A pathological protrusion on the walls of the intestine is called a diverticulum. The disease is characterized by a mild course without obvious clinical symptoms. Over time, intestinal disorders and dyspeptic syndrome develop. Diverticulosis is treated with medication, surgery and diet. If the disease is asymptomatic, specific treatment is not required.
About the disease
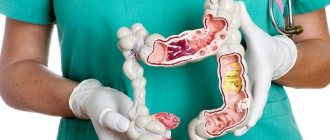
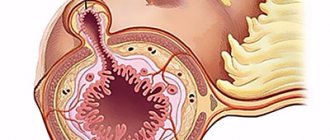
Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon manifests itself in protrusion of the walls of the intestinal tube in the sigmoid region. The sigma is the end of the colon. The projections consist of submucosal and mucosal tissue. They sag due to a weakened muscle component, so they resemble bags. In medical language they are called diverticula. Formations, as a rule, are multiple.
In acute cases, the discomfort from the protrusions is quite great. Severe pain, weakness, and intestinal disorders with bleeding may be present. “Peaceful” periods often pass unnoticed. They are easily confused with a slight malaise, a minor gastrointestinal disorder. Often the disease is discovered accidentally or only after complications. A large percentage of patients with this problem are over the age of 40. Women who have given birth, people with genetic abnormalities of the intestines and a sedentary lifestyle are especially at risk.
In the second half of life, the body begins to weaken and copes much worse with low-quality products and lack of diet. The aging mucosa no longer secretes the full amount of enzymes to break down food. Constant stress reduces the ability to resist viruses, the intestine is protected by compaction, and is constantly inflamed. As a result, undigested masses pull back the walls of the mucous membrane, get stuck on the protrusions, rot and wander.
Diverticulosis must be treated, otherwise the sacs may burst and lead to severe bleeding. Many doctors note the inextricable connection between diverticulosis and irritable bowel syndrome. Therefore, similar treatment regimens are proposed.
Reviews and results
The effectiveness of this nutrition has been appreciated by many, so the reviews and results are positive. Everyone notes that the diet is easy to tolerate and feasible in everyday life. The main thing is to choose vegetables and fruits that will be well tolerated and will not cause intestinal pain and bloating.
- “... I have been suffering from constipation for many years and lately I have started to worry about pain in my left abdomen, which gets worse after eating. With age, the problem worsened - many foods began to be poorly tolerated (milk, cabbage, legumes, grapes and grape juice) - all this began to cause bloating. After examination, a diagnosis of sigmoiditis and diverticulosis was made. I am convinced that dietary nutrition is very important for these diseases. If the diet is violated, pain and discomfort in the intestines again bother me, so I began to carefully monitor my diet”;
- “... I have been worried about constipation for many years, and this disease was recently discovered. I realized that I need to watch my diet, because bread, buns and pasta make me stronger and cause pain in my intestines. Diet and drinking water helps a lot. I can’t stand a lot of fresh vegetables - they cause pain and bloating. I liked the boiled beets and seaweed in salads”;
- “... A year ago I was diagnosed with diverticular disease. I was worried about pain in the intestines, mostly on the left, and constipation. They prescribed a diet and pills. With this diet, normal stool is restored within 5 days. And since I have a tendency to constipation, I need to constantly monitor my diet. At night I always drink kefir with bran, eat figs and prunes. I excluded fried and smoked foods, I don’t eat cabbage, radishes and radishes, as pain in the intestines immediately appears. I can say that thanks to nutrition, there has been no exacerbation for 2 years.”
The importance of therapeutic nutrition
If the disease is asymptomatic, specific treatment is not required. When clinical signs develop, medications (antibiotics, probiotics, etc.) and diet therapy are prescribed. In severe cases, surgical treatment is required to remove diverticula or part of the intestine.
Therapeutic nutrition for diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon involves a strict diet and consumption of large amounts of coarse fiber. It improves perilstatics, eliminates flatulence, constipation, nausea, diarrhea and other symptoms.
