Pain in the anus is the most common reason for visiting a proctologist. Unpleasant sensations can occur due to injury, infectious diseases and inflammation.
When establishing the cause of anorectal pain and prescribing treatment, the doctor must take into account the nature of the pain, under what circumstances pain appears (for example, in a standing position, sitting or during bowel movements), accompanying signs of pathology: itching, bleeding from the anus, a feeling of pressure and discomfort. Pain in the anus may indicate:
- trauma to the anus and rectum;
- hemorrhoids;
- venereal disease;
- paraproctitis;
- intestinal diseases;
- rectal cancer;
- rectal prolapse.
Rectal pain due to hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a common disease, a common symptom of which is anal pain. Hemorrhoids occur due to poor circulation in the venous plexuses of the anal canal. With hemorrhoids, the veins of the rectum become overfilled with blood, which leads to swelling of the vessels and surrounding connective tissue, followed by discomfort, including pain. In addition to pain in the rectal area, hemorrhoids may cause:
- feeling of pressure;
- itching and burning in the anus.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (USA), about half of people over 50 years old have hemorrhoids. The risk of disease is increased by constipation, hard stools, and strong labor during childbirth. If left untreated, hemorrhoids can enlarge several times and fall out of the anus, which is accompanied by increased pain and other symptoms. In advanced cases, hemorrhoids require surgical treatment.
Measures that can be taken before the ambulance arrives
Before the patient can see a doctor or an ambulance arrives, some measures can be taken to help make him feel a little better:
- Apply a bottle of ice, wrapped several times with a thin diaper, to the lower abdomen for abdominal pain of unknown etiology.
- If the patient has previously encountered such a problem and the doctor has prescribed rectal suppositories, they can be used during an exacerbation.
- If it is known that the cause of the pain that radiates in the anus is a spasm, then you can take an antispasmodic. A warm bath can also help, but for example, with hemorrhoids, it can cause heavy bleeding.
- For constipation caused by poor diet, you should drink as much water as possible. In an emergency, you can use suppositories or microenemas with stool softening substances. Long-term constipation leads to cracks and tears in the anus.
Sometimes the above measures help cope with unwanted symptoms
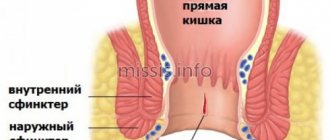
Anal fissure pain
Anal fissures are longitudinal tears (wounds, ulcers) in the mucous membrane in the anus. Anal fissures are accompanied by sharp pain during and after defecation, and can occur as a result of damage to the mucous membrane of the anus when:
- childbirth;
- circulatory disorders in the pelvic area;
- increased pressure in the rectum with sudden lifting of weights;
- diarrhea;
- anal sex;
- insertion of solid objects into the anus;
- passing hard stool during constipation.
Along with pain with anal fissures, small impurities of blood in the stool, a burning sensation in the area of the rupture of the mucous membrane, and itching may appear. If left untreated, anal fissures can become chronic and lead to long-term pain not only during and after bowel movements, but also during prolonged sitting.
Symptoms of chronic pelvic pain
The symptom of chronic pelvic pain is understood as periodically recurring or constant pain in the lower abdomen (in the sacrum, rectum, vagina) for several months or even years. The causes of chronic pelvic pain differ significantly from the causes of acute pain, which is why they are identified as a separate concept. Chronic pelvic pain is extremely common - affecting every sixth woman. Pain is relatively rarely caused by any one cause, but more often by a combination of various factors. Therefore, diagnostic and therapeutic methods are very diverse. There are also cases when obvious causes of pain cannot be identified, but even for such cases a specific treatment strategy has been developed, which requires mutual understanding and cooperation between the doctor and the patient.
Proctalgia
Proctalgia is a pain syndrome that occurs with muscle spasms in the rectum and anus. The duration of pain during the disease depends on the duration of the spasm. Painful attacks can last from a few seconds to several hours. The frequency of spasms during proctalgia can be influenced by defecation and its disturbances, and sexual activity. The pain can be sharp, sudden, and also intensifies when sitting.
Since painful attacks in most cases are short-term and end on their own, treatment is not carried out. With greater duration and frequency of pain, warm baths and local remedies to relieve spasm of the rectal muscles help reduce symptoms.
