- November 26, 2018
- Other states
- Cooper Luda
The abdomen is the area of the body that starts from the breastbone just below the pelvis and contains several important organs, such as the intestines. If these organs become infected or irritated, they usually cause pain. To better isolate the source of pain, you need to divide your abdomen into four quadrants. You can imagine if one line was drawn right down the middle of the belly and the other was drawn on the belly at the level of the navel. The lower right abdomen is the area below the navel on the right side of the body.
Classically, people think they have appendicitis when they start having pain in that area. There are a number of other causes of lower right abdominal pain that can also be life-threatening. However, most abdominal pain resolves spontaneously without intervention and the source is never identified. Thus, when it comes to lower right abdominal pain, it is worth thinking about the seriousness of the situation and your overall well-being. If you suspect that something is really wrong, you should consult a doctor immediately. Many people are interested in what it is: pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 37 in women, men or children.
Mechanical reasons
Mechanical reasons for pain in the lower back, lower abdomen and temperature 37:
- Gas: The accumulation of large amounts of gas in your colon can cause pain and discomfort when the colon becomes distended.
- Let. Various illnesses can cause your intestines to become stuck together or twisted, leading to pain as food or stool cannot move.
- Constipation: Long periods of constipation can cause significant abdominal pain.
- Trauma: Traumatic trauma can damage organs in the abdominal area.
Why is it necessary to distinguish between these diseases?
The group of people with weakened immune systems includes pensioners and children, people with chronic diseases. This means that their immune system is most susceptible to attack by pathogens. An incorrect diagnosis can lead to deterioration in the functioning of the entire body and incorrect treatment.
Due to influenza, the natural functions of the immune system are weakened, against the background of this, other infections can join and develop. These are mainly respiratory tract infections: the lungs are affected by streptococcal or staphylococcal flora. This contributes to the development of pneumonia, pulmonary hemorrhage, and edema.
Influenza in adults can be complicated by the development of sinusitis, sinusitis, pericarditis and acute cardiovascular failure. Influenza in children is complicated by otitis media, focal pneumonia, and bronchitis.
Influence of inflammatory processes
Inflammatory reasons for pain in the lower abdomen, temperature 37.1:
- Infection. Injury to certain organs in the abdomen, such as the appendix or intestinal structures called “diverticula,” can cause symptoms of fever and lower right abdominal pain. Diarrheal illness may also be associated with pain.
- Autoimmune. With an autoimmune disease, your immune cells can inadvertently attack tissue from your GI tract, causing damage and pain.
Other factors
Other reasons for pain in the lower back, lower abdomen and temperature 37:
- Tumors: Tumors in the gastrointestinal tract can grow and cause irritation, blocking the passage of stool.
- Urine: Some urological conditions, such as kidney stones, can cause pain that shoots into the right lower quadrant.
- Reproductive: In women, masses or infections of the reproductive organs may cause lower right abdominal pain.
- Poor circulation: Poor blood flow can cause pain in the right lower abdomen as the organs there seek help.
Appendicitis
The appendix is a small tubular organ attached to the large intestine, with no known function. It is located in the lower right side of the abdomen. A blockage (caused by intestinal debris, usually) inside the appendix causes appendicitis. The blockage leads to increased pressure, problems with blood flow and inflammation. If the blockage is not treated, the appendix can rupture and spread infection to the abdomen. In this case, you feel nauseous, have lower abdominal pain and a temperature of 37 or more.
Modern hospitals use laparoscopic procedures that require only 3 small (less than 1 inch) incisions. These procedures are now often carried out without an overnight hospital stay and healing occurs very quickly. You can expect to resume normal activities within a few days after surgery. Full recovery may take 4-6 weeks and you should avoid strenuous activity until then.
- Rarity: Rare.
- Top symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, pelvic pain, loss of appetite, diarrhea.
- Symptoms that always occur with appendicitis: abdominal pain.
- Symptoms that never occur with appendicitis: pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, in the upper left part, restlessness, pain in the lower ribs, easing of abdominal pain, migraine.
- Urgency: high.
Causes of high fever, nausea and vomiting, headache
The patient has a high temperature, nausea, headache - these signs do not provide a complete understanding of the reasons for poor health. To determine them, additional examinations are prescribed that will help identify hidden pathologies. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain insist that during the examination it is important to tell all the details, when the first signs began, in which area the pain occurs and with what frequency.
