For most older people, their health deteriorates with age, and this is due to the fact that tissues gradually wear out, processes slow down, and the body's resistance to harmful influences decreases. One of the common problems in old age is poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This is often encountered by health workers caring for bedridden patients, as well as relatives of the elderly. Let's consider the causes of such ailments and methods of treating them.
Age-related changes in the digestive system
The appearance of regular diarrhea in the elderly is directly related to the aging process of the body. The following changes occur:
• The amount of saliva, which is necessary for digesting food and good absorption of nutrients, decreases. Lack of saliva causes dry mouth, chewing muscles also weaken, and the esophagus becomes longer. Because of this, poorly chewed food enters the stomach, which can lead to both diarrhea and constipation. • The stomach muscles weaken and lose elasticity. The stomach itself also changes in size. Gastric juice is produced more slowly. Food is poorly broken down and often ferments in the stomach. Poorly digested, it passes into the intestines, thereby irritating it. The entire digestion process results in loose stools. • The gallbladder enlarges, producing either more or less bile. • Problems with the pancreas are caused by a lack of digestive enzymes. Food is poorly digested and the body quickly gets rid of it. Due to problems with the pancreas, a person feels nauseous, has heaviness in the stomach and loose stools. • Lactase deficiency leads to poor absorption and lactose intolerance. For this reason, consuming dairy products can cause gas, abdominal pain and diarrhea. • The work of the small intestine slows down, which prevents high-quality digestion of food. • Fecal stones are a common occurrence in the elderly. Stones occur due to deposits on the walls of the large intestine. They interfere with the normal movement of food, causing food to be excreted partially digested. Stones provoke the development of harmful bacteria, which create pathogenic microflora in the intestines. All this leads to severe diarrhea. • Decreased size and strength of the liver. It begins to work worse, which disrupts the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates. This weakens bowel function.
Prevention and treatment of acute intestinal infections
During bathing, we willy-nilly (and small children even on purpose) swallow water along with living organisms. In the vast majority of cases, such an invasion goes unnoticed, since our body has several degrees of protection, more powerful than that of a bank note. But sometimes the defense system fails, which provokes an acute intestinal infection.
When mentioning the dangers lurking in bodies of water, one cannot ignore the topic of the inhabitants of these bodies of water. We will talk about the most dangerous creatures inhabiting our rivers - piranhas. Oh, no, it’s a joke - piranhas are a little further south.
In fact, my story, of course, is about bacteria, about the prevention and treatment of intestinal infections. Sometimes you are surprised when we, so big and strong, who have inhabited all corners of the planet and even a piece of space, die from microscopic creatures. I remember the film “War of the Worlds” by Wells, where even the healthiest aliens gave in to germs.
However, I can’t vouch for aliens, but people have something to counteract harmful microorganisms. Our saliva contains a substance (lysozyme) that complicates the life of bacteria even when it enters the mouth. The lymphatic ring in the oral cavity, being a peripheral organ of the immune system, also reliably protects against the penetration of aggressive creatures. And gastric juice is aggressive to almost any flora. But under certain conditions (immature immune system in children, immunodeficiency, elderly people, alcoholics) bacteria take over, causing acute intestinal infections.
Where does the infection come from?
Life is seething in reservoirs, invisible to our eyes, and this life will gladly take advantage of the bodies of careless bathers. Intestinal infection is the most common problem of the summer season. Strictly speaking, acute intestinal infection occurs not only from swimming. This is a problem of unwashed hands, vegetables, fruits, and poorly processed food. The cause of intestinal infection is pathogenic bacteria (occasionally viruses and fungi).
By the way, in our digestive tract there are also beneficial bacteria (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, etc.), in other words, obligate flora. They participate in digestion, the production of enzymes, vitamins, and compete with pathogenic flora, suppressing its development.
Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci, Proteus, E. coli, etc.) also live inside the body, and if the immune status is preserved, they are harmless to us. But they can cause disease if the immune system is weakened.
But bacteria that enter from the outside are pathogenic flora. The diseases they cause are yersiniosis, salmonellosis, typhoid fever, cholera, etc. - can pose a serious threat to life.
How does the disease manifest itself?
