The condition “gastritis” refers to several types of ailments, so no one will undertake to guarantee a delay in this type of illness without knowing the details from medical examinations and anamnesis.
Cases of conscription or cases of deferment of conscription happen all the time. For those interested, we will explain in detail the nuances of conscription with this disease.
If the disease is chronic
With chronic gastritis, an adult citizen has a chance to receive a fitness category, which both completely exempts him from the army and gives only a temporary deferment. That is, fitness levels are assigned from categories “B”, “C” or “G”.
Surely those young people whose medical history is kept due to frequent requests for medical help receive a deferment. In addition, the medical board will be interested in how often the disease occurs with exacerbation and how effective therapeutic methods are to influence the disease.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of chronic gastroduodenitis include pain in the abdominal cavity of varying degrees of intensity and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. 1-2 hours after eating, cramps and discomfort appear in the upper abdomen on the right side. The pain is most often aching, moderate, and can radiate to the back or shoulder blade.
Other manifestations:
- dark yellow or white coating on the tongue;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- constipation gives way to diarrhea;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea, vomiting, increased salivation;
- flatulence, belching;
- signs of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system - weakness, increased sweating, finger tremor, tachycardia.
As the pathology worsens, the skin becomes pale, blood pressure and heart rate decrease. Sometimes the temperature rises to low-grade levels.
Exacerbation of the disease most often occurs in the spring and autumn months. The acute period can last up to 6-8 weeks, but the pain syndrome disappears after 7-10 days.
Fitness categories: types that are assigned to conscripts with gastritis
Chronic gastritis, occurring with rare attacks - “B” .
Chronic gastritis, manifested with impaired acid-forming and secretory functions, constant exacerbation and nutritional disorders (BMI 18.5 - 19.0 or less), provided that the conscript requires long-term (more than 60 days) hospitalization or re-hospitalization if the initial treatment failed ineffective - “B” .
Chronic gastritis, occurring acutely, with disruption of a number of functions of the gastrointestinal tract to such an extent that emergency therapy is required - “G”.
Most often, there are conscripts whose condition does not exempt them from service, although the disease itself is manifested in a large number of young people. Their exacerbations are rare and are mainly triggered by eating junk food or due to lack of nutrition according to a strict schedule.
Therefore, such people are called up for service, because in the armed forces the diet is regular and balanced, so that during the entire time allotted for the performance of military duty, a person may not experience symptoms of exacerbation. Doctors even advise serving, because in civilian life there are more temptations and the chances of provoking an exacerbation are high. Young people who, before the medical examination, sought medical help with an illness at least twice a year are more likely to receive exemption. Either they spend two months or more in the hospital during the year due to gastritis, or they are diagnosed with “stomach dysfunction”.
What to do if gastritis does not exempt you from the army
Based on the experience of our work, we can say that it is almost impossible to obtain a military ID and enlist in the reserves for this disease. Even the chronic form of the disease, if accompanied by occasional relapses, is not a contraindication to military service. To be released from the army, you will have to prove the need for long-term treatment in a hospital and impaired stomach function. It is difficult to confirm these conditions, since this disease rarely causes severe conditions prescribed in article 59 of the schedule of diseases. You can write off only if, after the appearance of erosions or inflammation, the disease turned into a stomach ulcer.
Another reason why this disease is called out is under-diagnosis. It is extremely rare to check for violations of the motor, acid-forming and secretory functions of the stomach, and without this it is extremely difficult to write off. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether someone with gastritis will be accepted into the army will often be in the affirmative.
How to act correctly to get a military ID due to gastritis
If you have gastritis, especially if it bothers you, it is important to seek help from a doctor. Thus, evidence of the severity of the illness, which the medical commission of the military registration and enlistment office will take into account, will gather itself. It is important to take medical documents with you when appearing on a subpoena.
Otherwise, the draft commission may not order an additional examination if the conscript declares that he has gastritis.
Additional examination is an important step in assigning the correct fitness category. Whether a conscript will join the army depends on what conclusions are drawn by doctors specializing in the treatment of gastritis. The final diagnosis must be formulated as the disease is mentioned in the Schedule of Diseases.
DELAY FROM THE ARMY FOR GASTRITIS
A deferment from conscription with chronic erosive gastritis is provided for in Article 61 of the schedule of diseases and is granted if during the period of conscription the disease manifested itself in an acute form: severe abdominal pain, disruption of the secretory or acid-forming functions of the stomach and other digestive problems. To undergo treatment, a conscript is assigned fitness category G, which implies exemption from conscription for up to 6 months. After the expiration of the granted health deferment, the conscript undergoes a medical examination again, based on the results of which the young man receives the final fitness category.
