Among the diseases of the human body, one cannot fail to note the development of paraproctitis in it. This inflammatory disease is accompanied by the development of pathology in the area of perirectal tissue. As a rule, this inflammation brings a lot of inconvenience and discomfort to a person. This disease is sometimes called a “perirectal abscess.” Under such a complex name lies the purulent nature of inflammation in the tissues. This pathology is quite common in adulthood after anal fissures and hemorrhoids. Recently, treatment of paraproctitis at home has been widely practiced.
How long does paraproctitis take to heal after surgery?
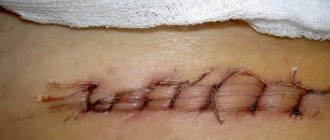
Surgery of this kind is associated with certain risks. But the wound, on average, heals after 20-25 days. Provided that the person strictly follows the doctor’s recommendations.
Various factors can influence the recovery process:
- The presence of systemic diseases. When there are pathogenic microorganisms in the body, the risk of complications increases due to decreased immune activity.
- Metabolic disorders. Endocrine and autoimmune diseases affect the regeneration process.
- The patient's weight. If a person is obese, tissue healing is slow due to swelling of the body.
- Disturbances in the functioning of vital organs. Such problems lead to weakness, resulting in slower recovery than usual.
- Weak immune system. The reason for this phenomenon is considered to be a prolonged course of inflammatory or other processes in the body that can affect the production of antibodies.
- It is worth paying attention to the form of the course; if it is chronic, then recovery will take longer, and the risk of complications is higher.
When it comes to the treatment of acute paraproctitis, regeneration after completion of the operation is faster. Compared with the chronic form of the disease. But this does not exempt the patient from following wound care rules.
SYMPTOMS OF PARAPROCTITIS
Signs of acute paraproctitis are characteristic of all purulent processes:
- Acute pain in the anus. The pain is constant, most often it grows, pulsates, intensifies with movements and after bowel movement. Defecation itself is often difficult.
- Swelling and swelling in the anus - may appear as a “bump”, a lump near the anus, or as an asymmetry of one of the buttocks; such swelling is usually sharply painful when pressed.
- Redness of the skin near the anus, above the location of the abscess.
- An increase in body temperature is also one of the most common signs of paraproctitis. Along with an increase in temperature, intoxication phenomena can also be observed - general weakness, chills, nausea, headache, dry mouth.
- Discharge of pus from the anus is an almost reliable sign of paraproctitis; most often this occurs when the abscess is emptied into the rectum through its internal opening.
- Difficulty urinating is one of the most dangerous symptoms; it is especially common with dangerous ulcers with anterior location and with pelvic-rectal paraproctitis.
The earliest and most pronounced symptoms of paraproctitis appear with superficially located abscesses - subcutaneous-submucosal. They are almost immediately accompanied by severe pain in the anus, and at the same time an abscess itself is detected - a dense, painful “bump” next to the anus, and difficulties arise during defecation. Such an abscess can quickly open outward, forming a fistula on the skin and draining pus. This brings the patient temporary relief and pain reduction.
In deep forms - ischiorectal paraproctitis - the disease begins with signs of general malaise, weakness, chills, and fever. You may experience dull, bursting pain in the rectum and perineum, which intensifies with walking and movement. Later, swelling and asymmetry of one of the buttocks is noted. Emptying pus outward or into the lumen of the rectum is accompanied by short-term relief, but never leads to a cure.
Complex forms of the disease, with a pelvic-rectal location of the abscess, are a common cause of late diagnosis. Usually the disease manifests itself in the first days with general weakness and other manifestations of intoxication, the temperature can rise to 39 - 40 0C. There may be pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, and difficulty urinating. Patients turn to a therapist, gynecologist, urologist, and often the diagnosis cannot be established for several days. Due to the location of the abscess deep in the pelvis, its local manifestations occur late - when the pus spreads down to the level of the anus and the skin of the buttocks. At this point, the phenomena of sepsis - a generalized infection - are usually added, the patient’s condition becomes severe, and disorders of the respiratory, circulatory and metabolic systems occur.
Treatment after surgery
When the surgical intervention is successfully completed, further treatment is divided into several stages, consider them:
| Wound treatment: | it is carried out in a hospital setting, as well as after discharge, to eliminate the possibility of pathogens getting on the tissue and developing complications. |
| Changing the dressing: | dressing is done daily, since sterility helps reduce existing risks. |
| Local treatment: | consists of using ointments, often they contain antibacterial components. Levomekol is most often prescribed. |
| Preparations: | It is practiced to prescribe immunostimulants to patients to speed up the regeneration process. |
| Physiotherapy: | prescribed if the inflammatory process in the tissues has been stopped. This type of therapy will help speed up recovery. |
| Diet: | is considered an integral part of treatment during the postoperative period. Involves avoiding certain foods. |
| Mode: | directly depends on the form of the disease; in case of acute paraproctitis, a short stay in bed is recommended. But for chronic cases, bed rest is prescribed for a long time (comparatively). |
After discharge, the person is given recommendations that can speed up regeneration, and they should be followed. As a rule, the regimen, diet and medication (if required) are prescribed by the doctor.