At first, microbial invasion manifests itself... but does not show anything. The incubation period lasts about two days, the time that the victim has to solve the last matters while the harmful microbes multiply and accumulate poisons. Then there is intoxication, fever, aching joints - for a day an incomprehensible condition that can be confused with the flu or something else.
This is followed by the flourishing of intestinal infection. These are, as a rule, spasmodic pain in different parts of the abdomen, repeated vomiting and, of course, repeated loose stools. Sometimes the liquid pours out of a pipe - like with cholera. Sometimes with an admixture of blood - as with dysentery. The degree of dehydration reaches extreme values, threatening the patient's life.
Dehydration is especially severe in young children. Very often such babies are brought to our department. The eyes are sunken, the cry is weak, the skin is as dry as a shoe. There is no time for jokes, life hangs by a thread.
Factors determining the severity of the condition:
- type of bacteria
(from staphylococcus only six times diarrhea, and from vibrio cholerae it will flow like from a fire hose until complete dehydration); - the number of bacteria
that have entered the body (a hundred or two will do nothing, but a colony of several thousand individuals will certainly cause suffering); - state of health
before an infectious lesion (a healthy person will run to the toilet and only become healthier, but the heart will have a worse time).
You need to stop self-medicating and herbal eating and immediately consult a doctor if: - The above symptoms are observed in preschool children, elderly people over 60 years of age and in people with chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. — Frequent, loose stools more than 5 times in adults. — There is an admixture of blood in the stool and vomit. - High fever with diarrhea and vomiting. - Cramping pain in the abdomen of any location, lasting more than an hour. - Vomiting after any meal or water. - Marked weakness and thirst.
What to do at home?
- First of all, you need to replenish dehydration.
Drinking is what you need!
If you cannot replenish dehydration with this method (vomiting or retching occurs), call an ambulance. How much should you drink? Until the thirst subsides. It's simple - drink while you want. The risk of overloading yourself with liquid is minimal. If you have concomitant pathology of the kidneys or heart, call an ambulance! Drink clean, bottled water. You can replenish the fluid with a solution of rehydron
- although it is terribly disgusting, but useful in microelements. - Enterosorbents.
Activated carbon, enterodesis and all sorts of similar tasteless, but useful and safe drugs. - If it is impossible to call a doctor, and vomiting worsens dehydration, find Cerucal (metoclopromide)
. - Medicines for intestinal disorders will be needed, if the disease does not recede, antibacterial drugs will be needed: the bacteria must be killed. The choice of drugs depends on the possible pathogen, the severity of the condition, the urgency of the situation, and the patient’s allergies. Therefore, “self-prescribing” medications is not a good idea. But if you do not have the opportunity to see a doctor, in a difficult situation (hiking, tourist trip) the best option is furazolidone
. This is something you can keep in your first aid kit. Take 0.1–0.15 g after meals, 4 times a day for adults. For children - 10 mg/kg body weight per day (daily dose is divided into 3-4 doses). Take no more than 10 days. - About food. In the acute period, it is better not to eat, but to drink, drink, drink. When it becomes a little easier, you can have low-fat broths and crackers. But the acute period must be endured.
- If you have abdominal pain, it is better not to take painkillers - do not erase the picture of the disease, in case you have appendicitis!
- If you have diarrhea, you should not take astringents such as imodium or loperamide - the body must get rid of toxins and bacteria.
And in conclusion, although this is trivial, I repeat: wash your hands before eating, wash vegetables and fruits, prepare food from quality ingredients. It's so simple, but incredibly effective. Be healthy!!!
Vladimir Shpinev
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Products by topic: [product](rehydron), [product](activated carbon), [product](enterodesis), [product](cerucal), [product](furazolidone), [product](imodium), [product] (loperamide)
Causes of diarrhea
Against the background of age-related changes, various causes of diarrhea in older people arise. A specialist can conduct a diagnosis and accurately determine the root cause of loose stools.
