The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Intestinal infections are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms are characteristic of almost all inflammatory bowel infections.
Intestinal infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria and parasites, but viruses and bacteria remain the leaders among this group of pathogenic microorganisms. Treatment of intestinal infections is aimed at completely destroying harmful flora and restoring normal functioning of the organ.
Drugs are selected depending on the type of infectious agent. If the disease is caused by bacteria, then antibacterial drugs are required. Antibiotics are not simply prescribed for intestinal infections. First you need to determine the type of microbe that caused the disease. Then a test is carried out to determine the sensitivity of the bacteria to a specific drug. This allows you to prescribe etiotropic treatment. A doctor must prescribe medications.
What antibiotics are prescribed for intestinal infections?
To treat intestinal infections, there are several antibacterial drugs that have a wide spectrum of action:
- Cephalosporin.
Drugs from this group may have the following names: Cefotaxime, Cephabol, Claforan, Rocesim. Their structure is somewhat similar to penicillin drugs. The most common side effect from the use of cephalosporins is allergic reactions.
- Tetracycline.
Drugs in this group: Vibramycin, Doxycycline, Tetradox. They are quickly absorbed in the intestines, have a pronounced antibacterial effect, but can cause various complications, sometimes even causing deafness. Drugs from the tetracycline group are not used to treat children.
- Penicillin.
Drugs in this group can be found under such names as: Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Monomycin, etc. The spectrum of activity of these drugs is wide, they are destructive to most bacteria. Drugs from the penicillin group are prescribed to children and pregnant women if there is a real need for it. The most common side effects of drugs in this group are allergic reactions.
- Aminoglycosides:
Neomycin and Gentamicin.
They are prescribed for the treatment of severe diseases caused by bacterial flora. Drugs in this group are prescribed only for health reasons, as they have a toxic effect on the kidneys, liver and other organs. - Fluoroquinolone
.
Drugs in this group: Levofloxacin, Tsiprolet, Ofloxacin, Normax, Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, etc. These drugs affect the enzyme that is responsible for the synthesis of bacterial DNA, thereby destroying pathogenic flora. Fluoroquinolones are not prescribed to pregnant women, people under 18 years of age, or patients with pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. - Macrolides.
Drugs in this group are marketed under the names: Azithromycin, Roxithromycin, Erythromycin. Macrolides can be used to treat children, as well as pregnant and lactating women. They are prescribed when it is not possible to use drugs from the penicillin group.
- Levomycetin.
In the past, this drug was often prescribed to treat intestinal infections, but is now rarely used. The fact is that it has a destructive effect on human bone marrow.
Drugs of the penicillin group and aminoglycosides most often treat colds rather than intestinal diseases. For intestinal damage, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides are predominantly prescribed. Medicines from the tetracycline group can also be prescribed, but this is rarely done, only in severe cases of the disease, when there is a threat to the patient’s life.
Antibiotics for intestinal infections are used only in the form of injections. The duration of therapy is at least a week.
Infusion therapy of infectious-toxic shock (ITSH)
The main pathogenetic directions in the treatment of ITS are: restoration of blood volume and improvement of microcirculation.
I degree ITS . The following therapy is carried out: 1. Prednisolone - at a dose of 15 mg/kg body weight per day intravenously. 2. Heparin - 100-150 IU/kg body weight per day (first injection intravenously). 3. Glucose 10% solution - intravenously in a stream, then in the form of a glucose-potassium mixture by drip. 4. Reopoliglyukin - intravenously. 5. Protease inhibitors - every 6-8 hours intravenously. Contri-cal - 10-20 thousand units, gordox - 20-100 thousand units. in an isotonic solution.
6. Pipolfen 2.5% solution - 1-2 mg/kg body weight intravenously. 7. Antibiotics - i.v. 8. Eufillin 2.4% - 2-4 mg/kg body weight per day. 9. Droperidol 0.25% solution - 0.3 ml/year of life intravenously. 10. Lasix 1% solution - 2 mg/kg body weight per day intravenously.
II - III degree ITS .
The following therapy is carried out:
1. Glucocorticoids (prednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexazone) in a ratio of 3:2:1. The total dose of glucocorticoids for prednisolone is 50-75 mg and is administered intravenously over 4-6 hours, the first injection is 1/2 - 1/3 of the calculated dose, after 30 minutes. - another 1/3 dose, then drips under blood pressure control. At the same time, DOXA is administered - 0.1-0.5 ml 3 times IM.
2. Glucose 10% solution - intravenously in a stream, then dropwise in the form of a glucose-polarizing mixture, rheopolyglucin.
