If you have cholecystitis, diet should become a way of life. Proper nutrition protects against the transition of the disease to the chronic stage and exacerbations during its chronic course. Natalya Meshikhina, a nutritionist of the highest category, talks about recommendations for choosing products and creating a daily menu.
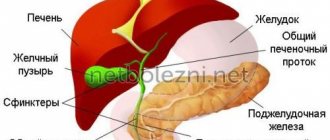
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the gallbladder. It occurs due to a violation of the outflow of bile. If it is too thick, it cannot clear the bile ducts, and if it remains in them, it forms stones and provokes inflammation.
It is believed that cholecystitis is a disease of older people. This is not true. According to statistics, the main patients of gastroenterological departments in Russia with attacks of acute cholecystitis are young people. Poor nutrition leads to illness:
- love for fast food;
- habit of snacking on the run;
- drinking soda;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- lack of breakfast and overeating at dinner.
It is necessary to stop an attack of cholecystitis in a hospital setting. It is accompanied by acute pain, so the patient has no doubt about the need to call an ambulance. The diet for cholecystitis begins from the moment the disease develops. In the first days it is a complete refusal to eat, only drinking plenty of fluids.
pixabay.com/Free-Photos
What do gastroenterologists say about yellow fruits?
After making a diagnosis, the specialist gives clear recommendations regarding nutrition, including whether it is possible to eat bananas with pancreatitis. Unlike many other fruits, the fruit has the following benefits:
- soft, enveloping consistency;
- low acidity and fat content;
- pleasant delicate taste.
The texture of the yellow fruit coats the stomach, helps normalize digestion and makes stool easier. However, the fruit has a significant sugar content and high calorie content. Both healthy people and those suffering from gastrointestinal diseases should consume it strictly in moderation.
For gastrointestinal diseases, preference should be given to ripe fruits
Is it allowed to use if you have pancreatic diseases?
Pancreatitis is a set of diseases of various etiologies that lead to inflammation of the pancreas. Before answering the question of whether bananas are good for pancreatitis, it is worth considering the types of this pathology. Highlight:
- chronic disease;
- acute recurrent pancreatitis;
- exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Chronic pathology manifests itself in regular or recurrent pain and other disorders.
Gastroenterologists give a positive answer to the question about the possibility of eating bananas for chronic pancreatitis. However, if the pathology worsens, the fruit is prohibited.
Another factor why you can’t eat fruit with pancreatitis is if the patient has an acute or acute recurrent form.
Is it possible to eat if you have gallbladder diseases or not?
Pancreatitis and gallbladder pathologies are often associated. Let's move on to consider patients suffering from cholecystitis or having had their gallbladder removed.
For chronic and acute cholecystitis
The disease is expressed in an inflammatory process localized in the gallbladder. The form of the pathology (acute, chronic, etc.) affects whether bananas are allowed for cholecystitis or not. Information on each type of disease is given in the table.
| Form | Symptoms | Can you eat bananas? |
| Chronic | Manifested by nausea, dull pain in the gallbladder area, discomfort after eating | Consumption of yellow fruits is acceptable, but no more than 1-2 pieces per day, preferably in the morning |
| Catarrhal form of cholecystitis | Severe pain, widespread not only in the right hypochondrium, but also in the epigastric region. Sensations radiate to other areas | Forbidden |
| Phlegmous | Severe pain, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, etc. | Forbidden |
| Gangrenous | The rapid course of the pathology, the body is unable to restrain the growth of bacterial flora | Forbidden |
It should be borne in mind that the data on whether bananas can be eaten with pancreatitis and cholecystitis are individual in nature. The patient may have other restrictions on consumption (allergies, obesity, diabetes, etc.).
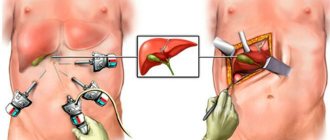
After removal (cholecystectomy)
Surgery is one of the key methods of treating cholecystitis. There is no prohibition on consuming yellow fruits in moderation after removal of the gallbladder. However, please note that the fruit is prohibited:
- in the period immediately after surgery;
- in the presence of some complications.