Signs of bowel disease
Pain in the lower intestines can appear not only with damage to the rectum, but also with diseases of the higher parts of the digestive tract. Rectal pain often accompanies rectal colitis and Crohn's disease, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Along with pain during a pathological process in the intestines, the following are observed:
- cramps and pain in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- bleeding from the anus or blood in the stool.
Sexually transmitted infections and anal pain
Sexually transmitted diseases do not always spread, but can spread from the genitals to the rectum, leading to pain. Pain in the anal area occurs when the intestines are damaged by the human papillomavirus, herpes, or chlamydia. Other symptoms that accompany sexually transmitted infections when they spread to the rectum include:
- itching and burning;
- liquid discharge from the anus;
- minor bleeding.
Rectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse is a disease that is diagnosed when the rectum partially or completely extends beyond the anus. The pathology is accompanied by pain and constant discomfort, which prevent the patient from leading a full life. The causes of rectal prolapse have not yet been established, but factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease include chronic constipation and straining during bowel movements, childbirth, and features of the anatomical structure of the pelvis and intestines.
Rectal prolapse progresses slowly and in the initial stages is characterized by only minor pain and a feeling of pressure in the anal area that occurs during bowel movements. As the disease develops, intestinal prolapse occurs with the slightest strain or without it, and the disease requires surgical treatment.
Causes of pain
Abdominal pain most often indicates pathologies associated with the gastrointestinal tract. Thanks to some symptoms, it is possible to make a correct diagnosis without additional diagnostics. So why do unpleasant symptoms occur?
Common causes of discomfort are:
- acute appendicitis;
- adhesive disease in the intestines;
- the presence of diverticula in the rectum;
- polypous growths in the lower intestines;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- helminthiases;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative inflammation of the colon;
- rectal cancer;
- acute intestinal infections.
Appendicitis
Acute, less often chronic inflammation of the appendage of the cecum. Until now, the exact cause of the pathology has not been determined. Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix are: severe pain in the lower abdomen, mainly on the right and extending to the anus or lower back, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
The inflammatory process is often accompanied by fever and a white coating on the tongue. In order to get rid of the inflamed appendix, a surgical operation is prescribed, during which the appendix will be completely removed.
Adhesive disease
A pathology in which adhesions form between intestinal loops. They can also appear between other organs of the abdominal cavity: liver, spleen, ovaries, uterus, etc. Most often, adhesions appear after surgical interventions, abdominal injuries, congenital anomalies, developmental defects, foreign objects and medications.
Signs of adhesive disease depend on the location of the adhesions; usually the pain is intense and occurs in the lower abdomen. It is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and both constipation and diarrhea may appear. The disease can be diagnosed using ultrasound. Treatment is carried out conservatively and surgically.
Polyps in the intestines
Benign neoplasms, which are protrusions on the surface of the mucous membrane, having different shapes. There are many reasons for their appearance in the gastrointestinal tract: long-term inflammation of the mucous membrane of organs, intestinal dyskinesia, chronic constipation, intrauterine malformations, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, heredity, infectious diseases and others.
Treatment of intestinal polyposis is only surgical, by excision of tumors
The most typical manifestation of polyps are the following symptoms: irregular bowel movements with alternating diarrhea and constipation, discomfort in the rectum, pain in the lower abdomen, feces with a high content of mucus, sometimes streaked with blood. The danger of polyps is that they have the ability to degenerate into cancer.
Crohn's disease
A chronic progressive disease of unknown etiology, characterized by granulomatous lesions of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract, from the oral cavity, esophagus and stomach, to the rectum.
Symptoms of Crohn's disease are diarrhea, a slight increase in temperature and general weakness, cramping abdominal pain of varying intensity, blood in the feces, ulcers on the mucous membrane, starting with the oral cavity, decreased appetite and weight loss, pain in the perineum and anus.
The danger of the disease lies in the development of complications that are difficult to respond to drug therapy: cancer of various parts of the intestine, fistulas, intestinal obstruction.
In our time, unfortunately, no treatment has yet been found that would help get rid of the pathology, but there is a set of measures that is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms, and even over a long period of time allows one to achieve remission.