DIAGNOSIS OF PARAPROCTITIS
The diagnosis of acute paraproctitis is established primarily on the basis of clinical data - as a result of interviewing the patient and clarifying complaints, examination and palpation of the perianal area, and digital examination of the rectum.
Upon examination , the doctor discovers an inflammatory infiltrate (seal) at the location of the abscess. This infiltrate can be determined from the outside, near the anus - with subcutaneous paraproctitis, or from the side of the rectum - with ischiorectal paraproctitis. Sometimes, to identify the location of the abscess, it is necessary to perform a digital examination of the rectum simultaneously with palpation of the perianal area, so that the tissue of the ischiorectal fossa is placed between two fingers. With pelvic-rectal paraproctitis, it is not always possible to achieve infiltration with a finger.
Instrumental studies (anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy) for acute paraproctitis are of secondary importance. Often they are impossible to perform due to severe pain. For pelviorectal abscesses, sigmoidoscopy helps to detect infiltrate in the area of the upper ampullary part of the rectum, protruding into its lumen. It is also often possible to identify the internal opening in the crypt area from which pus is released.
New opportunities in the diagnosis of paraproctitis have appeared with the development of ultrasound research methods. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) , performed from the perineum or from inside the rectum, can reliably detect an abscess and clarify its location, relation to the sphincter muscles, and the presence of communication with the intestine. For deep forms of the disease, this is one of the most successful diagnostic methods.
In difficult situations, when the diagnosis is unclear, magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvis is also of great help.
In differential diagnosis, acute paraproctitis must be distinguished from acute hemorrhoids, rectal tumor or presacral cyst, acute bartholinitis (inflammation of the gland of the vestibule of the vagina) in women or prostate abscess in men.
Patient hygiene
Hygiene rules will help to avoid the addition of a secondary infection, they are as follows:
- When using antiseptics, solutions are used regularly until the damage is completely healed. Antiseptics stop the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
- While washing. It is recommended to carry out them at least 2 times a day, using warm water. You can give preference to herbal decoctions, use: chamomile, oak bark, plantain.
- In changing bed and underwear, which is carried out daily. Preference is given to natural fabrics.
Folk remedies for the treatment of paraproctitis
If the suppuration is located under the skin and not deep in the pelvis, you can use home remedies to treat it, which are very effective and completely safe. If the paraproctitis is deep-seated, you should not joke with your health, but it is necessary to carry out treatment only under the supervision of a specialist and the drugs prescribed by him.
A bath with baking soda and sea salt quickly draws out pus and has a complete disinfecting effect. To carry it out, dissolve 1 large spoon of salt and soda in 1 glass of hot water. Next, pour 5 liters of warm water into the basin and add the solution from the glass. This sitz bath should be performed 2 times a day for 15 minutes. Once the abscess has opened, treatment should not be stopped. The full course lasts 14 days. If you interrupt it earlier, you can expect a recurrence of the disease due to pathogens remaining in the body.
Baths with mumiyo also have a positive effect. In order to carry out the treatment procedure, you need to dissolve 10 grams of the medicinal substance in a glass of water, and then proceed in the same way as prescribed in the first recipe. The duration of treatment in this case is slightly shorter and is 10 days.
Enemas with mumiyo and honey are used as an aid in the treatment of internal paraproctitis. 5 grams of mumiyo and 1 large spoon of fresh honey should be dissolved in 120 milliliters of warm water. The composition is injected into the rectum using a syringe in the evening before bed and left overnight. After the first use of such an enema, the patient notices a significant reduction in pain and a general improvement in condition. This drug can only be used for deep paraproctitis as an additional treatment, since it cannot completely eliminate the causative agents of the disease on its own.
Badger fat is also used in the treatment of any paraproctitis. In order to obtain a therapeutic effect, a tampon soaked in fat is placed in the anus overnight. The duration of treatment is at least 14 days.
Microclysters with calendula have a powerful disinfectant effect and eliminate pain. To prepare them, you need to place 50 grams of plant material in a glass with 120 milliliters of boiling water and leave, covered with a blanket, for 2 hours. After this, after filtering the medicine, it is injected into the anus overnight using a syringe. The duration of treatment is about 12 days.