Intoxication
The first reason why headache, nausea and vomiting can occur simultaneously, and the temperature rises is poisoning. The clinical picture is associated with the entry of toxins into the body by any means. They can penetrate with food, inhaled air, through the skin and mucous membranes. Depending on this, there are several main types of poisoning. They cause similar symptoms, so it is important to promptly determine which substance caused the intoxication.
- Food poisoning is the most common option. Symptoms appear several hours after eating poisonous or spoiled foods. The patient experiences nausea, vomiting, headache and general weakness. In case of food poisoning, taking sorbents and gastric lavage are indicated.
- Poisoning with drugs and alcohol develops according to a similar pattern. Their main cause is overdose. Both the metabolic products of ethyl alcohol and medicinal substances are strong toxins. In excess, they accumulate in tissues, poison nerve tissue, and affect brain function.
- Poisoning with pesticides is one of the dangerous types. The reason may be a violation of the rules for using preparations for treating soil and premises against pests. If they come into contact with the skin, wash them off immediately with water. If they enter the body with food, you should immediately consult a doctor and take a saline laxative.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning is a specific situation that can occur during a fire, as well as during inhalation of this gas in transport, industry or agriculture. When the first signs appear, the victim is evacuated from the danger zone, oxygen and symptomatic agents are used for treatment.
Mild poisoning can be treated at home. For this, bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids are indicated to reduce the concentration of toxins in the blood. Moderate and severe cases of intoxication require hospitalization and hospital procedures. The patient may be prescribed IVs, gastric lavage, and medications to restore the balance of electrolytes in the blood.
Infectious diseases
One of the most common causes of nausea, vomiting, headache, weakness, and fever is infectious diseases. Viruses and bacteria penetrate the gastrointestinal tract and multiply on the mucous membrane. Children are at risk because their immune system is not strong enough and cannot fully fight infection. There are several diseases that can cause a typical clinical picture.
- Stomach (intestinal) flu - the causative agent is rotavirus. The disease develops when consuming poorly washed foods (often vegetables and fruits), as well as contaminated drinking water. Characteristic symptoms are fever, acute abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and headaches. Treatment is symptomatic; the patient may need to be admitted to a hospital.
- Enteroviruses are diseases caused by enteroviruses. The pathogen is very stable in the external environment, so a person can easily become infected through food or water of questionable quality. At the onset of the disease, fever, abdominal pain, fever and weakness are observed. Over time, the infection can spread to the muscles, heart, nervous system and other internal organs.
- Toxic infections are a group of diseases caused by bacteria. The clinical picture is provoked by toxic waste products of microorganisms that poison organs and tissues. Toxins enter the bloodstream, spread throughout the body, causing a sharp deterioration in health, headaches and digestive disorders. Toxic infections include salmonellosis, staphylococcosis, clostridiosis, botulism.
Treatment is prescribed individually. If a bacterial infection is present, a course of antibiotics is prescribed and a regimen of symptomatic therapy is selected. The patient may need to be hospitalized and treated in an infectious diseases hospital.
Thermoneurosis
Under stress, prolonged tension, and fatigue, a person may experience high fever, nausea, and headache. The state of health deteriorates sharply, while the test results are within normal limits. In addition, pain in muscles and joints appears. The disease must be distinguished from pathologies of the thyroid gland, infectious diseases, and disturbances in the functioning of the thermoregulation center in the brain. For this, all the necessary studies are carried out, and a diagnosis can be made only after excluding other diseases. A characteristic sign is that after taking aspirin, the temperature does not decrease, as with viral infections and inflammatory processes.
Thermoneurosis usually goes away on its own within a few days. The main recommendations are rest, proper nutrition and moderate exercise. However, it can develop as a consequence of traumatic brain injury. In this case, treatment includes taking medications to improve cerebral circulation, physiotherapy and other techniques.
Brain diseases
Symptoms such as high fever, nausea, vomiting, and headache can signal dangerous disorders of the central nervous system. They can be caused by infectious pathogens, injuries, and various abnormalities in the development of structures. In addition, with such a clinical picture, it is important to exclude the possibility of tumors in the brain.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord. It can manifest itself as an independent disease or as a complication of other pathologies. Its cause is a viral, bacterial or fungal infection, and mixed varieties are also isolated. The greatest danger is bacterial meningitis, as it can lead to purulent inflammation.
