Anal fissure: definition, course, localization
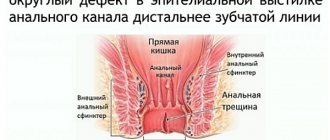
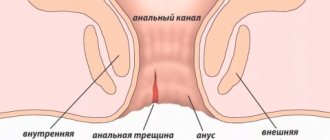
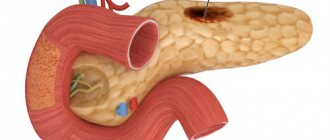
An anal fissure or anal fissure is a defect in the form of an ulcer or wound that occurs at the border of the skin of the anorectal area and the rectal mucosa.
The shape of the wound can be linear, elliptical or triangular. Depending on the location, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- posterior fissure (the patient lies on his back) – the wound is located in the midline on the posterior wall of the anus;
- anterior fissure - the ulcer is localized on the anterior wall of the anus, more typical for women;
- “mirror” fissure is a fissure localized simultaneously on the anterior and posterior walls of the anus.
The length of the wound, as a rule, does not exceed 10 mm, in rare cases it reaches 20 mm. A newly developed anal fissure is called acute, and in most cases the disease disappears after constipation or diarrhea is eliminated. If the wound exists for a month or more, they speak of a chronic anal fissure, which looks like a wound with thickened edges (overgrowth of connective tissue) and granulations at the bottom of the ulcer.
Early rehabilitation after surgery
Regardless of the chosen method of operation and anesthesia technique, after surgery, a tampon soaked in medicinal ointments is installed in the anus.
Then, throughout the early postoperative period (the first 2-3 days), dressings are performed daily. Gauze bandages soaked in levomekol ointment are applied to the anus.
Inpatients are advised to begin getting out of bed and walking the day after surgery. A slag-free diet is also prescribed (if there are no contraindications, a “chocolate” diet). The purpose of such a diet is to delay bowel movements for better wound healing.
From the third day, the diet expands, foods containing dietary fiber that stimulate bowel movements are prescribed. If on the third day it is not possible to achieve independent stool, a cleansing enema is used.
Why does the disease occur?
The development of anal fissure is caused by reasons that provoke increased tone of the anal sphincter. An anal fissure most often appears after:
- constipation (injury to the anal mucosa with hard feces);
- diarrhea, inflammatory processes in the rectum and anus;
- childbirth (tears in the anal canal mucosa during pushing);
- lifting heavy objects (creating increased pressure in the rectum);
- damage to the anal canal mucosa by foreign objects (enemas, medical instruments);
- anal sex.
Physical inactivity, sedentary work, heavy physical labor, hemorrhoids, alcohol abuse and adherence to spicy foods (provokes constipation) predispose to the development of the disease. There is also a high risk of anal fissure in people with thrombophlebitis, obliterating atherosclerosis, aneurysms, vasculitis, chronic pathology of the digestive tract (gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers).
Causes of pathology
There are several causes of the disease, and very rarely only one phenomenon plays a role in the formation of a crack. In most cases, the cause of pathology is a whole complex of disorders:
- insufficient blood circulation in the pelvic organs, which lead to changes in the condition of the mucous membrane;
- injury to the rectal mucosa;
- dietary errors leading to systematic constipation;
- hemorrhoids and other intestinal diseases.
Anal fissure: symptoms
The leading complaint of patients with a recent fissure in the anus is pain. It appears at the beginning of defecation, is very intense and persists for a long time after bowel movement. The pain can radiate to the perineum and sacrum. Since the pain is quite severe, patients delay defecation as long as possible, which aggravates constipation.
The second characteristic sign of pathology is bloody discharge from the anus. The blood is bright scarlet and may be present in the stool in the form of streaks or traces on toilet paper. Bloody discharge is caused by trauma to the mucous membrane during defecation. Significant bleeding during bowel movements indicates the presence of hemorrhoids or a rectal tumor.
A chronic anal fissure, when the wound itself has granulated and its edges have hardened, is characterized by the appearance of pain after bowel movement. Moreover, such pain persists much longer than during an acute process and intensifies in a sitting position. Bloody discharge is either absent or minimal. But a typical sign of a chronic anal fissure is sphincterospasm, which complicates the process of defecation and aggravates constipation. Due to spasm of the anal sphincter, patients develop “stool anxiety” (fear of relieving themselves due to pain). Constant pain and fear of impending bowel movement significantly worsen the quality of life of patients. They become irritable, emotionally unstable, and have trouble sleeping. Also, the chronic process in a small percentage of cases is complicated by itching of the anorectal area, more so in the area of the fissure.
Indications and contraindications
When suppositories and other therapeutic agents fail to have the desired effect, the patient will be sent to solve the problem using a radical method. It is the absence of positive dynamics with drug therapy that is considered the most important indication for manipulation.
If you do not help the patient at this stage of the pathology, then the acute period will become a provocateur of the chronic course of the disease. Then the treatment will last for a longer period. When it becomes clear that the crack is not healing, you should make an appointment with a surgeon.
If this is not done, then the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process with purulent complications increases several times. In the worst case scenario, you can wait until the surrounding tissues and mucous membrane of adjacent organs are damaged. Despite the fact that excision is the most optimal method of treatment, it has several significant contraindications:
- extensive bleeding;
- infectious lesion;
- skin diseases;
- viral disease.
Here you will first have to get rid of the reason for the ban on the intervention, and only then go to undergo clinical testing to receive a referral for surgery using the radio wave method or some other method.
How is an anal fissure diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the disease is not difficult.
