Medical terminology is difficult for patients unfamiliar with anatomy to understand. An erroneous interpretation arises not only in the nature of the disease, but also in the definition of the diseased organ. This concerns the question: “What is stomach bulbitis?”
The name "Bulbit" refers to inflammation of the duodenal bulb, not the stomach. “Bulbus” is the rounded upper part adjacent to the pylorus of the stomach. General inflammation of the duodenum is called duodenitis, and bulbitis is actually its local variety.
Clinicians identify several variants of the disease, which is associated with the possibility of a differentiated picture during endoscopic examination. But, according to the International Classification, only two types of bulbitis are considered as separate nosological forms (ulcerative and erosive).
Functions of the duodenal bulb
The bulbus (bulb) is located at the border of the transition of the stomach to the duodenum at the level of the twelfth thoracic and first lumbar vertebrae. Its length is no more than 5–6 cm. The wall consists of four layers:
- from the inside - a mucous membrane with folds, villi, and depressions;
- submucosal - forms a denser base of connective tissue along which vessels and nerves run;
- muscular - consists of muscle bundles, ensures contraction and transport of food to the lower intestines;
- on the outside there is a serous layer, necessary for protection from damaging factors.
You should pay attention to the absence of nerve endings in the mucous layer. This indicates that pain develops only if the inflammatory process spreads to the submucosal area. Another mechanism of pain is stretching or spasm of muscle fibers.
The sphincter of Oddi, through which bile and pancreatic juice enter the duodenum, is located in the lower part. This means that the onion contains no bile acids and digestive enzymes, except for the gastric juice pepsin and hydrochloric acid that comes with food.
The main task of the bulbus is to take the first “blow” of the acidic contents of the stomach, to begin neutralizing the reaction in order to provide an optimal environment for the further action of enzymes.
What changes occur with bulbitis?
When the digestive process in the stomach is disrupted, acidified, undigested food comes to the bulbus. Additional enzymes are required to process it. Retention of the food bolus contributes to stagnation of the contents and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
At first, the bulbite is in the nature of a superficial lesion, then it penetrates deeper, causing the formation of cracks and small wounds (erosions). The folds of the mucous membrane swell, dilated vessels fill the surrounding tissues with blood (the phenomenon of hyperemia). If bulbitis is not treated in time, the damage goes to a deeper level, the submucosal and muscle layers. Thus, a duodenal ulcer is formed.
Isolated inflammation of the bulb practically does not occur; the causes of inflammation are the same as with gastroduodenitis
Causes of bulbitis
The main causes of inflammation in bulbitis prove a connection with stomach diseases. The people most susceptible to the disease are:
- those who do not know how to organize a proper diet, who are addicted to fast food, chips, fried and spicy foods that irritate the mucous membranes;
- smokers who drink alcoholic beverages immoderately;
- often exposed to stressful situations, nervous stress;
- infected with Helicobacter pylori infection, helminths or parasites;
- with reduced immunity;
- with hypofunction of the adrenal glands;
- from families with a hereditary predisposition.
The bulb undergoes serious changes during reflux disease - the backflow of the contents of the duodenum with bile and pancreatic enzymes into the stomach. In this case, the mucous membrane is affected due to additional mechanical and chemical irritation.
Diet
A necessary condition for effective treatment is adherence to a diet, the basic principles of which are aimed at reducing the load and ensuring a state of rest for the duodenum and stomach.
Eating with bulbitis, as well as with gastritis, which may be the cause of its development, is necessary in compliance with the rules of food preparation.
Eating should be moderate, unhurried, and long breaks should not be taken between meals. It must be steamed, especially at first, without using seasonings or spices.
It is recommended to exclude from the diet all foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive system: spicy, sour, fried, salty, smoked, fatty, carbonated drinks, black coffee, alcohol.
For dietary purposes it is useful to use:
- milk or dairy products;
- lean meat: rabbit, chicken, veal;
- fish: pollock, hake, cod;
- white bread, pasta, cereals;
- compote, tea, jelly.
There are cases where strict adherence to a diet in the initial stages of the disease helped patients get rid of the disease without the use of medications.
