1.General information
The term “acute abdomen” appeared in Russian medicine and became commonly used by the mid-twentieth century, after the publication in 1940 of a translation of a monograph by French surgeon Henri Mondor on emergency gastroenterological diagnostics.
Below we use another figurative expression from A. Mondor’s book: “abdominal catastrophe.”
We are talking about a life-threatening condition in which the prognosis is directly dependent on how quickly emergency medical care is called and provided. Statistical and analytical studies have repeatedly confirmed that the mortality associated with the condition of an acute abdomen increases several times, even if the delay for one reason or another is about a day.
It must be recognized that in big cities the situation in this regard is still much better than in the periphery.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
2. Reasons
Acute abdomen as a special pathological status can develop as a result of gastroenterological diseases, their progression and exacerbation, or for reasons not directly related to gastrointestinal diseases.
Thus, the gastroenterological diseases that most often cause the development of acute abdomen include:
- perforated ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- purulent acute appendicitis;
- phlegmonous cholecystitis with perforation of the walls of the gallbladder;
- intestinal obstruction;
- acute pancreatitis;
- strangulated hernia,
as well as acute diffuse peritonitis that developed as a result of the listed or other factors.
Quite often, the cause of an abdominal catastrophe is severe gynecological diseases and complications, primarily ectopic pregnancy and polycystic ovary syndrome with ruptured cysts or torsion of their legs, as well as mechanical ruptures of the spleen, intestines, and bladder due to blunt or penetrating abdominal trauma.
In some cases, the condition of an acute abdomen develops following thrombosis or rupture of an aneurysm (with massive internal bleeding in the abdominal cavity) in the mesenteric blood vessels or the abdominal aorta.
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Causes of heaviness in the abdomen
Physiological factors
An unpleasant feeling of heaviness in the stomach is observed after heavy intake of fatty and high-calorie foods, abuse of weak alcoholic beverages (beer, champagne).
Discomfort develops immediately after a feast or already in the process of eating food. It becomes difficult for a person to take deep breaths, heaviness in the epigastric zone increases when laughing, bending or turning the body. Symptoms persist for up to several hours, but not more than a day. Often, overeating provokes nausea, vomiting, and stool upset may occur in the next few days. If heaviness in the stomach bothers you more often, and appears even when eating the usual amount of food, you should think about your health. This may be the first sign of digestive tract diseases.
Regular heaviness in the abdomen is observed in pregnant women, especially in the second half of the gestational age. An uncomfortable feeling develops even after a light lunch or drinking a glass of water. Women complain that they are “bursting from the inside,” and the heaviness increases when lying down or bending over. The condition is caused by the fact that the growing uterus puts pressure on the digestive organs.
Stomach diseases
Most often, heaviness in the upper abdomen is caused by chronic hypoacid gastritis. Due to a lack of hydrochloric acid, food is less digested and stagnates in the stomach cavity, which results in constant discomfort. Unpleasant sensations reach maximum intensity within 30-60 minutes after finishing a meal and subside after a few hours. In severe gastritis, heaviness is a constant concern, combined with rotten belching, nausea and vomiting.
Heaviness, bursting pain in the abdomen is observed with pyloric stenosis, complicating the course of gastric ulcer. The intensity of the symptom depends on the stage - during the period of compensation, discomfort occurs only after eating and does not last long, and during decompensation of the process, the person constantly feels painful heaviness and fullness of the stomach. Symptoms are complemented by vomiting, which brings relief.
Heaviness in the abdomen, accompanied by loss of appetite and rapid weight loss, are typical signs of stomach cancer in the early stages. The patient experiences early satiety, so reduces the number of servings. As a rule, taste preferences change, and an aversion to meat food appears. As the process progresses, heaviness in the abdomen is supplemented by dull pain, which is clearly not associated with any provoking factors.
Heaviness in the stomach
Pathologies of the hepatobiliary system
If the functioning of the liver and gallbladder is impaired, the patient almost constantly faces heaviness in the abdomen. Discomfort is most intense in the projection of the right hypochondrium. Damage to the hepatobiliary system is characterized by nausea, bitterness in the mouth, and belching of air or bitter food. The feeling of heaviness and fullness is accompanied by bowel disorders with alternating constipation and diarrhea. A similar clinical picture manifests itself:
- Chronic cholecystitis.
When the gallbladder is inflamed, discomfort and heaviness in the hypochondrium are provoked by errors in diet and consumption of fatty foods. Painful sensations appear 30-40 minutes after finishing a meal and bother the person for several hours. - Dyskinesia of the gallbladder.
