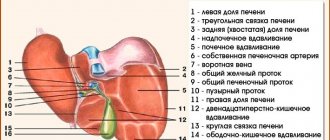
Symptoms of lipomatosis
Quite often, the disease goes away without symptoms, which, if felt, the patient could go to the hospital. Symptoms do not appear in cases where fat cells are located throughout the pancreas in small islands. The severity of symptoms depends on the number and size of fatty inclusions. For this reason, at the initial stage the disease occurs without any symptoms. Gradually, adipose tissue begins to increase, this leads to the appearance of the first manifestations of the disease. Due to the growth of the lipomatous lesion, structural disturbances occur in the gland, which prevent the entry of necessary enzymes into the intestine.
A person suffering from pancreatic lipomatosis feels symptoms characteristic of digestive disorders:
- Discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen that occurs after eating.
- Pain in the subcostal area.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Malaise and general decrease in performance.
Diet
Diet 8 table
- Efficiency: weight loss to the required level
- Time frame: long-term, until the expected effect is achieved
- Cost of products: 1120 - 1230 rubles per week
Fatty infiltration of the organ has a direct connection with nutrition, so diet takes a leading place in treatment. For patients with normal weight, the main goal of nutrition is to reduce the load on the gland, so Diet No. 5 . In case of obesity, it is important to reduce weight, so the basic principles of nutrition of table No. 5 are preserved, but in addition, patients are recommended to reduce calories by reducing fats and carbohydrates ( Diet 8 table ), while the diet should contain a normal amount of proteins. Daily calorie content is no more than 1500-1700 kcal. In case of disruption of the endocrine function of the gland, dietary Table No. 9 with a significant restriction of carbohydrates.
Saturated fats and fructose cause the progression of steatohepatitis and steatopancreatitis . At the same time, choline, a protein diet, unsaturated fats and antioxidants have a preventive effect. With lipomatous lesions of the pancreas, the digestion of dietary fat worsens. In the diet of such patients, the fat quota is reduced, and given the obesity of all patients suffering from this disease, this is all the more necessary. It is also important to avoid heating fats, since the substances formed when heating fats are difficult to digest. High-calorie, fatty, fried foods and smoked foods are excluded from the diet. At the same time, phospholipids, fat-soluble vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids are additionally introduced.
Dishes should be easily digestible, low-fat and steamed or baked. Such dishes do not require stress on the enzyme systems of the gastrointestinal tract. Recommended are cereal and vegetable puree soups, vegetable purees, stewed vegetables, meat and fish balls, boiled meat, steamed cutlets, non-sour cottage cheese, curd casseroles, omelettes, and fermented milk products. The volume of dishes should not cause discomfort. To prevent flatulence , dishes made from legumes and white cabbage are excluded.
Carbohydrates are the second component of nutrition, an excess of which in the diet leads to impaired lipid metabolism and the development of fatty infiltration of the pancreas. In this regard, the consumption of simple carbohydrates and sugary drinks is significantly limited. It has been established that sucrose and fructose influence the development of fatty infiltration of organs - they increase lipogenesis, cause insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia .
Malt and maltodextrose are widely used in the food industry (confectionery, dairy products, sauces), and their glycemic index is higher than sugar. If carbohydrate metabolism is impaired, carbohydrates should be evenly distributed throughout the day to avoid sudden fluctuations in glucose levels. Sources of carbohydrates for such patients are whole grain cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal), bran and whole grain bread, unsweetened berries and fruits, baked apples.
The third main point of nutrition is to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages!
Causes of lipomatosis
Lipomatosis provokes destructive changes that occur in the pancreas. Due to the growth of adipose tissue, metabolism is disrupted. There is an assumption that heredity may influence the occurrence of the disease.
The risk of developing the disease increases significantly due to hormonal imbalance, in the presence of complex chronic diseases, and excess body weight.
Among the reasons that provoke the growth of adipose tissue in place of healthy cells, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Inflammatory processes of the pancreas.
- Injuries.
- Diabetes.
- Toxic damage to the organ that occurs due to smoking abuse and irrational use of medications.
Forecast
Lipomatosis is a chronic, slowly progressive disease that ends with fibrosis of the gland tissue. The danger of the disease lies in the reduction of functional cells. The main goal of treatment is to stop progression. With adequate treatment, elimination of risk factors and lifestyle changes, the prognosis is favorable. If the recommendations are followed, the progression of fatty changes in the gland often stops and does not reach pronounced changes in the organ.
Degree of development of pancreatic lipomatosis
Clinicians identify several theories for dividing the degrees of lipomatosis. If we take the degree of spread of pathology as a criterion, then the disease is divided into three degrees:
I degree.
At this stage, the disease is asymptomatic. The work of the gland is compensated, and the pathological process covers no more than 30% of the organ.
II degree.
The degree of damage to the gland ranges from 30 to 60%. The first symptoms appear in the form of digestive disorders.
III degree.
The lesion covers more than 60% of the organ, disrupting its functioning. As a result, glandular cells cannot produce the necessary enzymes and hormones. In addition, because of this, insulin ceases to be produced. It is uncontrolled glucose levels that are the main cause of complications with lipomatosis.
There is another opinion of doctors, based on which two stages of lipomatosis are distinguished:
- Diffuse or small focal.
- Insular, in which large island spots appear.
Diagnosis of the disease
If symptoms of indigestion appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis.
Pancreatic lipomatosis is diagnosed only through ultrasound examination. The images show the normal size of the organ with increased echogenicity of its structure. It is this fact that indicates the occurrence of a pathological process of the pancreas.
