March 11, 2021
The effect of smoking on the body has been proven many times. Everyone knows that “the Ministry of Health warns” that “Smoking is poison.” However, people are in no hurry to give up their addiction. According to statistics, the number of smokers on the planet is increasing daily. Perhaps many people do not fully understand why this is dangerous for them. Let's figure out what changes in the body occur when smoking. We will also find out whether it is possible to get rid of this addiction and how long it will take for the body to recover.
What are cigarettes? Composition of substances in cigarette smoke
What is dangerous in a cigarette? First of all, tobacco smoke. Passive smoking also has an adverse effect on health. Substances in smoke reduce brain activity and have an extremely negative effect on the endocrine system. They pollute the entire body!
The harm of smoking, its effect on the body of a woman or a man will be slightly different. However, there are also common factors. They are due to the fact that with each puff, carcinogens enter the body. The temperature of a smoldering cigarette at the tip is 800 degrees. A person inhales air, it passes through a layer of heated tobacco and takes volatile substances with it. It turns out that the smoker inhales a heated “aerosol” filled with tiny particles. They contaminate the oral cavity, trachea, bronchi and even alveoli, settle on the teeth in the form of a characteristic plaque and enter the blood. What are these substances and why are they dangerous? Experts say that there are more than 4,000 components in tobacco smoke. The most dangerous among them are:
- Nicotine is a poison, a toxic alkaloid, a powerful drug that causes addiction on a par with heroin. Stimulates the production of adrenaline, accelerates the heartbeat, and even leads to the activation of pleasure centers and increased concentration. However, the “effect” from one smoked cigarette lasts barely 20 minutes. Then all processes, including brain processes, are greatly inhibited. Gradually, the smoker gets used to such stimulation, and nicotine is “built into” metabolic processes. Pleasure no longer arises, but the lack will be very pronounced. Nicotine as a drug provokes weakening of muscles, death of brain cells, and the formation of cancerous tumors.
- Tobacco tar and resin. Resins are deposited on the mucous membrane, on the teeth, and line the walls of the alveoli in the lungs. They disrupt the functioning of the ciliated epithelium, which is why the bronchi cannot be fully cleared of mucus and impurities. Resins suppress the immune system, make the voice hoarse, and the teeth dirty yellow, and increase the risk of pneumonia due to colds.
- Carbon monoxide is a product of burning tobacco. It is absorbed by hemoglobin 200 times faster than oxygen and is actively transported by blood cells. Carbon monoxide is a toxin that destroys nerve cells, blocking the passage of signals and impulses. It provokes memory loss and headaches, leading to the development of angina and heart attacks.
- Carcinogens and heavy metal compounds (nickel, chromium, cadmium, benzene). They penetrate the genetic material of cells and damage it, which is why malignant tumors develop. They also provoke mental and physical abnormalities, especially in children and adolescents.
- Hydrogen cyanide or hydrocyanic acid is a toxin that affects the nervous system and provokes a deterioration in oxygen metabolism in tissues.
- Arsenic is a powerful poison, a toxin that affects the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Causes mutations and cancerous tumors, provokes metabolic disorders, digestive problems, and memory impairment.
- Nitrosamine or nitrogen compound with high toxicity. Leads to the formation of cancerous tumors. The thyroid gland, lungs and esophagus are especially affected.
All these substances accumulate in tissues and pollute the body, contribute to the destruction of health, and provoke the development of serious chronic diseases. Conventionally, the health of a smoker with 40 years of experience will be worse than that of someone who has been smoking for only a year. Of course, not only length of service matters, but also the number of cigarettes smoked. But there is good news - the effects of smoking on the body are reversible. It is enough to “tie” and the recovery process will start. And this is true in all cases, regardless of whether the person is young or elderly.
Sense organs
When smoking, the senses also do not escape the negative effects. Their functions are disrupted by toxic
substances found in tobacco. Most smokers lose their sense of taste. After all, their tongue is always covered with thick viscous mucus, blocking the access of food to those receptors that are responsible for the sensation of taste. If a heavy smoker and an ordinary person who does not smoke are given a taste of slightly sweet and salted water, the first will not be able to tell the difference, while the second will easily cope with the task.
A person who smokes also has a impaired sense of smell. He begins to perceive smells poorly. As a result of smoking, the nasal mucosa becomes inflamed, which can result in a chronic runny nose. To clearly see how smoking affects your sense of smell, conduct a small experiment. Bring a lit cigarette to your dog's nose: when he inhales the smoke, he immediately loses his sense of smell.