How does bulbitis manifest itself?
The disease occurs in acute and chronic forms. Acute bulbitis accompanies severe infections, food poisoning, sepsis, and blood diseases. Chronic bulbitis is usually observed with duodenitis or duodenal ulcer. Formed in undertreated patients, with poor diet, or low immunity. During the period there are periods of exacerbation (spring and autumn) and remission.
Palpation reveals pain in the epigastrium on the right
The symptoms of the disease are similar to gastritis, duodenitis and peptic ulcers. Superficial inflammation does not cause pain. Manifested by discomfort in the epigastric area, heaviness, belching, heartburn.
When spreading to deep layers, patients complain:
Symptoms and treatment of gastritis of the antrum of the stomach
- for aching and bursting pain, less often cramping, occurring on an empty stomach or at night, located in the epigastric region, radiating to the navel, back, relieved by eating food, medications that reduce acidity;
- heartburn - the mechanism of occurrence of the symptom is explained by a violation of the transport function of the stomach, inconsistency in the work of the wall muscles and sphincters, and the reflux of acidic juice into the esophagus;
- constant bitterness, bad breath - confirms stagnation and reverse movement of the contents of the duodenum;
- belching air or eaten food is a sign of impaired motor skills;
- nausea, possible vomiting two to three hours after eating, relieving pain;
- tendency to constipation;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent dizziness, headache;
- sweating;
- irritability;
- insomnia.
The clinic of bulbitis is determined by its shape. Superficial and catarrhal changes do not cause severe pain. Erosive and ulcerative bulbitis occurs almost like a peptic ulcer.
Prevention
As in the case of duodenogastric reflux (DGR), the occurrence of bulbitis can be prevented if you live by the new rules:
- Following the principles of healthy food consumption.
- Quit smoking and all alcoholic drinks, even beer.
- Avoiding stressful situations.
- Attentive attitude to health and treatment of emerging diseases.
The prognosis for recovery is most favorable provided that you seek medical help in a timely manner and comply with all prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician.
Stomach cancer Gastric ulcer Gastritis Erosive gastritis Hiatal hernia Low stomach acidity
Types of bulbitis according to endoscopic picture
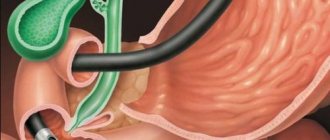
The procedure of fibrogastroduodenoscopy has become firmly established in the practice of doctors. It is carried out in every clinic. Patients are warned that they must come for the study on an empty stomach.
The equipment provides the opportunity to examine the surface of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, collect mucosal biomaterial from suspicious areas for histological and bacteriological examination, and measure acidity.
The normal mucosa of the bulb is brighter than that of the esophagus. The surface is smooth, shiny, evenly covered with a layer of mucus. The folds are elastic (quickly straightened when air is blown in). Arteries and veins are visible through the mucous membrane.
The forms of bulbitis differ in visual appearance, area of inflammation, and depth of the lesion. Endoscopists describe visual changes and give their opinion. Bulbitis is considered catarrhal when swelling of the folds, local areas of inflammation with hyperemia, and expansion of the capillary network are detected. It can also be characterized as superficial because no deeper lesions are found.
Hyperplastic is called bulbitis with areas of cell proliferation and rough folds. There are two options: granular - many pinpoint small formations, polypous - polyps up to 5 mm high are formed, the color does not differ from the mucous membrane. Cytological examination may reveal epithelial metaplasia (replacement with cells from another organ).
Hyperplastic growths are considered precancerous and cause concern
Lymphoid hyperplasia of the bulb has a lymphatic nature of growths and differs from ordinary hyperplasia by its tuberous surface. Atrophic bulbitis is usually detected during a long course of the disease, when conditions are created for deterioration of the nutrition of the mucous membrane and thinning. It is characterized by a pale gray color, with clearly translucent vessels.
The erosive process is accompanied by the detection of small cracks, wounds of various shapes, and bleeding vessels. Ulcerative bulbitis manifests itself as an ulcer in the bulb with an inflamed surface, undermined edges, and surrounding hyperemia.