The reasons may be as follows:
• Gastrointestinal diseases: colitis, pancreatitis, inflammation, Crohn's disease, intestinal tumors. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract provoke chronic diarrhea; • Infection. Age-related changes make the human body vulnerable to various bacteria, viruses and helminths. Once inside, they cause intestinal disorders; • Hormonal imbalances. Hormone imbalances and endocrine problems cause diarrhea in old age. To get rid of it, you need to treat the root cause; • Poor nutrition is a common cause of bowel dysfunction in old age. Diarrhea is typical for those who often consume salty, sweet, and spicy foods. The nature of nutrition in youth also affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract in old age. If for many years a person has often drunk alcohol or eaten unhealthy food, negative changes in the digestive system begin earlier; • Prolonged stress, excessive stress on the body and psyche. Strong emotions (fear, anxiety) increase intestinal motility, which can cause diarrhea; • Surgery in the gastrointestinal tract can disrupt intestinal motility. This can cause constipation and diarrhea; • Long-term use of medications that have loose stools among their side effects; • Poisoning is the cause of one-time diarrhea.
Defecation in an adult - norm and violations
The content of the article
Normal bowel habits vary greatly among individuals depending on age, individual health factors, diet, social and cultural backgrounds. For city dwellers, the frequency of bowel movements ranges from two to three times a day to two times a week, which individually can be considered normal.
Changes in the frequency, consistency, or volume of stools, as well as the presence of blood, mucus, pus, or excess fatty substances (eg, oil, grease, emulsion) in the stool may indicate a medical condition.
Nature of the disease in the elderly
Older people experience various stomach problems, which often results in diarrhea. Diarrhea is a symptom of internal disorders in the body that must be diagnosed. This problem cannot be ignored: diarrhea leads to dehydration, which is dangerous in old age. Against the background of age-related changes and chronic diseases, this dehydration leads to negative consequences.
Many people under 60 years old are characterized by ailments that are accompanied by periodic diarrhea. These problems can be caused by poisoning from poor-quality food, stomach bacteria or infections, or certain medications.
Age-related changes in the functioning of the body play a major role, causing disruptions in metabolism. This problem is typical for older people. Diarrhea can occur as a reaction to fear or shock. In this state, high-quality digestion of food does not occur; it passes from the stomach to the intestines and is excreted from it.
Regular diarrhea in old age may indicate Addison's disease or diabetes. You need to pay attention to diarrhea in a bedridden person. People who are bedridden are characterized by constipation. The appearance of diarrhea may indicate hormonal problems and gastrointestinal diseases.
Concomitant diseases
Often the causes of intestinal dysfunction are diseases of other organs. Problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes, and bad teeth can cause problems with food digestion.
Insufficient physical activity caused by leg pain can also lead to frequent constipation.
Walking in the fresh air not only improves the emotional state of an elderly person, but also stimulates intestinal function. Even if a person is completely immobile or does not walk independently, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract can be improved. Proper care for bedridden patients involves regular abdominal massage, which is performed by professionals.
Diagnostics
For proper treatment, an accurate diagnosis of the root cause of diarrhea is necessary. Various methods are used for diagnosis:
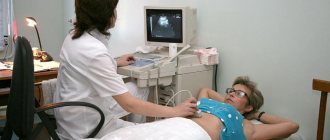
• Clinical blood test. It can be used to determine the inflammation that provokes diarrhea; • Coprogram. Examines stool to obtain information about the enzymatic and digestive functions of the gastrointestinal tract; • Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Allows you to determine the condition of organs and detect pathological processes; • Sigmoidoscopy - examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon; • Colonoscopy – examination of the large intestine; • Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) – study of mucous membranes in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum; • Culture of microflora to detect sensitivity to antibiotics.
Tests alone are not enough to make a diagnosis. Detailed comprehensive diagnostics allows you to accurately determine the pathological processes that lead to the appearance of loose stools. Based on the examination results, the specialist will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Diagnosis is carried out by a therapist, gastroenterologist, and proctologist.
Diagnosis of diarrhea in old age
Before starting treatment for diarrhea, it is necessary to establish the causes of its occurrence. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the most common and effective methods for diagnosing the disease:
- analysis of stool for coprogram;
- culture for bacterial microflora;
- clinical blood test;
- biomarker analysis to identify dysfunctions of internal organs;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- gastroscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colonoscopy.
Only after a comprehensive study of the data obtained during the examination, a therapist or gastroenterologist will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Read material on the topic: What does an examination of an elderly person include?
Symptoms
Diarrhea may be accompanied by additional symptoms. Common signs:
• Pulling, aching or cutting pain in the lower abdomen, the occurrence of spasms; • Seething and severe gas formation in the abdomen; • Feeling of nausea, vomiting; • Strong thirst, dry mouth; • The color of urine becomes darker; • Heat; • Deterioration of appetite; • Impaired attention and perception of the surrounding space; • Fatigue and lethargy.