Also, doctors at the military registration and enlistment office may lean toward article 61 of the Schedule of Diseases if, by all indications, gastritis falls under article 59, paragraph b, and implies exemption from military service, but the conscript does not have a medical history with regular complaints and treatment in an inpatient setting. Often, such a decision by the draft commission requires a challenge in court.
If a young man has chronic duodenitis
The diagnosis of “gastroduodenitis” refers to a pathological process on the mucous membranes of the duodenum and stomach. This disease is not a reason for exemption from the army, even if during its course there are slight disturbances in secretion or infrequent exacerbations.
Even at the time of service, soldiers are not transferred to the reserves, but undergo treatment in specialized medical institutions of the Ministry of Defense. And only a serious dysfunction of the secretion and formation of gastric acid, as well as constant intensification of symptoms and a decrease in body mass index less than 19, can become the basis for assigning a recruit category “B”.
Gastroduodenitis: important points of pathology and its forms
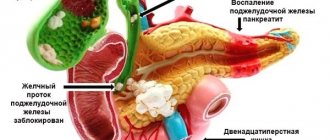
Gastroduodenitis is a disease in which an inflammatory-dystrophic process occurs in the lining of the stomach and duodenum. The pathology can be of varying degrees of severity - from mild with a minimal set of rarely manifested symptoms to a very severe form. The depth of dystrophic lesions also differs - it can be from superficial to atrophic. The disease typically occurs in different clinical forms, it can be gastritis-like, identical to peptic ulcer, pancreatic- or cholecyst-like, and others.
The disease is prone to frequent relapses, accompanied by severe pain, digestive problems, and, in complex cases, physical development disorders.
Despite all the difficulties described, if you ask the majority of medical workers and specialists whether they will enlist in the army with gastroduodenitis in 2019 , you will hear a positive answer. This is due to the fact that in almost all cases, in young people of military age, the pathology occurs in a mild form, less often - moderate severity and with very rare exacerbations. If this is “superficial” gastroduodenitis, then, in principle, it can be treated, and therefore is not considered a reason for exemption from military service. We can talk about a severe degree of chronic disease, which is not typical for young organisms, only in cases where the pathological process affected not only the stomach and duodenum, but also the pancreas, liver, and began to disrupt the functioning of the intestines.
Actions of a conscript in case of controversial issues of diagnosis and recognition of fitness for military service
With a diagnosis and supporting documents, conscripts undergo examination at the military commissariat. If the commission at the military registration and enlistment office issues a diagnosis of gastritis and suitability, with which the young man does not agree and wants to challenge the decision, a control medical examination is ordered.
Algorithm of actions in controversial issues:
• Appeal to the draft commission of a higher military registration and enlistment office. • Writing a statement of disagreement with the decision and a request to be called for a medical examination. The original is sent to the office, a copy to the district commissariat. • Confirmatory testing in civilian outpatient or inpatient settings. Referral to the state a medical facility can be obtained from the military registration and enlistment office. • Obtaining the conclusion of an independent military medical examination. • Repeated medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office. • If a conscript does not agree with the control examination at the level of a higher commission, he should contact the Arbitration District Court to appeal through a claim proceeding.
Important!
As soon as an application is submitted to a higher draft commission or a complaint to the court, the execution of the decision on conscription is suspended until full consideration and a new adoption.
Treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis
Complex differentiated treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of patients with chronic duodenitis and gastroduodenitis with the widespread use of new reflexology techniques allows you to achieve satisfactory results even with a pronounced clinical picture of the disease! Sarklinik knows how to treat duodenitis, how to cure duodenitis, how to get rid of duodenitis.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Wacpan | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Reflux esophagitis: symptoms, treatment, gerb, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Heartburn, burning in the stomach, treatment in Saratov, how to get rid of heartburn, what to do
Hepatomegaly, steatosis, fibrosis, alcoholic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, alcohol damage
Belching, treatment, frequent rotten belching of air, eggs, food
Stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer: treatment in Saratov
Comments ()
Acute duodenitis: symptoms, signs
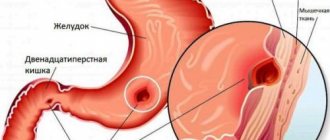
What are the signs and symptoms of acute duodenitis ? The clinical picture of acute duodenitis is characterized by symptoms such as epigastric pain , nausea, vomiting, general weakness, pain on palpation in the epigastric region, and increased temperature. The diagnosis is confirmed by FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), which detects inflammatory changes in the duodenal mucosa. With phlegmonous duodenitis, the patient’s general condition sharply worsens, tension in the abdominal wall muscles in the epigastric region is determined, a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign is detected, and an increase in temperature is noted.