Diagnostic methods
To more accurately determine the symptoms and prescribe treatment appropriate to the disease, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out. It includes an external examination and instrumental studies.
When palpating the abdomen, diverticulosis is indicated by swelling and tenderness of the large intestine, especially in the left side, while there is no tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
Instrumental diagnostics for suspected diverticulosis include:
- intestinal irrigoscopy (x-ray using a contrast agent);
- colonoscopy;
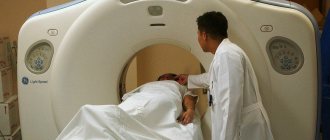
- computed tomography or virtual colonoscopy;
- plain radiography of the abdominal organs.
Additionally, ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs is prescribed. This study is carried out to exclude pathologies that are accompanied by symptoms similar to diverticulosis.
During diagnosis, it is important to exclude intestinal cancer or detect hidden diseases such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, intestinal polyps and others. No less useful is information about the localization of formations in the large intestine and their current condition: the presence or absence of inflammation, bleeding, etc.
Dietary rules for diverticulosis
A therapeutic diet is not only a list of prohibited and permitted foods, but also a complete description of the processes of preparing food and the rules for its consumption. Dietary nutrition for diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is based on the characteristics of the disease and has several important principles:
- It is recommended to eat in small portions at equal intervals throughout the day, with the last meal a few hours before going to bed. Foods should be chewed well.
- During the diet, it is important to maintain the correct drinking regime. Nutritionists advise taking at least 1.5 - 2 liters of water per day. However, tea, compotes, and juices are not included in this figure.
- Despite the fact that fish and meat are not plant foods and do not contain fiber, you cannot refuse to eat them. Excluding them from the diet negatively affects the functioning of the body, since fish and meat contain a lot of useful substances.
- The main part of the diet for diverticulosis is cereals, vegetables, and fruits. Dairy and fermented milk products should be chosen with a low fat content.
- If diverticulosis of the sigmoid intestine in a patient is accompanied by constipation, foods that have a laxative effect must be included in the diet. These include bananas, apples, prunes, vegetable oils, and oatmeal.
- Avoiding gas-forming products will help you cope with flatulence. It is necessary to exclude all types of cabbage, legumes, full-fat milk, fresh onions, and garlic.
- During therapeutic nutrition, it is recommended to prepare food by steaming, boiling, stewing, and baking. It is better to avoid frying, smoking and salting.
The transition to dietary nutrition should be gradual. A sharp restriction of certain foods and a change in diet can have both positive and negative effects on the condition of the body.
General rules
Diverticular disease (or diverticulosis ) is a pathological process affecting the intestines, a characteristic feature of which is the presence of protrusions of the intestinal wall.
Multiple pouch-like protrusions (diverticula) affect the mucous and submucous membranes and can be located in any hollow organ (intestines, gall bladder, bladder). However, their localization in the intestines is most common and can be observed in all parts of the digestive tract. The cause of the formation of protrusions is the weakness of the connective tissue of the intestinal wall, which develops with age. These changes are found in 80% of elderly people. In addition, impaired intestinal motor function (tendency to constipation ) leads to increased pressure inside the intestines and the appearance of protrusions in places of least resistance.
This disease is believed to be a consequence of poor diet. When consuming refined foods low in fiber, long-term constipation occurs, which leads to overstretching of the intestinal wall. If a chronic inflammatory process is present, then morphological changes occur in the intestinal wall. A sedentary lifestyle only aggravates the situation - intestinal motility and fecal passage slow down. In this regard, the appointment of therapeutic nutrition is of great importance in the treatment of this disease.
Diet for intestinal diverticulosis
Diverticulosis of the colon is more common than that of the small intestine. The main section of the large intestine is the colon. The length of the colon is 1.5 m, and it has sections: the ascending colon, transverse colon and sigmoid colon. The colon does not take part in digestion, but water and electrolytes are absorbed here, and the liquid contents from the small intestine are converted into solid ones in the colon.