The disease manifests itself in a characteristic picture:
- acute headaches, which are often concentrated in the back of the head;
- a sharp increase in temperature to critical levels;
- neck muscle tension;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fainting, unconsciousness, lack of coordination.
According to the nature of the course, they distinguish between chronic, acute and fulminant meningitis. The latter option poses a danger to the patient's life. It is severe and requires immediate medical attention. Even if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, there is a possibility of complications in the form of hearing loss, vision loss, and constant headaches.
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. This is a dangerous condition that can lead to disruption of vital functions and death. In most cases, encephalitis is caused by infectious agents and occurs in an acute form. Its main symptoms are headache, nausea, fever, hearing and vision impairment, as well as other signs.
Encephalitis can develop as a complication of viral or bacterial diseases, as well as as an independent pathology. There are two main types of it:
- encephalitis in epidemic form (caused by various viruses that spread quickly, including polio);
- sporadic cases (consequences of herpes, rabies, chicken pox and other diseases).
Tick-borne encephalitis poses a high degree of danger. The pathogen enters the bloodstream during the bite of an infected tick, spreads throughout the body and reaches the brain. 1–2 weeks after the bite, the victim begins to have a sharp headache, nausea, and the temperature rises to high levels. The disease is dangerous due to extensive damage to brain tissue, as well as inflammation of the cranial nerves.
Traumatic brain injuries
Headache, nausea and vomiting are common signs of traumatic brain injury. It is caused by a fall or blow, which leads to damage to nerve tissue. The most common form of traumatic brain injury is a concussion. The condition can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- acute pain in the area of impact, which spreads to the entire surface of the head;
- nausea, vomiting;
- possible loss of consciousness, short-term amnesia;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- arrhythmia, cardiac dysfunction;
- The duration of symptoms is no more than 7–10 days.
Traumatic brain injury is characterized by fainting and memory loss. Recovery time depends on the severity of the damage, the patient’s age and other factors. Headaches can persist long after the injury. The reason is prolonged hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), as well as insufficient blood supply to brain cells.
Inner ear diseases
It is important to distinguish diseases of the inner ear from disorders of the brain and acute infectious diseases. They also manifest themselves as headache, nausea, loss of coordination and other symptoms. This organ has a complex structure and is responsible not only for hearing, but also for balance. There are several pathologies that can develop in adults and children.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammatory process that affects the inner ear. It often develops as a complication of otitis and can occur in a purulent form. The patient experiences acute headache, nausea and vomiting, and hearing loss. In advanced cases, purulent discharge from the ear may occur.
- Vestibular neuritis is an inflammation of the nerve that innervates the inner ear. The disease most often develops with viral infections, including those that affect the upper respiratory tract. The main symptom of vestibular neuritis is a sharp headache, weakness, and possibly fever. Hearing acuity remains within the same limits.
- Meniere's disease is a rare disease that causes headaches, nausea, and vomiting. An increased amount of fluid forms and accumulates in the cavities of the inner ear and exerts additional pressure. The patient may experience symptoms such as impaired coordination of movements, memory lapses, deterioration or complete loss of hearing.
Diseases of the inner ear are very dangerous and can lead to complications if not treated promptly. Hearing loss and chronic headaches are common consequences of inflammation of the labyrinth. In addition, during infectious processes, there is a possibility of bacterial infection spreading to the tissue of the brain and its membranes, and the development of meningitis or encephalitis.
Normal Variation of Constipation
Constipation is a very common condition affecting the colon. It is characterized by difficulty passing stool or less frequent bowel movements. This is usually due to the fact that there is not enough fiber or the person does not drink enough liquids. Some medications can cause constipation, which causes pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 37.5.
The pain is variable but may resolve within a few days.
- Rarity: found everywhere.
- Top symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, constipation.
- Symptoms that always occur with normal changes in constipation: bloating, heaviness, dull pain in the abdomen.
- Symptoms that never occur with normal constipation:
vomit.
- Urgency: self-medication is possible.