If external paraproctitis is caused by the presence of cracks in the anus, through which infection constantly enters, you should think about potato treatment. In order to heal damage, one small piece of potato is used for one procedure; for this you need to cut off part of the potato and cut it into strips. Next, one such potato stick should be inserted into the anus before bed and removed in the morning. During the night, potato juice will actively stimulate regeneration processes and also have a disinfectant effect. Treatment can last up to 10 nights. If, despite the procedures performed, cracks recur, you should consider taking laxatives.
Red rowan berries can be effectively used in the treatment of paraproctitis, both as an internal and external remedy. In order to obtain the medicine, squeeze the juice from ripe berries, which you drink 120 milliliters 3 times a day before meals. The remaining pulp is used to apply compresses to the anus at night. The course of this treatment is about 2 weeks. While taking the juice, in addition to treating the underlying disease, the patient will also perfectly strengthen the immune system.
Baths using wood ash can help get rid of suppuration. To prepare the medicinal composition, 2 handfuls of pure (without impurities) wood ash are boiled in 7 liters of water for 30 minutes after boiling. Next, when the preparation has cooled, it is filtered very carefully and used for a sitz bath once a day. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. The duration of treatment is determined by the patient’s condition and can range from 5 days to 3 weeks.
Milk with garlic and onions is also used for sitz baths. In order to obtain the medicinal composition, you should take 5 crushed cloves of garlic, 2 medium onions and 2 liters of milk. All ingredients are combined, placed on the fire and after boiling, boil for 5 minutes. Next, the drug is allowed to cool. The strained product is used for baths lasting 15 minutes. The procedure is carried out once every 24 hours for 10 days. It is very important that the patient’s body is warm while taking a bath.
A compress of grated potatoes, which is placed once a day for 1 hour, will also be useful in treating the disease. To carry out the procedure, grate a large potato on a fine grater and, placing it on a cotton cloth, apply it to the sore spot. The duration of the course of treatment cannot be less than 10 days.
With external paraproctitis, patients are often recommended to use tampons with Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment at night. These compounds draw out pus and help quickly clear the abscess. A full course requires 14 procedures.
Diet after surgery
It is considered a component of treatment because it speeds up recovery and reduces the risk of complications. It involves giving up certain foods, which normalizes the functioning of the digestive system and reduces the unpleasant symptoms that are often observed in patients during the postoperative period.
The table shows the products that are not prohibited, as well as those that will have to be avoided:
| What is prohibited: | What is allowed: |
| meat broths; | vegetable broths; |
| cabbage in any form, due to the presence of coarse fiber; | green onions, spinach, beets (preferably boiled), carrots (can be eaten raw), cucumbers and radishes; |
| tea, coffee, sweet carbonated drinks; | compotes from dried fruits, fruit drinks from berries, vegetable and fruit juices, it is not forbidden to drink water, including mineral water, only without gas; |
| you should not eat rice, oatmeal, cruise cereal, as well as beans and peas; | you can eat buckwheat, semolina, barley and wheat porridge cooked in water; |
| sweet baked goods, various products made from refined flour: gingerbread, cakes, cookies; | do not exclude bread from your diet; |
| pork and beef; | you can eat boiled chicken, turkey or rabbit meat - these are dietary products; |
| fatty fish: herring, salmon. | low-fat fish varieties such as hake, cod, flounder. |
Despite the fact that it is not prohibited to drink fruit juices, you still have to give up fruits. Patients can only eat baked apples.
In this case, the food must meet certain characteristics:
- Easy to digest and does not burden the stomach.
- Do not provoke increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract, do not cause problems with stool.
- Completely digested in the intestines.
Fatty, salty, sour, spicy, smoked and hot foods are prohibited. You should not drink alcohol and its derivatives. You will have to give up fast food, instant noodles and processed foods.
Prevention
Prevention of paraproctitis is such simple things as:
- A balanced, proper diet with sufficient fiber. But fatty, fried and smoked foods must be limited.
- Quitting bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Competent adherence to personal hygiene rules. It includes regular washing of the perineum and anus both during the day and after each bowel movement.
- Timely treatment of constipation, anal fissures and other diseases of the rectum and anal area.
That is, the prevention of paraproctitis comes down to a healthy lifestyle and proper hygiene.
Possible problems
The probability of developing complications is perceived as problems, we list them:
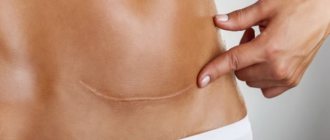
- the appearance of rough scars that narrow the anus;
- spontaneous opening of the abscess and outflow of pus into the vagina or rectum;
- involvement of nearby organs and tissues in the inflammatory process, more often the pelvic tissue becomes inflamed;
- disruption of the urination process due to the outflow of purulent masses into the urethra;
- suppuration of sutures, leading to sepsis, peritonitis;
- the addition of a secondary infection, the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
A non-dangerous complication is sphincter weakness, which is observed in a large number of patients who have undergone such an operation. It leads to incontinence of gas and stool. Special gymnastics will help get rid of the problem.