Of all its sections, diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is more common, which is due to its anatomical and functional features: smaller diameter, a large number of bends (has the shape of the Latin letter “sigma”) and high pressure, since the sigmoid colon performs a reservoir function and the consistency of the intestinal contents in it is more dense.
Diverticulosis can occur without clinical manifestations and be an incidental finding during examination. In the presence of clinical manifestations, abdominal pain, bloating and unstable stool appear - alternating constipation , diarrhea and normal stool. With diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon, mild pain is detected in the left iliac region and often occurs after eating. After the release of gases or bowel movements, the pain may disappear or disappear completely.
If an inflammatory process appears in the wall of the diverticulum, then diverticulitis , which can be acute or chronic and is a complication of the disease. Its clinical picture is more pronounced: severe pain appears in the left iliac region, which does not disappear after defecation or the passage of gas. Persistent pain lasts for several days, the temperature rises, nausea and vomiting, and severe bloating appear.
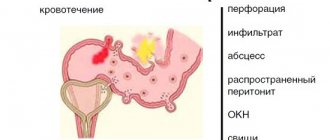
Other complications are also possible: perforation, intestinal bleeding and intestinal obstruction . Gradually, the diverticulum enlarges, its wall stretches, becomes thin and can perforate. Stagnation of feces in the protrusion contributes to the formation of ulcers and erosions , which can be complicated by bleeding. The consequence of a long-standing disease is adhesive disease, which can be complicated by obstruction.
If the disease is asymptomatic, there is no need for special treatment. In case of diverticulitis and the presence of complaints, laxatives and regulating motor function, antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, drugs that normalize intestinal flora ( Colibacterin , Bifikol or Bifidumbacterin ) are prescribed. Medical nutrition is required. In most patients, conservative treatment gives a lasting effect.
In 80% of patients, the disease progresses favorably without complications throughout life. In 20%, exacerbations of the disease are observed, and with each relapse the risk of serious complications increases. In such cases, surgical treatment is proposed - resection of a section of the sigmoid colon.
Nutrition during an exacerbation
In case of an acute process or a pronounced exacerbation of a chronic disease, diet therapy depends entirely on the severity of the symptoms: from eating easily digestible food ( Diet No. 4 as for exacerbation of chronic colitis) to creating complete rest for the intestines - hunger and intravenous nutrition.
During this period, fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, canned food, any pastries, pickled and pickled vegetables, legumes and mushrooms, halva, nuts, chocolate, any seeds, kvass, carbonated drinks, coffee, sour juices and alcohol are excluded.
The diet includes:
- porridge with diluted milk or water (buckwheat, oatmeal);
- cereal soups (possibly adding pureed vegetables with coarse fiber) and dairy;
- boiled fish and lean meats and poultry in the form of minced meat, steam cutlets, soufflé;
- steam omelettes or soft-boiled eggs;
- cream, kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, mild cheese;
- butter, olive and sunflower oils added to prepared dishes;
- boiled and pureed vegetables (potatoes, zucchini, pumpkin, carrots, cauliflower, broccoli) for soups and side dishes. Eat vegetables and fruits in small portions. In the first week after an exacerbation, they are used only after thermal cooking. Subsequently, they include coarse fruits without peel in the form of puree, finely grated carrots, fresh pumpkin and zucchini;
- sweet fruits and berries can be consumed in the form of jelly, baked apples (remove the skin), crushed or pureed dried fruits from compote; sugar, honey, marshmallows are allowed;
- warm weak tea with milk and sugar, bran decoction and rosehip infusion.
The diet for diverticular disease of the colon without exacerbation is balanced and contains an increased amount of plant fiber, since with diverticula the intestine slows down its evacuation function, constipation appears, which leads to progression of the disease.
