The text is for informational purposes only. We strongly urge you not to use diets, resort to any therapeutic menus or fasting without medical supervision. We recommend reading: “Why can’t you go on a diet on your own?”
Every person who is hospitalized with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis will necessarily undergo surgery to remove it. Naturally, this will be done only after a thorough examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. After removal of appendicitis, as after any other surgical intervention, you should be prepared for the fact that diet will become a mandatory item on the list of recovery measures. In addition to standard procedures and taking certain medications, you will need to adhere to a special diet. Diet after surgery to remove the appendix plays an important role in the postoperative period. It helps to quickly return to everyone’s usual lifestyle, as well as quickly restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is worth remembering that you must follow the diet for at least 14 days. A little longer if there were any complications during or after the operation.
The operation to remove appendicitis in most cases lasts no more than 20 minutes if everything goes well and without complications. Recovery after such surgery occurs quite quickly, but is not always easy. The most difficult thing is the first day after surgery. This is the day when the patient cannot eat or drink anything. Moisten dry lips as much as possible, no more. The first day is the time when the body needs to be given the opportunity to devote all its strength to restoring internal wounds. On the second day, mineral water without gas is allowed. Gradually, every day the list of foods that can be eaten again is expanding.
General rules
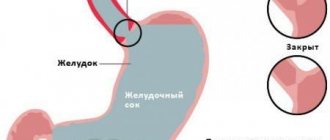
The appendix is an extension of the cecum, and its inflammation is called appendicitis.
It can be caused by bending of the appendix due to its excessive mobility (often occurs in children), blockage of its lumen with feces and undigested particles, infections, abdominal injuries and inflammatory bowel diseases. The only treatment for this disease is surgical removal of the appendix. The most common conventional surgical procedure is a traditional appendectomy , in which the appendix is removed through a regular incision. Endoscopic surgery is used less frequently, but provides less blood loss and trauma because a small incision is made.
Inflammation of the appendix that is not diagnosed in time and not eliminated can cause serious complications, which include appendiceal infiltration and peritonitis . In case of appendiceal infiltrate, when the inflammatory process involves not only the appendix, but also adjacent formations (small intestine, omentum, cecum), conservative treatment is first carried out in a hospital setting, and after resorption of the infiltrate, a planned appendectomy .
The formation of infiltrates is determined by the individual reaction to the source of inflammation in appendicitis. In some patients, the inflammatory-destructive process is limited (in the form of an infiltrate), while in others, diffuse peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) develops. Peritonitis occurs in destructive forms of appendicitis, and is observed in case of untimely treatment, in elderly people and those with intestinal pathology. Its development complicates the course of the operation; in case of peritonitis, the intestines and abdominal cavity are sanitized, and drainage is applied for constant outflow of discharge. More serious, complex treatment is prescribed in the postoperative period.
The recovery period lasts from the moment of surgery until the sutures are removed. At this time, the restoration of body functions (defecation, urination) and the condition of postoperative sutures are monitored. Recovery is different for everyone, but it is faster in younger and thinner patients. Its duration increases if there was a complex appendectomy . During this period, nutrition plays an important role at all stages.
In the postoperative period, a zero or surgical diet is prescribed. These are three gradually prescribed diets that make up a single nutrition system in the first week after surgery.
The purpose of prescribing a zero diet is:
- maximum unloading of the digestive organs and their sparing;
- flatulence warnings .
Nutrition after appendectomy
It is characterized by maximum mechanical and chemical sparing of organs, since the patient is allowed to consume only liquid, semi-liquid, pureed and jelly-like dishes. Salt restrictions are being introduced. The diet includes light and easily digestible foods, low in protein, fat and carbohydrates, the amount of which gradually increases throughout the week. Accordingly, the power consumption also increases.
