Lack of weight is a pathological condition that is characterized by a decrease in body mass index below a critical level. It can develop in people of any age and gender and can be either an independent pathology or a symptom of other diseases. In critical cases, being underweight can lead to death.
Causes
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired digestibility of food.
- Endocrine pathologies, which are characterized by disruptions in hormonal regulation. These include hyperthyroidism and adrenal insufficiency.
- Lifestyle features: poor nutrition, excessive physical activity, stress and lack of sleep.
- Psychological diseases: anorexia nervosa, panic attacks, etc.
- Oncological diseases. Weight loss can develop as a side effect of treatment, or as a result of the effect of the tumor on the body when cancer cachexia develops.
- In children, underweight may be due to intrauterine growth retardation, malnutrition, or incorrect selection of formula.
General characteristics of the disease
The gallbladder is one of the important visceral organs that is involved in liver function and digestion. As a result of exposure to provoking factors, the outflow of bile is disrupted and focal inflammation occurs, which is localized in the tissues of the organ. The inflammatory process gradually worsens, damaging the walls and changing the quality characteristics of bile.
More than 70% of patients with cholecystitis are middle-aged women.
Depending on the course and provoking factors, inflammation of the gallbladder is divided into 2 types:
- Acute calculous cholecystitis. It manifests itself during an intense course of the inflammatory process and is accompanied by pronounced clinical symptoms.
- Chronic cholecystitis (calculous and non-calculous). It is characterized by a long course, with periodic increase and attenuation of symptoms.
The acute form of biliary inflammation often progresses to the chronic stage. As a result of a long course, purulent foci and nodular formations appear in the tissues, then irreversible changes in the structural tissues occur.
Anorexia nervosa in adolescents: developmental features
Nervous weight loss in adolescents occurs very often due to mental immaturity and acute perception of other people's opinions. For example, even the slenderest girl begins to hate her body after a careless joke, or under the influence of the media she gets carried away with diets, calorie counting, etc.
Parents should be attentive to their children, create a comfortable environment at home, have heart-to-heart conversations more often, and not be solely interested in studies. You should also not divide foods into good and bad, which many people often do. Explain to your child that food is fuel for the body; without a varied diet within reasonable limits, the whole body will suffer.
If your son or daughter begins to lose weight sharply, avoid eating, or you notice strange behavior - do not self-medicate, but immediately consult a doctor. Timely adoption of measures greatly increases the chances of a successful outcome.
Causes of the disease
Cholecystitis is a consequence of the pathological activity of a number of provoking factors that affect the gallbladder both from the inside and from the outside. The following reasons can cause the inflammatory process:
- biliary stones (stones in the gall bladder and bile ducts);
- hypercholesterolemia;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- damage by pathogenic microflora or toxic agents;
- viral, traumatic or inflammatory liver diseases;
- disruption of the pancreas (damage to the gallbladder mucosa by pancreatic juice);
- varicose veins of the blood vessels of the abdominal cavity.
People with eating and metabolic disorders are more susceptible to the disease. A significant proportion of patients suffering from cholecystitis suffer from obesity and consume excessive amounts of fatty, sweet foods.
Causes of weight loss
Malnutrition
Common reasons for losing weight are voluntary restriction of food intake, increased physical activity. The condition is more typical for young and middle-aged women who, in pursuit of ideal body parameters, resort to strict diets.
With such rapid weight loss, weight loss can be up to 5-10 kilograms per month, which provokes problems with appearance and health. Hair begins to fall out and nails peel, the skin becomes flabby, and white stretch marks form. Typical complaints are general weakness, loss of strength, apathy, and constant drowsiness. In older people, malnutrition and weight loss are often caused by socio-economic lifestyle characteristics - the predominance of cereals and bakery products in the diet, insufficient consumption of nutritious meat and fish dishes. As a result, the percentage of fat and muscle tissue decreases, the body seems to “shrink,” and the ribs, collarbones, and pelvic bones become clearly visible. The skin is pale with a yellowish tint, saggy. Lack of nutrients causes problems in all organs, constant severe weakness and dizziness.
Depression
Depressive states are manifested by a complete loss of interest in current events and loss of appetite. Patients sharply reduce the amount of food they eat, even to the point of refusing to eat. Weight loss with depression reaches 10-15% of the initial body weight, weight loss is combined with severe weakness, drowsiness - sometimes a person sleeps 14-16 hours a day and does not feel rested. The appearance changes - the skin looks dry and pale, the hair on the head falls out, the nails peel and crumble. In such a situation, in order to prevent exhaustion of the body, qualified medical assistance is required.