- The consumption of plant fiber should be in the range of 30–35 g per day and it should be obtained from vegetables, fruits and grains (brown rice, sprouted grains, wholemeal bread). It is desirable to include wheat bran in the diet, which reduces intracavitary pressure and significantly accelerates the rate of movement of intestinal contents, thereby preventing its stagnation and increased pressure in the intestinal cavity. To a greater extent, this effect is exerted by coarsely ground bran.
- The amount of fiber should be increased gradually, and it is better to add bran and sprouted grains to dishes rather than eat them in their natural form, as there may be an increase in pain and flatulence .
- If tolerated, seaweed can be consumed.
- Drink plenty of fluids (1.5-2 liters per day) in the absence of contraindications.
- For constipation, be sure to include beets, prunes, and seaweed in your diet. Lactulose is the drug of choice if you are prone to constipation, but its preparations need to be used short-term, and they do not replace a diet with a high content of fiber and water.
- It is important to exclude foods that cause flatulence (legumes, lentils, raisins, grapes, onions, whole milk, cabbage, fruits with peels).
- For diverticula, it is necessary to exclude foods that cause constipation (blueberries, rice, strong tea, dogwood, jelly).
- You should exclude seeds and fruits with a large number of grains, which are not digested and irritate the intestinal mucosa.
- Vegetables and fruits containing excessively coarse fiber (pineapples, persimmons, turnips, radishes, radishes) should be excluded from the diet.
Diet for illness
Healthy foods for illness and after removal of the sigmoid colon are all those that are rich in plant fiber.
Since the primary goal for inflammation of the sigmoid colon is the normalization of stool, you should limit the consumption of foods that directly contribute to constipation, flatulence and gas formation. This is the “black list”:
- legumes
- Tea coffee,
- alcohol
- cocoa and chocolate
- fat meat
- mushrooms
- garlic
- semolina
- rice
- fresh wheat bread and pastry
- vermicelli
- canned products
- smoked meats
- hot spices
- White cabbage
- milk and dairy products (individually - such products do not provoke constipation for some, but quite the opposite)
But if you have diverticulosis and sigmoid colon cancer, you will have to completely forget about nuts, chips and seeds - hard, undigested particles of such products can easily get stuck in inflamed sacs (diverticula).
List of approved products
The table shows recommended products for diverticulosis patients. For the convenience of creating a diet, each item is accompanied by calorie content and nutritional supplements.
| Name | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories per 100 g |
| Zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| Cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| Carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| Eggplant | 2,1 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| Beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| Tomatoes | 0,6 | 6,0 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Sweet bell pepper | 1,8 | 0 | 6,0 | 38 |
| Pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| Apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10, | 41 |
| Watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| Avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| Bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| Mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| Melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| Peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| Plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| Apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
| Figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| Dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| Raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66 | 264 |
| Prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
| Buckwheat | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| Oatmeal | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| Pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
| Millet | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| Jachka | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
| Unpolished rice | 7,5 | 2,6 | 62,3 | 303 |
| Bread | ||||
| Grain bread | 10,1 | 5,4 | 49,0 | 289 |
| Bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| Whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
| Jam (average) | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| Jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| Zephyr white | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| Fruit and berry marmalade (average) | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| Pastila without additives | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Cookies "Maria" | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
| Oatmeal cookies | 6,5 | 14,4 | 71,8 | 437 |
| Honey (average) | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| Milk 2.5% | 2,8 | 2,5 | 4,7 | 52 |
| Kefir 1% | 3 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
| Ryazhenka 2.5% | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,2 | 54 |
| Cream 20% | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| Sour cream 15% | 2,6 | 15,0 | 3,0 | 158 |
| Cottage cheese 5% | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
| Natural yogurt without fruit 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
| Beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| Beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| Beef tongue | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| Veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| Rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
| Lean lean pork | 19,4 | 7,1 | 0,0 | 160 |
| Chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Quail | 18,2 | 17,3 | 0,4 | 230 |
| Turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
| Chicken egg | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
| Quail egg | 11,9 | 13,1 | 0,6 | 168 |
| Cod | 16,0 | 0,6 | 0,0 | 69 |
| Pike | 18,4 | 1,1 | 0,0 | 84 |
| Zander | 18,3 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 84 |
| Pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| Tuna | 24,4 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| crucian carp | 17,7 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 87 |
| Olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| Sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| Apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| Plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| Tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
List of prohibited products
| Group | Name |
| Vegetables and mushrooms | Garlic. Onion. Mushrooms. Cabbage |
| Fruits and berries | Strawberry. Raspberries. Kiwi. Strawberries |
| Cereals | Semolina. White rice. All legumes |
| Meat and poultry | Pork is fatty. Salo. Sausages, smoked meats. Duck. Goose |
| Fish | Mackerel. Halibut. Saira. Herring. Silver carp. Salmon |
| Bakery | Shortbread cookies. Baking. Cakes. Cakes |
| Dairy | Full fat milk. High fat fermented milk products. Butter. Fat sour cream. Fat cottage cheese |
Pickles, marinades, spicy seasonings, and canned food are also prohibited. Chocolate and cocoa can be consumed in minimal quantities occasionally.