Hemorrhagic bulbitis is a picture of hemorrhages in the mucous layer, and it is possible to identify a bleeding vessel in the center. According to their prevalence, focal changes are distinguished (areas of healthy tissue are preserved), diffuse changes concern the entire area of the bulb.
Diet food
First of all, the patient needs to give up rough food. Eating hot, smoked, spicy, pickled, salted, fried, too hot or cold food is not allowed. Meals should be eaten in small portions, at least 6-8 times a day, and should be eaten in small portions.
The patient's diet should consist of liquid and puree dishes, and their temperature should not be lower than room temperature. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, you can eat fermented milk products, jelly, boiled meat, and broths.
The therapeutic diet includes the use of herbal preparations, which should contain leaves and inflorescences of celandine, chamomile, yarrow, St. John's wort, fennel, and linden. In a state of remission of the acute form of bulbitis, it is recommended to use the mineral waters “Essentuki No. 4”, “Essentuki No. 17” and “Borjomi”.
What diagnostic methods are used?
In addition to esophagogastroduodenoscopy, for diagnosis, the doctor must identify the main cause of the disease, exclude bleeding and cancerous degeneration. The following studies are used for this:
- general blood test - will show the reaction to the strength of inflammation (leukocytosis, shift of the formula to the left, increase in ESR);
- feces for the Gregersen reaction - makes it possible to diagnose initial bleeding in ulcers and hemorrhagic bulbitis;
- pH-metry is necessary to clarify the type of gastric secretion and the subsequent prescription of special drugs for its correction; it is carried out during fibrogastroscopy with a special probe or a radiocapsule is used;
- the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection is confirmed by the detection of specific antibodies in the blood by enzyme immunoassay or gene structures using polymerase chain reaction; a simpler determination is a urease breath test and stool examination;
- analysis of biopsy material makes it possible to exclude cancerous degeneration, identify the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and atrophic changes;
- X-rays can be used to examine the bulb only after it has been filled with a contrast agent; local photographs help to identify polyps, impaired folding, tumor, and deformation based on the distribution of contrast.
Urease test is performed on an outpatient basis
Ultrasound is not used for diseases of the stomach and intestines, but if there is a suspicion of concomitant pathology of the liver, pancreas, or stones in the biliary system, the method may be useful.
If it is not possible to obtain the results of intragastric intubation, the acidity of gastric juice is determined by the level of uropepsinogen from daily urine or by the concentration of serum gastrin.
Folk remedies
Good results in the treatment of moderate bulbitis can be achieved with the help of medicinal plants with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. The use of alternative medicine recipes must be combined with therapy.
St. John's wort decoction
2 tablespoons of St. John's wort herb are poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for 1 hour. The drink should be taken before meals, 50 g. St. John's wort is prohibited for pregnant women due to the likelihood of miscarriage.
Decoction
You need to take equal quantities of cucumber herbs, cyanosis, fennel, flax seeds, meadowsweet and chamomile and brew 1 tbsp in a teapot scalded with boiling water. l. mixture and 0.5 liters of boiling water. The composition must be infused for 2 hours, then filtered and taken three times a day, 15 minutes before meals, 100 ml. For prevention, it is recommended to carry out a course of 3 months in autumn and spring.
Tincture of rosehip, hawthorn and red rowan
To prepare a medicinal drink, the mixture (1 tablespoon for each ingredient) is poured with 500 ml of boiling water. The composition is infused for 6 hours. Apply 3 times a day before meals, 200 ml.
Infusion of Icelandic moss and chamomile
You need to take 2 tablespoons of plants and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. The resulting composition should be heated in a water bath for 30 minutes. After time, the liquid is filtered. Use 100 ml three times a day, before meals. Duration of therapy is 2 months.
carrot juice
Only freshly squeezed juice from grated carrots is healthy. You need to take ¼ glass of juice 40 minutes before meals three times a day.
Plantain juice
It is recommended to use juice purchased at a pharmacy. 45 ml of juice should be mixed with 1 tsp. honey and use 1 tbsp. l. three times a day. The duration of treatment is 14 days, after which you need to take a break for 10 days and repeat the course again.