What is low-grade fever
Low-grade fever is a slight increase in body temperature above normal. Previously, this term was used quite actively, including abroad (low-grade fever), but now it is not in the international classification of diseases. Officially, the condition associated with an increase in body temperature sounds like fever of unknown origin. To make this diagnosis, the following conditions must be met:
- body temperature 38.3 °C and above;
- the duration of the condition is more than three weeks;
- unclear diagnosis after inpatient examination within a week.
A person's body temperature fluctuates throughout the day and changes depending on circumstances. The body under normal conditions maintains it within a certain range, regardless of environmental changes. Temperatures are usually a little higher in the evening, around 8:00 pm, and lower in the early morning. This is circadian type variability. The temperature recorded in the armpit ranges in a healthy person from 35.2 °C to 37 °C.
Indicators of the so-called subfebrile temperature are in the range of 37.1 - 38 °C. These values may be enough for a person to feel unwell, lack of strength, lack of appetite, drowsiness and discomfort in the body. But often the temperature is not accompanied by other symptoms, and in some cases its increase is considered normal. It should be noted that all of these symptoms are nonspecific and can occur without connection with an increase in body temperature.
Unlike high fever, an increase in body temperature of 1–2 degrees is not dangerous for the body. Low-grade fever does not lead to deformation of protein molecules and cell death. The norms for the duration of this state of the body are determined by the doctor.
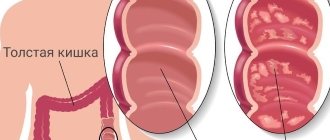
Intestinal inflammation (diverticulitis)
Diverticula are small pouches that bulge out through the colon. Diverticulitis is a condition in which the sacs become inflamed or infected, a process that can cause lower abdominal pain and fever, nausea, vomiting, chills, cramping and constipation.
It will likely recover within a few months or years without requiring surgery.
- Rarity: Rare.
- Top symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, constipation.
- Symptoms that never occur with intestinal inflammation (diverticulitis): pain below the ribs, pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Urgency: high.
In some cases, this pathology goes away without diarrhea in the child, the lower abdomen hurts and the temperature is 37 for several days.
Urinary tract infections
In women, the opening in the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body) is very close to the anus, and bacteria from the second can easily escape and travel through the urethra. These bacteria can infect the bladder and cause what is known as a urinary tract infection (UTI).
Symptoms most often disappear within 24-48 hours after starting treatment. The main one is that a person goes to the toilet often, the lower abdomen hurts and the temperature is 37 in men and women.
- Rarity: found everywhere.
- Top symptoms: abdominal cramps (stomach cramps), pelvic pain, sudden need to urinate, signs of urinary tract inflammation, changes in urine.
- Symptoms that always occur with a urinary tract infection: signs of urinary tract inflammation.
- Urgency: telephone call to the doctor or personal visit.
Where to get diagnosed and treated for flu and colds in Krasnoyarsk?
This can be done at the Medunion private medical clinic.
Is a child or an elderly person sick? Then do not wait to see a doctor, but simply call a specialist at home. It's not only fast, but also very convenient! The specialist will examine the patient in a familiar environment, prescribe tests, and prescribe the necessary treatment. And the nurse will take samples or vaccinate you.
Sign up for a medical appointment and take care of the health of your loved ones. You can do this in any way convenient for you - online or by phone on the website. The cost of an initial consultation with a doctor starts from 1100 rubles.
Ovulation pain or intermenstrual pain
Intermenstrual pain, also known as ovulation pain or mid-cycle pain, is a pulling and aching sensation in the abdomen that occurs around the time an egg is released from the ovary. Ovulation can sometimes cause some light vaginal bleeding, spotting, or brown discoloration of the blood. If a woman had pain in her lower abdomen and a temperature of 37.2, then it could be ovulation.
Since ovulation occurs monthly, you may experience this pain once a month.
- Rarity: found everywhere.
- Top symptoms: abdominal pain, last period about 2 weeks ago, vaginal bleeding, vaginal blood loss, pelvic pain.
- Symptoms that always occur with pain in the ovulation area: the last period was about 2 weeks ago.
- Urgency: self-medication.
Contraindications to the flu vaccine
- at least 6 months have not passed since the last vaccination;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic reactions;
- iron deficiency;
- diseases of the respiratory system in acute or chronic form;
- allergic reaction to chicken protein;
- heart failure;
- endocrine diseases;
- blood pathologies;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- severe renal failure;
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
To prevent flu and colds, follow a few simple rules:
- Strengthen your immune system. Exercise more often or give your body light exercise. Take a walk in the fresh air, this will saturate your lungs with oxygen.