If you maintain normal health and after the approval of a specialist, it is permissible to include a banana in your diet.
Diet for gallstone disease
Doctors often revise dietary recommendations, guided by the latest discoveries of scientists. And now, it seems, it’s the turn to change the diet for gallstone disease.
If you have ever been interested in what kind of nutrition is suitable for the treatment of a given disease, then you are probably very familiar with Pevzner’s dietary table No. 5. In general, dietary tables are the most common domestic system of nutritional prescriptions for various diseases today. In particular, the goal of diet No. 5 is to normalize the functioning of the liver, biliary system, fat metabolism, as well as a general gentle attitude towards the digestive system. The fifth diet is easy to find on the Internet if you wish, but we will move on.
You might be surprised, but dietary tables were developed back in the middle of the last century. Since then, world medicine has greatly advanced in its understanding of the nature of diseases. Therefore, in the article I decided to collect modern facts about the effect of nutrition on gallstone disease, which I was able to find in English-language medical scientific journals. Some of these facts are already used in American, European and Australian nutrition manuals, while others still require additional research.
Food allergies
Back in the forties, doctors suggested that food allergies could be the cause of gallbladder disease. This was shown in experiments on various animals: rhesus monkeys, rabbits, etc. One study showed how a diet in which all allergenic foods were excluded from the diet reduced the symptoms of gallstone disease in 100% of subjects in a group of 96 people who have this disease. Unfortunately, such few observations do not allow us to draw global conclusions. However, some practitioners write that they use an individual hypoallergenic diet to treat the symptoms of gallstone disease.
Cholesterol and saturated fat
It is known that cholesterol plays an important role in the process of stone formation—it is what the bulk of the stone consists of. But the link between the disease and a diet rich in saturated fat is still questionable. There are epidemiological data that indicate this: the abundance of cholesterol in the diet of the population is associated with a greater manifestation of symptoms of the disease. At the same time, a diet rich in unsaturated fatty acids (fish oil, oils, nuts, etc.) is associated with a reduced risk of disease. There are not enough observations to draw definitive conclusions about whether additional consumption of unsaturated fats helps in the treatment of gallstone disease.
I found only one study that showed how taking fish oil as a supplement reduced cholesterol in bile by 25% in a group of subjects. This connection requires additional study, but medical practitioners are again ahead of scientists and are already using this principle when preparing the diet of patients.
Vegetarian diet
A 20-year study of 80,898 women found that consuming plant-based protein sources significantly reduced the risk of gallstones. The same connections were found with the active consumption of vegetables and fruits, which is typical for a vegetarian diet. By the way, dietary table No. 5 according to Pevzner also places emphasis on a fiber-rich diet, although the diet is not vegetarian. Fiber has a beneficial effect not on the gallbladder itself, but on the intestines; however, as a result, cholesterol levels are normalized, and this helps patients.
Caffeine
Coffee deserves special attention, or rather, the caffeine it contains. It turns out that consuming it in moderation does not harm, and even helps to reduce the symptoms of gallstone disease. Unlike allergies or cholesterol, the topic of the effect of coffee on gallbladder diseases is being actively studied in both animals and humans. According to a cohort study, drinking this drink reduces the risk of the disease in men by 40–45% and in women by 22–28%, which is significant. However, due to the lack of scientific confidence in the detected effects, the recommendation to indulge in coffee for cholelithiasis is almost never found.
Vitamin C
Some animal experiments have shown that taking vitamin C can prevent gallstone disease. Vitamin C is involved in the process of converting cholesterol into bile acids, preventing the formation of stones and prolonging the period during which they form. The amount of vitamin C used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes is mentioned differently in different works - from 500 mg to 2 g per day. Although the effectiveness of the use of the vitamin is generally confirmed, the optimal dose has not yet been found - more research is required.
