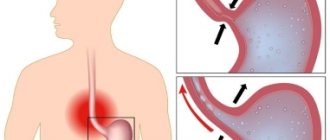
Failures in the functioning of the liver, the formation and transmission of bile can cause intrahepatic and intravesical cholestasis (cholestatic syndrome). It is very easy to identify this pathology, which causes a lot of problems for pregnant women. It is enough to take a biochemical blood test and undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, including ultrasound of the liver and ultrasound of the gallbladder - 1000 rubles.
CLICK TO SIGN UP
When liver tissue is damaged and the oxidation of cholesterol into bile acids is impaired, this is intrahepatic cholestasis. With reduced absorption and evacuation activity of the bladder of a patient with chronic non-calculous cholecystitis, they mean “mild” intravesical cholestasis.
Without proper production of bile, the process of digestion and removal of toxic substances from the body is impossible. One of the diseases of the internal organs or an external negative effect on the body can give impetus to the development of cholestasis.
What is cholestatic syndrome?
The content of the article
The pathology caused by the improper flow of bile into the duodenum and its stagnation inside the liver is called cholestasis. The manifestation of the disease will be shown by a blood test, where indicators of a high concentration of components that should leave the organs along with bile will be visible. An excess of complex components in the liver determines the clinical picture of the disease.
Factors that cause symptoms:
- the intestines contain less bile or none at all;
- the amount of bile that enters the blood is higher than normal;
- components of bile and its toxic metabolites affect liver cells and tubules.
In a healthy person, 80% of copper is excreted from the body with bile. Large accumulations of copper are detected by histochemical examination. The amount of copper is determined by biopsy. Copper binding protein is detected by orcein staining. Such studies provide second confirmation of the syndrome. Accumulated copper during cholestasis does not have a hepatoxic effect on the body, because the copper that enters the hepatocyte is in a non-toxic form.
Cholestasis is manifested by the liver excreting water, the basic ingredients of bile, and tubular flow decreases. With the further development of the disease, hepatocytes begin to enter the bloodstream of those components that the body of a healthy person removes. Therefore, bile is concentrated in hepatocytes, canaliculi, and damaged Kupffer cells. If such a process occurs outside the liver, then the accumulation of bile will be in the liver parenchyma and will also fill the ducts. The dysfunctions caused are reversible when the time interval of the disease is short. Over a long period of time, irreversible damage may occur, characteristic of biliary fibrosis, as well as cirrhosis.
Purpose of the gallbladder
The organ is a reservoir intended for the accumulation of secretion produced by the liver, which has a greenish or yellowish tint, secreted in a healthy body in an amount of 500-1400 ml/day. The physical composition of bile is presented in the form of cholic, deoxycholic acids, cholesterol, phospholipids, trace elements, enzymes, urea and vitamins. Among the functions performed by the secretion, experts name:
- The action of acids that ensure the release of pancreatic juice necessary for the digestion of food.
- Ensuring neutralization of the acid reaction of the stomach contents before the components enter the duodenum.
- The emulsifying effect of acids on fats, providing the possibility of their subsequent digestion by lipase, which is part of the secretion secreted by the pancreas.
- Pepsin binding occurs with the help of proteins that make up bile.
- Ensuring partial or complete removal of medications from the group of sulfonamides, salicylates, and alkaloids.
After extirpation of the gallbladder, the normal course of the digestive process is disrupted, to compensate for changes in which the use of medications is recommended.
Forms of cholestasis
Depending on the place of development and localization of the pathology, cholestatic syndrome can be: intravesical, intrahepatic.
The first type is characterized by bile stagnation, when the extrahepatic bile ducts are blocked, and for the second type, deposits will be in the intrahepatic bile ducts and hepatocytes.
According to the manifestations of jaundice in cholestasis syndrome, there are: anicteric and icteric.
When the color of the skin changes towards yellow, the icteric form of cholestasis is identified. Anicteric cholestasis is considered a prestage of the icteric form. Sometimes the anicteric stage lasts for months; this form of the disease is difficult to treat.
Based on the criteria associated with clinical symptoms, cholestasis occurs:
- acute , when symptoms appear sharply and clearly expressed;
- chronic , when symptoms increase over several months, are not always noticeable and to a weak degree.