3. Heparin - 100 units/kg body weight per day (for ITS II degree) intravenously under the control of a coagulogram, followed by dose reduction or withdrawal (for ITS III degree).
4. Fresh frozen plasma - i.v. in a slow stream to create a concentration of antithrombin III in the blood at an age-related dose.
5. Protease inhibitors - IV drip in an isotonic solution every 6-8 hours.
6. Antibiotics - i.v.
7. Dopamine 4% solution - starting from 1-2-5 mg/kg body weight per minute IV drip.
For ITS in young children, it is not recommended to use saline solutions (Ringer's solution, isotonic sodium chloride solution, Acesol, etc.) due to the risk of hypernatremia and the development of cerebral edema. If there is a threat of cerebral edema, mannitol, reogluman, lasix, and euflllin are used. For infusion I use 2-3 veins.
Control of infusion therapy for acute intestinal infections.
The adequacy of infusion therapy is monitored according to the following criteria:
1. Persistent normalization of central venous pressure (CVP) within 50-100 mm water column (0.5-1.0 kPa). An increase in central venous pressure is accompanied by cerebral and pulmonary edema.
2. Normalization of hematocrit (an increase indicates hemoconcentration; a decrease in hematocrit may be a consequence of anemia or hemodelution).
3. Normalization of the color of the skin and mucous membranes, pulse rate, which indicates stabilization of hemodynamics.
4. Normalization of diuresis (oliguria requires a reduction in the volume of infusion).
5.The increase in body weight should be no more than 2-3% of the deficit per day.
Treatment with intestinal antiseptics
For intestinal infections, antiseptic drugs are often prescribed. They selectively act on pathogenic flora, but the intestinal bacteria’s own bacteria remain intact.
Intestinal antiseptics are destructive for most bacteria (staphylococcus, proteus, shigella, etc.). They can be prescribed to children and adults.
Such drugs include:
- Ersefuril (nifuroxazide). This drug can be prescribed to treat children over 6 years of age. Its action is aimed at suppressing the vital activity of the bacterial flora that populates the intestines. Ersefuril is prescribed for rotavirus infection and dysentery.
- Furazolidone. This is a time-tested antibacterial drug that is destructive against many harmful microorganisms (salmonella, shigella, etc.). In addition to the antibacterial effect, Furazolidone can improve the patient's immunity.
- Intetrix is a drug that allows you to destroy not only harmful bacteria, but also fungi and parasites. It can be used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of intestinal infections, for example, during hiking.
- Phthalazole is an antiseptic with a wide spectrum of action. It should be used with caution in children as it has side effects.
- Enterol is a drug containing live yeast that destroys harmful bacteria. Enterol contains protease. Thanks to this enzyme, toxins released by bacteria will be destroyed and will not harm the human body. Enterol also contains probiotics, which stimulate the growth of the natural microflora of the human intestine. A single dose of the drug is enough to feel the therapeutic effect. However, Enterol should not be combined with antibiotics or adsorbents. It has no contraindications, so it is prescribed for the treatment of lactating and pregnant women, as well as children.
Complications of antibiotic use
When using antibiotics, there is a risk of developing unwanted reactions. Such complications include:
- Hepatotoxicity – liver damage. Most often observed when taking moxifloxacin, macrolides, and clavulanate.
- Cardiotoxicity is damage to the heart. Such a reaction can occur when using fluoroquinolones, azithromycin, clarithromycin.
- Neurotoxicity is damage to the nervous system. Occurs with fluoroquinolones.
- Allergy . Characteristic of penicillins and cephalosporins.
In fact, the wider the spectrum of antimicrobial activity, the higher the risk of adverse reactions..
What antibiotics are prescribed for children with intestinal infections?
To rid a child of an intestinal infection caused by bacterial flora, antibiotics are required. At the same time, the drug must be as effective and safe as possible.
Drugs that can be prescribed to treat children:
- Penicillins: Amoxiclav, Amosin, Augmentin, Flemoxin solutab. These medications are the safest for treating children, although the risk of allergic reactions cannot be excluded. For therapy, it is best to use penicillins protected with clavulanic acid, since many bacteria have developed resistance to penicillins in their pure form.
- Drugs such as Suprax, Cephalexin, Zinnat have low toxicity and sufficient effect in the treatment of intestinal infections. However, they cannot be used to treat children during the neonatal period.
- Clarithromycin, Vilprafen and Sumamed are antibacterial drugs that have been used for many years to treat intestinal infections. They rarely cause allergic reactions, but are capable of destroying many bacteria.
