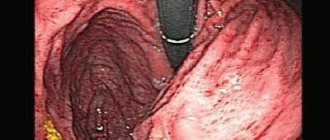
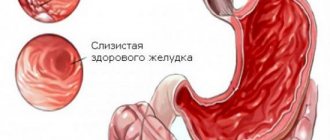
A special case of hypertrophic gastritis, inflammation of the stomach, combined with various disorders of the digestive functions, is considered “granular” gastritis, which received its name because of the characteristic tubercles in the inner surface of the stomach. Unfortunately, recently there has been an increase in clinical cases of the disease.
Granular gastritis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the gastric mucosa with the appearance of small growths - “grains” located throughout the internal area measuring several millimeters in height and a circumference of up to a centimeter, with folds between them. As the disease progresses, the number of tubercles increases, gastric juice and digestive enzymes accumulate between the formations, leading to the destruction of the mucous membrane and walls of the stomach. Granular gastritis occurs mainly in men over forty years of age and causes the development of serious diseases: stomach ulcers, even cancer. In addition to the above, granular gastritis can provoke swelling of the mucous membrane, metabolic disorders, and digestive disorders. In especially severe forms, internal bleeding develops, causing death.
Inflammation of the stomach with growths
Types of granular gastritis
Medicine classifies granular gastritis into a number of main forms. Let's look at each of them briefly.
Granular antral gastritis
Granular antral gastritis is the least common type, occurring in three out of ten cases. During an exacerbation, the patient experiences an abundance of mucus in the stomach, digestive disorders and narrowing of the antrum, severe swelling of the mucous membrane and increased acidity.
Granular hyperplastic gastritis
When suffering from granular hyperplastic gastritis, the patient develops small tubercles and the gastric folds become coarser. The posterior inner side of the stomach and the antrum are especially affected. The type develops asymptomatically and is manifested by heaviness in the stomach, increased frequency of heartburn attacks, and belching.
Why does it happen?
Chronic hyperplastic gastritis can result from internal and external causes. First, let's talk about exogenous factors:
- starvation;
- radical diets;
- abuse of fatty meat foods;
- bad habits: smoking, alcoholism;
- intoxication with acids and alkalis;
- taking certain medications.
..
With food, substances that corrode the mucous membrane can enter the stomach. If poor nutrition becomes a way of life, the cells of the mucous membrane do not have time to recover and the regeneration process is disrupted.
Fasting can be one of the causes of the disease
The disease can also occur under the influence of endogenous causes:
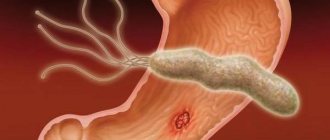
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- endocrine disorders;
- reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach;
- autoimmune processes;
- genetic predisposition;
- trophic changes in tissues.
People with food allergies, vitamin deficiency and kidney disease are at risk. It has also been found that long-term use of drugs that block the production of hydrochloric acid can lead to cell proliferation.
Reasons for appearance
It is impossible to name the exact cause of granular gastritis. External causes of gastritis include, first of all, improper and irregular nutrition, alcohol and smoking abuse, and incorrect, excessively frequent and abundant intake of medications.
Internal causes include nervous fatigue, frequent stress, diseases of the endocrine system, critical deficiency of vitamins in the body. These include the development of pathogenic bacteria, infections and excessive exposure to radiation in very rare cases. There may be a hereditary predisposition to granular gastritis.
Symptoms
Typically, granular gastritis is asymptomatic in the early stages, but later manifests itself with many symptoms:
- Pain in the upper abdomen, especially on an empty stomach.
- Attacks of nausea, heartburn and vomiting.
- Increased belching.
- Increased secretion of stomach acid.
- Bloating.
- Attacks of diarrhea or, conversely, constipation, flatulence.
- Weight loss.
- Loss of appetite in rare cases.
- Increased salivation.
- General weakness and sleep disturbances.
Characteristic signs
Symptoms of hyperplastic gastritis may vary depending on the type of disease. Nevertheless, for all types of stomach inflammation, the initial manifestations are very similar; patients complain of a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region. For a long period of time, the pathological process is asymptomatic.
What pain occurs with gastritis of the stomach?
