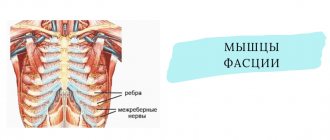
Osteochondrosis, as the most common disease of the spine, today occurs in people of completely different ages, although not so long ago it was considered an exclusively age-related disease. It is characterized by the occurrence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs, which leads to pain and creates the preconditions for the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias. The disease can affect any part of the spine, although osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is extremely rare. This causes significant difficulties with its diagnosis, because the symptoms of the disease mimic pathologies of the cardiovascular system. However, if a diagnosis is made, it is important to immediately begin treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis. Otherwise, it can cause extremely serious complications and loss of performance.
Expert Opinion of a Doctor
“Since there are quite a lot of nerve endings in the intervertebral discs, any changes in its structure lead to the transmission of corresponding signals to the brain, resulting in the appearance of pain in the affected area.” Konstantin Anatolyevich Gritsenko Neurologist, chiropractor, vertebroneurologist Experience: 29 years Ask a question
What is thoracic osteochondrosis and features of its treatment
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine occurs in less than 10% of the total number of cases diagnosed with this disease. This is due to low mobility of the thoracic spine. But this is the main insidiousness of thoracic osteochondrosis, since its symptoms are in many ways reminiscent of signs of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Therefore, patients often initially turn to a cardiologist or other specialist and undergo courses of treatment that do not bring results, but end up seeing a neurologist when the disease has already become advanced.
There are 12 vertebrae in the thoracic spine. Between them all there are intervertebral discs, but more often the first and last spinal motion segments of this department are affected by osteochondrosis.
In the future, the situation may be complicated by compression of the spinal roots, which exit in pairs at the level of each vertebra from the spinal cord and are responsible for regulating the functioning of the lungs, internal organs of the abdominal cavity, and the pelvis. As a result, there will be signs of disturbances in their functioning, as well as pain radiating to the ribs, which is called radicular syndrome.
In general, thoracic osteochondrosis can manifest itself:
- pain in the shoulder blades, which intensifies with deep inspiration;
- pain behind the sternum in the heart area;
- the occurrence of cough, shortness of breath due to the development of bronchitis, bronchial asthma, pneumonia and other diseases of the lungs and bronchi;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, resulting from disruption of the liver, gall bladder and its ducts, which may be due to the development of cholecystitis, metabolic disorders, etc.;
- pain in the left hypochondrium or shingles due to dysfunction of the pancreas, which leads to an increased risk of developing diabetes;
- decreased immunity, the occurrence of allergic reactions due to suppression of the innervation of the adrenal glands;
- urinary disorders due to malfunction of the kidneys and the addition of infectious diseases, in particular pyelonephritis;
- disorders of the female and male genital organs, including infertility.
In this case, severe pain provokes reflex tension in the back muscles, which causes unpleasant sensations in them and increases the risk of pinching the nerve structures.
The risk of changes in the functioning of internal organs increases sharply in the later stages of development of thoracic osteochondrosis, when protrusion of intervertebral discs is already observed, i.e. the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias. In such situations, the pathological protrusion will compress the nerve roots, which will provoke disturbances in the innervation of the corresponding internal organs and the development of their diseases.
Thus, although thoracic osteochondrosis is a fairly rare disease, it can affect the functioning of the entire body. Therefore, it requires immediate initiation of comprehensive treatment. To do this, you need to contact a neurologist who will assess the patient’s condition, study the available examination results and develop an individual treatment program. It will largely depend not only on the degree of thoracic osteochondrosis (there are 4 stages, of which the easiest is the 1st), but also on the nature of the manifestations of the diseases, the type of concomitant diseases present, age and a number of other factors. That is why, with the right approach, the treatment of patients with approximately the same degenerative changes in the discs can have significant differences.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is always complex. It is aimed at solving the following problems:
- elimination of unpleasant symptoms of the disease, which improves the patient’s quality of life and restores full functionality;
- improve the quality of blood circulation in the affected area, which activates metabolic processes and will facilitate regeneration processes in the disc;
- eliminating the causes of osteochondrosis;
- reducing the likelihood of complications of the disease.
For this, patients may be prescribed:
- lifestyle correction;
- drug therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- manual therapy;
- traction therapy;
- physiotherapeutic treatment.
Which specific methods will be recommended to the patient is determined by the attending physician, depending on the severity of degenerative changes in the spine. So, if thoracic osteochondrosis is diagnosed at the 1st stage of development, which, unfortunately, is quite rare, it is usually enough to limit yourself to making certain adjustments to your lifestyle, exercise therapy and manual therapy.