Other products and substances
Read also: Diet for exacerbation of gastritis
Among the products and substances associated with gallstone disease, there are some that have been studied very little, but they are also worth noting. Firstly, these are legumes, including peanuts. In countries where legumes make up a significant part of the population's diet, gallstone disease is less common. A reduction in disease symptoms was also found in those who consumed peanut butter, but only one such study has been conducted. Secondly, there is an assumption that taking iron supplements also helps in treating the disease, but the effect is shown only in animals. Thirdly, lecithin. Scientists hypothesize that consuming lecithin has a positive effect on the chemical composition of the stone. This effect is still being studied, and there is no definitive answer yet. Fourth, alcohol, moderate consumption of which is likely to reduce the risk of stone formation. And finally, there is no definitive evidence yet, but it is likely that consuming added sugar may contribute to the development of the disease. Most likely, indirectly - through increased cholesterol levels or obesity.
Compare with diet No. 5
Now let's see if the latest data contradicts how dietary table No. 5 works. The first thing you can pay attention to is coffee. In the mentioned diet it is excluded, while coffee can be a healing factor. The same applies to alcohol - it is categorically excluded in any quantities, although its positive effect is rather shown in small doses.
Diet 5 also eliminates legumes as a source of crude fiber. It has not yet been conclusively proven, but there is a possibility that this is being done in vain. And avoiding fatty fish seems even less justified, given the role of unsaturated acids in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels.
But regarding the previously mentioned fiber from vegetables and fruits, as well as fatty animal meat and fatty dairy products, there is amazing unanimity among nutritionists. Apples and carrots have the green light, but it’s better to abstain from steaks and sour cream.
Maria Danina
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Which form is preferable - raw or dried?
Not only the product consumed plays an important role, but also the type of processing. The main dilemma is which bananas are best to choose for consumption with pancreatitis - raw or dried. For this pathology, it is better to choose fresh, ripe fruits. Unripe fruits can cause digestive problems.
As for dried fruits, they contain the largest amount of sugars and carbohydrates, so you should not consume them if you have pancreatitis. Recommendations on whether it is possible to eat bananas with pancreatitis and whether their consumption is likely to occur with cholecystitis are identical to each other.
Diet rules
Despite a number of restrictions, nutrition for cholecystitis should be complete and contain the required amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
In modern Standards of therapeutic nutrition, diets for cholecystitis are classified as follows:
- for chronic cholecystitis in remission - this is the main option for a standard diet. Previously designated as Pevzner table No. 5,
- for acute cholecystitis - a variant of the standard diet with mechanical and chemical sparing. Previously - diet No. 5a.
Diet. You need to eat small meals, little by little, at least 5-6 times a day. Every meal you eat stimulates the secretion of bile, which allows the gallbladder to function continuously. Another nuance: eat at the same time. This will normalize the bile exchange of the hepatobiliary system.
Salt and liquid. Consumption of table salt should be limited to 4-8 g per day, depending on the severity of the disease, since salt causes fluid retention in the body tissues, which leads to thickening and stagnation of bile.
The amount of free fluid consumed during cholecystitis should be at least 1.5-2 liters - this improves the evacuation of bile from the gallbladder, and also activates the work of the kidneys, which remove harmful products from the body.
Food temperature. Food for cholecystitis should be neither cold nor hot. The optimal temperature for inflammation of the gallbladder is 15 – 60 degrees. It is preferable to eat food at room temperature.
Rules for eating. Food, as you know, should stimulate the appetite and bring pleasure. This is especially important for cholecystitis. Therefore, you need to sit down at the table in a good mood, in pleasant company, and the table setting should be pleasing to the eye. You should not force yourself to eat dishes that you do not want; by overpowering your desire, food will bring harm, not benefit. Bad mood and dissatisfaction adversely affect the flow of bile into the bile ducts. This is due to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which is accompanied by the release of stress-adrenal hormones.
Alcohol. Everyone knows about the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption, but with cholecystitis it is necessary to observe the “prohibition law”. Firstly, alcoholic drinks are usually consumed cold, which is harmful for inflammation of the gallbladder, secondly, alcohol promotes the formation of calculi (stones) in the bladder, and thirdly, in the presence of calculous cholecystitis, alcohol can provoke hepatic colic.