So, they start eating with a diet that contains only 5 g of protein, 150 g of carbohydrates and 15 g of fat. From the third day, the diet expands and already includes 40 g of proteins, the same amount of fat, 250 g of carbohydrates, and the amount of salt increases slightly. And after another 2 days, the patient can already consume up to 90 g of proteins, 70 g of fats and the physiological norm of carbohydrates (350 g). During these days, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids. Nutrition after surgery involves frequent meals, first in small portions (100-200 g in adults and 50 g in children) with a gradual increase in volume up to 300 g per meal.
Start eating with Diet No. 0A . Only liquid and jelly-like dishes (jelly) are allowed. Seven to eight meals a day are recommended. On a daily basis it looks like this:
First day
- strained compote;
- sweet rosehip decoction;
- weak sweet tea;
- weak meat broth;
- rice broth;
- berry jelly (strained);
- fresh juices, diluted 2 times with water (50 ml per serving).
Consumption of sour cream, whole milk, pureed foods, grape juice and vegetable juices, and carbonated drinks is prohibited. Vegetables and milk can cause bloating, which is extremely undesirable after intestinal surgery. Further meals are organized within Table No. 0B , which is prescribed for 2-4 days (depending on the patient’s condition). At one time, the patient can eat 350-400 g of food. Meals six times a day.
Second and third day
- liquid and pureed porridges (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat) in meat broth or broth diluted with water;
- slimy cereal soups;
- weak meat broths with the addition of semolina;
- steam omelettes and soft-boiled eggs;
- steamed meat and fish soufflés and purees from low-fat meat and fish;
- cream (100 g, added to dishes);
- berry jellies and mousses from non-acidic berries.
In the following days Diet No. 0B as a transition to a rational but dietary diet.
Fourth and fifth days
- pureed soups;
- pureed fresh cottage cheese (add cream or milk);
- meat, fish and chicken, ground in a meat grinder (added as minced meat to dishes);
- curd dishes (steam);
- 100 g white crackers;
- dairy products;
- pureed zucchini, potatoes and pumpkin;
- baked apples;
- pureed milk porridges;
- fruit and vegetable puree;
- tea with milk.
Nutrition after peritonitis does not differ from that described above, the only difference is that the transition from one version of the surgical diet to another is more delayed in time due to the serious condition of the patient. After completing three options of zero diets, the patient, depending on the state of health, is transferred to standard Diet No. 1 or surgical Diet No. 1 . It differs from Diet No. 1 in that it includes weak meat and fish broths and limits milk consumption. Nutritional issues are discussed with the attending physician.
The diet after removal of appendicitis should be followed for a month, and in case of complications and concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, or more. These questions are discussed with the doctor. During this time, food should be easily digestible.
Recommended:
- small and frequent meals;
- lean fish, chicken or beef, which is prepared by boiling;
- complete nutrition in terms of protein, vitamins and minerals;
- limit heavy fats, avoid fatty meats, smoked meats, any sausages, mayonnaise, hot sauces;
- exclude foods that promote fermentation and gas formation (coarse vegetables, legumes, any varieties of cabbage, carbonated drinks).
After surgery for appendicitis, the patient for 3 months should not:
- ignore wearing a bandage;
- perform unacceptable physical activity.
Within 1.5 months, muscle fusion occurs and the risk of hernia remains, therefore, after removal of the appendix, heavy lifting is prohibited. But daily slow walking (up to 2-3 km per day) is indicated as it prevents the appearance of adhesions.
Changes in the gastrointestinal tract after surgery
The most difficult period is the first day after surgery. During this time, the patient is prohibited from drinking and eating food so that the regenerative process begins in the digestive tract. You can only moisturize your lips with water to prevent the skin from cracking. When the first day has passed, they gradually begin to eat food in small portions to start digestion of the food bolus and intestinal motor function. Every new day new products are added, so the diet will be different. Full recovery can be achieved within 2-3 weeks.