Chronic cholestasis can be complicated by the formation of pigmented stones in the biliary tract, accompanied by cholangitis.
If you monitor the destruction of cells, you can distinguish cholestasis with cytolysis and without cytolysis. Cytolysis is considered a violation of the integrity of liver cells. It can occur when exposed to hepatotropic viruses, drugs, and toxic substances.
According to the mechanism of occurrence of the syndrome, cholestasis is distinguished:
- negative , when the amount of excreted bile decreases;
- dissociative , with a delay in the release of certain components;
- total , if the mechanism of passage of bile through the duodenum is disrupted.
What pathologies occur when there are disturbances in the process of bile formation?
A sedentary lifestyle and poor diet cause health problems.
The following reasons can disrupt the process of bile formation:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress conditions, nervous disorders;
- eating large amounts of fatty foods;
- abuse of flour products;
- insufficient amount of fiber in daily diet;
- passion for fast food;
- liver pathologies;
- improper diet: 1-2 meals a day;
- a hearty dinner before bed.
In the presence of these reasons, there is a threat of diseases associated with the formation of bile.
Cholestasis during pregnancy
What causes intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnant women is not clear. There are a number of theories that identify the main groups of reasons:
- increased sensitivity to sex hormones of liver cells due to genetic disposition;
- the normal synthesis of enzymes that ensure the transport of bile from cells through the ducts is disrupted;
- the synthesis of bile acids is impaired from birth due to a deficiency of certain enzymes. This disorder can cause the formation of atypical bile acids.
The main changes in pregnant women with the syndrome:
- the amount of bile components in the blood is increased;
- the level of secretion in the duodenum is reduced;
- on the part of bile, there is an effect on hepatocytes and biliary tubules.
Symptoms of the disease in pregnant women, which begin to appear by the third trimester, are irritation and jaundice. In some patients, skin itching can be pronounced and cause a lot of inconvenience, while others tolerate it easily. Intrahepatic cholestasis leads to excoriation of the skin in pregnant women, usually on the arms, legs, and forearms. Symptoms of jaundice appear in only a tenth of women; usually these signs disappear on their own after two weeks after the baby is born. Still, you should not rely on the fact that everything will go away on its own; if you feel any changes in your health, you should consult a doctor, since all the signs can reappear due to hormonal imbalance.
Treatment of pregnant women is complicated by their piquant situation, so non-traditional treatment methods, such as oatmeal masks and chamomile decoction, are used to reduce symptoms. You can even use cold water; it relieves the condition by slowing down the blood flow, so the urge to itch decreases. It is recommended to sleep in a cool room, as well as follow a diet.
Pediatric cholestasis
The causes of childhood cholestasis may be metabolic disorders from birth, consequences of viral diseases, cardiovascular failure, malignant pancreatic tumors, parasitic lesions, genetic predisposition, sclerosing cholangitis.
The manifestation of cholestatic syndrome in children depends on the age at which the disease began and the characteristics of the body. The disease should be treated after the root cause of the disease has been eliminated. For example, if bile stagnation is caused by a malignant neoplasm, then you need to fight the tumor first, and then the symptoms of the syndrome. The child’s therapy is comprehensive: in addition to medications, vitamins A, E, D, K, as well as choleretic drugs can be prescribed.
Often, cholestasis in this group of patients cannot be cured with medications alone; then a surgical operation is performed, which is aimed at removing stones and draining blocked ducts. The danger of cholestasis is that it develops in children in a latent form. To avoid complications and severe forms of the condition, you need to start treatment in a timely manner.
The functioning of the digestive system, symptoms and consequences of bladder removal
Normally, bile is secreted and flows through the ducts into the duodenum after the action of an irritant, which can be food intake. The rate of secretion depends on the type and quantity of food consumed. When the gallbladder is removed, the ducts ensure continuous delivery of secretions to the intestines, independent of the action of the irritant. A constant supply of the enzyme can cause a number of consequences, among which are symptoms and conditions such as:
- The accumulation of large volumes of digestive juices and their stagnation, causing irritation of the intestinal mucosa.