But if the disease has already progressed to the 2nd and especially the 3rd stage, additional drug therapy, traction therapy, etc. will definitely be recommended. Moreover, if osteochondrosis has already provoked the formation of intervertebral hernias, especially large ones, and is accompanied by severe radicular syndrome, which cannot be eliminated by conservative methods, improvement of the patient’s condition can only be achieved through surgery.
Thus, in case of thoracic osteochondrosis, as well as similar lesions of other parts of the spine, treatment is aimed at stopping the further progression of degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs and improving the patient’s well-being. With existing, especially large lesions, it is not yet possible to achieve complete restoration of cartilage tissue, not only of intervertebral discs, but also of any other joints. So, let's look at the main methods of treating thoracic osteochondrosis and their features.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the abdominal area and find out the cause of pain, it is not enough for a doctor to just conduct a visual examination, collect anamnesis and palpate. Laboratory and instrumental research methods are required.
Each disease has its own characteristics, and they must be taken into account when prescribing a particular diagnostic procedure. They are as follows.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An alternative is computed tomography (CT).
- X-ray (you need to take either a picture of the spine or lungs, depending on the situation).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart, kidneys, and digestive tract.
- Irrigoscopy.
- Gastroscopy.
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Blood test (usually a general analysis).
The patient also gives a blood sample to determine the biochemical markers that appear during inflammation and necrosis of the heart myocardium.
Diagnosis is the first step in pain treatment
Often, a patient may be diagnosed with, for example, osteochondrosis and related diseases. In this case, the doctor is tasked with assessing the patient’s condition and finding out what the root cause of the pain is.
This is usually done by a general practitioner, but sometimes he could use some help. And then the following doctors come to his aid:
- vertebrologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- cardiologist;
- neurologist;
- gynecologist;
- pulmonologist
To understand whether it is possible that the patient has pain in the abdominal area due to the spine, the doctor needs the results of a full examination. Then it will become clear what the actual origin of the pain is - vertebrogenic or is it associated with diseases of the internal organs.
Hirudotherapy
Lifestyle correction
After diagnosing thoracic osteochondrosis, the doctor necessarily recommends making certain changes to your usual lifestyle. If a patient shows signs of excess weight, he is advised to take measures to reduce it. But any diets for weight loss, especially monocomponent ones, are contraindicated. Nutrition must be complete and varied so that the body receives all the substances necessary for proper functioning, and metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs proceed properly. Therefore, it should comply as fully as possible with the principles of rational nutrition.
It is also recommended that all patients increase their level of physical activity, especially those who lead a sedentary lifestyle. This could be daily walking, swimming, yoga, or Pilates. But serious physical activity, in particular intense training on simulators, jumping sports, and weightlifting are contraindicated.
If the patient’s profession involves heavy physical labor, such as heavy lifting, it is recommended to try to change it. This is due to the fact that increased loads on the back in the presence of osteochondrosis can play the role of a trigger for the rapid progression of degenerative changes in the discs.
Absolutely all patients with thoracic osteochondrosis are recommended to change the mattress to an orthopedic one with medium hardness, as well as purchase an orthopedic pillow. This will ensure that the physiological curves of the spine are maintained and will prevent further disc degeneration.
Drug treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
When treating osteochondrosis, patients are usually prescribed a complex of medications. Some of them are recommended to be taken only occasionally, in particular during exacerbation of the disease, while others should be used in courses, the duration of which is selected by the doctor.
When prescribing specific drugs, the neurologist must find out whether the patient has concomitant diseases and their nature. This is necessary to exclude contraindications to taking certain medications.
In general, for thoracic osteochondrosis, the following groups of drugs can be prescribed:
- NSAIDs;
- corticosteroids;
- muscle relaxants;
- vitamins;
- chondroprotectors;
- products for topical use;
- means to improve microcirculation.
NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are one of the most extensive groups of drugs, since they have a huge list of indications for use, which includes thoracic osteochondrosis. They have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, therefore they are indicated for exacerbations of the disease and the occurrence of pain.
Today, there are 4 generations of NSAIDs, among which the latest, 4th generation drugs are considered the safest and most effective. They are distinguished by their selective action and have virtually no negative effect on the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum. At the same time, earlier drugs in this group should not be used, especially for a long time in the presence of gastritis and peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, as they can cause their exacerbation.
NSAIDs are available in almost all possible dosage forms, which allows you to select the drug according to the method of use. Therefore, in the early stages of thoracic osteochondrosis, the use of ointments, gels or creams is indicated. For more severe pain, preference is given to capsules or tablets, and if there is no effect, intramuscular injections of drugs are allowed.