Periodic heaviness in the abdomen is typical for functional disorders, but, unlike cholecystitis, the symptoms pass faster and do not occur as regularly. Dyskinesia is more common in childhood and young adults. - Hepatomegaly.
An enlarged liver is accompanied by constant heaviness in the right hypochondrium, which is not associated with diet or other external factors. Symptoms are aggravated when the body is tilted to the right, when palpating in the liver projection area.
Enzyme deficiency
A decrease in exocrine pancreatic function is the cause of disturbances in the digestion of chyme and stagnation in the small intestine, which provokes heaviness in the abdomen. Patients notice a deterioration in their condition half an hour to an hour after finishing a meal. There is moderate pain in the left hypochondrium, which is usually accompanied by discomfort, rumbling in the intestines, a feeling of fullness or distension. The severity decreases slightly after defecation.
Bowel diseases
Heaviness in the intestines occurs with chronic constipation, when bowel movements occur a couple of times a week or less. The patient is concerned about bloating and intestinal overcrowding. Discomfortable sensations are localized mainly in the left iliac region. Due to constant heaviness in the stomach, appetite decreases and general health worsens. After bowel movement, discomfort decreases or disappears completely.
Heaviness throughout the abdomen is a characteristic manifestation of colitis and enteritis. The symptom often develops in the structure of nonspecific intestinal pathologies: ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease. In children, complaints of heaviness in the abdominal area are mainly due to congenital anomalies, which include Hirschsprung's disease, dolichosigma, and megacolon.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
A feeling of heaviness in the intestines, increasing after eating, is observed with dysbiosis, which occurs as a result of long-term use of antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs, and cytostatics. Discomfort appears on average 5-7 days from the start of treatment. Patients report that on a full stomach they experience flatulence, rumbling in the stomach, a feeling of fullness and distension. Frequent loose stools with a foul odor are typical.
Rare causes
- Vascular pathologies
: mesenteric ischemia, atherosclerosis or abdominal aortic aneurysm, portal hypertension. - Cardiac diseases
: chronic heart failure, heart rhythm and conduction disorders. - Gynecological diseases
: chronic adnexitis, endometritis, cysts or voluminous neoplasms of the ovary. - Rare stomach diseases
: gastroparesis, acute dilatation of the stomach. - Anomalies in the location of internal organs
: nephroptosis, gastroptosis, visceroptosis.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
There are clear criteria and diagnostically significant signs of acute abdomen. In particular, obligate symptoms include uncontrollable spastic muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall, especially pronounced in the “catastrophe” area, and hypersensitivity of the abdominal skin.
Another mandatory sign is intense pain, which, however, does not always reach extreme severity. Depending on the etiology, the pain may not be dagger-like, but quite tolerable, dull, wave-like - which in such cases often leads to fatal waiting instead of immediately seeking help.
The patient himself, as well as those providing first aid, should interpret bloating, lack of peristalsis and the urge to release gases from the intestines as a very alarming sign.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the general condition of the patient (usually it progressively worsens), dry mouth, accelerated pulse, painful inhalation and exhalation, which forces the patient to breathe frequently and shallowly. The so-called acute abdomen is very characteristic. the mask of Hippocrates - a sallow, pale, haggard face with sharpened features and a frozen expression of suffering.
Arriving health workers apply standard diagnostic protocols and criteria for differential diagnosis: the suspected acute abdomen may not be confirmed, since many diseases and conditions imitate typical symptoms to one degree or another. In particular, it is necessary to exclude lower lobe pleurisy or pneumonia, myocardial infarction and other factors of acute heart failure, renal colic, etc. A prompt and, if possible, detailed history taking should also exclude fractures of the pelvis, ribs, and spine. An external examination, palpation and auscultation are performed, and it is very important to first reassure the patient and, among other things, warm your hands before palpation (if assistance is provided in the cold season) in order to maximally objectify the clinical picture and prevent involuntary aggravation (exaggeration of symptoms). In general, a lot depends on the qualifications, experience, tactile sensitivity and skills of the doctor. When diagnosing a suspected acute abdomen in young children or people with abnormal body weight, a digital examination through the vagina or anus (if the patient is male) is indicated - careful palpation with this access is often the most informative diagnostic technique and brings decisive arguments.