Symptoms can occur in different combinations. If you find them, you need to contact a specialist. It should be remembered that an elderly person has a weak body, so when he gives alarming signals, you need to immediately pay attention to them. If diarrhea is accompanied by fever, fainting, blood appears in the stool, the pain becomes very severe, you need to call an ambulance.
Causes of diarrhea that require and do not require treatment
At the beginning of the 20th century, Dr. Stanislav Breuer wrote in his "New House Doctor": ... diarrhea (diarrhea) is not always harmful, for example in children during teething; if the condition is not excessive; it prevents swelling. In addition, after eating unhealthy or excessive food, diarrhea is a symptom of self-healing, promoting the rapid elimination of harmful contents, so drugs that quickly suppress it are almost always harmful... Speaking of diarrhea, the author states: ... diarrhea occurs due to overeating or unhealthy food, unripe fruits, cold water, medication abuse, colds, often occurs in children during weaning and poor nutrition.
According to the teacher. Robert Hegglin, diarrhea occurs in the following conditions:
- Infections with a known microbe are an infectious disease transmitted through an intestinal infection.
- Diffuse anatomical lesions of the intestinal wall, the causative agent of which is unknown - catarrh of the small intestine, colitis, ulcerative colitis.
- Limited changes in the intestinal wall - tuberculosis, cancer, segmental ileitis, syphilis, actinomycosis, gonorrhea.
- Fermentation and putrid indigestion.
- Diarrhea of gastric origin.
- Sprue - primary and secondary mold.
- Diseases of the pancreas.
- Intestinal lipodystrophy - Whipple's disease.
- Endocrine disorders - hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), parathyroid insufficiency, diabetes.
- Diarrhea of allergic origin.
- Diarrhea of nervous origin.
- Toxic changes in the intestines - uremia, severe general infectious diseases, mercury and arsenic poisoning.
- Infections with intestinal parasites.
Diabetes
Another division, depending on the pathophysiological mechanism underlying the excessive excretion of water in the feces, divides diarrhea into 5 main groups:
- Osmotic diarrhea
is when the absorption of water from the intestinal lumen is difficult due to the presence of osmotically active food components. Substances such as sugar or osmotically active sulfate salts and phosphates, such as those administered as laxatives, can increase stool bulk. Sugar intolerance and excessive intake of substances that replace sugar in dietary products (sorbitol, hexitol, mannitol) are often the cause of diarrhea. An example is diarrhea caused by chewing gum, where peristalsis is stimulated by chewing and the sugar substitutes contained in the gum inhibit absorption. - Secretory diarrhea
is most often observed in the practice of a gastroenterologist. Diarrhea occurs as a result of the presence in the intestinal lumen of substances that increase the secretion of water and salt into the lumen of the digestive tract. These substances are bacterial enterotoxins, viruses, bile salts, fats (due to improper digestion or given as a laxative), certain hormones such as secretin, calcitonin or VIP (vasoactive intestinal peptide) secreted by certain hormonally active tumors or drugs, for example prostaglandins. - Diarrhea due to malabsorption syndrome
- observed when diarrhea occurs due to the accumulation in the gastrointestinal tract of unabsorbed water-soluble products with an osmotically active effect or water-insoluble fats with a secretory effect. - Exudative diarrhea
is the root cause - a lesion caused by pathological processes in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. The cause may be limited inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis and neoplastic diseases. Damage to the mucosa causes loss of blood, plasma, water, electrolytes and mucus, and damage to the rectal mucosa can cause a feeling of urge to defecate and severe pain. - Diarrhea as a result of impaired intestinal transit
is very often observed after surgical resection of the intestine, stomach, or anastomotic bypass, which leads to faster discharge and insufficient absorption of water from the gastrointestinal tract. Some drugs, hormones and prostaglandins have similar effects.
It is also useful to divide diarrhea into acute ones, lasting up to 14 days, most often caused by infections. The most common reasons include:
- rotaviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- Norwalk factor;
- bacterial infections caused by bacteria from the Yersinia group, Salmonella, Shigella, enetrotoxin-producing E. coli, Clostridium difficile, Campylobacter jejuni and Klebsiella.