- Enterofuril is used more often than other drugs to treat intestinal infections. Its active ingredient does not have a systemic effect on the body, “working” only in the intestines. This drug can be used to treat children older than one month and to treat pregnant women.
If the disease is mild, then there is no need to give the child an antibiotic; the use of intestinal antiseptics is sufficient. In cases of moderate severity, drugs such as Ampicillin or Amoxiclav can be used. Provided that the child is allergic to them, or there are any other contraindications to their use, it is possible to prescribe drugs from the group of macrolides, for example, Azithromycin.
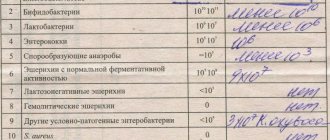
How much E. coli should there be?
Escherichia coli appears in the intestines from the first days of life. The amount of Escherichia coli with normal enzymatic activity throughout life should remain at the level of 107–108 CFU/g. If deviations from this value are observed during stool analysis, this is a sign of dysbacteriosis. Escherichia coli with reduced enzymatic activity (lacto-negative) is a sign of incipient dysbiosis and an indirect sign of the possible presence of worms or protozoa in the intestines. Exceeding its level of 105 causes infections of the urinary tract, abdominal cavity, intestines and upper respiratory tract. If the number of pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli exceeds, probiotics are used along with basic therapy.
Advantages and disadvantages of antibacterial therapy for intestinal infections
Taking antibiotics always carries the risk of side effects. Thus, women often develop thrush. There is a risk of dysbiosis, AAD (antibiotic-associated diarrhea), intestinal disorders, etc.
The advantages of antibiotics in the treatment of diarrhea include:
- Medicines act on the cause of the disease.
- The therapeutic effect is achieved in the shortest possible time, but only if the drug is selected correctly.
- Bacteria cease to have a toxic effect on the human body.
- Bacteria will be completely destroyed.
The disadvantages of treating intestinal infections with antibiotics include:
- They have a systemic effect on the body.
- Each drug has a number of contraindications.
- Many antibiotics cannot be used to treat children, pregnant women and nursing mothers.
- Antibiotics can cause side effects.
The role of Escherichia coli in the intestinal microflora
The number of Escherechia among other representatives of the intestinal microflora should not exceed the norm - 1%. These bacteria play an important role in the gastrointestinal tract. Escherichia coli with normal enzymatic activity is a direct competitor of opportunistic microflora. It, together with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, prevents its reproduction. E. coli is involved in cholesterol metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, helps the absorption of iron and calcium, promotes the hydrolysis of lactose, produces B vitamins, and produces antibiotic-like substances that inhibit the growth of pathogenic E. coli.
special instructions
The most effective and safe drug for the treatment of intestinal infections is Norfloxacin (Normax) and Levofloxacin. They can also be used to treat traveler's diarrhea, cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, salmonellosis, shigellosis, etc. However, Norfloxacin is not prescribed to children, nursing and pregnant women. It should be taken with caution by epileptics, people with atherosclerotic disease and gastric ulcers.
Many women use Enterofuril to treat their children. It is also prescribed by most pediatricians when an intestinal infection is suspected. This medicine meets all safety requirements and quickly brings relief to the child, relieving the severity of symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea.
Author of the article:
Danilova Tatyana Vyacheslavovna |
Infectious disease specialist Education: in 2008, received a diploma in the specialty “General Medicine (Therapeutic and Preventive Care)” at the Russian Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov. I immediately completed an internship and received a diploma as a therapist. Our authors
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is the term for resistance to antibiotics. Who is to blame for this? The main reason is the excessive and uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents. This applies not only to medicine.
Prescribing antibiotics should always be justified.
Causes
- Application in medicine. Unjustified prescription on an outpatient basis, in a hospital, self-medication (over-the-counter). The main emphasis is on counteracting the unjustified prescription of antibiotics in primary care (at the outpatient stage). For this purpose, clinical recommendations and algorithms for prescribing antibiotics to children are specially developed and implemented in practical healthcare. Also, through the media, explanations are provided to the population about the need for the judicious use of antimicrobial agents and the dangers of their independent use.
- Use of antibiotics in veterinary medicine.
- Application in the agricultural industry.
Symptoms
The main signs of the disease, regardless of the type of infection, are constant diarrhea. It is significantly different from the usual disorder. The stool is copious, liquid, and may contain blood and mucus. The urge is very frequent and does not bring relief.
Other symptoms may include:
- muscle weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- cutting pain in the abdomen;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- rumbling in the stomach.
In half of the cases, frequent vomiting, problems with urination, and dehydration are also observed. If the disease is mild, then these symptoms may not be observed, but in an aggravated situation, the symptoms may become more pronounced.