It should be noted that the widespread opinion about the inadmissibility of pre-medical use of analgesics in such a situation (so as not to “blur” the symptoms) is exaggerated and unsubstantiated: the analysis of the clinical picture is always complex, including not only subjective pain sensations.
All necessary, in this particular case, additional diagnostic methods, laboratory and instrumental, are carried out urgently immediately after hospitalization - if there is time for this, taking into account the patient’s condition.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
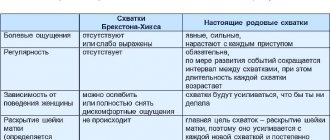
Problems associated with abdominal muscle separation occur more often in women. Statistics say that more than 70 percent of women in the third trimester of pregnancy suffer from such pathologies.
After childbirth, the muscle tissue completely returns to its original position, but approximately 30 percent of women in labor experience diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles. The gap that appears between the muscles leads to the formation of a convex, flabby abdomen, spoiling the figure.
The name of the disease diastasis has Greek roots from diastasis, which translates as division. This case describes a problem that most women face during pregnancy when the rectus abdominis muscles become separated. (ICD-10 code - M62.0 Muscle divergence)
Doctor Alexander Alexandrovich Markushin will ensure the rapid restoration of the aesthetic appeal of the figure.
Signs of diastasis
It will be easier to understand the essence of the problem if you understand the structure of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The rectus muscle is located in the center of the abdomen. At one end it is attached in the area of the costal arch, at the other it goes to the pubic bones. It is made up of two parts connected in the middle by connective tissues.
During fetal development, strong, prolonged muscle tension is observed, which affects intrauterine pressure, gradually increasing it. Constant loads lead to tissue divergence. As the fetus grows, the distance between the two parts of the rectus muscle increases, diverging to the sides. A furrow appears and the stomach protrudes forward. Pathology can be clearly expressed above, below the navel, or have mixed forms.
At first glance, the pathological changes look like a hernia, but an experienced surgeon will immediately identify diastasis. There is no need to be afraid of infringement, but even in the early stages of development, such decoration greatly spoils the aesthetics of the appearance. The figure loses its grace and attractiveness, causing a lot of trouble for ladies who jealously watch their shape.
Men rarely face such problems. Women who have had multiple pregnancies may need the help of an experienced plastic surgeon.
According to the degree of divergence of the tissues of the rectus abdominis muscles, three stages of diastasis are distinguished.
- The distance between the edges of the two parts of the rectus abdominis muscles is 2.5-5 cm.
- The discrepancy between the edges of the muscles is 5-8 cm.
- The increase in discrepancy affecting the convexity of the abdomen exceeds 8 cm.
You can independently determine at home what degree of diastasis the patient is experiencing. By the shape of the convexity of the anterior abdominal wall, it is possible to determine which adjacent muscles are affected by the pathology. Experts divide three types of diastasis according to the number of adjacent areas affected.
- A classic, when exclusively the rectus abdominis muscle is affected.
- The process involves the inferolateral muscle sections.
- Significant expansions are visible in the areas of the bladder and lower ribs.
- There is a serious curvature of the waistline.
Women with the development of pathology feel gradually increasing pain in the womb, lower back, and pelvis. The gait gradually changes. There are problems getting up after resting or when trying to lie down. You have to resort to outside help. Regular attacks of pain lead to depression, psychological breakdowns, and the inability to properly perform the simplest work or usual household chores. Sexual activity decreases, which is accompanied by hormonal imbalances.
Important!
When the first signs of diastasis appear, you should immediately consult with an experienced surgeon. The plastic surgery clinic of Dr. Markushin will offer the optimal solution to the problem that has arisen.
Reasons for the development of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
Changes in the body that spoil the figure do not occur without reason. Diastasis can occur:
- if the elasticity of muscle tissue is lost due to sudden weight loss;
- there are large, constant physical activities;
- with dysplasia or abnormal development of organs and tissues, often accompanying varicose veins, hernias, hemorrhoids or other chronic diseases;
- in most women after bearing a child. Hormonal levels change, the supply of collagen sharply decreases, and muscle tissue loses elasticity. The increasing size of the uterus sharply increases the pressure in the abdominal cavity, forcing the two parts of the rectus abdominis muscle to separate.
The first noticeable changes in your figure begin to appear after the second trimester of pregnancy. The growing fetus requires more space, and increasing pressure pushes the muscle tissue apart.
More than half of women recover quickly after childbirth. The uterus takes on its usual size, the pressure on the muscles decreases sharply, and the linea alba returns to the standard 2 centimeters in width.