Dental problems
Dental diseases (caries, pulpitis), lesions of the oral mucosa of a traumatic or infectious cause lead to severe pain and fear of eating food. With extensive pathological processes, food refusal and rapid weight loss occur. If the pain is of infectious origin, the temperature usually rises and general malaise is expressed. In elderly patients, in the absence of some teeth, chewing is impaired, food enters the stomach insufficiently processed. Because of this, the absorption of nutrients decreases, as a result, a person loses weight.
Damage to the pancreatobiliary system
In case of pathologies of the liver, biliary tract and pancreas (hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, etc.), sudden weight loss is caused by enzyme deficiency, due to which most of the food is not broken down and absorbed in the small intestine. At first, appetite does not suffer, patients eat food in the usual volumes, but lose weight. In this case, after eating, there is heaviness and pain in the abdomen. Subsequently, appetite decreases and constant nausea and flatulence are a concern. The amount of food consumed is reduced by 2-3 times, up to 10 kg of weight is lost. Typical stool disorders are alternating diarrhea and constipation, periodic tenesmus.
Gastrointestinal diseases
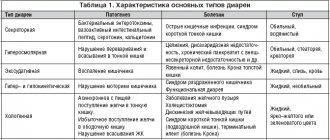
With any inflammation or destructive pathologies of the intestinal wall, the absorption of nutrients is reduced. Weight loss develops gradually, weight loss rarely reaches 10%. Symptoms are associated not only with insufficient calorie intake, which causes general exhaustion and reduced performance, but also with vitamin deficiency. Vitamin deficiency is manifested by a deterioration in the appearance of the skin and hair, characteristic changes in the tongue - it becomes bright red and shiny. Common gastroenterological causes of weight loss:
- Inflammatory processes
: gastroenteritis, duodenitis, colitis. - Functional disorders
: pylorospasm, gastroptosis, dyspepsia. - Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases
: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis. - Pancreatic enzyme deficiency
.
Infections
Any infectious process is accompanied by intoxication of the body, fever and general malaise, during which the appetite worsens and the person loses weight. With prolonged viral or bacterial diseases, significant weight loss is observed, up to exhaustion. The skin becomes pale with a cyanotic tint, the eyes are sunken, and the skeletal bones are well contoured. Malnutrition leads to vitamin deficiency: hair becomes dull and brittle, nails peel. Weight loss with increased appetite is pathognomonic for helminthiases and protozoal infestations.
Endocrine pathology
Hormonal changes and metabolic disorders are often accompanied by sudden weight loss. With a deficiency or excess of certain hormones, all metabolic processes change, catabolism prevails over synthesis. The breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates causes rapid weight loss by reducing the volume of adipose tissue and muscle fibers. Weight loss occurs evenly, body proportions do not change. In addition to the general signs of exhaustion of the body, specific symptoms are noted. The main endocrine causes of noticeable weight loss:
- Diabetes
. Weight loss is more common in type 1 diabetes in children and young adults. Lack of insulin provokes the activity of counter-insular hormones, which are responsible for catabolic reactions. Despite the sharp increase in appetite, a rapid loss of body weight of 5-10 kg occurs. There is also general weakness and headaches, severe thirst, and the volume of urine increases. - Hyperthyroidism
. An increase in the concentration of thyroxine in the blood increases the level of basal metabolism. Appetite is pathologically increased, patients constantly want to eat, but at the same time their weight is steadily decreasing. Then the amount of food taken decreases, due to difficulty swallowing due to an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland. The skin remains pink and moist for a long time. - Hypopituitarism.
A sharp decrease or cessation of the production of pituitary hormones disrupts all types of metabolism and provokes rapid weight loss. Pituitary causes accelerate the breakdown of fats and the destruction of muscle tissue proteins, muscle tone and strength decrease, and the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. The skin is dry, thinned, hanging in folds on the arms, stomach, and thighs.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Weight loss is most often associated with the use of cytostatics for the treatment of tumor pathology and severe collagenosis. The drugs disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, cause destruction of the epithelium of the entire digestive canal, which causes loss of appetite and a sharp decrease in the absorption capacity of the small intestine. Frequent causes of clinically significant weight loss are the use of antibacterial drugs that inhibit the microflora in the intestines and provoke dysbacteriosis. Weight loss is also observed with regular use of laxatives, antipsychotics, and tranquilizers.