The appendix becomes inflamed when pathogenic microorganisms accumulate, forming a focus of inflammation. Gradually, the tissue becomes thinner, which can cause its rupture. All this is accompanied by acute pain, which is an indication for appendectomy. It is recommended to completely remove the inflamed intestinal outgrowth to prevent re-accumulation of infection and the risk of peritonitis. The procedure is absolutely safe and allows the patient to recover in a short period. It is performed laparoscopically. That is, the doctor pierces the patient’s skin with special instruments, viewing the area of the appendix through a probe, then eliminates it.
Many people believe that the appendix is just a vestige, but this is not true. Without indications, the operation is not performed, since the appendix retains some functions in the body:
- appendage of the cecum;
- an immunological organ that prevents the activation of opportunistic bacteria in the intestinal microflora.
As soon as severe abdominal pain occurs, it is recommended to contact a clinical facility. The pathology may be asymptomatic or cause slight discomfort, which becomes dangerous, since the appendix can suddenly rupture, causing peritonitis.
Once the appendectomy procedure is completed, the patient is sent to a ward where his well-being is monitored. On the first day, eating is prohibited. The diet begins on the second day, the doctor is obliged to advise the patient about the characteristics of his diet during the rehabilitation period. High-quality nutrition is required to maintain tissue regeneration without straining the digestive tract. If the diet is not used, serious complications may not occur, but the gastrointestinal tissue will take a long time to heal.
Peritonitis is an extremely dangerous condition that leads to blood poisoning and rapid death. This is the most severe complication of acute appendicitis.
Complications
If the patient does not consult a doctor or the operation is performed too late, the complications listed in the table may develop.
| Complications | Characteristic |
| Epididymal rupture | The caecum ruptures and its contents exit into the abdominal cavity. Bacteria spread through tissues and enter the systemic bloodstream. The patient's body temperature rises, blood pressure drops, and without emergency help he dies |
| Phlegmon | A purulent plaque forms on the blind process on the inner and outer sides. Fluid may accumulate in the abdominal cavity, containing particles of pus and bacteria |
| Gangrene | Due to the accumulation of pus and bacteria, the vessels of the appendix become clogged. This leads to damage to the tissue of the appendix and neighboring parts of the intestine. |
To prevent complications, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination.
Authorized Products
- Puréed soups are prepared in water or weak meat broth made from oatmeal, buckwheat, semolina, and rice. You can add an egg-milk mixture, a small amount of cream (50-100 ml) and butter (5 g) into soups. From the fourth day, boiled minced meat is added to soups, and after 7-9 days, meatballs.
- White crackers 75-100 g per day.
- Meat and poultry are first prepared in the form of a soufflé, a little later in the form of cutlets and quenelles; a month after the operation, you can eat lump meat.
- Fish is also prepared in the form of a soufflé, twisted boiled minced meat, and then in the form of cutlets, meatballs and quenelles. For cooking, choose low-fat fish (cod, hake, pike, blue whiting, pollock, ice fish).
- Porridges are prepared pureed and semi-liquid, adding milk and butter.
- From the fourth, potato, pumpkin, carrot, zucchini and beet puree are introduced, for the preparation of which cream or milk and butter are used. If desired, vegetable dishes can be replaced with vegetable baby food.
- Eggs are consumed daily (soft-boiled or steamed omelet).
- Milk is used as an addition to cereals, in tea, you can eat pureed cottage cheese every day, adding milk or cream. Cream is also added to soups or tea. The use of these products in their natural form is not permitted due to the possibility of developing flatulence .
- The berries are used to make jelly and jellies. Apples are consumed only baked or stewed, and only towards the end of the month can they be consumed fresh.
- Honey and sugar (40-50 g).
- Butter (butter) is added to dishes.
- You can drink weak tea with milk and cream, herbal teas, diluted berry juices, rosehip infusion.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fifth day after surgery
By day 5, the menu can again be diversified. The following types of products are added:
- porridge;
- fermented milk products (yogurt with bifidobacteria, kefir, low-fat and unsweetened cottage cheese);
- baked apples;
- rosehip decoction;
- boiled carrots.