Typical patient complaints and examination of the anorectal area can reveal a mucosal wound. In some cases (if the fissure is small and located deep in the anal canal), a digital examination is performed, which allows us to identify sphincterospasm. If there is a visible defect in the mucosa, digital examination is not recommended (the risk of additional injury to the mucosa is high). In the presence of an acute anal fissure, severe pain and sphincter spasm, instrumental diagnostic methods are contraindicated; they are performed only according to strict indications (heavy bleeding, suspected tumor, proctitis, suppuration). In this case, sigmoidoscopy is performed, but only after the wound mucosal surface has healed.
Mandatory training
To ensure that the applicant is not overtaken by any serious complication, he is sent for tests before surgery. It’s not for nothing that such an operation is called elective. The standard test package includes:
- blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry, as well as examination of the quality of its coagulation;
- testing for HIV, viral hepatitis, syphilis;
- fluorography of the lungs;
- electrocardiogram;
- therapist's conclusion.
Sometimes permission from a gynecologist is also required if we are talking about women. The most difficult thing begins when, during the initial examination, it turns out that the crack is not the only lesion in the specified area. To exclude the risks of other anomalies, the patient may be sent to undergo sigmoidoscopy. This is the name for the study of the sigmoid and rectum. This is necessary to confirm the absence of related pathology.
If the proctologist suspects that the primary source of the fissure is problems with the organs of the digestive tract, then to exclude damage to the large intestine along the entire length, you will have to undergo a colonoscopy.
Sometimes proctological defects are “side effects” of a neoplasm. To check whether there is a benign or malignant tumor with or without metastases in the intestine, you need to use irrigoscopy. Much less often, the patient is sent for profilometry, which is necessary to eliminate the risks of dysfunction of the obturator function of the rectum.
But usually the proctologist limits himself to more standard areas such as ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, as well as culture of discharge from the wound surface. The latter is necessary in order to identify pathogenic microflora from the inflamed crack itself.
Anal fissure: treatment
Therapeutic measures are carried out by a proctologist, who, after examination and diagnosis, will decide how to treat an anal fissure.
The goals of treatment are to numb the wound in the anorectal area as much as possible, relax the anal sphincter, normalize the patient’s stool and achieve complete healing of the fissure. Conservative therapy is carried out for newly formed cracks, its effectiveness reaches 70%. First of all, they start with correcting the patient’s diet. A diet is prescribed that activates the intestines, which helps ease bowel movements. The diet should contain a lot of plant fiber and fermented milk products. It is important to exclude spicy, too salty foods, various seasonings and alcohol. To eliminate constipation, it is recommended to include beets and dried fruits (dried apricots, prunes, dates, figs) in your diet. Dried fruits are pre-soaked in boiling water. Beets can be consumed either raw, grated, or boiled, in the form of a salad with sour cream or vegetable oil.
Conservative therapy also uses medications with local and general effects. Local treatment includes warm baths with a weak (pink) solution of potassium permanganate for 15 minutes three times a day, nitroglycerin ointment (relaxes spastic sphincter), Botox (also relieves sphincterospasm), suppositories with ointments containing anesthetics (novocaine, lidocaine). To accelerate the healing of cracks, methyluracil and sea buckthorn oil are used. Laxatives and calcium channel blockers (Corinfar) are included in general treatment. They facilitate defecation and eliminate sphincterospasm.
Surgical treatment is carried out according to indications:
- pronounced cicatricial changes in the “old” crack;
- significant spasm of the anal sphincter;
- lack of effect from conservative therapy.
Excision of the anal fissure is performed in parallel with dissection of the section of the internal sphincter of the rectum. Thus, two effects are achieved: elimination of the mucosal defect and relaxation of the sphincter. The former anal fissure heals better after surgery, and dissection of the sphincter muscle does not cause fecal incontinence.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is a logical step after it becomes clear that alternative methods do not bring long-awaited relief. Its volume will depend on many factors, including the degree of neglect of the disease and the characteristics of its course. Also, the volume and outcome of treatment can be affected by the specific type of operation, which differs in the medical instruments used. Because of this, only the attending physician can say exactly what kind of professional help will be needed in such a delicate matter.
Schematically, the classification of excision techniques is as follows: surgical intervention and minimally invasive procedures, which can be performed in different ways. The division is based on the device used for treatment, providing the following types:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser treatment;
- electroradiosurgical coagulation.
Regardless of the choice made, the patient will spend no more than 15 minutes on the medical couch. In this case, the patient himself will be able to choose where the intervention will be performed. If he was taken to the hospital emergency department, the operation will take place within its walls. But almost any private clinic offers to go home almost immediately after the procedure.
Before the operation, no matter how it is carried out, it is necessary to undergo a preliminary examination and obtain the results of clinical studies, as well as the opinions of specialized specialists. During the preparatory stage, the doctor will also explain how to properly maintain the diet and what hygienic measures should be preferred.
Prevention of anal fissure
To prevent the occurrence of anal fissure, following simple rules:
- adherence to proper nutrition (refusal of spicy, fried foods, pickles, marinades, as well as alcohol. Consumption of foods rich in fiber);
- maintaining personal hygiene (regular washing of the anorectal area);
- maintaining an active lifestyle (regular walks, physical exercise every 15 - 20 minutes during sedentary work);
- drinking enough fluid (at least 1.5 - 2 liters per day);
- avoiding eating too cold or hot food.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner in case of complaints, you can achieve favorable results without resorting to surgery.
And compliance with preventive measures will allow you to forget about the problem or the likelihood of its occurrence forever. Text: Anna Sozinova