Why don't laxatives solve the problem of constant constipation?
When faced with constipation after an unusual dinner or as a result of stress, we think about laxatives. Indeed, in such a situation, a properly selected remedy relieves unpleasant symptoms, and we forget about the problem for a long time.
But chronic constipation requires thorough treatment, which cannot be reduced only to eliminating symptoms.
Many laxatives have an irritating and stimulating effect on the colon, and therefore quickly deal with the problem. But regular use of such drugs causes a decrease in intestinal tone, and it is no longer able to work independently. Intestinal motility decreases and metabolism is disrupted. A person increases the dose of a laxative, but the effectiveness only decreases. As a result, there is no cure for the cause of constipation.
Taking the drug in adults
It is better to take a laxative during breakfast.
If the doctor has not suggested another regimen, Duphalac is used by adults for constipation, 15-45 ml during the first dose, and 10-25 ml to consolidate the effect of using a laxative.
This medicine is used once, the best time to take it is in the morning, during breakfast. You need to drink it with plenty of liquid - tea, milk, water or fruit juice.
If this condition is met, the drug will enter the large intestine as soon as possible, where it will begin its activity. As soon as the desired effect is achieved, the dose of Duphalac is reduced.
Diagnosis of the causes of constipation
To properly treat chronic constipation, you need to determine the causes of its occurrence.
They can be different, so treating this problem requires an individual approach.
For some, it is enough to change their diet, but for others, treatment will be more thorough. A more thorough diagnosis may be required to rule out organic causes of chronic constipation.
Constipation can be a symptom of irritable bowel syndrome, colitis, ulcers, anal fissure, hemorrhoids, paraproctitis1.
If all these reasons are excluded, you may need to consult a neurologist or psychotherapist (to exclude psychogenic causes), as well as an endocrinologist (disorders of the endocrine organs can also cause constipation).
Pharmacological properties of Duphalac
The main effect of Duphalac is to activate intestinal motility and facilitate the excretion of feces. This property determines the secondary function of the medication - cleansing the body of toxins, harmful microorganisms and their metabolic products.
In addition, the product promotes better absorption of phosphates and potassium salts and the removal of ammonium, which has a toxic effect on the body.
The drug is broken down in the colon. The active component of Duphalac reduces the level of acidity, increases the contents in the intestines, and softens the consistency of stool. Thanks to this effect, the passage of feces is facilitated and the natural process of defecation is restored.
By normalizing bowel movements, the medication promotes excretion from the body:
- toxins;
- slags;
- nitrogen-containing products;
- ammonium;
- pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products.
Thus, Duphalac significantly reduces the risks of intoxication and the development of pancreatic and endotoxic shock.
Removing harmful bacteria helps restore the balance of beneficial microflora in the intestines and normalize digestion processes. The laxative also inhibits the growth of salmonella.
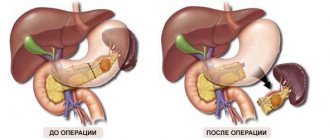
Effect on the pancreas
Constipation very often accompanies pancreatitis. This is explained by taking a large number of medications, painkillers, as well as a decrease in physical activity and forced fasting. The inability to promptly empty the intestines of accumulated feces significantly worsens the patient’s condition and leads to the development of symptoms such as:
- bloating;
- nausea;
- colic;
- increased gas formation;
- yellowness of the skin may occur.
The medication does not directly affect the pancreas and does not affect the production or activity of digestive enzymes. Duphalac for pancreatitis is prescribed to eliminate such a negative consequence of the disease as constipation, in order to normalize the natural process of bowel movements and accelerate the cleansing of the body from toxins.
Subsequently, its intake helps to improve digestion, prevent the development of pancreatic shock and create conditions for the restoration of the pancreas.
Whether Duphalac can be taken for pancreatitis is decided only by a doctor based on the patient’s medical history, symptomatic picture and characteristics of the course of the disease. Basically, the drug is prescribed only in cases where inflammation of the pancreas has led to severe constipation.
Composition of the drug
The active ingredient of the product is Lactulose. 100 ml of medication contains 66.7 grams of the active ingredient, the rest is water.
Cost and release form
The product is produced in the form of a solution (syrup) for internal use. The liquid may be colorless or light yellow and has no distinct taste.
The price of a 1000 ml bottle of syrup is 950-975 rubles, a 500 ml bottle costs 495-540 rubles, a 250 ml bottle costs 285-315 rubles. You can also find the product packaged in 15 ml sachets; a pack of 10 sachets costs 298 rubles.
Duphalac with a plum flavor recently appeared on sale; a 500 ml bottle costs 547 rubles.