Recommended video:
REASONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PARAPROCTITIS
The reasons for the development of paraproctitis are factors that contribute to a decrease in local protective immune factors in the rectum. Such factors may be hypothermia, trauma (for example, bruise of the perineal area), constipation and, conversely, diarrhea, which contribute to the formation of minor damage to the rectal mucosa. Very often, paraproctitis develops against the background of hemorrhoids and anal fissures; it can be a complication of rectal and anal cancer and inflammatory bowel diseases - ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. As a result of the influence of predisposing factors, favorable conditions are created for the infection to “break through” the protective barriers and the development of suppuration in the tissues surrounding the rectum.
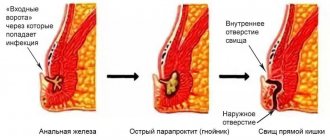
The most modern and generally accepted theory of the occurrence of paraproctitis is the theory of cryptoglandular infection. To understand the process, it is necessary to recall the structure of the rectum.
In the final part of the rectum - the anal canal - the mucous membrane forms multiple vertical folds, between which there are depressions similar to pockets - crypts . At the bottom of the crypt pockets, in the submucosal layer, there are special anal glands , their number can reach 16 - 20. These are microscopic glands, vaguely reminiscent in structure of the sebaceous glands of the skin. When exposed to various unfavorable factors, bacteria from the rectum can penetrate the crypt and cause purulent inflammation of the anal gland, in its place a small abscess forms. This abscess (abscess) initially communicates with the rectum through an internal opening at the bottom of the affected crypt - where the infection has entered. Pus from the inflamed gland can spread in various ways through the space between the muscles (sphincters) of the anus, and form large purulent cavities in the tissue of the pelvis and perineum surrounding the rectum. These abscesses are called paraproctitis proper, and always communicate with the lumen of the rectum through the internal opening in the crypt.
Depending on which areas of the peri-rectal tissue the pus spreads, forms of paraproctitis are distinguished - subcutaneous-submucosal, intersphincteric, ischiorectal, pelviorectal and retrorectal.
Subcutaneous submucosal paraproctitis is the most common and mildest form of the disease. In this case, the abscess cavity is located relatively superficially - under the skin of the anus and the mucous membrane of the rectum.
Intersphincteric and ischiorectal paraproctitis are complex forms of the disease. With an intersphincteric abscess, pus accumulates between the muscles of the internal and external sphincter of the anus. Ishiorectal paraproctitis is a deep abscess located between the ischial bones and the rectum, to the right or left of it. Sometimes purulent cavities are located on both sides; such paraproctitis is called horseshoe-shaped.
Pelviorectal (or pelvic-rectal), and its variety - retrorectal (or retrorectal) paraproctitis - are the most severe, and fortunately, rare forms of the disease. Large purulent cavities occupy huge spaces around the rectum, deep in the pelvis, bordering the abdominal cavity - sometimes, in a figurative expression, the rectum “floats in pus.”
Why doesn't the wound heal?
The recovery process has certain variations and can be delayed for various reasons that are not considered pathological.
So why doesn't it drag on:
- Attachment of a secondary infection, infection of a wound provided there is a source of infection in the body.
- Daily surface damage due to over-processing of fabrics.
- Non-compliance, repeated violation of hygiene rules and inadequate wound treatment and dressing.
- Incorrect selection of antibacterial drugs, failure to bring the course of treatment to its logical conclusion.
- Failure to comply with diet and other doctor’s recommendations by the patient.
- The chronic course of the inflammatory process in tissues, in which surgery may not bring the desired result.
When the wound does not close for a month, its edges are inflamed, the person is bothered by severe pain, secretory discharge - it is worth contacting a doctor for help.
The wound does not heal even in the presence of autoimmune, inflammatory and metabolic disorders in the body. A similar phenomenon is observed in the case of a patient with syphilis, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus and oncology.
Features of nutrition for paraproctitis
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of this disease. In order to speed up the recovery process, you should create your own menu, which should include options selected from the following requirements:
- before each meal, drink 50 milliliters of red rowan juice;
- drink 1 glass of fresh carrot juice in the morning on an empty stomach;
- on an empty stomach, consume from 100 to 150 grams of boiled beets;
- drink 1 glass of sauerkraut brine at least 3 times a day;
- Avoid consuming large amounts of red meat.
All these nutritional features help strengthen the immune system and also produce a laxative effect, which helps reduce the load on the affected area. As a result, without being subjected to excessive stress, the inflamed area recovers much faster.