Fully or partially limited products
- Spicy dishes, sauces, horseradish and mustard greatly irritate the mucous membranes and disrupt the function of the gastrointestinal tract. You should limit foods that cause constipation - rice, semolina, noodles, sago, vermicelli, potatoes, as well as legumes, which can cause bloating.
- You should exclude dishes with a viscous consistency - these are slimy soups, mashed potatoes, mashed porridges and jelly, as they move slowly through the intestines.
- They stay in the stomach for a long time and are difficult to digest fatty types of meat (duck, goose) and fish, canned food, smoked meats, hard-boiled and fried eggs. In this regard, they must be excluded from the diet.
- Also excluded are dishes containing tannins - strong tea, cocoa and coffee, jelly from quince, pears, bird cherry, blueberries, dogwood.
- Chocolate and all kinds of products with cream are also not allowed. It is worth excluding bread made from high-grade flour, as well as baked goods made from yeast dough and puff pastry, and eating unsweetened pastries is limited.
- You should avoid vegetables rich in essential oils and coarse fiber (onions, radishes, turnips, radishes, peppers), as well as mushrooms.
- Limit the consumption of animal fats and give preference to vegetable ones.
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| dogwood | 1,0 | 0,0 | 10,5 | 44 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| sago | 1,0 | 0,7 | 85,0 | 350 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Menu for diverticulosis
With certain skills, creating a menu for a diverticulosis patient is not difficult. Examples of table No. 5 from sanatoriums and hospitals are freely available. Dishes and products can be easily adjusted to the taste of a particular patient by looking at such a cheat sheet.
On any day of the week you can take a full diet or one meal from the proposed:
| Eating | Meal options |
| Breakfast | Steam omelette, cucumber salad, herbal tea; cottage cheese casserole with raisins (banana or apples), tea with lemon; buckwheat pancakes, rosehip infusion; boiled egg, tomatoes, tea; oatmeal, fruit salad with yogurt, juice; buckwheat porridge (any unsweetened cereal), cheesecakes, compote; baked fruit puree, Maria cookies or whole grain pie, mint tea; carrot pancakes with sour cream, drink; cottage cheese with berries, juice; bran pancakes with banana puree and honey, tea |
| Second breakfast (snack) | Yogurt with fruit; biscuits, apple or banana cookies; cottage cheese with dried fruits; a couple of bananas; salad of grated carrots and apples; fruit jelly, cookies; kefir with pie, bran or cookies; berry mousse; baked apples with cottage cheese or yogurt |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup, boiled chicken, dried fruit compote; okroshka with kefir, fish cutlets, tea; broccoli soup, stewed or baked fish, rosehip broth; pumpkin soup, stewed beef with carrots, compote; baked rabbit with vegetables, tea; turkey soup, beet salad, boiled buckwheat, tea; steam cutlet, zucchini baked with egg, compote; potato soup with fish, vegetable salad, drink; cabbage rolls, buckwheat or oatmeal soup, tea; tomato soup, meatballs with rice, compote; chicken noodle soup, buckwheat with cucumber, tea |
| Dinner | Buckwheat with stewed vegetables; steamed cutlets with barley porridge; vegetable salad with a piece of fish, meat or chicken; stewed zucchini, cottage cheese with fruit; brown rice with warm salad of baked tomatoes, eggplant and zucchini; steam omelette, pumpkin with honey and raisins; vegetable pilaf, baked apples with cottage cheese; pasta with vegetables and chicken; potato casserole with fish, vegetable salad; lazy dumplings with sour cream; beef stew with prunes, baked potatoes (sometimes mashed potatoes); baked potatoes with vegetables in foil |
Immediately before bed, it is useful to drink a glass of kefir, fermented baked milk or other fermented milk product at room temperature.