Treatment of constipation
Non-drug treatment of constipation always begins with lifestyle changes: normalizing eating behavior and increasing physical activity.
It is worth following the following recommendations2:
- introduce more foods containing dietary fiber into your diet;
- drink at least two liters of water per day;
- eat at the same time in small portions, but often (at least 5 times a day);
- exclude pomegranate, some spices and spices (bay leaf, cloves, cinnamon), black tea, cocoa and red wines from the diet, because they contain tannin, which has a fixing effect. It is also not recommended to eat pureed, mushy food;
- increase motor activity. Walking and physical exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the abdominal wall not only increase the tone of the whole body, but also help to increase the motor activity of the intestines.
If non-drug methods fail, you can resort to laxatives. For chronic constipation, it is not recommended to take drugs that have an irritating effect for a long time, as this threatens to weaken the tone of the intestinal muscles.
Duphalac for children
Duphalac for infants is used in the form of syrup.
The only remedy approved by Russian pediatricians to relieve constipation in infants is Duphalac. Stool disorders are very common in children, and especially in babies in the first year of life.
Immature intestines and fragile unstable microflora are constantly at risk of imbalance between beneficial and pathogenic bacteria.
Digestive disorders, improper feeding, and poor quality food can disrupt the child’s well-being and cause constipation. The use of an enema is not advisable, since it causes reverse peristalsis and perpetuates hypotension of weak intestinal muscles.
Duphalac is not addictive, does not upset the electrolyte balance, and is not absorbed into the child’s blood. For children, especially infants, only one form of this laxative is applicable - syrup. Rules for taking Duphalac for children:
- Child from 0 to 12 months – dose is 5 ml.
- Child from one to 6 years of age - the initial dose is 10 ml, the maintenance dose is 5 ml.
- Child from 6 to 14 years old - the initial dose is 15 m. The maintenance dose is 10 ml.
It is best to take this anti-constipation remedy in the morning, immediately after a night's sleep. For infants, you can mix the required dose with milk or formula and administer the drug using a disposable syringe, after removing the needle. To achieve the best effect, you should not limit your child's fluid intake. On the contrary, it must be given in large quantities.
You can expect normalization of stool already on the second day from the start of taking the drug, although stool is possible after 2-6 hours. Any bloating should go away within 1-2 days without any additional measures. The dosage should be carefully observed to avoid side effects: diarrhea, intestinal colic. Before using Duphalac, consultation with a pediatrician is required, especially in order to eliminate constipation in infants and newborns.
Mild laxative Duphalac®
You should choose a laxative that not only eliminates the symptom, but also cures constipation.
Such a drug is Duphalac®, containing the active ingredient lactulose.
Lactulose enters the intestines unchanged and begins to act there, triggering the natural mechanism of intestinal cleansing. There is an increase in the volume of feces, a softening of stool consistency, and increased intestinal motility. In addition, lactulose promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria and normalizes the natural rhythm of intestinal cleansing.
Duphalac® can be taken by people of all ages, including newborns and pregnant women4.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis
Treatment of patients with intestinal dysbiosis should be comprehensive and aimed not only at curing the underlying disease and normalizing the microflora, but also at increasing the resistance and immunological reactivity of the body. It should be carried out taking into account the opportunistic microflora that caused the development of dysbacteriosis, contribute to the normalization of intestinal microflora, relief of motor disorders and inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa, elimination of toxic products from the intestine, restoration of disrupted types of metabolism.
The basis of therapeutic nutrition for dysbiosis are functional nutrition, probiotics, vitamins and microelements.
If during treatment with antibiotics a clinical picture of chronic enteritis or enterocolitis develops, antibiotics should be discontinued immediately. Fasting is prescribed for 1-2 days, which provides the intestines with complete functional rest, and promotes the rapid subsidence of the inflammatory process, deprives microorganisms of nutrition and leads to a decrease in their vital activity. To normalize the electrolyte composition of the blood, electrolyte solutions are given intravenously, corticosteroids and parenteral supplements are prescribed (protein hydrolysates, amino acid mixtures, glucose-insulin-potassium mixture).
Treatment complexes for patients with intestinal dysbiosis should be composed differentially depending on the severity.
With I-II severity of dysbiosis (reduction by 1-3 orders of magnitude in the number of bifidobacteria, lactobacilli and full-fledged Escherichia coli), clinical manifestations are absent or mild. To restore microbiocenosis, functional nutrition is recommended in combination with lactic acid products, vitamins and microelements (seaweed, spirulina).