Rare causes
- Oncological diseases
: leukemia and lymphoma, cancer or sarcoma of any location. - Joint diseases
: rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis. - Degenerative neurological processes
: senile dementia, discirculatory encephalopathy, consequences of strokes. - Cardiological pathology
: decompensated heart failure, myocarditis, endocarditis.
Symptoms of pathology
The inflammatory process in the gallbladder is accompanied by a number of characteristic signs that are taken into account when making a diagnosis. The following symptoms of cholecystitis are distinguished:
- loss of appetite;
- dyspeptic disorders (heartburn, nausea, vomiting, flatulence);
- defecation disorders (constipation, diarrhea);
- change in color of stool to black-green or white;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the right shoulder blade and arm.
In chronic cases, signs of obstructive jaundice appear. The skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow or greenish, which indicates stagnation of bile secretion.
Hepatic colic may indicate a ruptured gallbladder and requires immediate medical attention.
One of the most unpleasant symptoms is hepatic colic. This condition occurs as a result of spasms that occur when the gallbladder is full (blockage of the neck or cystic duct with stones prevents the outflow of bile). A characteristic sign of hepatic colic is acute throbbing pain that spreads to the right hypochondrium and the adjacent abdominal area.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
It is impossible to independently diagnose and cure cholecystitis - the symptoms are similar to liver pathologies and do not provide a complete clinical picture. To make a diagnosis, you must urgently contact a gastroenterologist. The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe a diagnosis, which includes a comprehensive examination:
- laboratory tests (CBC, OAM, blood biochemistry);
- hardware research methods (ultrasound, MRI, CT).
Diagnostic studies allow you to localize the lesion, assess the severity of the disease and select the correct treatment tactics.
Health care
Conservative treatment of cholecystitis is prescribed to patients with a chronic or labile course of the disease. The therapeutic plan includes the following drugs:
- antibiotics to suppress pathogenic flora;
- antispasmodics to relieve pain, suppress spasms and prevent organ rupture;
- choleretic agents to restore the flow of bile;
- removal of gallstones.
Drug therapy is prescribed outside the exacerbation phase and is carried out over a long course.
In case of acute cholecystitis of the organ, abdominal or laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed. Surgery to remove the gallbladder is indicated for patients with an acute attack, rupture of the organ, or in the absence of positive results of conservative treatment.
Lifestyle correction
Comprehensive treatment of cholecystitis includes normalization of nutrition. Patients are recommended a therapeutic diet that is aimed at gradual weight loss and minimizes the damage that fatty foods cause to the biliary tract. Alcoholic drinks are also completely excluded from the diet. Optimized physical activity is a prerequisite for patients, especially those with obesity. A complex of therapeutic and preventive gymnastics allows you to lose weight and helps restore the flow of bile during physiological stagnation.
Medical offers treatment of cholecystitis in Lobnya. Help for patients with inflammation of the gallbladder consists of an integrated approach in which the patient receives:
- consultations with a highly qualified gastroenterologist;
- fast and accurate diagnosis;
- a treatment plan developed in accordance with the severity of the condition and the individual characteristics of the body.
Our clinic specialists recommend combining conservative therapy with normalization of nutrition and lifestyle correction.
Complications of being underweight
Being underweight can lead to a wide range of adverse effects:
- dystrophy and prolapse of internal organs;
- hypovitaminosis;
- tendency to persistent severe infections that are difficult to treat;
- infertility, menstrual irregularities;
- depression;
- neurological and mental disorders - paralysis, loss of consciousness, coma, etc.;
- in severe cases, death occurs.
Symptoms
Normal body mass index (BMI) is 18.5–24.9 kg/m². Underweight is diagnosed when a BMI is below 18.4 kg/m². With a BMI below 16.5, severe weight deficiency is diagnosed, which requires medical intervention.
Symptoms of being underweight are:
- reducing the expression of subcutaneous fat;
- swelling;
- general weakness, decreased performance;
- decreased mood, depressive disorders;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- brittle hair and nails, increased hair loss;
- dizziness, tendency to faint;
- decreased libido in women, impotence in men.
Diagnostics
Detection of underweight is made on the basis of a physical examination, which includes the following procedures:
- measuring the patient's body weight and calculating BMI;
- measuring the thickness of subcutaneous fat;
- determination of skin elasticity;
- with severe cachexia, the degree of consciousness disorder is determined.
Further, in order to identify the causes of weight loss, the patient may be prescribed additional laboratory and instrumental examination:
- general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test;
- examination of the digestive system: ultrasound, endoscopic techniques, radiography, etc.;
- CT and MRI;
- If necessary, specialists of different profiles are involved.