Corticosteroids
Drugs in this group belong to the hormonal group and contain synthetic analogues of adrenal hormones. Therefore, they have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and are indicated for severe inflammatory processes. But due to the possibility of causing a number of negative side effects, they are usually prescribed in the form of injection solutions and only in short courses.
In addition, corticosteroids in combination with local anesthetics are used to perform paravertebral blocks. They are indicated for very severe pain that deprives a person of his ability to work, but can only be performed in a medical institution. Blockades help to quickly relieve even very severe pain and consist of introducing a prepared solution into points in the immediate vicinity of the spine, in the area where the spinal roots pass.
It is recommended to carry out such procedures no more than 4 times a year.
Muscle relaxants
Muscle relaxants are a group of drugs designed to relieve muscle spasms. Let us remember that they often act as a reflex reaction of the body to pain. Therefore, the use of muscle relaxants will help reduce the severity of pain in thoracic osteochondrosis.
Vitamins
When treating thoracic osteochondrosis, vitamin complexes containing increased amounts of B vitamins can be additionally prescribed. This is necessary to improve the quality of the passage of bioelectric impulses along the nerves, which is especially important in case of radicular syndrome. In this way, the development of disturbances in the functioning of the organs innervated by the spinal roots of the intervertebral discs located at the level of the lesion is prevented.
Chondroprotectors
Chondroprotectors are a relatively new group of drugs actively prescribed for thoracic osteochondrosis. Their active ingredients include mainly glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. These compounds are absolutely natural for the human body and are used by it for the regeneration of intervertebral discs and other cartilage.
But at the same time, there is still no convincing evidence of the effectiveness of drugs from this group in advanced forms of osteochondrosis, although in the initial stages they work quite well. At the same time, the natural origin of chondroprotectors ensures a high level of safety.
These medicines are available in different forms, including capsules, topical preparations, powders, and injection solutions. The best results are observed with the administration of injectable chondroprotectors. But despite all the positive aspects of drugs in this group, they are characterized by a high cost, which, combined with the need to use them in courses of 30 days or more, makes their use not accessible to everyone.
Topical products
In addition to the ointments, creams and gels containing NSAIDs and chondroprotectors discussed above, treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis may include the use of warming and local irritants. Their principle of action is based on irritation of skin receptors at the site of application. This leads to active blood flow to the area of application, and therefore an influx of nutrients. As a result, the quality of nutrition of the intervertebral discs improves, and pain decreases.
Products for improving microcirculation
Drugs in this group are also used to improve the quality of blood circulation and activate metabolic processes.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic physical education plays one of the leading roles in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, since it allows:
- strengthen the muscle corset, which will ensure the creation of high-quality support for the spine;
- normalize muscle tone;
- activate blood circulation, which will improve the course of metabolic processes in the affected intervertebral discs.
But patients should understand that using general sets of exercises can negatively affect the course of the disease and well-being, since they do not take into account individual characteristics, the degree of osteochondrosis and existing concomitant diseases. Therefore, for effective treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, it is necessary to develop an exercise therapy program on an individual basis.
Initially, so that the patient can master the correct exercise technique, it is recommended to exercise under the supervision of an exercise therapy instructor. He will be able to correctly calculate the load in accordance with the level of physical development of a person and adjust his movements so that the exercises performed bring maximum benefit. The program will gradually become more complicated, and after it has been fully mastered, the patient can practice at home. But for classes to give good results, they should be carried out daily.
When performing all therapeutic exercises, it is important to avoid sudden movements.
Manual therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis in Moscow
One of the most effective ways to treat thoracic osteochondrosis is manual therapy, since it not only allows you to work out the muscles well, but also involves influencing the spine. This is how it differs from therapeutic massage, which is also very useful for osteochondrosis, but is not able to have the same effect as manual therapy, since it does not involve the spine.
But for manual therapy to bring only benefits, you need to be careful when choosing a specialist to carry it out, because the effect on the spine must be carried out with pinpoint precision. Otherwise, there is a high risk of complications.
Manual therapy sessions begin with stroking and relaxing the muscles. The doctor works well on each area of the back, eliminating spasms and preparing the soft tissues for more active action. After this, he begins to use mobilization and manipulation techniques, which may sometimes be accompanied by minor discomfort and crunching.
The method of manual therapy by Gritsenko A.G. deserves special attention, according to which you can undergo treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis in Moscow at the Institute of Human Restoration clinic. It is distinguished by the use of special techniques that have proven themselves over the course of 20 years as one of the most highly effective. They allow not only to have a beneficial effect on the affected intervertebral discs, but also to improve the quality of functioning of all internal organs, because, as mentioned above, they have a close relationship with the spine.