Helminthiasis
Parasitic diseases caused by intestinal worms. Most often in the intestines these are roundworms and tapeworms. Parasites can enter the human body in several ways: through dirty hands, toys or food, water, or through contaminated meat that has not undergone normal heat treatment.
Over a long period of time, worms may not make themselves felt, but when they become significantly more numerous, the following undesirable symptoms may appear: abdominal pain after eating, which can radiate to the anus, bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea), nausea and vomiting , increased gas formation, bloating, itching in the rectum.
Treatment is carried out conservatively and surgically.
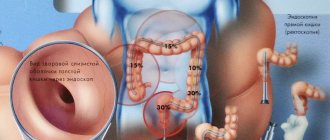
Rectal cancer
A tumor formation of atypical cells that is malignant in nature. There are many reasons why a tumor appears: chronic inflammatory diseases, hereditary predisposition, intestinal polyposis, Crohn's disease, etc.
With some diseases, you can see mucus and blood in the stool
At an early stage of its development, cancer may not manifest itself in any way; only general weakness, malaise and loss of appetite appear. Many patients do not even pay attention to these symptoms.
Over time, the tumor grows and other signs of a neoplasm appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the anus;
- the shape of feces resembles a ribbon;
- blood may appear in the feces;
- sensation of a foreign body in the rectum;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- pallor of the skin.
Treatment for cancer depends on the extent of the disease and includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Acute intestinal infection
A group of diseases characterized by a common route of transmission and location of pathogenic microorganisms. Infection usually occurs by eating unwashed fruits and vegetables, dirty water, and poor-quality food.
With almost all infections that affect the intestines, there is a rise in body temperature, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and pain in various parts of the abdomen. Treatment involves taking drugs that have antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal effects.
There are other causes of pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the anus and puts pressure on it. They are different for men and women. The following pathologies are most common among different sexes.
| In men | Among women |
| Urinary tract stones | Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs |
| Prostate cancer | Various ovarian pathologies |
| Inguinal or scrotal hernia | Ectopic pregnancy |
| Injuries of the genitourinary system | Threat of miscarriage |
| Malignant tumors of the rectum | Rupture of a cyst or abscess |
| Complicated hemorrhoids | Painful periods |
| Abnormalities of the genital organs (atresia) | |
| Ovarian hyperfunction before IVF | |
| IUD that did not take root |
Pain after anal sex
The sensitivity of the skin around the anus not only provides arousal, but can also cause minor injuries and pain during anal sex. Friction during sexual intercourse leads to the occurrence in the anus:
- irritation;
- swelling;
- bleeding.
Most often, injuries to the anus during anal sex occur due to the lack of its own secretion, which would facilitate the movement of the penis and reduce friction. Using enough lubricant in most cases prevents pain and makes anal sex as safe as possible.
Rectal pain as a symptom of rectal inflammation
Pain syndrome is one of the main signs of the inflammatory process in the rectum. Proctitis or inflammation of the rectal mucosa can occur against the background of various intestinal diseases, due to a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet and other reasons. In addition to pain, proctitis may be accompanied by:
- diarrhea;
- feeling of pressure in the anus;
- bleeding from the anus or blood in the stool;
- mucous secretions.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To prevent pain that appears under the influence of external irritants, you should choose comfortable underwear, take regular breaks during sedentary work, adjust your diet, and exercise enough to prevent constipation. The likelihood of accidental injuries can be reduced by avoiding unconventional sexual practices and self-medication.
Drug therapy is not indicated until the cause of the pain is determined. In case of general hyperthermia, intense pain, excessive bleeding, it is necessary to urgently consult a proctologist. If pain in the anus is accompanied by urinary disorders, you need to make an appointment with a urologist-andrologist.
Conservative therapy
To create conditions conducive to the treatment of proctological diseases, a man is prescribed a special diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, salty foods. If you are prone to constipation, you should increase the amount of plant fibers and ensure the possibility of comfortable bowel movements at certain times of the day.