- Violation of the process of absorption of nutrients.
- Nausea, belching and vomiting in case of reflux of secreted secretions.
- Possibility of damage to the intestinal walls with the release of bile into the abdominal cavity.
- Disturbance of the intestinal microflora, leading to flatulence.
- The appearance of liver or intestinal colic.
- There is a danger of penetration of pigments that make up bile into the bloodstream, which can result in general intoxication of the body.
- Disruption of metabolism and metabolic processes that regulate the supply of necessary substances and fats, associated with damage to muscle tissue in the area surrounding the channels for the passage of bile into the duodenum.
- The development of inflammatory processes and dysbacteriosis associated with disruption of metabolic processes.
- Stagnation of bile, formation of stones and an increase in the likelihood of secondary development of cholelithiasis, the elimination of which in most cases is possible only with the help of surgery.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the disease, the onset of one or more of the listed conditions, called post-chocystectomy syndrome by specialists, is possible.
Surgery and the stress that follows is a normal reaction of the body to a surgical procedure. During the time required to restore the body's functioning, the patient may feel weakness, increased formation of gases, a bitter taste in the mouth and other symptoms.
Main signs of cholestasis
Cholestasis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Skin itches. A primary symptom that may appear on its own for some time. It is characteristic that it is stronger at night than during the day.
- Brown or yellow formations (xanthomas) appear on the chest, back, and elbows.
- Yellow symmetrical formations appear on the eyelids (xanthelasmas).
- Purulent rash, scratching depending on the degree of itching.
- Scratching in different areas, pustular rash.
- There is a change in the color of the surfaces of the eyes, mouth, mucous membranes, and skin to a yellow color (jaundice).
- Melanin levels decrease, the skin becomes dark (hyperpigmentation).
- A large amount of fats is excreted along with feces, due to insufficient processing of them by the body (steatorrhea), feces are characterized by an unpleasant odor, and excrement is difficult to wash off.
- The stool becomes discolored and the urine becomes dark.
- Due to reduced absorption of vitamin K, which dissolves intestinal fats, bleeding increases.
- Changes in metabolism due to stagnation of bile in the liver lead to a lack of vitamins (hypovitaminosis) A, D, E, and a deficiency of component A leads to night blindness - poor twilight vision, dry eyeballs, and skin.
- Body weight decreases.
- Stones may form in the gallbladder and ducts (cholelithiasis).
Functions of bile
Not everyone knows what exactly the gallbladder does? What is the role of bile in the human body? What is it for?
Functions of bile:
- improves the functioning of pancreatic juice;
- dissolves fats entering the digestive system;
- helps the absorption of vitamins and nutrients;
- participates in intestinal function.
The main function of the liver is related to the breakdown of fats in the body. Without it, the body cannot process foods containing fat.
Causes of pathology
The disease can develop for various reasons. The intrahepatic form of cholestasis is manifested by a smaller flow of bile into the duodenum. This may occur due to hepatocellular pathology. If the tubules are damaged due to damage to the intrahepatic interlobular duct, then the syndrome is called canalicular, as well as extralobular ductular cholestasis, and if hepatocytes are destroyed, then hepatocellular.
Viruses, medications, alcohol, and toxic effects make it difficult for the liver to function normally. Canalicular cholestasis with hepatocellular cholestasis can be caused by any form of liver damage, as well as impaired metabolism and heart problems. The etiology of introlobular cholestasis is in the malfunction of the vacation, basolateral membranes. If the epithelium of the bile duct is damaged, patency is complicated, the composition of bile and acid metabolism are disrupted, then ductular cholestasis develops.
Intrahepatic cholestasis may appear due to factors such as ductopenia, hypoplasia of the extrahepatic and intrahepatic ducts, Alagille syndrome, infection, viruses, exposure to the drug Thiabendazole, cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, istiocytosis X, reactions associated with transplant rejection, cholangiocarcinoma, hepatitis, autoimmune deficiency A1- antitrypsin, cholangitis, amyloidosis, congestive liver, circulatory disorders, hepatic vein thrombosis.
Extrahepatic cholestasis begins to manifest itself when the positive effect of the main intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts is counteracted. One of the common causes is the presence of stones in the bile ducts.