Chronic diarrhea lasting more than 14 days can be caused by infectious agents (E. coli, Giardia, amoebiasis, cryptosporidium, and Clostridium difficile) and other conditions, such as:
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- cystic fibrosis;
- Johanson Blizzard syndrome;
- disturbances in the production and outflow of bile salts;
- celiac disease;
- immune disorders, including HIV;
- short bowel syndrome;
- food intolerance, allergic causes;
- neoplastic diseases, including diseases located outside the gastrointestinal tract - nonruoblastoma, Ganglioneuroma;
- Hirschsprung's disease;
- intensive chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
These, of course, are not all the reasons that can cause diarrhea.
It should be remembered that any diarrhea, especially in the elderly or in children, can quickly lead to dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, metabolic acidosis, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Symptoms of diarrhea are especially dangerous, such as the appearance of fat, mucus, blood, and purulent discharge in the stool.
That's why it's important to be aware of the many diseases that can cause diarrhea. The mechanisms themselves, presented earlier, are not very mysterious and, recalling them, one can easily explain why the patient experiences disturbances in the frequency, quality and quantity of bowel movements. On the other hand, the most important element is to notice all the symptoms of the disease, and not stop at the diagnosis and simple treatment of diarrhea.
Why is it important to treat diarrhea early?
Diarrhea disrupts the normal functioning of the entire digestive tract of the elderly, which is difficult to restore.
If you do not pay attention to the problem in time, diarrhea will lead to complications. The main complication is dehydration due to impaired intestinal absorption and rapid fluid loss. Dehydration, together with reduced immunity and chronic problems, leads to disruptions in the functioning of the entire body. It is especially dangerous in old age.
If left untreated, dehydration will worsen even with plenty of fluids. Lack of moisture affects all systems and organs of the body, causing weakness, lethargy, decreased blood pressure, and increased pulse.
It is important to maintain a healthy hydration balance. Pay attention to the lack of moisture in the body. This may be indicated by dry mouth, a decrease in the amount of urine and the urge to go to the toilet, and a drop in blood pressure. If an elderly person experiences such manifestations of a lack of moisture, it is necessary to replenish it.
In addition to fluid, a person loses useful minerals that are necessary for healthy metabolism. This leads to worsening problems due to dehydration. Malnutrition develops, due to which a person does not receive the energy he needs. All this provokes decreased immunity and intestinal problems.
Intestinal protection is lost: with infectious diarrhea, beneficial intestinal bacteria, which protect its microflora, cannot cope with a large influx of pathogenic microorganisms. Beneficial microflora decreases, the infection spreads. Toxins are released, causing diarrhea.
If you eat improperly, frequent loose stools lead to irritation of the intestines and anus, and cracks appear on the skin. Such complications are typical for bedridden patients. To prevent skin problems, you need to carefully observe intimate hygiene. You can use antiseptics, medicated ointments and moisturizers to restore the skin.
Great damage is caused to the weakened intestinal microflora of the elderly. To cope with the problem, you need competent professional treatment and subsequent long-term recovery. The recovery period can be accompanied for a long time by gastrointestinal problems in the form of unstable stools and discomfort.
Old people often do not attach importance to their loose stools. They get used to it, like other digestive system disorders typical of old age. Pensioners ignore diarrhea, not understanding the importance of the situation, and thereby miss the onset of a serious illness.
Relatives should closely monitor the condition of an elderly relative and inquire about his health. If symptoms of loose stool are detected, treatment should be started as soon as possible.
Symptoms and complications of diarrhea in older people
Diarrhea in older people is sometimes accompanied by:
- lack or deterioration of appetite;
- dry mouth;
- sharp pain and severe cramps in the stomach and intestines;
- apathy, constant causeless fatigue;
- nausea;
- flatulence;
- darkening of urine.
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, be sure to make an appointment with a specialist. If a high temperature occurs with diarrhea in older people, or if there is pain during bowel movements or blood is visible in the stool, call an ambulance as soon as possible. In no case should signs of deterioration in health be ignored; the health of people in old age must be taken care of as carefully as the health of infants.