Functional nutrition includes pectins and dietary fiber, i.e. prebiotics, the hydrolysis products of which are generally recognized in the homeostatic regulation of carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism. The microflora of the lower gastrointestinal tract plays a key role in the metabolic processes of the colon. The main substrate for bacterial fermentation is dietary fiber: polysaccharides of the plant cell wall, inorganic substances, protein complexes, as well as glycoproteins of the parietal mucus layer, descended epithelial cells. Under the influence of intestinal bacterial enzymes, dietary fiber is degraded to low molecular weight metabolites CO2, NH3, CH4, and volatile fatty acids, the amount of which depends on the level of fermentation of polysaccharides by intestinal microflora. Bifidobacteria play the largest role in the hydrolysis of polysaccharides.
Short-chain fatty acids are rapidly absorbed, stimulating the simultaneous adsorption of sodium and water, as well as the entry of bicarbonates into the intestinal cavity. One of them - butyrate - acts on DNA synthesis, proliferation and trophism of colonocytes, the other - propionate - is involved in lipogenesis, gluconeogenesis, amino acid synthesis and cholesterol metabolism.
Amino acids provide great metabolic support for the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, arginine exhibits anabolic and immunostimulating effects, glutamine is a source of synthesis of nitrogen, purine, and macroergs.
During bacterial fermentation of dietary fiber, the components of their hydrolysis (short-chain fatty acids, membrane phospholipids, complex proteins) in the colon contribute to the restoration of microbial associations, colonization resistance, intestinal immune status, epithelial proliferation and mucus secretion. Low molecular weight metabolites affect not only the function of the intestinal epithelium, but also the body as a whole - thermoregulation, immune status. This explains the advisability of using functional nutrition as a basic therapy, which is a modern physiological approach to correcting the microbial biocenosis of the colon. The source of pectin and dietary fiber is cereals (bran), root vegetables (beets, carrots), cabbage, fruits, mushrooms, and algae.
In order to ensure the stability of the microbial balance, in addition to the above therapy, it is recommended to use dairy products (kefir, yogurt, cheeses, cottage cheese, butter) enriched with active lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
In case of III severity of dysbiosis (significant suppression of bifidobacteria up to 105-106 and lactobacilli), the treatment complex includes functional nutrition and probiotics (bifi-form, hilak-forte), which are prescribed differentially depending on the nature of the intestinal microbiocenosis disorders. Their sanitizing and restorative effect on the intestinal microbial balance is due to the production of antibacterial substances that inhibit the growth of potentially pathogenic bacteria and their high adhesion ability. This increases the colonization anti-infective resistance of the intestinal barrier and stimulates its lymphoid apparatus.
In case of IV degree of dysbiosis (absence of bifidobacteria, significant decrease in the number of lactobacilli, profound changes in the quantitative ratios of obligate and facultative microorganisms, accumulation of entero- and cytotoxins), in addition to functional nutrition and probiotics, antibacterial therapy is indicated. At the same time, it is necessary to clearly understand what antibacterial drugs should be used to restore intestinal microbiocenosis, since their administration against the background of already developed dysbacteriosis can increase the degree of its severity or contribute to the “transfer” of one type to another. It has been established that the use of antibiotics suppresses the viability of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, their adhesive properties and antagonistic activity. In addition, antimicrobial therapy reduces colonization resistance of the intestine, increases the permeability of the intestinal wall, facilitating the penetration of protein macromolecules and opportunistic microorganisms into the internal environment of the body.
Diet is important. Its main purpose is to provide adequate nutrition in case of digestive disorders, normalize the functional state of the intestines and other digestive organs often involved in the pathological process (liver, biliary system, stomach, duodenum, pancreas), stimulate natural immunity and regeneration processes, normalize metabolism, reducing the degree of degenerative processes in organs that arise from digestive disorders in the small intestine.
The diet should be indifferent, low-slag, non-irritating, but containing a sufficient amount of proteins (at least 120-140 g), fats (up to 100-120 g) and carbohydrates (300-450 g), i.e. complete with more or less pronounced mechanical and chemical sparing, depending on the stage of the disease.
During the period of exacerbation, diet No. 4 is prescribed (for 2-5 days), with a subsiding exacerbation - diet No. 46, with developing remission - diet No. 4c, during the period of remission - diet No. 15. For persistent constipation, mild abdominal pain and gastric manifestations They recommend a diet with an increased amount of food stimulants of peristalsis (diet No. 3).
The duration of use of diets should be strictly individualized and determined by the patient’s condition and concomitant pathology. Nutrition should be varied and balanced. If you are intolerant to certain foods, you should exclude them from your diet.
