The article was checked by gastroenterologist E.G. Melnikova. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, diagnostics and treatment of diseases are carried out, in which there is stool with blood, mucus, and black feces. Quick diagnosis includes all the necessary tests - blood, urine, feces, and modern research methods - ultrasound, endoscopic with advanced capabilities (in monochrome light, endosonography), real and virtual colonoscopy (CT version). Conservative and high-tech surgical treatment is carried out (including endoscopic and laparoscopic, abdominal and proctological operations).
Blotches or streaks of blood in the stool appear against the background of the following factors:
Haemorrhoids
The disease is characterized by varicose veins of the anus and rectum. This condition is accompanied by the appearance of hemorrhoids. It develops against the background of stagnation due to a sedentary lifestyle, constipation and excessive body weight. Hemorrhoids also occur during pregnancy.
Characterized by the appearance of dark red blood during bowel movements. It does not mix with feces. Accompanied by itching and burning.
Anal fissure
Accompanied by a rupture of the intestinal mucosa mainly on the wall of the anus. In this case, pain is felt during defecation. The discomfort persists for several hours. Over time, the cracks change - replacement of the mucous tissue with connective tissue is observed.
Colorectal cancer
The malignant process develops due to the degeneration of polyps. Most often it is a hereditary disease. Risk factors include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The progression of the malignant process occurs slowly. It is characterized by the presence of hidden blood in the stool, weakness, weight loss and anemia.
Ulcerative colitis
Chronic inflammation of the colon mucosa is characterized by the appearance of bloody diarrhea. There are also mucus impurities in the stool. Abdominal pain is not a characteristic symptom. The stool is watery and contains mucus. The complicated course of a chronic disease is accompanied by fever, intoxication of the body, spastic pain and an increase in anemia.
Intestinal inflammation
The inflammatory process occurs against the background of various infectious diseases of a bacterial, viral or parasitic (protozoal) nature: enterovirus, salmonellosis, dysentery, amoebiasis, etc.
Ulcer perforation
If the ulcer perforates, intense bleeding occurs. Accompanied by severe pain in the upper abdomen, dry mouth, excessive sweating and vomiting (black-brown masses).
Intestinal diverticulosis
It is characterized by inflammation of hernial protrusions, which are located on the intestinal walls. The disease does not manifest itself until the inflammatory process develops. Accompanied by hyperthermia and abdominal pain on the left side. Diarrhea or constipation, nausea and vomiting are also common. In case of rupture of diverticula, the development of peritonitis is observed.
Crohn's disease
An inflammatory process affecting the intestinal walls. Accompanied by the appearance of nodules (granulomas). This condition cannot be completely cured - you can only achieve remission. Numerous ulcers appear on the mucous membrane. Bleeding is observed only when the disease is complicated.
Manifestation
If you find traces of blood in your stool, underwear or toilet paper, you should consult a doctor. Additional signs may also indicate dysfunction of internal organs.
Blood
There are two types of bleeding:
- Spicy. It is characterized by large blood losses and occurs in a matter of minutes. Accompanied by weakness, pallor of the skin, a drop in blood pressure (blood pressure) and increased heart rate. The patient needs emergency medical care.
- Chronic. Accompanied by regular blood loss in moderate quantities. This condition is accompanied by the development of anemia.
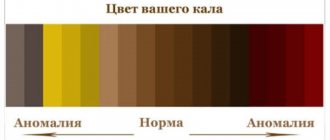
Blood in the stool may not be visualized, but can be detected during laboratory testing. This phenomenon is called occult blood.
Other symptoms
Blood in the stool may be accompanied by abdominal pain, false urge to defecate, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth, weight loss, and increased body temperature.
Anemia
With chronic or acute bleeding, iron deficiency anemia progresses. Anemia is manifested by pale skin, general weakness, dizziness, and palpitations during exercise.
In any case of acute blood loss, you should immediately consult a doctor.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, you can undergo express diagnostics of gastrointestinal bleeding, establish and eliminate its cause (ligation of a blood vessel, endoscopic puncture of a stomach ulcer, removal of tumors and polyps).
In addition to bloody spots, the development of pathologies may be accompanied by the presence of mucus or pus in the stool. Any unusual event during bowel movements is a good reason to immediately make an appointment with a doctor. Our specialists will be able to identify and fix the problem. Sign up for a clinic at a convenient time and forget about illnesses.
Serious diseases that cause bleeding in the anus
Serious gastrointestinal diseases can be recognized by the release of a large amount of scarlet blood, sometimes with clots. Typically, this color of discharge indicates damage to areas located above the anus - in the rectum or colon. Serious damage to the body that may cause bleeding includes:
- Diverculosis
- formations on the mucous membrane, localized at the site of small blood vessels. During defecation, the excreted feces begin to injure such processes, which causes bleeding. - Cancer of the rectum or colon
- when the tumor grows, feces during bowel movements disrupt their integrity. Because of this, scarlet blood is released from the anus. - Polyps
are growths of the intestinal mucosa that can be injured during bowel movements. If the discharge of blood is caused by such an illness, it is usually mixed with the feces.