Smoking can also damage your vision: tobacco smoke negatively affects the retina and optic nerve. In this case, color blindness may develop. And of course, smoking can damage your hearing organs. After all, toxic substances lead to inflammation of the nasopharynx, which is connected to the tympanic cavity. As a result, inflammation can spread to the auditory nerve.
Although the sense organs are complex, this is just the initial stage in the process of sensing the outside world. All these perceptions are transmitted through nerves to the brain, and there they are analyzed. This means that smoking negatively affects both the sensory organs and the central nervous system. In this case, the entire system of sensation of the external world is disrupted.
How does nicotine addiction form?
Nicotine is an organic alkaloid that accumulates in nightshade leaves. For plants, this is a protective reaction, since their leaves become unsuitable for food for animals. Any doses of nicotine are dangerous for humans, especially if they enter the body constantly and directly into the blood. The problem also lies in the fact that this poison quickly accumulates in the body and penetrates the brain relatively freely, breaking the blood-brain barrier. But why doesn’t the body defend itself? How is addiction formed?
The biomechanics of this process is due to the fact that nicotine is directly associated with H-cholinergic receptors and leads to excitation of the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine receptors are activated and the level of adrenaline in the blood increases. Therefore, literally from the first puff, a person feels euphoria, slight excitement and a surge of strength. Dopamine is produced, the smoker feels joy. I take the next cigarette because I want to repeat the sensation. This is how addiction develops (as in the case of drugs), and each subsequent “dose” must be larger. Because of this, sensations become dull and the body becomes “contaminated.” Constant exposure of smoke to the lungs provokes chronic intoxication.
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system
Smoking and healthy blood vessels are two incompatible concepts. Nicotine increases the development of cardiovascular diseases such as:
- atherosclerosis;
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- hypertension15.
Nicotine causes vasospasm, thereby increasing blood pressure. The walls of blood vessels are damaged, and cholesterol plaques are deposited on them. These factors are the main cause of the development of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction. The blood vessels in the smoker’s brain are also damaged - due to deterioration of blood supply, memory decreases and the risk of paralysis increases15.
Up to contents
What harm do cigarettes cause to the human body?
Smoking is an extremely bad habit. When nicotine enters the body, it begins to destroy all organs and tissues without exception. The circulatory system and heart, as well as the lungs, are primarily affected. The gastrointestinal tract, liver, and kidneys are also affected.
So, what happens in the body when a person smokes constantly? The body receives a colossal dose of carcinogens with each puff. The most common causes of death among smokers are heart attacks, strokes and lung cancer. Thus, 9 out of 10 cases of diagnosed cancer are associated with prolonged smoking. The risk of heart attack increases on average three times!
Also, a person begins to get sick more often, his visual acuity decreases, his thought processes slow down, his face looks yellowish and unhealthy, and his breath always smells bad.
How smoking affects all organs and systems
- Circulatory system. Blood viscosity increases, which creates a high risk of thrombosis. Oxygen binds less well to hemoglobin, so tissues, organs and systems constantly lack it. Hypertension occurs.
- Heart. Nicotine increases the load on the myocardium and provokes vasospasm. As a result, tachycardia develops and there is a high risk of heart attacks. Necrosis of the heart muscle is five times more common in smokers.
- Mucous membrane and teeth. Nicotine has an irritating effect on them. This results in inflammation of the gums and an extremely unsightly yellowish-brown color of tooth enamel.
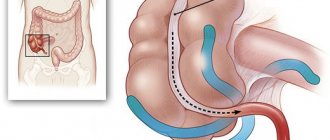
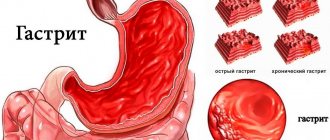
- Digestive organs. The destructive effects of nicotine affect the intestines. stomach, liver, gall bladder. It makes it difficult to produce enzymes necessary for normal digestion. Chronic gastrointestinal diseases are worsening, including colitis, peptic ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis. The mucous membranes are colonized by pathogenic microflora. The load on the liver increases significantly.
- The immune system. Since all organs and systems suffer, a person ceases to look healthy. His hair and nails become brittle, his skin loses its radiance and blush, age-related changes and wrinkles become more pronounced.
- Respiratory system. Tobacco smoke passes from the oral cavity to the alveoli through the pharynx, trachea and bronchi. Swelling and spasms occur, the course of infectious diseases worsens, and the person has difficulty breathing. Diseases such as chronic bronchitis and laryngitis appear. As tar accumulates, filling the alveoli, the person develops the characteristic “smoker's cough.” Physical endurance also decreases.
- Reproductive system. Nicotine significantly reduces the chances of having a healthy baby. Men have a significantly increased risk of developing prostate cancer. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. In both sexes, hormone production is disrupted.