Main products: boiled lean meat, fish, buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, white stale bread, noodle products, bran, pectin-containing products (boiled beets, baked apples, raw grated carrots).
During fermentation processes, carbohydrates, milk, and fiber are limited, especially in raw form. Boiled protein products, broths, fish soup, and eggs are prescribed. Decoctions of mint, chamomile, lingonberry, barberry, izil, rose hips, calendula, sage, raspberries, and strawberries are recommended. Use aur leaf and cloves.
For putrefactive dyspepsia, meat and fats are limited, and vegetable dishes are recommended throughout the week. Herbs and plant products that suppress putrefactive processes include apricot, currant, rowan, cranberry, lemon balm, caraway, and wormwood.
For fungal dysbacteriosis, capsicum and lingonberries are recommended.
The most physiological effect is on the intestinal microflora through food. All of the above is of auxiliary importance in the treatment of patients with intestinal dysbiosis. The development of certain types of dysbiosis (seasonal, food, age-related) can be prevented, and its course in a number of diseases can be alleviated by prescribing a balanced diet. Refined foods adversely affect the intestinal microflora. A monotonous diet and bland diets can contribute to the development of intestinal dysbiosis.
Mechanically and chemically gentle food should be used only in cases of severe pain, as well as candidiasis and staphylococcal enterocolitis. The use of vegetables, fruits and plants that have antimicrobial activity is important.
Many antibacterial substances isolated from plants stimulate the body's immunobiological reactions and inactivate bacterial exotoxins and hyaluronidase.
The following fruits and berries have the most pronounced antibacterial effect.
Apricot.
Has a bactericidal effect on putrefactive bacteria, Proteus,
Pseudomonas.
Barberry.
The antimicrobial effect is due to berberine; significant activity is noted against staphylococci, streptococci and dysentery bacteria.
Cowberry.
Fresh and autoclaved juice (whole and diluted), inhibits the growth of
Candida fungi.
Pomegranate.
Sweet pomegranate juice inhibits the growth of dysentery bacteria. Pomegranate peel powder is taken to treat diarrhea.
Wild strawberry.
The essential extract of the fruit is most active against staphylococcus.
Cranberry.
The berries have a bactericidal effect on enteric typhus and putrefactive bacteria. Cranberry juice increases the activity of penicillin.
Raspberries.
The fruits and leaves have antibacterial properties against staphylococci.
Rowan.
Parasorbic acid exhibits a bactericidal effect.
Staphylococci are sensitive to this acid, Candida fungi are insensitive.
In what cases is a laxative prescribed?
The product can be used in the following cases:
- Constipation.
- Softening the consistency of stool.
- Encephalopathic liver damage in adults.
The product can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The effect of the active ingredient on the body's systems is minimal, so the drug will not harm the health of the expectant mother, the fetus, or the infant.
Contraindications to taking the medicine
The medication is contraindicated for use when:
- Intestinal obstruction.
- The formation of through holes in the gastric tissues, intestines, pancreas and other organs of the digestive tract.
- Lactase deficiency.
- Intolerance to fructose, galactose.
- Intolerance to the components of the drug.
With caution, the medication should be prescribed for bleeding from the rectum, colostomies, ileostomies. If, after using the drug, pain of unknown etiology begins or the medication does not produce results, you should consult a doctor.
If the patient has diabetes mellitus, this dose increase should be approached with caution, since Duphalac contains sugars.
For children, medication can only be prescribed by a doctor, and therapy should be carried out under his supervision. At the same time, you need to understand that during the treatment process, infants may experience disruption of the natural process of defecation.
Development of side effects
Basically, the medication is well tolerated by the body. Lactulose is absorbed exclusively by the walls of the large intestine and, with small doses of consumption, is completely metabolized, and with a large dosage, the residues are excreted in the feces.
Among laxatives, Duphalac is considered one of the most harmless. The most common side effect of taking the medication is diarrhea. After all, the drug is designed to create conditions to facilitate bowel movements.
In case of personal intolerance or violation of the rules of administration, the drug can cause:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- flatulence;
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- Occasionally, the use of Duphalac leads to disruption of water and electrolyte balance.
This adverse reaction usually occurs if the medication causes severe, prolonged diarrhea or is used for a long time, or the patient drinks too little fluid during treatment.
In case of overdose, prolonged use of the drug may cause diarrhea and abdominal pain. With such symptoms, the amount of medication should be reduced or its use should be stopped completely for a while. At the same time, it is important to maintain water balance and drink at least 2-2.5 liters per day to prevent the risk of dehydration.