As the disease progresses, the following complaints from patients appear: nausea, heartburn, severe pain in the abdominal area, aching pain can radiate to the area of the shoulder blades, lower back, chest, bloating, heaviness after eating.
There is a feeling of fullness in the stomach, vomiting of food debris, belching with an unpleasant odor, coating on the tongue, general malaise: weakness, increased fatigue, slight increase in temperature. With erosive changes in the mucous membrane, pain may intensify when walking and bending the body. In the autumn and spring, exacerbations occur.
Blood may be present in vomit and feces. Some patients note a decrease in appetite and weight loss.
Patients complain of heaviness and pain in the epigastrium
Methods for diagnosing granular gastritis
Granular gastritis is diagnosed using ultrasound, probing and fibrogastroscopy with biopsy. An ineffective diagnostic method is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS), since with such an examination the gastroenterologist-endoscopist can clearly see neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the stomach wall. FGDS shows the location of the “grains”, their size and quantity. During the procedure, a special tube with a video camera is used that films what is inside the stomach - a fibrogastroscope.
In addition to X-ray examinations and FGDS, diagnostic tests are also used to detect Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Modern research claims that these bacteria do not serve as causative agents of gastritis, but act as a factor predisposing to inflammation of the stomach. Moreover, the bacterium is easy to detect in the stomach secretions of healthy people. To examine the body for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, a stool test is used, which is then examined in the laboratory for antibodies. In addition to stool analysis, doctors use a breath test - a study of exhaled air after the patient has taken a special drug. Thus, these studies can detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori. If the test result is positive, in the treatment of granular gastritis, among other things, antibacterial treatment is used, aimed at creating an unfavorable environment for the life and reproduction of bacteria.
In addition to all of the above, esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy is used to diagnose granular gastritis; during the study, gastric secretions are collected for bacteriological examination. If necessary, during EGD, the doctor collects tissue material from the growths for subsequent histological examination. If probing is contraindicated for the patient, an acid test is used to determine the acid level. This is a urine test for acidity levels. The patient first takes a specialized drug.
Chronic hypertrophic polyadenomatous gastritis (Ménétrier's disease)
Blood tests reveal a decrease in the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin, associated with obvious or hidden blood loss, but severe anemia is detected in patients with Ménétrier's disease relatively rarely. Neutrophilic leukocytosis is sometimes observed. ESR and platelet count in the blood are most often within normal limits.
In a biochemical study, 70-80% of patients experience a decrease in albumin levels. The occurrence of hypoalbuminemia is facilitated by a significant loss of protein with gastric juice, which is confirmed by the detection of labeled albumin in the gastric juice, previously administered intravenously. The loss of protein from gastric juice is in turn associated with an increase in the permeability of the gastric mucosa. Not all authors, however, agree that hypoproteinemia is a characteristic sign of Ménétrier's disease, and believe that a decrease in albumin levels in the blood serum is found only in patients with severe edema.
The secretion of hydrochloric acid in Ménétrier's disease is most often reduced, which is explained by a decrease in the mass of parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. Serum gastrin levels may be normal or slightly elevated.
X-ray examination is of great importance in the diagnosis of Ménétrier's disease , which makes it possible to identify changes characteristic of this disease. The folds of the gastric mucosa in a limited area or over a significant extent turn out to be sharply thickened, tortuous, and swollen. The interfold spaces are significantly expanded. The folds of the gastric mucosa can be so hypertrophied that sometimes, when the stomach is tightly filled with a suspension of barium sulfate, they give the picture of a “filling defect,” thus simulating a tumor lesion of the stomach. However, the arrangement of the folds of the mucous membrane maintains a certain order, and their breakage in Menetrier's disease, as a rule, is absent. The walls of the stomach remain elastic, peristalsis is clearly visible along both curvatures. When the stomach is distended with an additional portion of barium sulfate suspension, stretching of the folds of the mucous membrane is observed, which makes it possible to differentiate hypertrophic polyadenomatous gastritis with the “frozen” relief of the mucous membrane during tumor infiltration of the stomach wall. More accurate diagnostic data can be obtained with parietography, which allows not only to determine the thickness of the wall and contours of the stomach, but also to study in detail the relief of the mucous membrane.