The progression of the extrahepatic form of the syndrome may be due to the presence of stones, malignant neoplasms in the ducts, damage to the duodenum, hepatic artery aneurysm, pancreatitis, malfunction of the pancreas, the appearance of cysts, hemobilia, abscess, parasitic and other infections.
Intravesical cholestasis (mild chronic) can occur in the chronic form of non-calculous cholecystitis, when the activity of the gallbladder decreases - an unbalanced composition of bile is formed.
Part 1. The most important things about choleretics
According to the classification, choleretics are divided into two groups: those that increase the secretion of bile and the formation of bile acids, as well as those that increase the secretion of bile due to the water component.
The first group is drugs that contain bile acids. Such choleretics, in addition to lyophilized animal bile, include extracts of liver tissue, pancreatic tissue and mucous membranes of the small intestine of cattle, activated carbon and extracts of medicinal plants.
Note: choleretics with synthetic bile acids increase the volume of bile produced, and preparations containing animal bile both stimulate bile formation and directly perform a replacement function [3].
Synthetic drugs, in addition to choleretic, also have antispasmodic, hypolipidemic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effects, and also suppress the processes of putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines.
Choleretics of plant origin, which include corn silk, tansy, birch buds, Far Eastern lily of the valley herb, turmeric root, oregano herb, immortelle flowers, etc., increase the functional capacity of the liver, reduce the viscosity of bile, increase the secretion of bile, increase the content in bile cholates
Along with increasing bile secretion, most plant choleretics increase the tone of the gallbladder and at the same time relax the smooth muscles of the biliary tract and sphincters of Oddi and Lutkens. This facilitates the flow of bile.
Herbal medicines that have a choleretic effect also have a significant effect on other functions of the body - they normalize and stimulate the secretion of the glands of the stomach and pancreas, increase the enzymatic activity of gastric juice, and enhance intestinal motility during atony.
The second group is drugs that increase the secretion of bile due to the water component (mineral waters).
Mineral waters make bile less viscous. Mineral salts help increase the colloidal stability of bile; and this, in turn, indicates the preservation of cholesterol in a dissolved state and prevents the development of cholelithiasis [4].
Indications for the use of choleretics
: chronic cholecystitis and cholangitis, treatment of biliary dyskinesia and constipation. If necessary, choleretics are combined with antibiotics, analgesics and antispasmodics, as well as laxatives [5]. The mayor must remember that choleretics are contraindicated in acute forms of cholecystitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, hepatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers. Taking them against the background of the listed diseases can provoke a deterioration in health and the need for surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of intravesical and intrahepatic cholestasis
The media and the Internet should not become sources of treatment for the disease. Only special diagnostic methods reveal pathology, and competent specialists prescribe the necessary treatment.
The patient is physically (externally) examined by a doctor. At this stage, abrasions, rashes, redness, scratching, and icteric skin color may be detected.
Biochemical laboratory experiments and analysis of the concentration of serum bile acids will help diagnose the disease with greater accuracy. If the syndrome is detected, blood biochemistry will show elevated cholesterol, bilirubin, phospholipids, acids, and enzymes.
Patients continue to be evaluated to identify extrahepatic “surgical” cholestasis. It may appear at first glance to be intrahepatic in symptoms.
The next step in diagnosis will be an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, where an enlarged gallbladder is observed and manifestations of blockage of the bile ducts are identified.
If an increase in the volume of the ducts is detected, cholangiography is prescribed, otherwise the diagnosis is indicated by the clinical picture. For example, if the presence of stones is suspected, then ERCP is performed. When this study does not detect stones, they may be referred for a liver biopsy, but before that the doctor determines the absence of an extrahepatic type.
Recommended medications after bladder removal
To minimize the consequences and eliminate the occurrence of complications after cholecystectomy, the patient must follow the recommendations of a specialist during the recovery period, which, according to gastroenterologists, takes from 1 to 3 months. During this time and, if necessary, during subsequent life, the patient is recommended to take medications that provide:
- normalization of bile production and outflow;
- relief of pain symptoms;
- relaxation of smooth muscles during spasms that occur during the release of secretions into the intestines;
- breakdown of food upon receipt after surgery of insufficient bile.