How is the treatment carried out?
General treatment of bulbitis and stomach is usually prescribed. The plan must provide:
- diet and nutrition;
- use of medications;
- possible physiotherapeutic procedures;
- use of traditional herbal medicine techniques;
- Spa treatment.
Each patient requires an individual approach, studying the examination results, and taking into account concomitant diseases. Complex therapy helps cure the acute form and prevent exacerbations.
Features of the mode
In case of bulbitis and damage to neighboring organs, the patient will need to get rid of strong coffee, alcohol, soda, and smoking. Eliminating provoking factors helps improve immunity.
You will have to learn to relax and avoid stressful situations. The optimal diet includes frequent meals of heated food (5-6 times a day), avoidance of long breaks and feelings of hunger, good chewing (eating slowly).
Diet features
Maximum functional unloading of the duodenal bulb is achieved by using dietary table No. 1. Fatty and fried foods, rich soups, smoked meats and pickles, spicy seasonings, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits, and fermented milk products are strictly prohibited.
For 2 weeks, the patient is recommended: low-fat chicken soup, baked vegetables (without mushrooms and cabbage), twisted minced meat dishes (steamed cutlets, meatballs), omelet, liquid milk porridge, dry white bread. Then they move to table No. 5.
There are exceptions for fried and fatty foods, smoked sausage. But the consumption of cottage cheese, kefir, milk noodles, and pasta is allowed.
The broth should not be greasy, the addition of boiled vegetables (potatoes, carrots), meatballs is allowed
Medications
Only a doctor can select the necessary medications. Tolerability, the presence of additional diseases, age, and stage of the disease are taken into account. Typically used:
- antibiotics and eradication agents to get rid of Helicobacter pylori infection;
- antispasmodics to relieve pain;
- drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice when its level is elevated;
- astringents and enveloping agents that protect the mucous membrane;
- drugs that promote the healing of erosions and ulcers;
- symptomatic agents (vitamins, immunocorrectors) with a general strengthening effect.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
If bleeding and the fact of metaplasia are excluded, physiotherapy methods have a good effect:
- galvanization;
- electrophoresis with novocaine on the epigastric zone;
- magnetotherapy.
They contribute to the reverse development of the inflammation process and the healing of damage. In sanatorium conditions, the patient consolidates the effect of medications, uses biological substances from natural mineral waters, and mud applications.
Folk remedies
Recommended after a period of acute symptoms. Can be combined with a maintenance dose of medications and diet. The selection of herbal remedies depends on the level of acidity. More often they use herbal tea with plantain, chamomile, and calendula flowers.
You can brew it in a thermos in the morning and drink it warm throughout the day before meals. It is recommended to add a spoonful of honey. Plantain and aloe tincture are contraindicated in case of high acidity. Oatmeal jelly and a decoction of oats have an analgesic and healing effect. This plant can be taken regardless of acidity.
Detection of bulbitis is no less significant than other diseases of the stomach and intestines, since the chain of digestive disorders continues and spreads to all organs. Timely initiation of treatment and compliance with the regimen and diet requirements help prevent more severe pathology.
Natural Medicines
Doctors recommend a combination of medications and home treatments. Traditional medicine has accumulated a large number of recipes that perfectly help cope with bulbitis.
Recovery will be accelerated by taking plantain juice with honey. The mixture not only relieves pain and inflammation, but also helps the mucous membrane to quickly recover. An infusion of chamomile and Icelandic moss has an anti-inflammatory effect. Cloves, tansy and wormwood will help cope with parasites. A good antiparasitic agent is birch (leaves), especially in combination with oregano and elecampane. St. John's wort tea and propolis tincture are useful. Erosive bulbitis is effectively treated with oak decoction.
Bulbit, especially in acute form, reduces the patient’s quality of life. This can be avoided, because the main risk factors depend on the person. Self-medication is unacceptable; careful diagnosis and doctor’s prescriptions are required depending on the examination results. With adequate treatment, the prognosis for life is favorable.