general characteristics
Heartburn is felt as a burning or heat along the esophagus, often accompanied by sour belching, choking and coughing.
A discomfort sensation occurs in the epigastric region, spreads up behind the sternum, can radiate to the neck and is felt in the throat. Often the symptom appears half an hour after eating. In a healthy person, heartburn is usually preceded by overeating, eating spicy, smoked and fried foods, alcoholic beverages, strong tea, and coffee. In gastrointestinal pathology, a retrosternal burning sensation is associated with the intake of both irritating and regular food. Rest in a horizontal position, bending the body forward, and physical activity immediately after eating contribute to increased heartburn. After a burning sensation in the esophagus, a sore throat often occurs. If episodes of retrosternal burning become more frequent up to several times a week, accompanied by a cough and other signs of dyspepsia (frequent sour, putrid belching, nausea), it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist. The combination of heartburn with vomiting blood, dark stools, intense pain in the chest and back is an indication for seeking emergency medical help.
High temperature and gastrointestinal problems
Service price from 1500 rubles
High temperature, which is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and epigastric pain, are signs of a gastrointestinal tract disease. This condition requires qualified medical care.
High temperature and abdominal pain: causes
Hyperthermia indicates that there is an inflammatory process in the body, which can be infectious or non-infectious in nature.
Food poisoning. Occurs after a person has eaten food poisoned by pathogenic and microorganisms that produce toxins. Most often this happens when eating spoiled foods:
- dairy products,
- meat,
- fish,
- eggs,
- cream cakes and pastries.
High temperature during poisoning is caused by severe intoxication of the body; it is often accompanied by headache and chills.
Gastroenteritis. This is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines that is caused by
- Escherichia coli - campylobacteria, staphylococci, shigella;
- viruses - rotavirus, adenovirus, norovirus.
The clinical picture includes high fever, severe abdominal pain, muscle weakness, lack of appetite, vomiting and diarrhea. Symptoms may include an intense headache and bloody stools.
Staphylococcal food toxicosis. The causative agent of this infectious disease is Staphylococcus aureus, the nutrient medium for which is sauces, salad dressings, protein and curd cream. Symptoms of the disease are:
- heat;
- diarrhea;
- vomiting and nausea.
Salmonellosis. Acute gastrointestinal infection is caused by salmonella strains that are found on eggs, meat, fish and dairy products. The patient's condition is very serious. The temperature rises to 39–40°, loose stools take on a greenish tint, there is severe abdominal pain and profuse vomiting.
In addition to gastrointestinal infections, high temperature also accompanies inflammatory pathologies.
Gastritis. Characteristic signs, in addition to nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, are:
- sour belching;
- heartburn;
- feeling that the stomach is full.
The thermometer shows 37–38°; “hunger pains” occur.
Stomach ulcer. The clinical picture includes:
- nausea immediately after eating;
- heartburn;
- temperature rise to 37–38 degrees;
- sour belching.
Pain in the epigastrium during the chronic course of the disease is dull and aching in nature. During an exacerbation, it becomes cutting, its intensity increases.
Where to go if you have a high temperature and a stomach ache?
The medical appointment is conducted by experienced therapist Yu. A. Bobkova. She also specializes in the field of gastroenterology, so she is able to provide highly qualified medical care.
The cost of an initial consultation is 1,500 rubles. During the appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis, palpates the abdomen, identifies the patient’s subjective sensations, assesses the severity of symptoms and the nature of their course. The patient is prescribed a general blood and urine test, and stool testing for intestinal infections and viruses. If necessary, Yulia Alexandrovna performs ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity.
As a result of diagnostic measures, our doctor accurately identifies the disease and prescribes a treatment regimen. It is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
The “Private Practice” clinic is located within walking distance from the “Varshavskaya” and “Chistye Prudy” metro stations. Call us at the phone number listed on the website - we will make an appointment for you on any day convenient for you, from 9 am to 9 pm.
