Gastritis is a very common disease and occurs in people of different ages and genders.
The pathology is also observed in middle school students, as well as in adolescents. The disease has many varieties and even more causes. Follicular gastritis is a very rare type of disease, which occurs in a ratio of 1/100 patients, however, this form exists. Its second name is lymphoid or leukocyte. In the international classification of gastritis, the type of disease is formulated as “special”. Pathology develops on the basis of already damaged gastric mucosa, that is, due to the chronic form of gastritis.
What kind of pathology is this
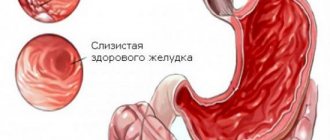
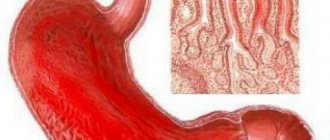
The pathological process manifests itself in the appearance of follicles on the gastric wall, which are formed from leukocytes. They disrupt digestion and cause dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract. Pathologists consider chronic gastritis caused by H. pillori to be the main cause of development.
Bacteria penetrate the epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa, and the acids they secrete disrupt the functioning of the digestive tract. Motility and secretory activity of the gastrointestinal tract decreases. The human immune system, trying to protect the stomach from the harmful effects of microbes, tries to destroy them by sending leukocytes to the sites of damage.
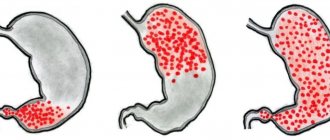
As a result, an accumulation of leukocytes occurs on the lining of the stomach, which turn into follicles, sometimes reaching large sizes. By inhibiting the vital activity of bacteria, such formations harm the functioning of the digestive system, since they reduce the secretory ability of the glands of the gastric epithelium. As gastritis progresses, the follicles cover the inner walls with a dense layer, significantly thickening them. This reduces the release of hydrochloric acid necessary for digesting food.
Causes
The follicular form of gastritis is a secondary pathology and is formed on the basis of damaged mucosa caused by a chronic type of disease. The main reason for its appearance is considered to be damage to the inflamed membrane by the bacterium X. pylori. But there are other factors that can provoke the onset of the development of this rare form of gastritis:
- errors in nutrition (a lot of fatty foods, fast food);
- improper diets (fasting);
- stress;
- constant emotional stress;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
In addition, the development of follicular gastritis is provoked by addiction to alcohol and smoking, constant snacking “on the go”, as a result of which food is poorly chewed and systematically irritates the stomach wall.
Diet features
Nutrition for gastritis of this form is selected individually. A therapeutic diet is of great importance in recovery. There are also nutritional principles, including:
- split meals in small portions every 3–4 hours;
- food products should not irritate the mucous membranes - nothing fatty, spicy, sour, hot or cold;
- you need to eat, chewing each piece thoroughly;
- the meal should take place in a calm atmosphere, without haste or stress;
- before going to bed you can’t overeat, but you can allow yourself a glass of kefir, milk, yogurt;
- You cannot fry foods, only boil, bake without forming a crust, and stew.
Considering that follicular gastritis can develop into a malignant form, you should be under the supervision of a doctor and undergo regular tests.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of follicular gastritis is similar in symptoms to other forms of pathology and manifests itself in the form of:
- heartburn;
- burps sour;
- “ hunger pain ” that occurs in the morning or some time after eating;
- bowel dysfunction ( constipation , diarrhea );
- lack of appetite (due to stagnation of food in the gastrointestinal tract).
Digestive disorders lead to the formation of stagnant processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, patients complain of heaviness in the stomach that appears after eating, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Due to decreased gastrointestinal motility, such patients often alternate between diarrhea and constipation. Due to poor breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients, patients are visually noted to have pale skin, brittle hair and nails, emaciation, and a white coated tongue. In addition, their appetite decreases and they feel constantly tired.