All of the listed products are easily digestible and do not cause the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. If the patient has prolonged bed rest, constipation may occur. Therefore, doctors advise eating apples and carrots to soften stool. If these methods do not help, medications are used. Prolonged constipation can cause stretching of the intestinal walls, which will negatively affect the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Only the leading doctor should diversify the menu on the fifth day so that the restoration of the gastrointestinal tract occurs as planned. First, he must familiarize himself with the patient's medical history.
To speed up the recovery of the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, it is recommended to consume foods rich in beta-carotene. For example, pumpkin. It contains not only beta-carotene, but also other beneficial substances that cause the following processes:
- softening of stool;
- strengthening intestinal motor function;
- increased metabolism;
- normalization of blood clotting.
Nutrients help all foods to be absorbed better. It is recommended to pre-bake the pumpkin in the oven or cook it in a double boiler. It is then ground into puree, which can be eaten plain or in porridge.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet after appendicitis includes exclusion from the diet:
- beans, peas, beans, lentils, cabbage, which cause gas formation and can provoke intestinal colic;
- salt for 2 weeks (or sharply limit);
- for a month or more smoked foods, fried foods, fatty meats, coarse meats, sausages (smoked and boiled), mayonnaise, ketchup and sauces, fatty fish, salted and smoked fish;
- mushrooms (as a difficult-to-digest product);
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks, strong tea and coffee;
- sauces, vinegar, ketchup, mayonnaise and seasonings.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables | 2,5 | 0,3 | 7,0 | 35 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What is better not to eat after surgical treatment of appendicitis?
- wholemeal rye bread;
- pancakes, pancakes;
- puff pastry and fresh pastry;
- fatty fish, as well as salted, smoked, canned fish;
- hard-boiled eggs;
- whole milk, cream;
- ice cream;
- salo;
- buckwheat, pearl barley porridge, legume dishes;
- vegetables with a lot of coarse fiber, essential oils (cucumbers, radishes, peppers), pickled mushrooms;
- some soups: milk, okroshka, legumes;
- hard fruits, berries with rough skin, grains (raspberries, gooseberries), figs, halva;
- fatty, hot sauces, mustard, horseradish, pepper;
- carbonated drinks, grape juice.
Gradually, the patient returns to the usual menu and does not observe strict dietary restrictions. But to maintain health, you should not eat spicy, salty, smoked foods, or abuse alcohol. If the postoperative period is completed successfully in compliance with the recommendations of the therapeutic diet, the person will return to a full life without strict restrictions.
Menu (Power Mode)
The nutrition menu after surgery reflects a gradual expansion of the diet and amount of food consumed. Of course, in the first week (or more) the food is non-caloric and does not correspond to the physiological norms of a healthy person. However, it is sufficient for a patient who has undergone surgery and is on bed rest. A gradual increase in food load on the digestive organs trains them and prepares them for proper nutrition. Below is the menu by day.
First day
| 8:00 |
|
| 10:00 |
|
| 12:00 |
|
| 14:00 |
|
| 16:00 |
|
| 18:00 |
|
| 20:00 |
|
| For the night |
|
Second day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
The third day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Fourth day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Fifth day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Sixth day
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
The first 3 days after surgery
To diversify the diet, the patient must not have the following symptoms:
- inflammatory process in the scar area;
- increased body temperature;
- inflammation in the intestinal area.
The absence of these complications is indicated by the doctor after re-examination of the patient. The first 3 days are the most difficult period after surgery, so eating should be done with extreme caution. Permitted types of products:
- low-fat chicken broth and fillet;
- boiled rice without salt;
- pumpkin and zucchini ground into puree;
- homemade low-fat yogurt without adding preservatives, dyes, or sugar.
Each meal should be divided into 5-6 servings per day. If you eat food in small portions, there will be no load on the gastrointestinal tract.
Reviews and results
Postoperative nutrition has many restrictions, especially the first 2 weeks. However, then the diet can be diversified by introducing new dishes of stewed vegetables and soups with the addition of vegetables. Reviews from patients indicate that this type of nutrition has a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract, and a gradual expansion of the diet and volume of food prepares for normal nutrition without discomfort in the intestines.