Among the various complications of diarrhea in older people, the most common is dehydration. As a result of loose stools, the body's moisture reserves quickly run out and a variety of serious ailments arise. Because the immune system does not work very well in older people, and because many old people suffer from chronic illnesses, dehydration is very dangerous. In some cases, diarrhea in older people can even lead to the death of the patient.
Accordingly, complications such as dehydration should not be allowed. Carefully monitor the state of your body: if your lips are chapped, your blood pressure has dropped sharply, your mouth is dry and you don’t want to go to the toilet for a long time - these are alarming signs. It is necessary to restore the water-salt balance as quickly as possible.
Diarrhea is even more dangerous in elderly people who are bedridden patients. They may experience such unpleasant complications as itching, irritation, ulcers and cracks near the anus. Therefore, it is so important to carefully monitor personal hygiene, moisturize the skin and lubricate it with regenerating and disinfecting ointments.
We recommend
“Treatment of cerebral ischemia in the elderly: features and recommendations” Read more
Treatment of diarrhea
Treatment of diarrhea in older people should be comprehensive. This includes: taking medications, eating a healthy diet with sufficient water intake, and following doctor’s recommendations.
Medicines
The treatment program is drawn up by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s situation and the cause of diarrhea. The individual scheme takes into account the person’s age and well-being. Treatment should be such as to eliminate the cause of diarrhea while avoiding dehydration. You should not take medications unless prescribed by a specialist.
The following drugs are prescribed for drug therapy:
• Medicines for rehydration – to restore water-salt balance; • Antimicrobial agents; • Adsorbents – to get rid of toxins; • Antibiotics – for bacterial diarrhea. The selection of funds occurs according to the type of microorganisms; • Probiotics – to restore healthy intestinal microflora.
Let's take a closer look at how these groups of drugs work:
• Rehydration medications. During diarrhea, a lot of fluid is lost through stool and vomit. It is not always possible to quickly restore a healthy water balance in the body by drinking plenty of fluids. To help the patient, mandatory rehydration medications are prescribed that effectively cope with the problem of dehydration. • Means for reducing intestinal secretion and reducing intestinal motility. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, which are good for bacterial diarrhea. Patients with Crohn's disease are prescribed steroid medications. Octreotide is often prescribed to slow down bowel function. If the patient experiences pain, antispasmodics are included in the therapy. It is impossible to slow down intestinal motility if there are infections in the gastrointestinal tract. • Drugs for removing toxins. Prescribed for infectious intestinal disorders. These products must be used wisely so as not to cause intoxication of the body. If the patient has impaired intestinal absorption function, these medications should be taken strictly in consultation with a specialist. • Medicines to restore intestinal microflora. These drugs may be prescribed: Hilak-forte, Enterol, Acylact.
Nutrition
Nutrition for diarrhea in the elderly is the second important point in treatment. It is necessary to establish a healthy diet: follow the rules of the diet, include healthy foods, exclude harmful ones.
Basic recommendations for nutrition during diarrhea:
• During the first 24 hours, you need to restore a healthy water balance. To do this, you need to drink plenty of fluids (water, compotes, tea) and take medications for rehydration. Eating is not recommended. • On the second day you can switch to a light diet. Food should be healthy and not cause gas. These can be cereals and vegetables without strong spices. After 2-3 days, you can include some dietary meat, such as chicken, in your diet. • Later, vegetable soups and broths are added to the diet. Meat should not be fatty and cause allergies. Dairy products are also gradually introduced: cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir and others. Dairy products must have a natural composition without chemical additives.
Nutrition after diarrhea in older people follows the rule: introduce new foods and dishes gradually, every other day or two, thus expanding the menu. This is necessary so that the digestive system can easily get used to a varied diet. This approach will protect her from irritation.
A healthy diet can include any food that is nutritious and well digestible, rich in beneficial vitamins and microelements, and does not cause irritation or severe gas formation. Products containing potassium, calcium and iron are especially useful. It is worth eating in small portions, food should be well digested, warm, and semi-mashed. A diet for diarrhea involves avoiding irritating foods and products with a laxative effect.
Healthy dishes and products include: lean meat and fish, seafood, eggs, low-fat dairy and fermented milk products, light broths and soups, whole grain cereals, vegetable oils, vegetable and fruit salads, compotes and fruit drinks. Lean meat and fish, light cereals and fermented milk products are especially useful. It is useful to heat-treat vegetables, fruits and berries.
