Many people who care about their health try to lose weight. A correct lifestyle, which is directly related to health, can help them with this. It's no secret that in order to eat less you need to try to normalize the size of your stomach: a person's appetite and the amount of food he needs depends on the volume, condition and shape of the stomach.
In order to reduce the size of the stomach, obese people even undergo surgery. The size of the stomach is different for every adult and is constantly changing. The shape of this organ is also constantly subject to change. Why is this happening? This depends on many factors: on the amount of food consumed daily, on physiological characteristics, a history of stomach diseases, and even on the person’s physique.
How does the stomach work?
The stomach is the main one in the digestive chain.
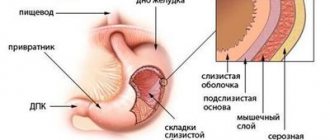
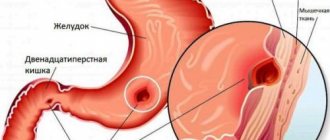
The stomach is part of the digestive tract and is an organ made up of muscles. It is located in the upper third of the abdominal cavity and connects the esophagus and duodenum. An interesting fact is that the stomach can move when breathing. Its location directly depends on the fullness of neighboring organs. In a person who eats a small amount of food at one time, the stomach is located under the ribs. Main functions of the stomach:
- Chemical processing of food, the reagent of which is gastric juice. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, chymosin, lipase and pepsin, which are digestive enzymes.
- Absorption of certain substances: water, sugar, salt.
- Synthesis of vitamin B12 to ensure iron absorption.
- Protecting the body from bacteria and microorganisms with the help of hydrochloric acid contained in gastric juice.
- The production of certain hormones and biologically active substances, including serotonin and histamine.
The main function of the stomach is to mix food with gastric juice and break down protein. All this is the beginning of a chain of a long process - digestion. In crushed and processed form, food is sent from the stomach to the duodenum. Gastric juice is a kind of reagent for food. It has neither color nor odor; up to two liters are produced per day. The amount of hormones produced by the stomach directly depends on the state of the chopped food. For example, more liquid food, bypassing processing, is immediately sent to the intestines, while coarse and solid food remains inside the stomach until it is completely processed.
The stomach has three sections: body, fundus and mucous membrane. The mucous membrane is a tissue consisting of three layers: its own, epithelial and muscle. The shell has folds, dimples and fields. The lining of the stomach is completely renewed every three days. This happens so that hydrochloric acid does not damage it. Its walls are protected by constantly produced mucus.
Reversibility of the process and methods of correction
A distended stomach is not a death sentence. You can return it to normal physiological sizes using radical or natural methods. The first are surgical interventions. The second involves performing special physical exercises and correcting nutrition.
Surgical methods
Gastric resection
Resection using the Billroth method.
Resection is the removal of part of the stomach by excision. Today, this technique is considered outdated, but is still valid in some hospitals. In essence, it is a cavity surgical intervention, which rarely goes unnoticed for the patient. During the operation itself, you can lose a lot of blood. Upon completion, a number of unpleasant “surprises” may also arise: the risk of internal bleeding, the likelihood of dehiscence and suppuration of the sutures, complications in the form of impaired digestive function, pancreatitis, etc. Read more about gastric resection here.
Bandaging
Banding is a correction of the size of an organ by applying a “blockade” in the form of a restrictive ring to part of it. The digestive organ is divided into two chambers: the upper, smaller one, is quickly filled with food, as a result of which the brain quickly receives a signal of saturation. Then food from this chamber moves to the lower one, where it is digested. This method also involves abdominal surgery with all its disadvantages. In addition, the patient may experience difficulty passing food through the ring area and the development of gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Gastroplasty
Vertical gastroplasty is a complex manipulation in which the upper part of the organ is transformed into a continuation of the esophagus. This is done for the same purpose as with banding (an accelerated feeling of satiety), but it also has the same disadvantages.
Ballooning
Ballooning is an endoscopic surgical method that involves inserting a balloon filled with liquid into the stomach. If you delve into the essence of the operation, it becomes clear that the size of the stomach does not decrease with this method. The container simply takes up a certain amount of space intended for food. The probable consequences of ballooning are quite serious: the risk of pressure sores of the walls of the operated organ and the closure of the exit to the duodenum.