Endoscopic examination plays an important role in recognizing Ménétrier's disease . The endoscopic picture observed in this case is characterized by the presence of sharply thickened folds of the mucous membrane (mainly in the body of the stomach along the greater curvature), taking the form of cerebral convolutions or “cobblestones”. The folds often appear pale and swollen, but they can also have a normal color, and sometimes even be hyperemic. The mucous membrane of the stomach in Ménétrier's disease is characterized by slight vulnerability; erosions are often found at the tops of the folds. Hypertrophied folds are located mainly in parallel, less often - transversely or chaotically, their height is at least 2-3 cm. The total number of folds most often remains normal, and only in rare cases does it increase.
The method of dosed inflation of the stomach with air, which makes it possible to objectify the results of endoscopic examination, helps to distinguish Menetrier's disease from the usual forms of hypertrophic gastritis. At the same time, it is advisable to classify as giant folds those folds of the gastric mucosa that do not straighten when the pressure in the stomach is more than 15 mm Hg. Art.
Targeted biopsy does not have much diagnostic value in Ménétrier's disease, since it allows one to obtain material only from the most superficial part of the mucous membrane, while its altered glands usually do not get into the biopsy sample. However, thanks to a targeted biopsy, in some cases a tumor lesion of the stomach is detected. Using the aspiration biopsy method, it is possible to obtain large areas of the mucous membrane for histological examination, often including those layers where the gastric glands are located. This sometimes allows the diagnosis to be confirmed histologically. At the same time, the aspiration (“blind”) biopsy method produces a significant percentage of errors, since the biopsy material may not be taken from the areas where the pathological process exists.
Due to the fact that morphological verification of Ménétrier's disease is not always possible, the final diagnosis is often made only through dynamic monitoring of patients and repeated X-ray and endoscopic examinations.
Differential diagnosis . Ménétrier's disease is differentiated from ordinary hypertrophic gastritis, gastric polyps and common familial polyposis, gastrointestinal tract (Peutz-Touraine-Jeghers syndrome, Cronkite syndrome - Canada), benign and malignant tumors of the stomach, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, gastric lesions in tuberculosis and syphilis. The correct interpretation of clinical signs as well as the results of radiological, endoscopic and histological examinations is crucial.
Particularly difficult in many cases is the differential diagnosis of Ménétrier's disease and gastric cancer. In doubtful cases, it is necessary to re-examine the patient after 1-1.5 months or immediately perform a trial laparotomy so as not to miss a stomach tumor. Surgical biopsy allows you to take areas of sufficient size for examination, which ensures the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Therapeutic treatment
Like most other diseases, granular gastritis is much easier to cure in the early stages, so if symptoms are detected or become more frequent, it is not recommended to postpone a visit to the doctor. Otherwise, episodic attacks can turn into chronic granular gastritis with many complications; treatment is expected to take significantly longer and is much more difficult, both for the gastroenterologist and nutritionist, and for the patient himself.
During the therapeutic course, the patient needs to give up bad habits, such as addiction to alcohol and smoking abuse. It is recommended to avoid stress and overexertion, normalize your daily routine, alternate work and rest, sleep at least eight hours a day, and exercise whenever possible. It is advisable to avoid fried, spicy and fatty foods.
If we talk about traditional medicine, then for granular gastritis, herbal medicine, which consists in the use of medicinal herbs, plants and berries, will have a healing effect.
Treatment of granular gastritis is prescribed only by an experienced gastroenterologist, taking into account all factors and contraindications for the use of drugs. It is strongly not recommended to treat gastritis without prior consultation with a professional; this leads to the development of multiple complications and aggravation of the symptoms of the disease.
In addition to diet, in the treatment of this type of gastritis, antibiotics and, in some cases, enzyme substances that have a beneficial effect on digestion are used. At the beginning of treatment, the patient takes antibiotics that suppress the growth rate of harmful bacteria, and medications that regulate gastric secretions. The analgesic effect during acute attacks is provided by antispasmodic drugs. Later, in the second stage of therapy, drugs are used that restore metabolism in the stomach and help regenerate the lining of its walls.
If therapeutic treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is used; during the procedure, grain-like growths are removed from the inner walls of the stomach.