Power Menu (Power Mode)
Taking into account the list of recommended products, you can create a menu. Every day you need to take juices with pulp, dried fruit compote, infusion of prunes or rose hips. If you have constipation at night, you need to consume kefir daily with the addition of wheat bran (1 tbsp - 2 tbsp), they can also be added to dishes.
Depending on the condition of the intestines (constipation or normal stool), you can increase or decrease the amount of bran in the diet. For the whole day you can consume 200 g of wholemeal bread, 200 g of rye bread and up to 50 g of sugar.
Monday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Tuesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Wednesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Nutrition during exacerbation of diverticulosis
In case of acute symptoms or exacerbation, the diet is changed. Moderate pain allows the consumption of easily digestible foods. In such cases, the table is set according to model No. 4 (chronic colitis). Severe pain and bleeding may require complete rest of the gastrointestinal tract with fasting and intravenous feeding.
Exacerbations require you to exclude raw vegetables and fruits, and switch only to pureed baked versions. The peel needs to be removed to make it easier for the intestines. Berries only in the form of jelly, dried fruits - from compotes.
Soups are preferably in the form of purees, milk. The porridge is boiled well and made semi-liquid.
Fish, poultry, and meat are prepared by boiling or steaming in the form of cutlets and soufflés. Hard-boiled eggs are replaced with soft-boiled eggs. Omelettes are left.
Among sweets during an exacerbation, small portions of honey, marshmallows and marshmallows without additives and chocolate are allowed.
It is good to drink bran or oatmeal jelly, rosehip decoction, chamomile or mint tea.
Healthy recipes
Fruit-cereal mixture – cleanses the intestines and the formed diverticulum. Grate green apples and mix with the same amount of ground sprouted wheat. Used on an empty stomach.
Oatmeal jelly - has a beneficial effect, is well absorbed: non-hot boiled water - 3 l, kefir - 200 ml, oatmeal - 500 g.
Mix water with kefir and add flakes, mix. The mixture is infused for several days in a cool room, then filtered and washed. Leave the strained concentrate for another day. Finally, you can cook the jelly. Mix 2 liters of water with 2 tablespoons of the mixture, bring to a boil, cool. The remaining product should be stored in the refrigerator.
Treatment with traditional methods
If there is such a diagnosis, the patient is recommended to resort to traditional medicine such as:
- carrot powder. You need to take four tablespoons of carrot seeds, grinding them to a powder. Take a teaspoon up to three times a day with plenty of liquid. The course of treatment is no more than two weeks, after which it is recommended to repeat the therapy with a week's break;
- flaxseed or olive oil. Take one tablespoon of oil every day on an empty stomach;
- aloe tincture. Two hundred grams of the crushed plant must be mixed with 300 grams of honey. Leave it for a day, then start taking a tablespoon at least an hour before meals. The course of treatment should not exceed two weeks.
If you have any of the above symptoms, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis. Self-medication is fraught with negative consequences, including death. Take care of your health.