Natural Methods
Special gymnastics
A few simple physical exercises borrowed from yoga will help work the diaphragm and strengthen all the muscles of the body:
- Breathing while lying down. It is necessary to lie down on a hard horizontal surface and slowly take a deep breath, carefully drawing in the anterior abdominal wall below the ribs. Then also slowly exhale. And so on for at least 10 approaches, each time trying to draw in the stomach more strongly.
- "Breath of a Dog" Starting position – half lotus position, back straight. Next, inhale three times through the nose, then exhale three times - as animals do when running.
- "Cup". Lying on your back, you need to alternately inhale and exhale, arching your body so that the retracted stomach resembles the shape of a bowl. In this case, your hands should be kept behind your head. For the first time, 4-6 times will be enough; in the future, the number of approaches can be increased.
Regular running, race walking, oriental belly dancing and jumping rope will also benefit.
Diet correction
Small meals, mandatory breakfast, consumption of foods rich in fiber (cabbage, carrots, beans, spinach, cereals, lentils, apples, bananas), minimizing salt and spices, avoiding sour, fatty foods and alcohol. Consume fruit in small portions at least half an hour before meals. Chewing food slowly.
It is not recommended to eat too hot foods and you should avoid combining food with drinks. It will be much healthier to drink a glass of water 30 minutes before or after a meal.
"The Five Spoon Rule"
In the course of practical work with patients, nutritionists were able to determine the ideal size of a single portion of food, which stimulates the return of the stomach to normal size.
5 tablespoons or 150 g of food - just enough to eat so that the stomach gradually shrinks to the required parameters.
This is enough to satisfy the feeling of hunger and replenish the body’s energy reserves. To achieve a lasting effect, it is recommended to maintain an interval between meals of at least three hours. This approach allows you to return your stomach to its previous size in 3-6 months and tighten your figure.
With the help of a surgeon’s hands, you can quickly achieve your goal, but you must remember that any operation is always a risk for the body’s condition, a certain time for its rehabilitation and the possibility of irreversible consequences. The natural approach to reducing gastric volume requires a lot of time and developed willpower, but allows you to avoid negative results. Which option to choose is up to each person to decide individually.
Lots of food - big belly!
The size of the stomach changes when food enters it.
When food enters the stomach, its size increases and the walls stretch. After the stomach has completed its function of processing food, it returns to its form. An empty stomach constantly moves, and at this time a person experiences a feeling of hunger. The shape of the stomach depends on the height and size of the person.
For example, in short and overweight people, the shape of the stomach resembles a horn. In tall and slender people, the shape of the stomach can be compared to a stocking. In people of standard build, the stomach is shaped like a hook. The size of the stomach can be easily adjusted. It depends on the amount of food a person consumes at one time. The walls of the stomach stretch and more and more food will be needed each time to become full (feeling of a full stomach). This can lead to an increase in the size of the stomach.
Healthy stomach size
The size of an adult's stomach when empty is no more than 500 ml; when full it can reach four liters. The average length of a healthy stomach is 25 cm, height is about 13 cm. The distance between the surfaces of the stomach (anterior and posterior) is about 8.5 cm. The distance between the lesser and greater curvature is 11 cm, in an empty stomach - 7.5 cm. In a hungry person The length of the stomach is 19 cm, while its walls touch each other.
Can it be stretched with water?
There are common fears (not as widespread as slag phobia, of course) that drinking water causes the stomach walls to stretch. This is again a myth. Water does not stay in the body for a long time, passing through it in transit, and it is needed only for metabolism.
We talked about this in detail in the article “Water before, during and after meals: is it possible or not?” .
We hope we have explained everything regarding how to shrink your stomach in detail!
What disease is an enlarged stomach a symptom of?
An enlarged stomach is not only a harbinger of obesity, this indicator can be a symptom of other diseases. Such diseases include:
- Stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach. In which the size of the stomach increases, a sour taste is felt in the mouth, a constant feeling of a full stomach appears, and frequent vomiting.