Diagnostic procedures
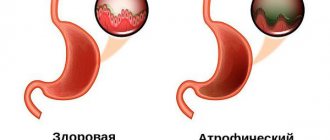
The difficulty in establishing an accurate diagnosis is that this type of gastritis is rare and does not have specific manifestations characteristic only of it. Therefore, during diagnosis, it is necessary to distinguish the follicular form of gastritis from atrophic and hypertrophic, since round formations and folds with erosions appear on the surface of the gastric epithelium, as in these pathologies.
To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopy is mandatory and the affected area of the gastric mucosa is examined using a probe. In addition, material is collected for histological examination. Cytology is performed to exclude oncology, as well as to determine the type of gastritis.
After questioning and collecting anamnesis, the patient is prescribed:
- general and biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- abdominal echocardiogram;
- stool analysis.
Studies help identify deviations from the norm in the blood formula, as well as the presence of foreign impurities in feces and urine.
Symptoms
If the ulcerative form of gastritis is difficult not to notice that follicular gastritis often occurs with mild symptoms. As a result of chronic inflammation, the following are observed:
- heartburn, sour belching;
- a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen or pain in the upper abdomen;
- there may be nausea;
- increased formation of gases in the intestines.
We recommend: How to treat gastritis during pregnancy?
Acute painful attacks, as with a stomach ulcer, are extremely rare. But the frequently recurring symptoms listed above should alert you. To distinguish ordinary gastritis from the lymphoid form, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. Based on the results, the gastroenterologist prescribes treatment.
Treatment
If the diagnosis of follicular type of gastritis is confirmed by research, then treatment should be started immediately. Self-medication should not be carried out, because, despite the fact that the disease passes without pronounced symptoms and periods of exacerbation, it is dangerous. The follicles themselves do not degenerate into oncology, but the glands of the mucous membrane, which atrophy due to pathological processes occurring on the walls of the stomach, can transform into an oncological form. Therefore, you should strictly follow the doctor’s advice and the outcome of the disease will be positive.
Treatment of follicular gastritis involves the following steps:
- drug therapy;
- dietary nutrition;
- diet;
- folk treatment during remission.
To relieve symptoms, therapy is carried out with medications, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the bacterium H. pylori and restoring the gastric mucosa.
- Two types of antibiotics are used. They contribute to the inhibition of the vital functions of microbes and their death. The course of treatment is 10-14 days. If the effect is not complete, then one group of drugs is replaced by another ( Metronidazole , Klacid , Amoxiclav ).
- Antacids. Their action is aimed at reducing the acidity of hydrochloric acid and reducing the aggressive effect on the walls of the stomach ( Almagel , Phosphalugel ).
- Enzymatic medications are prescribed to improve the digestion process and normalize the gastrointestinal microflora ( Panzinorm , Mezim ).
- Alginates create a protective film that can protect the walls of the stomach from the harmful effects of food and hydrochloric acid ( Gaviscon ).
- Antispasmodics relax smooth muscles, relieve pain ( No-shpa , Spazmolgon ).
- Vitamin preparations help accelerate the processes of regeneration of mucous tissue and increase the immune properties of the body.
Treatment with medications should be carried out strictly according to the regimen suggested by the doctor. Antibiotics for X. pylori infection are taken for the period prescribed by the doctor. It is not worth stopping the medications on your own, even if your general condition improves, since the bacteria have not completely died, but only the process of their reproduction has slowed down.
Interrupting the use of antibiotics contributes to the development of microbial addiction to this medicine.
Proper nutrition
Diet is of great importance in the therapy. It is developed individually by a nutritionist or gastroenterologist, depending on the clinical picture and condition of the patient.
But there are certain rules that must be followed by all patients with follicular gastritis, without exception.
- Meals should be frequent (5-6 times a day), but in small portions (200-250 g) so as not to create a burden on the digestive tract. For the same reason, you should chew your food well and take your last meal 3 hours before bedtime. Under no circumstances should you overeat.
- Preference should be given to boiled, baked or stewed dishes. The food should be light, tasty and aesthetically presented in order to awaken the patient’s appetite, since during illness it is absent.
- The diet should be dominated by vegetable fats, lean meat, free of coarse fibers, and low-fat fish.