Acute catarrhal duodenitis and erosive-ulcerative duodenitis often end in self-healing within a few days. With repeated duodenitis, a transition to a chronic form is possible. Complications of acute duodenitis are intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall, and the development of acute pancreatitis.
Treatment methods for chronic gastroduodenitis
Therapy for the disease includes several stages - diet selection, drug and non-drug treatment.
Diet therapy
For chronic gastroduodenitis, diet is one of the important components of treatment. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that require prolonged digestion. All food should be boiled, pureed or mushy.
Authorized products:
- slimy or pureed first courses in vegetable or weak meat or fish broth;
- lean varieties of meat and fish, steam, boil, stew;
- buckwheat, semolina, rice, vermicelli;
- seasonal vegetables, stewed or boiled;
- butter and vegetable oils - add to prepared dishes;
- dried wheat flour bread, white crackers;
- steam omelette, soft-boiled eggs;
- jelly, jelly, sweet fruit compote;
- casserole, low-fat cottage cheese soufflé;
- dairy products;
- marshmallows, biscuits, honey, sweet jam;
- weak black or green tea with milk.
During an exacerbation of the disease with high and normal acidity, table No. 1 is prescribed. With low acidity - diet No. 2. After improvement of the condition - diet No. 15. For constipation - No. 3, with stool disorder - No. 4. In the first 24 hours after the onset of relapse Fasting is indicated; you can drink water or tea without sugar in small quantities.
If you have gastroduodenitis, you should not eat hot or cold foods, fatty or fried foods. The list of prohibited products includes any canned food, marinades, smoked meats and marinades, sauces and spices. Alcohol and carbonated drinks, raw vegetables, and mushrooms are contraindicated.
Pharmacotherapy
The goal of drug treatment of chronic gastroduodenitis in children and adults is the same - to relieve unpleasant symptoms, eliminate the causes of the pathological condition, reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease and the development of complications.
Groups of medications:
- antimicrobial drugs, bismuth-based agents to eliminate Helicobacter pylori infection;
- antispasmodics;
- antacid drugs, proton pump inhibitors;
- dopamine receptor antagonists, enzymes;
- vitamin complexes;
- antidepressants.
When diagnosing a phlegmonous form of pathology, duodenal obstruction, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Non-drug therapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed during remission and exacerbation of the disease.
Effective physiotherapy:
- medicinal electrophoresis and galvanization;
- ultrasound therapy - for normal and increased acidity of gastric juice;
- treatment with diadynamic or sinusoidally modulated currents;
- DMV therapy;
- inductotherapy;
- laser or magnetic laser therapy;
- applications with ozokerite, paraffin, mud therapy;
- treatment with mineral waters, pine, pearl baths.
Physiotherapy has a beneficial effect on the main pathogenetic mechanisms of disease development. The procedures help normalize the functioning of the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. The treatment helps to reduce the manifestations of inflammation and improve microcirculation, has a pronounced analgesic effect, and restores the trophism of the affected organs. The positive results obtained last for several months.
During remission, physical therapy is prescribed. The specialist selects exercises to improve blood circulation in the abdominal cavity and trophism of the gastric mucosa, accelerating reparative processes.
Additionally, patients are recommended a course of psychotherapy to learn methods of dealing with stress and nervous tension.
Erosive gastritis and emergency service
Erosive gastritis is characterized by symptoms such as the appearance of wounds on the gastric mucosa. These erosions cause severe pain, nausea and vomiting.
If this type of gastritis worsens, the patient needs hospitalization and treatment in a hospital setting. He is also prescribed a strict diet. Due to these nuances, a conscript cannot be accepted into the army with such a diagnosis. It is worth noting that the release will be temporary.
If the diagnosis is confirmed during an additional examination, the military commissariat issues a deferment for six months. During this time, the conscript must undergo treatment and upon expiration of the period he receives a summons for another examination.
Often, erosive gastritis causes stomach ulcers and can cause gastric bleeding. Given such serious complications, the conscript can count on transfer to the reserve and release from the army.
Prevention
To avoid exacerbation of chronic gastroduodenitis, doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- eat properly and balanced;
- do not forget about moderate physical activity;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- carry out anti-relapse therapy once every 2 months.
With chronic gastroduodenitis, it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Various factors can trigger a relapse - stress, dietary errors, overwork. But if you follow all the recommendations of the gastroenterologist, you can avoid systematic exacerbations.
Self-medicating chronic gastroduodenitis is dangerous. Without proper therapy, dangerous complications develop - peptic ulcer, gastric bleeding, cancer of the stomach or duodenal papilla, anemia, atrophic gastritis.