In general, a course of manual therapy sessions provides:
- restoration of the correct anatomy of the spine with the return of the vertebrae to their assigned places;
- increasing the distance between the vertebral bodies, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the intervertebral discs by reducing the pressure exerted on them;
- normalization of muscle tone;
- elimination of functional blocks;
- improving the functioning of the lungs, bronchi, heart, and gastrointestinal tract;
- increasing immunity and reducing exposure to allergens.
At the same time, an improvement in well-being is observed after the first session. Subsequently, patients note a progressive reduction in pain and improvement in general condition, increased performance and mood.
Pain due to osteochondrosis
Speaking about the cervical spine, it is necessary to explain that it consists of only 7 vertebrae. They are superimposed on each other in the form of a pyramid, in the middle of which is the spinal cord. The sixth vertebra is unique: its opening contains an artery that carries oxygenated blood to the brain. To prevent the pieces of the “pyramid” from rubbing against each other, nature provided spacers between them, i.e. intervertebral discs. When the human body is attacked by disease, these same pads suffer. Accordingly, the vertebrae are affected, the pain radiates to the head, the flow of blood to the brain worsens, which is manifested by many signs:
- nausea;
- "goosebumps" on the skin;
- pain in the eyes;
- sensitivity to light and sounds;
- noises and ringing in the ears;
- disorientation in space;
- decreased sensitivity in the area of the collarbone, scapula, and shoulder.
Taking painkillers does not have a strong effect. If the pain occurs less than 15 days per month, then the person is dealing with episodic pain. Otherwise, it will be classified as chronic.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis after the completion of the acute stage of the inflammatory process. They can further reduce the severity of back discomfort, and also have a number of other positive effects on the body.
Most often, for thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are prescribed:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of drugs - this method allows for deeper penetration of the drug components into the tissues and enhances their therapeutic effect through the use of a weak electric current;
- magnetotherapy is a method of physiotherapeutic treatment, which is based on the beneficial effects of a magnetic field on the body, which helps stimulate blood circulation in the area of influence, which leads to the activation of metabolic processes, a decrease in pain and swelling;
- laser therapy is a method that allows you to achieve a pronounced anti-inflammatory and vasodilator effect, which will also lead to an improvement in the condition of the intervertebral discs and a reduction in pain;
- Ultrasound therapy is a physiotherapeutic procedure that provides an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect;
- diadynamic currents are an effective method of physical influence, thanks to the use of which there is a decrease in the severity of pain, an increase in metabolic rate and an improvement in the condition of muscle tissue.
As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in courses of 10-15 sessions. But each of them has its own contraindications, which must be taken into account when choosing a specific type of exposure.
Electrophoresis
Treatment
Treatment of spinal diseases is an extremely serious procedure. It must be comprehensive, since one type of treatment will be ineffective in combating pathologies. Therefore, most often modern courses of treatment include such methods of influence as:
- Drug treatment. The patient is prescribed many medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, analgesics and chondroprotectors.
- Ethnoscience.
- Therapeutic physical education (physical therapy).
- Treatment in sanatoriums and resorts.
- Massage and manual therapy courses.
- Hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches).
- Acupuncture (acupuncture).
- Physiotherapy.
Traction therapy
Traction therapy allows you to increase the distance between the vertebrae of the thoracic spine, which will reduce the pressure on the intervertebral discs affected by osteochondrosis. This will stop the progression of the disease and create optimal conditions for the restoration of cartilage tissue. Traction therapy or spinal traction is performed on a special table under the supervision of medical professionals.
Thus, although thoracic osteochondrosis is not a common disease, it can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and lead to the development of a number of pathologies of internal organs. At the same time, the difficulty of diagnosing it works against the patient, since without proper treatment, degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs continue to worsen. As a result, complications often develop in such situations, including the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias. Therefore, it is important not to ignore changes in well-being and immediately consult a doctor, and when diagnosing thoracic osteochondrosis, strictly follow the recommendations received from him.
Pain due to lumbar osteochondrosis
This species, according to statistics, accounts for half of the total diversity of the disease. And if with its thoracic variety the organs suffer less, since they are surrounded and held by the ribs, then the picture is completely different with the lower back. There are many nerve endings here, so the pain will be severe and sharp. Possible acute, subacute and chronic course. Acute pain syndrome in lumbar osteochondrosis is called lumbago or lumbago. At the same time, the person, as they say, cannot breathe or gasp, his lower back burns or goes numb. The duration can be up to a week, and from time to time, if a person is hypothermic, turns sharply, or physically works for a long time, it can come again and last a whole month. Irradiation is observed in the leg, buttock, and sacrum.