- Avoid hypothermia. This occurs due to a sharp temperature change and the action of the air conditioner.
- Use antibacterial agents, especially during cold season.
- Eat a balanced diet. This will provide the body with the necessary microelements.
Ovarian cyst
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs in the ovarian tissue. This may be normal (an estimated 15% of women have no problems with these cysts after their menstrual cycle), infectious, or cancerous.
Most benign cysts resolve spontaneously, but some may be permanent. If there is pain in the lower abdomen and temperature, then this may indicate such a pathology.
- Rarity: Rare.
- Upper symptoms: bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, lower abdominal pain, lower back pain.
- Urgency: high.
Prevention of flu and colds
The most reliable way to prevent influenza is vaccination. The flu shot is effective, but does not provide long-term immune protection, so vaccination should be done annually. Regular flu vaccination increases the production of antibodies to the virus.
The vaccine has no side effects, and the improved composition protects against mutated strains of the virus. Timely vaccination prevents infection. Even if infected, the disease will be mild.
After getting a flu shot, your temperature may rise to 37.5℃, you may experience chills, sweating, a general feeling of weakness and poor appetite. Redness, slight swelling, itching and pain may be observed at the injection site. This is an indication that your body is developing immunity to the flu. After vaccination, it is strictly forbidden to visit a bathhouse/sauna, swim in open water, engage in tiring physical activity, or drink alcohol.
Pain in the ovaries
This pathology can lead to blood loss in both the ovary and the fallopian tube. When diagnosed, this condition is considered an emergency and requires immediate surgery.
Patients are usually discharged home within 24 hours after surgery in uncomplicated cases. The patient follows the surgeon 1 week after surgery, and additional follow-up is adjusted as needed.
- Rarity: Rare.
- Top symptoms: nausea or vomiting, mild abdominal pain, loss of appetite.
- Symptoms that never occur with ovarian torsion: diarrhea, pain under the ribs, mild abdominal pain.
- Urgency: high.
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive structures, such as the uterus, fallopian tube, ovary, and surrounding abdominal wall. It is usually caused by N. Gonorrhoeae or C. Trachomatis.
The prognosis for recovery after treatment within 3 days from the onset of symptoms is high (88% -100%). For those who have been hospitalized or are elderly, treatment may take longer.
- Rarity: found everywhere.
- Top symptoms: fever, abdominal pain or unusual vaginal discharge, nausea or vomiting, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain.
- Symptoms that always occur with pelvic inflammatory disease: fever, abdominal pain, or unusual vaginal discharge.
- Urgency: individual visit.
Pregnancy
In women of reproductive age, symptoms, including that there is a delay, pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 37, weight gain becomes obvious and nausea, indicate pregnancy.
- Rarity: found everywhere.
- Top symptoms: fatigue, nausea or vomiting, bloating, vaginal blood loss, vaginal bleeding.
- Symptoms that always occur during a possible pregnancy: missed period.
- Symptoms that never occur during possible pregnancy: painful urination, severe abdominal pain.
- Urgency: Symptoms will subside over time.
Pain in the lower right abdomen is always a cause of concern for patients, although it may resolve spontaneously, for example in the case of pain caused by gas. Most patients may never know the root cause of their pain, which ends on its own. Everyone needs to know their own body and be able to look out for warning signs that suggest there may be something more serious going on.
Home treatment
Home treatments:
- Rest: Some types of abdominal pain are temporary and may go away on their own if the patient calms down and relaxes a little.
- Hydration: Severe abdominal pain or related symptoms may make it difficult to eat and drink. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor your water intake to make sure your body is getting enough.
- Food: It is not recommended to eat heavy food when your stomach hurts. There is no need to rush into eating; you need to eat in small portions until you feel better.
Treatment with medical supplies
Professional procedures:
- Imaging testing and blood testing. Doctors may order imaging or other tests to help diagnose the cause of abdominal pain.
- Endoscopy: Doctors may use a special camera (scope) to look at the inside of the digestive tract.
- If there is dehydration, or the body cannot retain fluids, doctors replace lost volumes. You can also get certain electrolytes, such as potassium, if your levels are low.