- CNS. Smoking provokes irritability, apathy, drowsiness, migraines, and memory impairment.
- Bones. Nicotine is washed away by calcium, which extremely quickly leads to the development of osteoporosis. Teenagers who start smoking at an early age are usually short in stature and have fragile bones that are prone to frequent fractures.
- The skin suffers greatly due to constant attacks from free radicals from the inside. This leads to early aging as the rate of collagen formation decreases by 35-45% on average. Since blood circulation also deteriorates, poor wound healing is observed.
- Vision decreases, as tobacco smoke provokes atrophy of the optic nerve. Redness and watery eyes also occur.
Smoking has an extremely detrimental effect on the fetus in the womb, including genetic disorders and the development of mental disorders, since nicotine freely passes through the placenta. Many experts believe that such children are already born with drug addiction and have difficulty breathing. In addition, they experience chronic oxygen starvation of the brain. Adverse effects may continue after birth if nicotine enters the child's body through mother's milk.
But it is worth remembering that all these processes are reversible. It is believed that after 5 years the bronchi are completely cleared and all the risks of “smoking” are completely removed. But the positive effect of quitting smoking is observed already in the first month!
Possible consequences
Poor chewing of food, suppressed or increased secretion of gastric juice, impaired intestinal motility causes “hunger” pain, nausea, heartburn, bloating and spasms in the intestines, as well as problems with appetite and stool. Moreover, often all this is at the same time. An experienced gastroenterologist can find out the smoking history without even asking about it - simply based on the patient’s complaints. So, in the first years of smoking - from 1 to 5 years, the motility of the stomach and intestines and the secretion of gastric juice increase, which is why abdominal pain, heartburn and diarrhea occur.
A little later - after 6-7 years of smoking, the endocrine glands begin to work much worse, less gastric juice is produced, and the gastric mucosa gradually atrophies. At this stage, sharp pains may stop bothering the patient; now his constant “companions” will be nausea, heaviness in the stomach, poor appetite and chronic constipation.
Many smokers who have been diagnosed with “gastritis” or a stomach ulcer and have not stopped smoking are happy, thinking that if their pain has stopped, then the disease has stopped or has stopped its development. But in fact, the disappearance of the clinical symptoms of the disease only indicates that the process has gone deeper and it will be much more difficult to cure it.
Unfortunately, it is only possible to completely eliminate the harmful effects of cigarettes and nicotine on the stomach if the smoker’s experience does not exceed a couple of years; after this, changes in the mucous membrane of the digestive organs can become irreversible.
But the sooner you quit smoking, the greater the chance that safe gastritis will become your companion for life, and not a perforated stomach ulcer or gastrointestinal cancer.
Why is it so difficult to quit smoking
The Russian Ministry of Health claims that more than 30% of the country's adult population, both men and women, are active smokers. But if you just go outside, you get the impression that there are many more of them. At the same time, about a quarter of smokers are trying to get rid of this craving, but each of them knows that quitting smoking is extremely difficult. Why is this happening?
The fact is that every cigarette smoked is remembered by the brain as a “reward”. This is a powerful stimulus that even overcomes the pleasure of eating. Moreover, it becomes dominant after 10 cigarettes have been smoked.
Constant smoking leads to an increase in the number of acetylcholine receptors in the brain, which provoke the release of dopamine, but their sensitivity decreases. Gradually, the amount of nicotine required for “happiness” increases, and a pronounced physiological dependence is formed.
Nicotine has the highest narcotic potential. This is why they say that “there are no former smokers.” After all, half of those who were able to quit and even lasted more than six months return to smoking again and quickly increase their pace. Even alcohol is not as addictive as nicotine. This is why addiction is so difficult to cope with alone, without medication support and the help of specialists.
Risk of developing cancer due to smoking
The main harm of smoking (cigarettes, cigars and pipes) is their ability to cause cancer. This addiction can lead to malignant neoplasms 11:
- lungs;
- lips, tongue and other parts of the oral cavity;
- pharynx;
- larynx;
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- liver;
- Bladder;
- kidney;
- cervix;
- colon.
In 30-35% of cases, nicotine is the main cause of the development of the above diseases11.
Tobacco smoke is the most common known carcinogen12 Smoking causes irreparable harm to the body : components of cigarette smoke are capable of forming mutagenic compounds with DNA, which lead to gene damage, the occurrence of mutations and the subsequent development of cancer12.
Tobacco consumption not only increases the risk of tumors , but also reduces life expectancy after cancer and increases the risk of relapse13.
Thus, quitting tobacco products helps prevent cancer: it helps prevent the emergence of new mutations , and also has a beneficial effect on the prognosis of existing cancers13.
Up to contents