Development mechanism
Typically, heartburn is associated with damaging effects on the esophageal mucosa. Most often, the symptom is provoked by reflux of gastric juice and digested chyme. In this case, both hydrochloric acid and proteolytic enzymes have an irritating effect, and the appearance of heartburn often indicates the presence of esophagitis. In the course of esophagomanometric studies, it was found that in the majority of patients experiencing a retrosternal burning sensation after eating, the cardiac sphincter is weakened; the pH level in the distal part of the esophagus does not exceed 4.0.
The reflux mechanism of symptom development is characteristic of both gastroenterological diseases and heartburn during pregnancy. During gestation, the weakening of the cardia is facilitated by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to an enlargement of the growing uterus. An additional pathogenetic link in pregnant women and patients suffering from gastric and duodenal ulcers, hyperacid gastritis, and helicobacteriosis is the high aggressiveness of gastric juice due to an increase in its acidity and increased incompetence of the cardia against the background of gastric hypermotility.
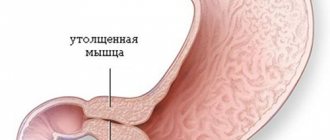
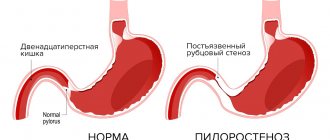
The mechanism of heartburn development in atrophic gastritis, pyloric stenosis and stomach cancer is based on insufficient digestion of food, the predominance of fermentation processes, and the formation of large amounts of lactic, butyric and other organic acids. Stagnation of chyme caused by impaired evacuation is accompanied by stretching of the gastric wall and cardiac sphincter with reflux of contents into the esophagus. After a total gastrectomy, a burning sensation is provoked by the action of bile and pancreatic enzymes entering through the formed anastomosis on the esophageal mucosa.
Less commonly, a retrosternal burning sensation is caused by stretching of the esophageal mucosa with achalasia cardia, large neoplasms, and strictures. The pathogenesis of heartburn with hypermotor dyskinesia of the esophagus is the same, but the aggravating factor is often a decrease in the sensitivity threshold against the background of autonomic disorders. A special pathophysiological mechanism underlies the formation of symptoms in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. With somatosensory paroxysms, a burning sensation behind the sternum is caused by the presence of a focus of pathological impulses in the brain.
Heartburn causes and consequences
When this symptom is mentioned at a therapeutic appointment, patients immediately wince, remembering their sensations: an unpleasant burning sensation behind the sternum, rising up the esophagus, to the oral cavity and the sudden appearance of a sharp sour taste in the mouth.
We are talking about heartburn, which affects a variety of people - thin and fat, young and old - and often do not know what to do about it.
For years, sufferers have been trying to cope with the merciless burning sensation on their own, resorting to various means, for example, drinking mineral water, or taking over-the-counter heartburn remedies, and sometimes using household products such as soda. At the same time, many never get to the doctor because they do not consider heartburn a serious cause for concern. And in vain.
Heartburn and cancer: when is it time to worry?
The appearance of heartburn indicates the presence of reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus, which in medicine is called gastroesophageal reflux and reflects the process of reverse digestion. The mucous membrane of the esophagus and pharynx, with frequent irritation by hydrochloric acid of gastric juice, becomes easily vulnerable to the development of first precancerous diseases of these organs, and then adenocarcinoma.
Important: heartburn that occurs more than once a week is a direct indication for examination.
For those who are “not sure” about going to the doctor, I suggest you answer the questions on the Richter scale
(ACG “Understanding GERD”):
1. Are you often bothered by at least one of the following?
- Burning in the back of the throat.
- Bitter, acidic taste in the mouth.
- Discomfort in the chest that seems to move upward from the stomach to the mouth.
2. Do you often experience the sensations listed above AFTER EATING?
3. Do you suffer from heartburn two or more times a week?
4. Does taking over-the-counter medications only provide temporary relief?
5. After the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor, did the symptoms appear again?
If you get more than two affirmative answers, it is necessary to conduct a rather unpleasant, but very informative examination, which is EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy), but more often they say simply gastroscopy.