However, there are factors under which the development of pathology is inevitable.
- Several pregnancies in a row before normal shape was completely restored.
- Pregnancy in adulthood, when the skin and muscles begin to lose elasticity.
- Excess weight before, during, after pregnancy.
- Carrying twins or triplets, as well as with large fetuses.
- Various complications during childbirth that affect the formation of muscle tissue.
- Starting active sports immediately after childbirth or excessive exercise before the body has managed to recover from pregnancy.
Sometimes diastasis can develop even in children. The cause of the development of pathology at an early age may be a lack of microelements necessary for the formation of muscle tissue or prematurity. With age, problems will increase, manifestations of diastasis will become obvious.
In most cases, early diastasis goes away on its own if you consult a pediatrician in time and undergo a special course of treatment. Increasing muscle tone and strengthening ligaments evens out the shape of the abdomen. Children with Down syndrome most often suffer from rectus abdominis muscle separation. No more than 1.5 men go to a plastic surgery center for diastasis. Most often these are heavyweight athletes or people who have suddenly lost excess weight.
Treatment options
During the examination, the doctor determines the degree, type, and type of diastasis, after which a method of treating the pathology is selected. For those who have the first stage, strict adherence to simple recommendations is sufficient.
- Bring your body weight to acceptable numbers.
- A balanced diet, reducing the amount of sweets and fats consumed will strengthen muscle tissue.
- Drink the optimal amount of liquid per day, giving preference to natural juices.
- Use a bandage to support your stomach.
- Regularly undergo a strengthening course of massage, engage in physical exercise according to a special program.
- Go to the pool, attend yoga classes, Pilates, don’t sit still.
Important!
All exercises, especially at the initial stage, should be supervised by a specialist who monitors the changes occurring in the body. You need to pay special attention to the oblique and transverse abdominal muscles.
There are special sets of exercises for pregnant women that promote the correct formation of the fetus, helping to rebuild the body, preparing the woman for childbirth. Classes must be conducted together with a specially trained trainer who is well versed in the peculiarities of the transformation of the female body before the birth of a child.
Late stages of diastasis require the intervention of a qualified plastic surgeon. Alexander Alexandrovich will help restore a beautiful figure, strengthen the muscle corset, get rid of complications and unpleasant symptoms.
- Local tissue grafting is used by many patients. The doctor uses the patient's tissue to correct pathological changes. Excess tissue is removed, after which the edges of the muscles are stitched, giving the abdomen the desired shape.
- Prosthetics during tension plastic surgery. Plastic surgery is carried out as in the first case, only the strength of the muscle corset is added by a special polypropylene mesh corset placed in the abdominal cavity.
- The insertion of an endoprosthesis under the stretched area, followed by fixation of all tissues in the new position, will significantly strengthen the muscle structure, guaranteeing the ideal shape of the abdomen.
- A combination of several techniques that give the ideal result for restoring a beautiful figure.
After examining the patient, the doctor chooses the optimal surgical method for weakened muscles. The patient, together with the attending physician, can see on a 3D model how his body will change after completion of rehabilitation. Recovery of the body after plastic surgery takes 1-3 months. It all depends on the complexity of the operation, the condition of the body, and strict adherence to all the instructions of the attending physician.
Prevention of diastasis
Experts' recommendations for strengthening abdominal muscle tissue come down to simple rules that will help you maintain a beautiful figure for a long time, even after several births.
- Follow your diet, balancing it with different foods that are beneficial for the body.
- An active lifestyle, frequent walking, sports, and daily exercise will strengthen your muscles and make your abs powerful.
- Pay special attention to strengthening the muscle structures of the lower back and abdomen.
- Don't overexert yourself in the gym by lifting weights.
- Take care of strengthening the diaphragm by doing special sets of exercises.
- Monitor your weight to avoid obesity.
Important!
Immediately after you find out that you are pregnant, start using special oils, creams, gels that increase the elasticity of the skin and muscles. Watch your nutrition, follow a diet, and after giving birth, monitor how the abdominal muscles are recovering, so that at the first signs of pathology you can immediately contact a specialist.
Exercises for prevention
Any sports to strengthen the abs should be started under the supervision of an experienced trainer to avoid possible complications.
With diastasis you cannot:
- do exercises to strengthen your abs from a supine position;
- do push-ups;
- exercise with a barbell or dumbbells;
- do deep lunges with sharp squats;
- do not use any exercises when the lower limbs are suspended;
- pull up on the horizontal bar;
- bend back strongly, lean sharply to the sides;
- perform power crunches;
- use a jump rope.