Diet for acute cholecystitis
The goal of following a diet in acute forms of the disease is to chemically spare the liver, improve bile production and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract.
In the first 3 days of exacerbation of cholecystitis, it is necessary to observe only the drinking regime.
Nausea and vomiting make it impossible to eat. You should drink at least 1.5-2 liters per day, in small sips, but often.
weak tea, still mineral water mixed with boiled water, sweet juices, juices from fruits and berries, rosehip decoction
Allowed:
- weak tea
- weakly concentrated fruit juices
- herbal infusions (chamomile, mint, lemongrass, rosehip),
- still mineral water, diluted half with boiled water.
After the pain syndrome begins to gradually decrease (usually within 2-3 days), the diet becomes more varied.
Gradually pureed dishes are introduced (slimy soups, boiled pureed porridges), low-fat cottage cheese, wheat crackers, steamed or boiled dishes from lean meat and fish are gradually added.
As your well-being improves, products from the permitted list are gradually added, they can already be served unprocessed (with the exception of stringy meat and fiber-rich vegetables - cabbage, carrots, beets)
Fried foods are prohibited.
The diet includes a normal content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates:
- proteins – 85-90 g, incl. animals 40-45 g;
- general fats – 70-80 g, incl. vegetable 25-30 g;
- total carbohydrates – 300-350 g;
- dietary fiber (plant fiber) – 20-25 g.
Energy value 2170 - 2480 kcal.
Diet for chronic cholecystitis in remission
Outside the acute stage, according to the 2017 Medical Nutrition Standards, the chemical composition of dishes remains virtually unchanged, carbohydrate consumption and, accordingly, calorie content are slightly reduced:
- proteins – 85-90 g, incl. animals 40-45 g,
- general fats – 70-80 g, incl. vegetable 25-30 g,
- total carbohydrates – 300-330 g,
- dietary fiber (plant fiber) – 25 g.
Energy value 2170 - 2400 kcal.
The diet is enriched with vitamins C, group B, A, PP, K.
Review of usage reviews
It is impossible to get a competent answer to the question about the possibility of eating bananas for pancreatitis and cholecystitis, based on reviews. All information received should be discussed with your doctor. Patient reviews highlight the following advantages of the yellow fruit:
- excellent taste and aroma;
- the ability to improve the taste of other products (cookies, kefir, etc.);
- a quick way to satisfy your hunger;
- relief of mental and physical fatigue.
However, some people, after including the fruit in their diet, experienced a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and even nausea. This is probably due to excess consumption of the fruit, eating fruit before bed, or an incompatible combination of the product with other foods.
Products
Authorized Products
Products that are allowed to be consumed for cholecystitis should maximally relieve not only the gallbladder and liver, but also the stomach, pancreas, and intestines.
Allowed foods must be boiled, steamed or baked, but without crust. Eating vegetables and fruits in large quantities helps to utilize bile, move it through the bile ducts, and stimulate intestinal motility.
Prohibited Products
When following a diet for cholecystitis, a number of foods are prohibited, which not only cause a pronounced choleretic effect, thereby increasing the load on the inflamed bladder, but also force the entire digestive tract to work hard, which negatively affects both the functioning of the gallbladder and the body in in general.
Also, some of the prohibited foods contribute to the thickening and stagnation of bile, which can become a starting point in the formation of stones.
Products that enhance the processes of putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines, stimulate the formation of gastric juice, pancreatic secretions and irritate the liver are not recommended.
| Category | Forbidden | Allowed |
| Bread and pastries |
|
|
| Soups |
|
|
| Meat |
|
|
| Fish |
|
|
| Milk |
|
|
| Eggs |
|
|
| Side dishes |
|
|
| Vegetables and fruits |
|
|
| Fats |
|
|
| Seasonings |
|
|
| Dessert |
|
|
| Beverages |
|
|