A biopsy is performed to make a definitive diagnosis. If pathological fat cells are detected, the specialist will prescribe the required treatment.
Tests and diagnostics
- Transabdominal ultrasound. Signs of steatosis of the gland are: an increase in its echogenicity while maintaining the homogeneity of the structure, possibly a slight increase in the size of the organ. Such changes are referred to as diffuse changes in the pancreas. Its echogenicity is assessed indirectly by comparing it with the echogenicity of the liver and kidneys. The echogenicity of a healthy gland is the same as that of the liver. In fatty liver disease, the echogenicity is higher than that of the kidneys. The information content of ultrasound is quite low, since patients have abdominal obesity and flatulence .
- Multislice CT. Accurately determines the presence of fatty inclusions, layers, and allows you to detect fibrosis. The examination also gives a picture of the condition of the peripancreatic tissue.
- MRI. It is considered the best diagnostic method. Modern MRI technology determines homogeneous changes in the structure of the gland; with proton MR spectroscopy, the content of triglycerides is assessed quantitatively.
- Endosonography. It is an invasive procedure and allows you to obtain highly accurate images, as well as reliably confirm steatosis. The resolution of this method is superior to CT and MRI, but there is a risk of complications.
- From clinical and biochemical examinations, determination of the level of glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins.
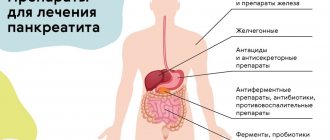
Treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis
Most often, pancreatic lipomatosis is treated with conservative methods. It implies the following:
- Review and correction of the daily diet.
- Fight against excess body weight.
- Getting rid of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
In addition, additional therapy is prescribed, which is aimed at normalizing digestion and restoring hormonal deficiency.
Conservative treatment also includes treatment of concomitant diseases (if any), such as:
- Hepatitis.
- Thyroid disease.
- Selection of therapy for diabetes mellitus.
If conservative treatment does not have the expected effect, areas of lipomatosis are removed surgically.
4. Treatment of steatopancreatitis
If you seek medical help in a timely manner, treatment for pancreatic steatosis is carried out conservatively. First of all, a strict diet is developed, lifestyle correction is carried out, changes are made to diet and physical activity. It is recommended to eat foods in fractional doses every 3-4 hours, excluding fatty, spicy, and fried foods. Lipotropic products, on the contrary, need to be administered in larger volumes. These are fish, beef, low-fat cottage cheese, soy.
When lipomatous nodes are large and obstruct the outflow of pancreatic secretions, surgical intervention is necessary. It is worth understanding, however, that prompt assistance may turn out to be a temporary measure if in the future the person continues to abuse alcohol, smoke, or eat fatty foods. Very quickly, an unhealthy lifestyle triggers mechanisms that create a lipid depot in all tissues and organs, including the pancreas.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for life expectancy depends on the degree of damage to the body and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Following a diet and quitting alcohol and smoking increases the chances of recovery and restoration of organ function. If simple rules are followed, healthy tissues will continue to produce the necessary hormones with enzymes for food digestion and metabolism.
Refusal of the doctor's recommendations can cause severe damage to the tissues of the stomach, liver and intestines. Repeated intoxication of the body with serious consequences is possible.
Pathology of the pancreas is incurable and develops slowly. It will not be possible to completely cure the patient, but it is possible to block further growth of atypical cells and normalize the functioning of the organ. This requires taking prescribed medications and eating right.
Classification
The classification of pancreatic cancer depends on the histological structure of the tumor and the location of the tumor. According to histological structure, malignant neoplasms of the pancreas are divided into:
- Squamous;
- Adenocarcinoma;
- Cystadenocarcinoma;
- Glandular-squamous;
- Unspecified cancer;
- Ductal adenocarcinoma.
The most common form of pancreatic cancer is adenocarcinoma. The tumor is formed from the epithelial cells of the ducts. It is accompanied by an intense fibrotic reaction. Cystadenocarcinoma has a generally favorable prognosis. Acinar cancer is observed in 5% of patients. Pancreatic sarcoma is a rare disease that is usually diagnosed in childhood.
In accordance with the location, cancer of the head, body, and tail of the organ is distinguished. In 65% of cases, the tumor is localized in the head of the pancreas, in 30% in the body and tail, and in 5% only in the tail. Malignant neoplasms of the head of the pancreas penetrate the duodenum.
The exocrine part of the pancreas has a well-developed network of lymphatic ducts that are located along the blood vessels. Tumors localized simultaneously in the tail and body of the pancreas spread through the lymphatic ducts.
Treatment with alternative medicine
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed after consultation with your doctor. It is worth combining the methods with conservative therapy methods. Medicinal herbs stimulate the natural production of pancreatic enzymes necessary to normalize the digestive process. The healing properties of herbs remove toxins from the body and improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
Nettle, yarrow, plantain, St. John's wort, rose hips, valerian, immortelle and calendula are used as infusions and decoctions. Herbs (1 tbsp) are poured with boiling water (500 ml) and placed in a water bath. You need to keep it for 15 minutes. After this, remove from heat and cool. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 21 days.
What is fibrolipomatosis?
Pancreatic fibrolipomatosis combines the characteristic features of fibrosis and lipomatosis. It is a fatty degeneration of the gland, in which there is an uneven distribution of fatty and connective tissue throughout the parenchyma. Most often, this term directly refers to a negative change in the structure of the pancreas, the processes of formation of nodules and seals on the organ.
Lipofibrosis goes through three stages of progression:
- Damage to a third of the entire organ.
- Defeat up to 60 percent.
- The spread of fibroids is more than 60 percent.