Harmful foods that are best avoided: fatty meat, rice, egg yolk, confectionery, sweets, fatty dairy products, legumes, carbonated drinks, smoked foods, fried foods, sauces and spices.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies play a supporting role; they cannot replace traditional medicines. When choosing a prescription, be sure to consult with your doctor: the folk remedy must correspond to the diagnosis.
Treatment of diarrhea with folk remedies in the elderly:
• Rice water. 1 tsp. pour 2 cups of boiling water over rice, put on fire and cook for 15-20 minutes. Next, the broth is filtered. The product is used in 2 tbsp. l., possible before or during meals; • Strawberries. It has a positive effect on the digestive system, improves immunity and fights infectious diarrhea. 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes, then strain and cool. Take 50 ml of decoction once an hour. The remedy is used until the symptoms of the disease disappear; • Infusion of oak bark. Dilute 1 tbsp. l. crushed oak bark in one glass of boiling water and leave for 2 hours in a warm, dark place. Then strain and take 1 tsp. every 2-3 hours for three days until bowel function returns to normal; • Sage tincture. 1 tbsp. l. Mix sage with 300 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours in a thermos, strain through a sieve. Drink the medicine in small portions throughout the day. Sage helps the intestinal microflora recover and removes loose stools.
The folk remedy should not cause allergies in humans. It gently solves the patient's problem, taking into account the state of his digestion. Traditional medicines are aimed at normalizing intestinal function. They help restore its microflora, establish a healthy digestion process, and remove inflammation.
Proper nutrition for older people with diarrhea
A healthy diet for diarrhea in older people will not only help get rid of this disease, but will also prevent its occurrence, as well as the occurrence of many other diseases. Elderly people need to carefully monitor what they eat. You can’t get carried away with junk food, but it’s best to stick to a certain diet. And this is not at all in order to lose weight, but to ensure that the digestive system is healthy.
Proper nutrition for diarrhea in older people involves a diet of easily digestible foods that do not cause flatulence and are rich in nutrients. The most important thing for an elderly person is to eat food that compensates for the lack of calcium, iron and potassium in the body. It is also necessary to reduce the calorie content of meals, since the body’s energy consumption is no longer as large as in youth.
So, what diet should you follow for diarrhea in older people?
You can and should use:
- Oil from corn, soybeans, sunflower seeds.
- Lean meat, such as poultry.
- Egg white.
- Milk and sour milk with low fat content.
- Soups made from fish, poultry or vegetable broths.
- Lean fish.
- Seafood.
- Cereals except rice.
- Salads from vegetables and fruits.
- Liver (except pork).
- Whole grain baked goods.
- Berry fruit drinks and fruit compotes.
- Herbal, green and black teas.
- Chicory drink as an alternative to coffee.
Should not be consumed if elderly people have diarrhea or consumption should be reduced:
- Pork and other meats with high fat content.
- Egg yolks.
- Fat milk and sour milk.
- Muchnogo.
- Rice cereal.
- Sweet.
- Fizzy drinks.
- Bobovykh.
- Fried and smoked.
- Salt and spices.
- Spicy food.
We recommend
“High temperature in an elderly person: causes and signs” Read more
Prevention of diarrhea
• To avoid the development of diarrhea in old age, it is necessary to establish a healthy diet. It is better to accustom yourself to a healthy diet and diet from a young age and stick to it throughout your life. • Maintain a healthy water balance in the body by including clean water, fruit drinks, healthy herbal teas and infusions in your diet. • With your doctor's permission, you can take enzyme agents and probiotics. • If there are any problems with the digestive system, you need to solve them. It is necessary to cure all gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner. • Maintain intimate hygiene. • It is useful to visit the dentist periodically. • Avoid prolonged stressful situations.
Diarrhea in old age is most often not a one-time symptom of poisoning, but a consequence of age-related changes and internal health problems. For an elderly person, prolonged diarrhea is dangerous: remember about dehydration and its consequences.
To prevent loose stools, preventive measures and a healthy diet should be followed. If you notice symptoms, you should go to the doctor without delay to avoid dangerous consequences. Do not self-prescribe medications or self-medicate. Undergo a high-quality diagnosis and follow medical recommendations. Taking into account all these points, an elderly person will be able to properly treat diarrhea.