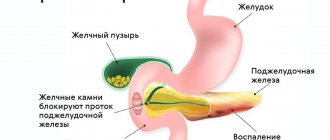
Endoplasmic reticulum stress; role of mitochondria
- Energy production by mitochondria is associated with the work of 2 mechanisms: the respiratory electron transport chain (ETC);
- oxidative phosphorylation.
- free radicals: superoxide ion (O−2);
- hydrogen peroxide (H2O2);
- lipid peroxidation;
protein oxidation;
- damage to structures that provide insulin synthesis;
- a significant decrease in ATP reserves;
- superoxide dismutase (SOD);
Diabetes and cancer of other organs - which organs are affected and what increases the risks?
Diabetes and cancer of other organs
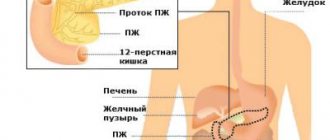
Oncological diseases of other organs in diabetes develop as a result of both systemic and local carcinogenesis. Scientists conducted research not only in cases of liver and pancreatic cancer, but in tumors of other organs.
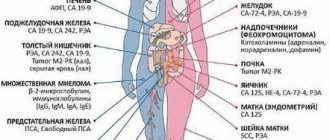
The kidneys are one of the target organs affected by CD-specific hyperglycemia. Kidney cancer has been shown to develop due to general factors - hyperinsulinemia, obesity, and specific factors, mainly hypertension and diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetics have a slightly higher incidence of bladder cancer. Hyperinsulinemia is not the only common factor in carcinogenesis in this case. Frequent urinary tract infections can also contribute to the development of cancer.
Cancers of the female reproductive system are also more common in women with diabetes. It has been proven that diabetics are more likely to develop breast and uterine cancer, regardless of whether they are obese or not. As you know, obesity is one of the main causes of breast cancer. But the development of these types of cancer is determined by several mechanisms, among which the action of sex hormones is important.
- Hyperinsulinemia increases the level of bioactive estrogens in a woman’s blood because the concentration of hormone-binding protein decreases.
- Excessive insulin concentration also stimulates the synthesis of androgens in the ovarian stroma.
- Also, one of the mechanisms for the development of cancer of the reproductive organs of a woman is a delay in the first menstruation, especially in girls with type 1 diabetes. Such women are more prone to infertility, irregular menstruation and other fertility problems.
Most studies suggest that type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased incidence of colon carcinomas and adenomas. The risk of developing colorectal cancer is increased in both women and men.
When describing the mechanisms of pathogenesis, a number of reasons are mentioned:
- hyperinsulinemia;
- slower transit of contents in the intestines;
- increased concentration of bile acid in the stool, which is typical for diabetes.
Based on the results of published large prospective cohort studies and case-control studies, diabetics were found to have a slightly higher likelihood of developing non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. This is explained by disruption of the immune system due to dysfunction of neutrophils and changes in cellular and humoral immunity in patients with diabetes.
Autophagy
- Cellular damage and apoptosis are associated with autophagy, the process of removing damaged organelles from the cell through lysosomal degradation and the formation of new ones in their place.
- Some diseases, including diabetes, are believed to have multiple etiologies. In particular, autophagy is called among the reasons.
- Studies examining the relationship between diabetes and autophagy in humans have found that when β cells and islet cells of Langerhans are exposed to hyperglycemia or hyperlipidemia, autophagy stops.
- This leads to the accumulation of oxidized, damaged or incorrectly folded proteins in cells.
- β death is also observed as a result of oxidative stress.
- The process of autophagy is regulated by various signals.
- The mTOR signaling complexes 1 and 2 proteins (mTORC1 and mTORC2) are of particular importance in the mechanism.
- These proteins are kinases involved in several cellular processes, for example: the formation of insulin resistance (IR);
- adipogenesis;
- angiogenesis;
- autophagy.
- improper protein folding;
Is there a connection between diabetes and prostate cancer?
Although diabetes is a risk factor for many organ cancers, epidemiological studies show that prostate cancer is less common among diabetics.
A meta-analysis of 14 studies where PSA levels were not used as an early diagnosis tool and 5 studies where PSA levels were used confirmed a statistically significant reduction in the risk of prostate cancer in men with diabetes.
The risk is reduced by an average of 16%. This is most likely due to decreased testosterone levels in diabetes. It has been suggested that other metabolic and hormonal factors, such as altered insulin and leptin levels, statin and metformin use, may influence this relationship.
Defective folding
- In recent years, defective folding in the ER has been implicated as a cause of several chronic diseases, including: diabetes mellitus;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD);
- cancer;
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Ca deposition;
- They found that in the presence of prediabetes, proinsulin synthesis in β-cells occurs more actively, and due to this, protein folding is disrupted. Misfolded proteins accumulate in the ER, causing stress.
- insulin resistance (IR);
- causes ER stress in β cells;
- CCAAT/ homologous protein binding enhancer gene;
Risks of developing cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus
The content of the article
Risks of developing cancer
According to data provided by oncologists, diabetes increases the risk of damage to the liver, pancreas, colon, kidneys, bladder, uterine lining, breast and the development of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
There are two types of mechanisms that contribute to the development of malignant neoplasms in diabetes.
- The first type
is general mechanisms that contribute to oncological processes in many organs. For example, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, the activity of drugs used in the treatment of diabetes, since they affect all tissues. - The second type
is certain mechanisms that influence carcinogenesis in only one of the organs.
Due to its chronic course without obvious symptoms, diabetes often goes undiagnosed for a long time. According to an epidemiological study conducted in the United States, 3-5% of adults have no diabetes. It has been proven that diabetes is one of the factors that increases the risk of developing malignant neoplasms - cancer is definitely more common among people with CD