If you have frequent diarrhea, it is recommended to avoid foods that stimulate motility, increase fermentation and gas formation. Preference should be given to steamed dishes. The drug therapy regimen for pain in the anus includes the following medications:
- Rectal suppositories
. Suppositories with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and softening effects reduce the severity of symptoms. Enveloping components provide protection to the mucous membrane from injury during the passage of feces. - Antibacterial agents
. Prescribed for acute inflammatory diseases, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory pathologies. Medicines are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. - Hormonal drugs.
To quickly eliminate swelling and inflammation, men with severe proctitis and complications of hemorrhoids are prescribed medications from the group of corticosteroids. - Phleboprotectors
. Used for chronic hemorrhoids. They strengthen the walls of blood vessels, slow down the progression of the disease, and reduce the likelihood of thrombosis and bleeding. - Local procedures
. In the acute phase, to increase the effectiveness of treatment, microenemas with painkillers, anti-inflammatory and emollient solutions are performed. After eliminating acute phenomena, use potassium permanganate baths and perineal showers. - Physiotherapy
. To eliminate burning and pain, men are prescribed laser therapy, diadynamic therapy, and ultrasound.
Drug treatment of prostatitis involves long-term antibiotic therapy. Non-drug treatments include prostate massage, ultrasound, laser therapy, and microenemas. For prostate cancer, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy are possible.
Paraproctitis
Paraproctitis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the tissue around the rectum and anus, which is accompanied by the discharge of pus. The disease is caused by bacterial pathogens and is accompanied by severe, acute pain. Pain syndrome with paraproctitis is often accompanied by:
- purulent discharge from the anus;
- swelling of surrounding tissues and irritation of the skin around the anus;
- false, painful urge to defecate;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness.
How to get rid of pain in the anus?
The most reliable way to eliminate pain in the anus is to identify and treat their cause. Different medications are used for different diseases to both relieve and eliminate symptoms. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to treat infectious diseases, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to eliminate inflammation, and laxatives are prescribed to ease bowel movements.
While treatment continues, you can relieve pain by taking warm baths for 15-20 minutes. To normalize bowel movements, prevent constipation and prevent excessive strain during bowel movements, you should adjust your diet by consuming more fluids and foods rich in fiber. You can also use local anesthetics, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic drugs to eliminate pain in the anus. In many cases, rectal pain does not last long and goes away on its own without the need for treatment.
Diagnostics
A specialist proctologist determines the etiology of pain in the anus. Men with prostate pathology are examined by an andrologist. Based on the survey and physical examination, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- Proctological examination.
Includes assessment of the condition of the anus, examination in rectal speculums, digital examination, and other techniques. Makes it possible to detect cracks, fistulas, signs of hemorrhoids, foreign objects, neoplasia, inflammatory infiltrates. - Rectal examination of the prostate.
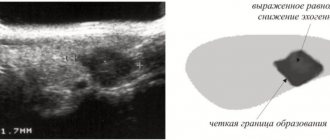
Indicated for suspected prostatitis or prostate cancer. During the procedure, the doctor determines the shape, size and structure of the prostate, identifies signs of inflammation, and space-occupying formations. - Ultrasound methods
. Patients are referred for transrectal ultrasound of the rectum to diagnose cancer, polyps, hemorrhoids, cysts, fistulas, and injuries. Ultrasound of the prostate can be performed transrectally or transabdominally; it confirms inflammatory changes, areas of calcification, and changes in echostructure characteristic of a cancerous tumor. - Endoscopic techniques
. Sigmoidoscopy and anoscopy are highly informative for erosions, ulcers, inflammatory processes, polyps, malignant tumors, fistulas, and internal hemorrhoids. It is possible to collect material for subsequent morphological research. - Anal manometry.
The technique is recommended for proctalgia, fecal incontinence, and other conditions accompanied by a decrease or increase in the tone of the anal sphincter. - Lab tests
. A general scatological examination is prescribed to identify signs of inflammation and bleeding, and to detect parasites. Based on the culture results, the etiology of the inflammatory process is determined. According to cytological or histological examination, the nature of the tumors is determined. - Other methods
. For diseases of the colon, plain radiography of the colon, colonoscopy, and biochemical analysis of stool are performed. In some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is required. A PSA test is recommended for men with suspected prostate cancer.