Self-prescription of drugs should be excluded, since their use may not only not lead to the desired result, but also provoke complications.
Painkillers
Since experts call pain among the most common symptoms of postcholicystectomy syndrome, antispasmodics are used to relieve such manifestations and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment, prevention of the syndrome
Preventive measures for bile stagnation are aimed at preventing disturbances in the function of the liver and bile ducts. Patients are recommended to walk in the fresh air, light jogging in the morning, race walking, exercises for the abdominal muscles, therapeutic massage, avoidance of harmful alcohol, overeating, and adhere to a strict diet.
The purpose of treatment depends on the form of the syndrome, the stage of the disease, aggravating factors and the characteristics of the organism. Conservative treatment algorithm:
- Diet therapy, correct diet.
- Etiological treatment consists of treating diseases that accompany the development of the disease.
- Basic therapy - ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is prescribed to reduce cholangiocytes damaged by bile acid.
- Therapy aimed at reducing painful manifestations and relieving the symptom of itchy skin.
- Treatment of exacerbations.
If the stage of the syndrome is advanced, then surgical intervention can be used. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, then in such forms the disease can cause irreversible consequences.
Part 2. The most important things about cholekinetics
Cholekinetics are also divided into two groups:
- Actually, cholekinetics, which include:
- magnesium sulfate;
- polyhydric alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol);
- sunflower, olive oils, essential oils;
- herbs and plants containing bitterness;
- juices of lingonberries, cranberries, etc.
- Cholespasmolytics:
- hyoscine butyl bromide;
- papaverine;
- drotaverine
Indications for the use of cholekinetics:
- atony of the gallbladder with stagnation of bile;
- gallbladder dyskinesia;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- anacid and strong hypoacid gastritis;
- carrying out duodenal sounding.
Cholespasmolytics are prescribed for the hyperkinetic form of biliary dyskinesia and for cholelithiasis. They are used to relieve pain of moderate intensity, often accompanying pathology of the biliary tract [6, 7].
Such drugs are contraindicated
in acute liver diseases, with exacerbation of hyperacid gastritis and peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. In this case, taking cholespasmolytics will only worsen the situation.
Treatment with folk remedies
After consulting with a doctor, you can resort to traditional medicine to relieve inflammatory processes:
- Recipe for a drink made from birch leaves: pour a small amount of leaves into 0.5 liters of boiled water, boil for 10 minutes on fire. You can take 100 ml up to three times a day. Children, pregnant women, and people with acute liver failure should not drink.
- Herbal decoction. Method of preparation: pour boiling water in equal parts of St. John's wort, corn silk, immortelle flowers, 30 minutes. boil on fire. After straining, take the decoction 25 ml up to three times a day half an hour before meals. Use is contraindicated for more than two weeks, as well as for high acidity and stomach problems.
- Nettle and rosehip 10 g and 20 g, respectively, pour 200 ml of boiled water, leave for about an hour. Take twice a day for no more than two weeks. Cannot be used for thrombosis, varicose veins, or individual intolerance.
- Oil remedy recipe: 1 tbsp. Mix honey with 3 drops of mint oil. Application: 3 times a day, no more than 4 weeks. Contraindications: men over 50 years old, with individual intolerance, children, pregnant women and during lactation.
- Lemon oil can be added to drinks 1 drop. Use: up to 2 times a day for no more than 4 weeks. Contraindications: allergies, childhood, pregnancy.
- Beet salad. Take 1 tbsp four times a day. l. Restrictions on use for stomach diseases.
Traditional methods are used only with the permission of a doctor.
How to get rid of bile stagnation
First of all, you need to change your diet to improve your health.
Dietary rules for gallbladder diseases:
- limit the consumption of fried foods;
- do not eat spicy food;
- exclude carbonated drinks;
- do not eat fatty foods;
- It is recommended to eat the dishes warm;
- choose dairy and fermented milk products with a low fat content;
- It is preferable to add cold-pressed vegetable oils to dishes;
- Alcoholic drinks are not allowed;
- follow the correct diet, eat at least 4-5 hours a day;
- do not overeat;
- When preparing, use gentle methods: boiling, baking in the oven, steaming;
- limit the consumption of strong tea, coffee, cocoa;
- add a variety of porridges to the daily menu, for example, oatmeal, rice, semolina;
- drink more compotes, herbal teas, decoctions.