Bleeding from the anus requires careful monitoring by the attending proctologist.
Diagnostics
- determines the inflammatory process;
- diagnoses anemia caused by blood loss;
- determines dysbacteriosis, worms, hidden blood;
- (CA 19-9, CA-50, REA) – establishes the presence of malignant processes in the body.
Diagnosis of diseases accompanied by bloody stools involves identifying the degree of anemia and inflammation, establishing the location and cause of bleeding.
At the medical center on Yauza you can undergo a full range of diagnostic tests: general analysis of urine, blood, stool, stool examination for dysbacteriosis, worms, occult blood, all types of biochemical and oncological markers.
Ultrasound diagnostics, intestinal radiography, computed tomography on a modern tomograph (including virtual colonoscopy) will help to visually determine the pathological process.
Experienced and qualified radiology and endoscopic diagnostic doctors, together with gastroenterologists, surgeons, and coloproctologists, will give an objective assessment of the health status of the patient with blood in the stool and help eliminate the threat as soon as possible and achieve good results in individually selected treatment.
Approximately 30-50% of people over 25 years of age have intestinal diseases, which subsequently develop into serious chronic pathologies. Don't be fooled by false modesty. Make an appointment with your doctor today for a healthy tomorrow.
Why does constipation hurt?
As a result of impaired mobility, feces accumulate inside the intestines, which gradually provokes intoxication. Accumulated feces put pressure on the intestinal walls, causing pain. In addition, with constipation, gas formation increases and the passage of gases is disrupted. This also causes pain and discomfort. In some cases, pain can be felt not only in the lower abdomen, but also on the right, left, as well as in the right hypochondrium and lower back.
Researchers note that the acute pain of constipation is more likely to result from cramping. Thus, Shulpekova draws attention to the fact that stool retention is accompanied by “spastic pain.” (Shulpekova Yu. O., 2007, p. 1165). Indeed, spasms of smooth muscles that occur in response to a mechanical stimulus in the form of dense feces and accumulated gases are felt by us as sharp, cramping pains. The localization of pain can be completely different. It all depends on the specific part of the intestine that is currently affected, as well as upon exposure to other factors previously.
Treatment
All diseases in which bloody stools are observed require medical attention. If this symptom is detected, you must contact a proctologist or surgeon and undergo an examination. Based on the results obtained, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Surgical
If necessary, doctors at the Yauza Clinical Hospital perform endoscopic, laparoscopic or abdominal operations to remove tumors, ligate (ligate) bleeding vessels, and laser coagulate them.
Conservative
Conservative treatment at the Yauza Clinical Hospital may include:
If blood appears in the stool due to hemorrhoids or fissures, then conservative treatment methods are often sufficient. Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating pain and spasm of the sphincter. Medicines that normalize stool are also prescribed. The need for enzymatic support arises only in case of lactose deficiency and allergy to cow's milk proteins.
Constipation in adults - symptoms and treatment
Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist. You need to start therapy with diet and normalization of your lifestyle. If ineffective, drug treatment is necessary.
Lifestyle
One of the most common causes of constipation is a sedentary lifestyle, which affects the contractility of the colon. Exercising can be an effective way to combat constipation.
Another important point of treatment is the development of a reflex to the act of defecation. It is necessary to develop the habit of going to the toilet at the same time and create the same daily external conditions for bowel movements (the sound of water or silence, air temperature, privacy, peace, etc.).
Diet for constipation
You need to learn to eat not only right, but also on time. Limit the intake of spicy, smoked, fatty and fried foods, reduce the consumption of chocolate, canned food, marinades, spices, alcohol, carbonated drinks, concentrated juices, very strong coffee or tea, bread made from premium flour, rich flour and confectionery products, exclude from the diet fatty meat, fish and chicken.
It is healthier to steam or bake food in the oven. It is advisable to include in the menu stale second-class bread, vegetarian vegetable or cereal soups in meat broth (except millet and corn), porridge, boiled potatoes, lean meats (beef, veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey), poultry and fish in boiled or steamed form (cutlets, meatballs, mashed potatoes, soufflé), egg white omelet.
Doctors recommend eating four to five times a day and eating at least 500 g of vegetables and fruits (salad, cauliflower, beets, carrots, bananas, apples, plums, apricots, prunes, dried apricots), drinking at least 2-3 liters of liquid (for example, Donat Magnesium mineral water, weak tea, natural juice), and every evening - up to 500 ml of fresh 1% kefir. It is important that the kefir is fresh (up to three days from the date of manufacture), since 1-3 days of kefir weakens, after this period it strengthens. It is also allowed to consume up to 10 g of non-acidic cottage cheese, sour cream and cream, up to 5 g of butter and up to 15 g of refined sunflower or olive oil. In the morning you need to drink 200 ml of cool water. This promotes bowel function.