Diagnostics
The examination begins with a consultation with a gastroenterologist. The final diagnosis can be made after the conclusion of the endoscopist. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy will help assess the condition of the mucous membrane.
During this study, you can determine the acidity of the stomach, as well as test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. The doctor may also prescribe an ultrasound or x-ray. A clinical and biochemical blood test will also help to comprehensively assess the patient’s condition.
Diet for granular gastritis
If granular gastritis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are used in treatment, but the main and main condition for recovery is diet. The regimen is prescribed taking into account many factors, such as acidity in the stomach and many others. Sometimes mineral waters obtained from natural sources are used. Typically, the course of treatment needs to be repeated periodically; it takes a month, but varies depending on the stage of advanced disease and the complications caused by it.
When eating food, you must chew it thoroughly without rushing. Food portions are minimal, food must contain vitamins, essential minerals and proteins, and be beneficial for the body. The optimal number of meals per day is five or six times. The temperature of the food is important - it does not need to be too hot, or, conversely, cold.
If we specify the list of products consumed when following a diet, then usually all kinds of flour products, fatty fish or meat dishes (including soups), canned foods, smoked, fried, salty and sweet foods are excluded from the diet. All kinds of carbonated drinks, strong tea or coffee are harmful. It is strongly recommended to avoid fruits with a sour taste (citrus fruits, grapes) and dark chocolate; it is not recommended to eat fresh, just baked bread. It is advisable to coordinate the addition of various dietary supplements to food, the use of medicinal tea and the use of traditional medicine with the attending physician.
The main diet of a patient with gastritis consists of various cereals, vegetable soups, and butter. Non-acidic dairy products, cheese, non-acidic compotes and fruit drinks from dried fruits, durum wheat pasta are welcome. Soft-boiled eggs, scrambled eggs and baked apples are suitable. It is possible to eat lean meat - chicken, beef and turkey. All products included in the patient’s diet have a delicate, non-sour taste. When preparing dishes, it is preferable to boil, stew or steam them.
It is strictly not recommended to create a diet for granular gastritis on your own; it is more prudent to use the qualified help of a nutritionist who has the necessary knowledge to competently create a diet, taking into account the stage of the disease, complications and characteristics of the patient.
How to treat?
Treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis, since the progression of hyperplasia is fraught with cancerous degeneration. Effective treatment is a change in overall lifestyle: proper nutrition, reduction of tension and stress, giving up bad habits: smoking and alcoholism.
Emotional stress leads to spasm of the mucous membrane
Medication methods
For hyperplastic gastritis, experts prescribe the following medications:
- for the hyperacid type, drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid or blockers, antacids are prescribed;
- Enveloping agents help relieve heartburn and relieve the inflammatory reaction;
- Enzyme preparations will help improve digestion;
- when Helicobacter pylori is detected, antibacterial drugs cannot be avoided;
- in case of dysbacteriosis, agents are prescribed to improve the microflora;
- Mild laxatives will help combat constipation;
- for diarrhea, it is necessary to take fixing and enveloping drugs;
- antispasmodics will help relieve pain.
People's Councils
Non-traditional recipes are a good addition to drug treatment. They will help relieve inflammation, regulate acidity, and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract. Traditional medicine advice is safe if used correctly.
Reviews from people show that unconventional advice improves metabolism and appetite. Moreover, such treatment will help speed up the process of restoration of damaged gastric mucosa.
Let's look at the most effective recipes:
- St. John's wort. St. John's wort tincture will help stop the inflammatory reaction and normalize digestive processes. Two tablespoons of dry raw materials must be poured with a glass of boiling water and placed in a thermos. The product must be infused for two hours. After the tincture has been filtered, it is taken 125 g in the morning and evening;
- burdock. It is recommended to drink burdock infusion in the morning on an empty stomach. This recipe even helps with erosive changes in the mucous membrane;
- for hypoacid gastritis, it is useful to drink cabbage juice or chicory decoction;
- for the hyperacid type, it is recommended to take a little propolis after waking up;
- a decoction of chamomile and mint leaves will help calm the inflammatory reaction and relieve spasms;
- prepare a gastric mixture from celandine, St. John's wort, chamomile, dried grass and yarrow.
Traditional recipes will help relieve the symptoms of hyperplastic gastritis