Causes of colon diverticulosis
The main causes of diverticula on the intestinal walls are dystrophic changes in their muscle layer and impaired peristalsis. Often such changes are accompanied by ischemic and degenerative changes associated with age-related changes in the body. That is why the largest percentage of patients diagnosed with diverticulosis are elderly.
The onset of pathological changes in the intestines can be provoked by:
- lack of plant fiber in the diet, which provokes chronic constipation;
- lack of physical activity, as a result of which intestinal motility worsens;
- excess weight.
Other diseases can also affect the intestinal walls, however, their nature is often associated with the above phenomena. For a diverticulum to form, weakening of the muscles and connective tissues of the intestines is not enough.
They are formed only against the background of increasing intraintestinal pressure and resistance to the movement of too thick feces. In the presence of even small defects in the walls, protrusion of the mucous membrane occurs through the muscular layer of the intestine.
Residents of Canada and the USA are considered to be the record holders for the incidence of diverticulosis, and the smallest number of patients with this pathology was recorded in Asian countries and Japan.
Prognosis for the use of diet as treatment
The successful outcome of diet therapy depends on the stage of development of the pathology. With asymptomatic detection or the first attack, a positive effect occurs in 70% of patients. After 2-3 exacerbations, in 6% of cases, a stable improvement is achieved by a combination of proper nutrition and medications.
Constant use of the diet helps prevent complications in most patients. This tactic avoids surgical interventions in 20-30% of cases. When bleeding, the right food perfectly complements drug therapy and allows you to replenish your strength without harming the intestines.
Is diverticulitis always an operation?
No. Treatment of diverticulitis most often, in 80% of cases, is carried out conservatively. Antispasmodic and antimicrobial agents are prescribed. If necessary, detoxification therapy is carried out. Mandatory and primary treatment is the prescription of a diet and normalization of stool. Often, after recovery, relapses of the disease occur.
Modern methods make it possible to relieve the patient from serious complications of diverticulitis in a minimally traumatic way.
If there is a diverticulum abscess, its treatment can be carried out using a gentle, technological method. Diverticulum abscesses measuring 2 cm or more can be treated without incisions in the abdomen. To treat an abscess, drainage tubes are connected to the abscess through a puncture on the anterior wall of the abdomen under CT control. Through them, pathological contents are drained and antiseptic treatment of the lesion is carried out.
Surgical treatment of diverticula
In the presence of large protrusions, multiple diverticula, perforation, fistulas, it may be necessary to remove a section of the intestine (resection). According to indications, laparoscopic resection is possible, without large incisions and a long recovery period. Indications for surgery and its scope are considered in each individual case and depend not only on the nature of the complication, but also on the general condition of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the results of histological examination of biopsy specimens.
How to eat properly?
During an exacerbation of the disease, nutrition is determined by the severity of symptoms. In acute diverticulitis, gentle table No. 4 is indicated. In severe cases, the patient is prescribed fasting for several days or intravenous nutrition. Diet No. 4 excludes fried foods, smoked foods, baked goods, marinades, raw and pickled vegetables, sour juices, and coffee. Menu includes:
- porridge with water;
- milk soups;
- cream soups from tomatoes, pumpkin, potatoes;
- boiled fish, poultry;
- steam omelettes, soft-boiled eggs;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- soft fresh or baked fruits;
- marshmallow;
- honey;
- warm tea;
- pureed non-acidic berries.
When clinical signs develop, medications (antibiotics, probiotics, etc.) and diet therapy are prescribed. In severe cases, surgical treatment is required to remove diverticula or part of the intestine.
Diet result
Diet is a powerful helper for the body during exacerbation of intestinal disease. Proper nutritional therapy helps to get rid of the symptoms of the disease, and sometimes completely cure intestinal diverticulosis even without drug intervention. But drug treatment without diet is much less effective.
The disease can be prevented with proper nutrition. By consuming healthy foods in moderation and at the right time, you can make your body highly resistant to various diseases. After treatment for the disease, especially after diverticulitis, you should stick to the therapeutic diet for some more time, or better yet, completely reconsider your diet for the rest of your life.