention to the size and condition of the uterus and determines the location of pain. When examined in the mirrors, the doctor clarifies the condition of the reproductive organs, vaginal mucosa, etc.;
- Ultrasound is a visual diagnostic method that helps assess the condition of the appendages and uterus, establish pregnancy, find various neoplasms, and inflammation. It allows you to exclude diseases of the distal parts of the intestine, as well as inflammation of the appendix of the cecum;
- laboratory methods. They include blood, urine, and mucous tests. They help clarify the cause of the infection, determine the balance of hormones, and find the inflammatory process;
- X-ray. Hysterosalpingography is often used to diagnose pain. It allows you to find fibroids, endometrial polyps, determine tubal obstruction, tumors of various etiologies, and developmental abnormalities of the structure of the reproductive system. Irrigoscopy and excretory urography are also used for diagnosis;
- endoscopic methods. Characterized by high accuracy. For example, hysteroscopy helps to detect tumors and inflammation. Colonoscopy helps determine UC and Crohn's disease. If necessary, a tissue sample will be taken during a biopsy for further histological examination.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing the causes of a feeling of heaviness inside the abdomen and pain can sometimes be quite difficult, since pain can appear due to various diseases. To determine the cause of pain, it is extremely important to initially identify the disease that led to such pain. To do this, you need to make an initial appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor, based on the results of an in-person examination, will make initial assumptions about a possible diagnosis and prescribe the necessary diagnostic and laboratory tests.
Diagnostics includes:
- In-person examination by a specialized specialist (history collection);
- Gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (a study that can help detect dysfunction of the reproductive system organs);
- MRI of the uterus (a research method to determine the presence of tumors);
- Colposcopy (examination of the surface of the cervix using a colposcope).
Laboratory tests include:
- Flora smear;
- Cytological examination of a cervical smear;
- Femoflor (to exclude sexually transmitted infections);
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Blood test for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis.
Pain in the uterus can be a manifestation of various diseases, therefore, first of all, it is necessary to identify the underlying disease, and only then begin treatment. The treatment plan is selected for each patient by a gynecologist individually, depending on the nature of the pain, the primary disease and the condition of the body. The FSCC FMBA has developed a special comprehensive program for checking women's health. The program will help to identify hidden pathologies that cause pain and assess the condition of the woman’s reproductive system.
Principles of assistance before specifying a disease accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen
If minor discomfort is observed during pregnancy, it is recommended to rest well. Do not lift heavy objects, try to avoid exercise. It is also important to follow a diet: do not eat foods that cause gas formation. They often contribute to the occurrence of abdominal pain during this period. If discomfort increases, cramping or bleeding occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If you have painful periods, you can start with non-drug methods. Take care of your own psychological state, try to lie in the fetal position, applying a warm heating pad to the place where discomfort occurs. To prevent more spasms in the area, avoid coffee, tea, spicy foods, and smoked foods. Give preference to herbal teas with mint.
Symptoms
Various diseases of the female reproductive system cause severe muscle spasms, which lead to pain in the lower abdomen. The pain can be sharp, nagging, aching, growing and recurring regularly. After a detailed examination, the doctor will be able to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If you experience similar symptoms, we advise you to make an appointment with a gynecologist at the Federal Scientific Center for Medical and Biological Agency. Timely diagnosis will prevent negative consequences for your health!
Conservative treatment of pathologies that cause pain in the lower abdomen in women
The doctor chooses the treatment tactics after an examination. The medications will be prescribed to you after the clinical picture has been clarified. At the same time, it is important to adhere to the specialist’s recommendations regarding the daily routine, nutrition, and water regime. Afterwards you may be recommended to take the following medications:
- antibiotics. Required for infections. The doctor selects a group of drugs based on their underlying cause;
- hormones. Used to correct fibroids, endometriosis, severe dysmenorrhea and other pathologies. Combined oral contraceptives are often prescribed. They are selected individually for each patient;
- painkillers. Analgesics and antispasmodics can be taken for inflammation, as well as dysmenorrhea.
Gastrointestinal diseases
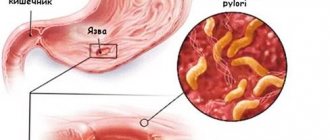
Sharp acute pain can be caused by a burn of the mucous membranes or poisoning. A burning sensation indicates an exacerbation of ulcers and gastritis (with gastritis, pain occurs either after eating or when a feeling of hunger occurs). A dull, aching pain is a common manifestation of a chronic disease. Cramping pain that bothers you at night is a characteristic sign of an ulcer. Severe cramping pain is a sign of gastrointestinal infections (in such cases, abdominal pain is accompanied by a rise in temperature).
What to do : if you have an established chronic disease, take the necessary medicine and consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Surgical treatment of diseases that cause pain in the lower abdomen in women
Some conditions accompanied by this symptom require surgical treatment. Some of them are urgent, including ectopic pregnancy. In this case, removal of the fallopian tube or tubotomy is performed - an intervention that helps preserve reproductive health.
You can also undergo an oophorectomy, wedge resection of the ovary, or adnexectomy if indicated. Hernias and appendicitis also require surgical treatment.
Conclusion
Pain in the lower abdomen in women significantly reduces the quality of life. Don't try to endure the discomfort. Acute conditions can become chronic, which often leads to complications. Acute intense pain is a signal to immediately seek medical help. It may be a sign of a life-threatening condition.
doctor
Specialized multidisciplinary clinic
Our staff consists of high-class doctors - members of the Russian and European Societies (EA).
We have a day hospital
We guarantee constant care for the patient and control over his recovery in the most comfortable conditions.
Low-traumatic treatment methods
We carry out operations with minimal intervention in the body using modern equipment of the new generation of intraoperative X-ray systems.