- Malignant neoplasms in the stomach (cancer). Increased stomach volume, heaviness, blood in the stool, weakness, loss of appetite.
- Hernia in the area of the stomach and esophagus. Pain while eating and while moving.
- Gastric obstruction. Obstruction of food, retention in the stomach, formation of polyps or tumors.
- Hyperplastic gastropathy. During the disease, there is an increase in the folds of the gastric mucosa in size, due to which the stomach becomes larger. Patients experience delayed digestion, a feeling of bloating, pain and heaviness.
- Menetrier's disease. Multiple polyps in the stomach. The stomach is enlarged, frequent pain, weight loss, nausea, diarrhea, bleeding.
If any of these symptoms occur, you should undergo a full examination.
What is the difference between PRJ and more complex operations?
Cholecystectomy
- Cost: 100,000 - 160,000 rubles.
- Duration: 25-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 3 days in hospital
More details
A patient who has undergone pancreatic cancer usually does not require lifelong doses of vitamin and mineral supplements that are absolutely necessary after gastric bypass or biliopancreatic bypass. The likelihood of metabolic side effects (protein, vitamin and calcium deficiency) is also less here. PGC does not require removal of the gallbladder, although if gallstones form in the gallbladder during weight loss, this may be necessary later. At the same time, if we talk about the stability of weight loss, biliopancreatic bypass undoubtedly leads here. Due to the fact that the operation of prostate cancer is relatively young, no one can yet say how stable its results are after 5-10 or more years. Therefore, we warn all patients who are considering the option of longitudinal gastrectomy that if over time the result of PRG turns out to be insufficient, a second stage of treatment may be required - gastric bypass or biliopancreatic bypass. In this case, the second stage will be easier to complete, since the “gastric” stage of biliopancreatic bypass has actually already been completed.
How is the size of the stomach determined?
Fluoroscopy can be used to determine the size of the stomach.
To diagnose an enlarged stomach in modern medicine, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray
- Gastroscopy
- Computer diagnostics
To determine the size of the stomach using fluoroscopy, the patient is given a special liquid to drink. Then the specialist uses X-rays to obtain an image of the organ on a fluorescent screen. Today, X-ray television examination is used, during which the resulting image can be further processed in order to better diagnose the disease. The image remains in the device's memory and on the film.
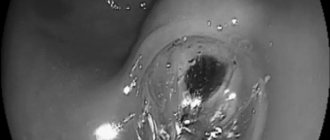
Gastroscopy is performed to examine the inner surface of the stomach and its mucous membrane. A tube with a camera is inserted through the throat and esophagus into the patient's stomach. The image from the camera appears on the monitor. If necessary, the image is recorded. During the procedure, it is possible to conduct additional diagnostics: taking tissue for a biopsy. Computed tomography of the stomach has a number of advantages compared to other diagnostic methods:
- No special liquid is used during the study.
- Provides a more complete image in several projections compared to radiography.
- Does not cause pain during the procedure, compared to gastroscopy.
What should you be afraid of?
A distended stomach is not always as harmless as it seems. The danger is that this pathology can be a consequence of serious diseases, among which are often found:
- gastric hernia;
- polyps and tumors of the digestive system;
- gastropathy;
- pyloric stenosis;
- malignant neoplasms on the walls of the stomach - cancer.
Gastroenterologists deal with gastrointestinal problems. For preventive purposes, it would be a good idea to visit their office at least once a year. Timely diagnosis will help prevent many problems associated with the gastrointestinal tract, saving the patient’s nerves and money.
RepostTweet
Benefits of Gastric Bypass
The operation helps to achieve better results than banding, resection or plication even in patients with severe obesity and BMI ≥ 50. With the help of the procedure, it is possible to stop the progression of secondary pathologies associated with obesity:
- diabetes mellitus;
- arthritis;
- varicose veins;
- hypertension;
- coronary heart disease;
- cholesterolemia;
- urolithiasis;
- impotence;
- fatty liver;
- urinary incontinence;
- chronic headaches;
- infertility.
The procedure is reversible - after the patient gets rid of obesity, the natural path of food movement can be restored.