Carrying out diagnostics
Using a thin flexible tube with a light at the end, inserted through the mouth into the patient's esophagus and stomach, the endoscopist can examine the condition of the mucosa throughout the upper gastrointestinal tract and take part of the mucosa for a biopsy. This examination will quickly and reliably answer the main question: is there an oncological process or suspicion of it.
If, fortunately, the most important fear is not confirmed and the growth of atypical cells is not detected, then every effort must be made to find out and eliminate the causes of heartburn.
It has been reliably proven that if chronic long-term heartburn is ignored, there is a high risk of developing such changes in the structure of the cells of the esophageal mucosa, which, with continued exposure to harmful factors (aggressive food, stress), can transform into atypical, cancer cells.
How to get rid of heartburn
Nowadays, great strides have been made in the treatment of many diseases of the digestive tract. But, unfortunately, esophageal cancer is currently almost impossible to effectively treat successfully. But gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the manifestation of which is heartburn, on the contrary, can disappear forever after proper adherence to the regimen and taking medications.
A patient interested in success should maintain his normal weight and eat wisely, avoiding foods that affect the lower esophageal sphincter, such as chocolate, citrus fruits, and bread. It is recommended not to overeat, not to go to bed after eating, and to raise the head of the bed (but not to sleep on a high pillow). If you have heartburn, you should not wear tight clothes or a tight belt. The tone of the lower esophageal sphincter is negatively affected by drinking strong alcohol and smoking.
It is also necessary to establish a reasonable, gentle nutrition for the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and carry out high-quality treatment using modern means that affect the cause and development of inflammation of the digestive organs under the supervision of an experienced gastroenterologist or therapist.
And it is imperative to undergo endoscopy at least once a year to identify precancerous conditions in order to be sure to identify and treat them.
For the treatment of GERD in the arsenal of a modern doctor there are two schemes:
- step down (lower tension) - when treatment begins with the most effective potent drug and ends with mild antacids;
- step up (increase tension) - start with mild antacids and, if ineffective, gradually add more potent agents.
To determine which regimen is preferable in each specific case, the doctor collects anamnesis (medical history), conducts a thorough examination and interprets test results. After the correct selection of a treatment regimen, final relief from gastroesophageal reflux is most likely.
If you experience heartburn sporadically, no more than once a month, you should take antacids or proton pump inhibitors in low dosages to alleviate the condition, do not overeat and do not wear a tight belt. But do not miss the moment if the symptom begins to appear more often - in this case, be sure to consult a doctor.
Anna Averina
Photo istockphoto.com
Classification
Taking into account the predominant localization of discomfort, a distinction is made between the more common heartburn in the chest and the less common form with a burning sensation in the throat. To determine the severity of a symptom, the frequency and circumstances of its development, intensity, connection with food intake, and other features of the discomfort experienced are usually used. This approach is effective for conducting a diagnostic search and selecting optimal methods for correcting heartburn, taking into account the causes of its occurrence. Based on the proposed criteria, three degrees of severity of the disorder are distinguished:
- Mild heartburn
. A retrosternal burning sensation appears no more than once a month, is usually provoked by dietary errors, and quickly goes away on its own after correcting the diet. May be accompanied by belching of air or acidic stomach contents. It is observed in 51.4% of men and 48.5% of women without chronic pathology of the digestive organs. - Moderate (moderate) heartburn
. Disturbs the patient 1 to 3 times weekly. It is observed after eating both irritating and familiar foods to the patient. It is often detected as part of a dyspeptic syndrome with nausea, sour or putrid belching. Usually indicates the development of gastroenterological pathology. - Severe (severe) heartburn
. It appears almost every day, combined with belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, stool instability, and abdominal pain. Often associated with food, although it may occur on an empty stomach. Urgent diagnosis is necessary to determine the disease that caused the symptom. Found in 1.2% of men and 3.4% of women.