- Patients can eat puree soups, stews, porridges, casseroles, jellies, mousses and soufflés.
- It is better to steam or bake meat products without using fat.
- Vegetable oil is used only in salads, but is not subjected to heat treatment.
- It is advisable to eat vegetables boiled, and when choosing fruits and berries you should pay attention to the content of fruit acids in them (sour varieties are not allowed).
For follicular gastritis, the following should not be included in the diet:
- green pea;
- beans;
- radish, radish;
- peas, beans;
- corn;
- mushrooms;
- sour berries and fruits;
- onion garlic;
- spices;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- baked goods and sweets with cream.
Also, patients are strictly prohibited from smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee.
How is it treated?
The main method of control is eradication therapy. A large number of studies have been conducted that have confirmed complete regression of the tumor in half and even all patients. A standard type of treatment is prescribed, the effectiveness of which is assessed after 1-2 months. In the absence of eradication, repeated courses are carried out. Sometimes lymphoma fades away after first-line therapy, for many after second and third. Only in a small number of patients eradication was not achieved.
Treatment must be started as soon as possible, since a rapid therapeutic start significantly increases survival and increases the chances of a complete cure. The rate of tumor regression, as studies by German scientists have shown, also varies. In a study of 120 patients with this diagnosis, 81% of them achieved complete remission after 48 months. Partial cure is observed in 9%, and in 10% of cases there was no effect from the therapy. Large cell lymphoma of the stomach is characterized by a fairly long regressive period, during which careful medical supervision and constant diagnostic procedures are required. To monitor effectiveness, endoscopic examination and biopsy are performed every six months.
Lymphoma of the 4th stage, MALT tumors of a high degree of malignancy or with damage to the deep layers of the submucosal layer, or in the absence of eradication effect, is treated with chemotherapy or surgery. A combined type of treatment (surgery and medications) is also used.
Prevention
In order to exclude relapses of follicular gastritis, during the period of remission you should not violate the menu suggested by the doctor, and also use infusions of herbs that can improve the regeneration processes of the gastric mucosa. A decoction of medicinal plants (chamomile, calamus, St. John's wort, mint), propolis tincture (10 drops per 100 ml of water 3 times a day before meals), honey helps in this case.
Sea buckthorn oil has a healing effect (drink 1 tsp 30 minutes before meals). A glass of freshly prepared potato juice, drunk on an empty stomach, neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid.
In addition, people with gastritis need to avoid stressful situations and try to always be in a good mood. Exercise daily, lead an active lifestyle, but do not overwork. You should also eat on time to prevent the release of gastric juice “idly”.
Very important. It is necessary to get rid of bad habits, undergo regular examinations with your doctor, and if unwanted symptoms appear, then visit him unscheduled. There is no need to self-medicate, since at the wrong time, the follicular type of gastritis threatens to develop into a more serious disease.
Traditional medicine to help
Treatment is based on three main areas - drug therapy, diet and traditional medicine methods. A gastroenterologist will definitely recommend folk recipes that have come down to us from time immemorial and have not lost their relevance. These methods are quite effective, as proven by many years of practice.
- Potato juice is used for heartburn. It is necessary to peel 3-4 ripe fruits, grate them on a plastic grater (contact with metal is undesirable) and squeeze the resulting mass through gauze. You should drink half a glass three times a day, half an hour before meals.
- Wormwood tincture helps with diarrhea. A teaspoon of dry herb is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. Drink warm three times a day half an hour before meals. Diarrhea can be cured in a matter of days.
- Sea buckthorn oil helps strengthen the immune system, heal wounds, relieve inflammation and coat the walls of the digestive organ. Take a teaspoon in the morning before meals and in the evening after dinner 2-3 hours later. Oil improves the production of bile, which means food is digested better.
But traditional methods should be discussed with your doctor, since despite the naturalness of the products, there are a number of contraindications. For example, sea buckthorn oil sometimes causes allergies; you should not use it if you have liver problems, or if you have gallstones.