- “... I ended up in the department with appendicitis. Recovery was easy because the removal was through a small incision. On the second day I was already sitting up and walking around the ward a little. The food in the hospital was bad (dietary, of course), but from the third day there was no longer enough cottage cheese and I wanted fish, so they brought it all from home, as well as vegetable purees for normal bowel function. 1.5 months have already passed, I have fully recovered, but I continue to monitor my diet and do not eat fried, smoked or spicy foods. My wife boils or bakes everything. A healthy diet and you need to stick to it constantly, increasing the amount of fish, chicken and cottage cheese”;
- “... I had this food after my appendectomy. The condition was serious, so for a long time I ate everything pureed and slimy. I also started having problems with stool. So it turns out to be a vicious circle - you can’t eat vegetables, you can’t use laxatives, and juices and kefir don’t help. They brought baby vegetable food and well-ground boiled beets from home. When I started moving more, everything got better. Well, at home it became generally easier. By this time I switched to steam cutlets, meatballs and various soups”;
- “... With chronic appendicitis, you have to constantly adhere to a diet. I even regret that I didn’t have the operation earlier, but now every year it gets worse and I don’t want to anymore. Errors in diet, as well as intestinal disorders or constipation can cause an exacerbation. It’s certainly not strong, but it’s still unpleasant to feel constant discomfort in the right side. I completely eliminated all spicy foods, cabbage, peas, soybeans and soy products. It's worse after smoked sausage and fish (sometimes I allow myself). It’s not very convenient to organize such meals at work (you have to take everything with you and warm it up).”
Water treatments
Surgery, blood, a surge of adrenaline, vomiting and the patient realizes that after the operation he smells unpleasant. But you will have to wait a bit with water procedures.
Until the stitches are removed, bathing and showering are prohibited. It is allowed to wipe the body with water, wash your face, and wash your feet.
After the stitches and bandage are removed, the restrictions are removed, but you should not rush to the bath or sauna. Doctors recommend short-term bathing in the shower.
The suture area should not be rubbed or massaged. It is not advisable to use decoctions of medicinal herbs while bathing, as they dry the skin.
Recovery time
The main thing that influences the recovery period is how difficult the initial situation with the disease was. There are two options for the course of the disease: the development of a gangrenous process that turns into peritonitis, or simple inflammation of the appendix without its rupture. In the first case, hospital stay may last a month or even more. It is difficult to determine how many days it will be necessary to stay in the hospital after surgery, since the recovery of each individual organism cannot be predicted. In addition, with the development of purulent inflammation, it is impossible to do without a full-fledged abdominal operation, which significantly increases the period of observation by doctors. How many days do you have to wait after surgery to remove appendicitis using laparoscopy?
Recovery after this type of intervention is much faster. The maximum time a patient can spend in hospital is 14 days if there are no complications.
Complications
With appendicitis, as with any other disease, development is possible. What may cause concern: • Pus in the suture area; • Weakening of the abdominal wall muscles and the development of a hernia; • Constipation or intestinal obstruction; • Peritoneal adhesions; • Impaired liver function and bile flow. If anything from this list appears, you must immediately go to the hospital.
What can you eat with phlegmonous form?
Phlegmonous appendicitis is one of the stages of the inflammatory process. Purulent melting of the walls of the vermiform appendix of the colon occurs, but the integrity of the organ is not compromised. The phlegmonous stage is characterized by increased pain, nausea, weakness, and dry mouth.
On the first day after phlegmonous appendicitis, it is forbidden to eat and drink
Products should be consumed in soft, liquid and mushy form. What you can eat and what you cannot eat is decided by your doctor, and it is important to follow his recommendations. You should absolutely not eat solid food in the first days. If you don't know what's best to take to a hospital patient after an appendectomy, prepare mashed potatoes and low-fat broth. You can also buy low-fat kefir.