Phytotherapy
Some of the most common herbal remedies for constipation include licorice root, senna, buckthorn, psyllium, oregano, and foods high in fiber. At the initial stage of treatment, the doctor may recommend Psyllium (psyllium husk), as well as Fitomucil or Mucofalk[18]. Products based on soluble fibers absorb water in the intestines, swell, turn into a mucous gel and soften the stool, which facilitates its easy elimination.
Drug treatment
If all of the above treatment methods are ineffective, a gastroenterologist may prescribe drugs from the following groups:
- Prebiotics - normalize the composition of the microflora of the colon, which has a positive effect on its contractility and ability to digest food.
- Osmotic laxatives are first-line drugs. Promote the accumulation of fluid in the colon, creating osmotic pressure necessary for normal bowel movements. Osmotic laxatives are produced based on macrogol, lactitol and magnesium sulfate [19][21][23][24][25][27][28].
- Stimulant laxatives are second-line drugs [17]. Stimulant laxatives (Bisacodyl, Sodium picosulfate, anthraquinone derivatives - preparations of senna, buckthorn, rhubarb) increase contractility by stimulating the nerve endings of the intestinal mucosa [29]. However, they often cause an addictive effect and contribute to the development of “lazy bowel syndrome,” when the intestines stop working on their own without the help of medications [17]. With prolonged use of laxatives, degenerative changes in the cells of the submucosal and myenteric plexuses occur, and the water balance is disturbed.
- Prokinetics - improve intestinal contractility. The only drug of this class available in Russia is Prucalopride[30][31].
- Lubricants - their action is based on the lubrication effect. The feces soften, the intestinal walls are lubricated and become more slippery, which improves the passage of feces. Can be used in the form of flaxseed or mineral oil or glycerin suppositories. The oil is used in the form of enemas or drunk on an empty stomach.
- Antispasmodics - relieve spasm of intestinal smooth muscles and promote its relaxation. They are prescribed only for spastic constipation, which is based on spasms of the intestinal wall. In other cases, the opposite effect occurs.
The sequence of taking medications depends on the cause of constipation. They can only be taken under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
Surgery
Severe forms of inert colon, which manifest as intestinal obstruction, do not respond to medications and do not respond to other types of therapy, are treated with surgery [32]. There are many surgical treatments available, ranging from sphincterotomy, puborectal stretching, removal of the sigmoid colon, and colectomy (removal of the entire colon). They are carried out quite rarely.
Prevention
Preventive measures include timely diagnosis and the appointment of adequate treatment for the pathological process in the body. Also organize proper nutrition to prevent bowel movements.
FAQ
What to do if there is blood in the stool?
If you have bloody stools, consult your doctor to determine the cause. The doctor refers the patient for a comprehensive examination and, based on the results obtained, prescribes treatment.
What examinations need to be completed?
Laboratory diagnosis is required. Recto- and anoscopy are also prescribed to determine pathological changes in the intestinal mucosa.
You can see prices for services
Discharge during the formation of an anal fistula
If left untreated, an abscess will form - pus will accumulate and eventually come out through the skin. An anal fistula is a small tube between the infected anal area and the skin. Develops in half of patients with an abscess.
Rarely, a fistula is formed against the background of tuberculosis, sexually transmitted infections, or chronic intestinal diseases.
An anal fistula is characterized by pain, redness, swelling around the anus, bleeding, painful urination and defecation, fever and discharge.
Sometimes a fistula closes on its own and then appears again, although this should not be allowed to happen - this can lead to a serious, life-threatening complication. Therefore, if any of the above complaints occur, you should definitely contact a specialist. The fistula is treated surgically.
Possible complications of constipation
Frequent constipation may be accompanied by heaviness in the abdomen and pain before, during or after bowel movements. Such problems can lead to unpleasant consequences. Most common complications:+
- poisoning of the body;
- exacerbation of hemorrhoids;
- rectal fissures;
- risk of cancer.
General intoxication due to stagnant feces can cause deterioration in health and decreased performance. Disruption of the intestinal microbial balance during chronic constipation leads to exacerbation of allergic diseases, skin rashes, and a decrease in the body's resistance to infections.
It is known that the risk of developing colorectal cancer is higher in people with chronic constipation. Delayed bowel movements lead to disruption of cholesterol metabolism and the development of atherosclerosis, and consequently, cardiovascular diseases.
Diseases of the anorectal area often accompany constipation. This is due to the fact that dense feces injure the mucous membranes of the rectum, which causes the appearance of anal fissures. And an increase in intra-abdominal pressure can lead to the formation of hemorrhoids.