By gradually increasing the load you can achieve excellent results. To do this, follow simple rules.
- Start by gradually strengthening the transverse abdominal muscles. This will take up to two months.
- Then we move on to strengthening the oblique muscles using lateral bends.
- When doing exercises for diastasis, make sure that the abdominal muscles do not protrude. The pelvic floor muscles should be kept tense and the abs retracted.
- Constantly monitor the condition of your abdomen by wearing a special bandage during the day. When doing physical work, pull in your stomach.
Regularly performing several simple exercises for three months will ensure a quick recovery of your figure after childbirth. Remember to eat right so that excess weight does not aggravate existing problems.
Restoring the gracefulness, sculpted shape of the abdomen, and eliminating extra centimeters at the waist is a process of painstaking work. Start with running or walking. Strengthening your abs should start with simple exercises under the supervision of a trainer.
- A vacuum or regular abdominal retractions stimulate blood circulation and accelerate the movement of lymph. A smooth deep breath is taken so that the walls of the abdomen are as close to the spine as possible. Hold your breath and remain in this position for a count of thirty. Two short exhalations are made. The abdomen returns to its original position.
- Planks begin two months after the start of classes. For diastasis, a side plank is done. Lie on your side, resting on the back of your forearm. The legs are straightened, the second hand rests on the waist. Next, we tear off the pelvis, resting on the hand and foot from the floor. The body forms a straight line. Freeze for 1-2 minutes. Make sure your buttocks and abdominal muscles are tense.
- The cat's movements are healing, strengthening the spine, while simultaneously strengthening the abdominal muscles. Kneel down with your palms on the floor. The stomach is drawn in, the back is rounded, the head drops to the floor as you inhale. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
- The butt bridge quickly strengthens your abs while training your pelvic floor muscles. Lying on your back, bend your legs. Extend your arms along your body. As you inhale, pull your stomach in and slightly lift your buttocks. The arms and upper body should remain on the floor. When exhaling, return to the original position.
- Kegel exercises are done while lying on your back. The legs bend slightly. Tighten the muscles of the perineum in the same way as you do when trying to hold back urination. Lie in this position for 10-20 seconds. Then gradually relax.
- Traction to prevent diastasis. Standing on our knees, we rest our palms on the floor. As you inhale, we draw in your stomach, while simultaneously raising your arm and leg on one side. As you exhale, return to your previous position, then repeat the exercise on the other side of the body.
Diastasis after childbirth
Equally negative effects on the body are caused by both complete inactivity and improper work with the muscles. After childbirth, hormone levels greatly affect the condition of muscle tissue. The linea alba diverges under the influence of the enlarged uterus. During normal pregnancy, after childbirth the body quickly returns to its previous shape.
If the abdominal tissues have lost their elasticity, it may remain saggy and flabby, spoiling the aesthetic appearance. The development of diastasis is influenced by genetic abnormalities, heredity, poor muscle tone, and other reasons. By contacting Dr. Alexander Markushin, patients will receive any help to quickly cope with the existing problem.
Diastasis during pregnancy
Stretched muscles of the white line affect the tone of the anterior abdominal wall. This puts more strain on your back when performing daily household chores. The ligaments soften under the influence of hormones to prepare the pelvic joints for the upcoming birth. The stronger the diastasis, the greater the load the spine is exposed to during pregnancy. Negative sensations appear in the lower back, sacrum, and womb.
With diastasis during pregnancy, almost 60 percent of women experience pelvic floor dysfunction, which can lead to organ prolapse after childbirth. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first signs of diastasis. By doing the simplest sets of special exercises it is easy to maintain muscles in proper tone.
If after the birth of your baby, diastasis begins to bother you, contact Dr. Markushin’s plastic surgery center to quickly eliminate the pathology.
4.Treatment
Almost all cases of acute abdomen create absolute indications for emergency surgery. Currently, the standard of care, based on extensive statistical material, requires making and implementing a decision within a time period not exceeding six hours from the moment of the onset of diagnostically significant symptoms.
Therefore, it is worth recalling once again that in any situation and in any area, with any refusals and any dissimulation (deliberate concealment of sensations) on the part of the patient - who, before the onset of symptoms characteristic of an acute abdomen, could be as strong and healthy as he likes - as well as with any doubts among relatives, the time factor is critical, and the faster help is provided, the higher the chances of avoiding death. The question should be posed precisely in this formulation.