We recommend watching a video about treating bile stagnation:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uIwh7bCip9w
In addition, there are a number of products that have choleretic properties:
- celery;
- spinach;
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- fruits, berries, vegetables with a lot of pectin;
- citrus.
Traditional medicine has been using recipes for centuries that relieve bile stagnation.
Choleretic drugs:
- dandelion;
- immortelle;
- birch leaf;
- strawberries;
- corn silk;
- sagebrush;
- calamus root.
As a rule, the course of herbal treatment is 2 weeks.
Proper diet
Together with drug treatment for a patient with bile stagnation, the doctor creates a proper nutrition menu. Patients exclude spicy, fried, various types of baked goods, canned goods, spices, rich meat broths, and any fatty foods from their diet. The diet is formed from dishes containing vegetables and fruits.
The patient's morning should begin with drinking medicinal mineral water; it is also recommended to consume fermented milk products daily. Eating before bed is prohibited, and during the day you need to eat in modest portions, but often (from five to seven times a day). Without strict adherence to dietary recommendations, cholestasis cannot be cured.
More than half of all food consumed must be heat-treated and served warm. You can eat oat and buckwheat porridge. Please note that you need to cook by steaming, in a slow cooker and in the oven. It is recommended to exclude cold drinks or warm them to room temperature before drinking; to do this, you can leave the drink in a warm room for a while.
What you can and cannot eat if you have bile stagnation
The diet includes rye bread, savory products, honey, and jam. Dairy products include sour cream, cheeses, and curd products (low-fat). Juices and drinks made only from sweet berries and fruits. You can also drink compotes and weak tea. You should eat a lot of greens, vegetables, fruits, and berries. Soups should be vegetable with cereals, pasta, or lean meat: rabbit, veal, chicken, turkey. It is recommended to limit vegetable fats in the diet to 50 g per day.
When dieting, it is prohibited to consume lard, animal fats, soup made from fatty meats and fish. Not all greens are allowed; green onions, sorrel leaves, and spinach should be avoided. You can't have radishes, radishes. As for drinks, alcohol, strong coffee, and any cold drinks are prohibited. Nutritionists also do not recommend canned foods (pickled vegetables, caviar, smoked foods) for consumption. Exclude from the menu confectionery pastries, chocolate, ice cream, spices, mustard, horseradish, sour varieties of fruits and berries.
For treatment, it is very useful to drink skim milk - it is a good source of calcium. When a sign of cholestasis occurs in the form of itching, you need to see a doctor for a liver examination; this symptom may appear much earlier than others; it should not be ignored, because delays often lead to liver failure. Treatment started in a timely manner can relieve symptoms and improve liver function.
Indications for gallbladder extirpation
The operation, characterized by trauma, involves making incisions in the peritoneum in 4 places. This procedure is prescribed in rare cases, taking into account not only the high cost of its implementation, pain, discomfort for the patient, but also residual consequences.
These include the need for long-term medication and scars or scars remaining at the surgical site. Nevertheless, there are a number of indications, the detection of which indicates complete or partial dysfunction of the gallbladder or the possibility of potential complications. Among the situations in which cholecystectomy is prescribed, experts include:
Diagnosis of postcholicystectomy syndrome
Difficulties in accurately determining the causes that led to the development of PCES and the vagueness of the very definition of the syndrome require a thorough examination of the patient. In order to choose the right treatment, it is necessary to clearly establish what led to the appearance of PCES.
That is why effective diagnosis of postcholicystectomy syndrome includes several methods:
- collection of anamnesis data - the doctor carefully studies old medical reports and records, paying close attention to preoperative diagnostics and the protocol of the operation;
- clinical examination of the patient;
- laboratory tests - clinical and biochemical blood test, stool test for protozoa and worm eggs, general urine test;
- ultrasonography;
- endoscopy of the bile ducts;
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography of the abdomen6.