- Medicines: You may be offered painkillers, anticancer drugs or antibiotics. Some causes of abdominal pain can be effectively treated with medications.
- Surgery: Some causes of abdominal pain require rapid response through surgery.
You should seek help immediately if you have:
- Abdominal pain that begins centrally and moves to the lower right region.
- Sudden onset of severe abdominal pain.
- Severe abdominal pain is worsened by light touch or small movement.
- Inability to retain fluids for long periods.
- Heat.
- Recent abdominal surgery.
- Severe confusion, dizziness, or loss of consciousness.
- If you are elderly or have a serious illness.
- Pregnancy or the likelihood of it occurring.
How are colds and flu treated?
Hospital mode
The first thing the doctor will prescribe for such a disease is bed rest. Carrying an illness on your feet is extremely dangerous for both you and those around you. The influenza virus is highly contagious. Everyone you come into contact with will also get sick. You, in turn, risk getting a bacterial complication of the flu.
It is also necessary to adhere to a certain diet: try to drink as much warm drink as possible (herbal teas, milk with honey, berry fruit drinks, water), do not eat heavy fried foods. If you or your child suffering from a disease does not want to eat, there is no need to force it. Decreased appetite is a common symptom of the disease.
Drug therapy
First of all, antiviral drugs are prescribed for influenza and colds , which inhibit the vital activity and spread of the virus inside the human body. Such medications are prescribed for severe or moderate severity of the disease. The drug is most effective in the first days of the disease.
Antipyretics are used only at very high temperatures to help the body cope with the fever and prevent complications from developing. These drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Antibiotics for colds are taken only after a doctor's prescription. When, against the background of the development of influenza, an acute bacterial infection appears that the body cannot cope with on its own. Important: if you start taking antibiotics, the course cannot be interrupted.
Antihistamines relieve the unpleasant consequences of the disease, such as redness, itching, lacrimation, swelling of the nasopharynx and nasal discharge.
Immunostimulants help strengthen the body's defenses and help the immune system independently repel attacks from viruses and bacteria.
Drops for a runny nose relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, allow the nose to breathe normally and prevent the occurrence of microbial complications. However, the drug should not be taken for more than 5 days, because there is a risk of chronic swelling of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of abdominal pain with fever
Sudden abdominal pain, even without fever, is already alarming, and if there is a fever, it requires immediate medical advice. In this case, the delay can be fatal. For symptoms such as abdominal pain and high temperature, it is necessary to keep the patient calm; if vomiting occurs, turn your head to the side so that he does not suffocate from vomiting, and call an ambulance.
The patient is not recommended to give anesthetic drugs (so as not to distort the clinical picture) and never apply a heating pad to the abdomen. Even if the temperature is not critical, and the syndrome is mild and tolerable, it is better not to allow the patient to go to the clinic, but to call a doctor at home.
Fever and abdominal pain are just symptoms of a very long list of diseases that will be treated depending on the diagnosis.
If necessary, the patient immediately undergoes surgery; in doubtful cases, the patient will be placed under observation in a surgical hospital for several days. If severe pathologies are detected, the patient is hospitalized in the appropriate department; in milder cases, outpatient treatment is prescribed.
How is the flu different from a cold?
- Onset of the disease . Flu symptoms develop rapidly. And it progresses quickly in the body.
The source of influenza is sick people during the incubation period or the height of the disease. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets when sneezing, coughing, shaking hands, and also through dirty food (it has not been thermally processed enough). The infection begins to manifest itself in the period from 4 hours to 3 days. In general, the disease goes away in 5-7 days.
A cold is a disease of the body associated with hypothermia. A cold develops gradually, progressively, and painful symptoms appear within a day or two. It is usually easy to treat. But in advanced forms it can develop into other more severe diseases.
- Temperature . With the flu, there is a high body temperature, which can reach 39-40 degrees. With a cold, the temperature usually remains at the standard level.
- Weakness . People with a cold often ignore symptoms such as cough and runny nose, thinking that it will “go away on its own” with time. A cold can be carried on your feet, although it is undesirable.
But during the flu, the patient immediately realizes that he is sick; often he cannot even have the strength to get out of bed. Aches all over the body, severe headache, fever - these symptoms cannot be confused with anything else.
- Cough and runny nose . During the flu, these symptoms do not appear immediately (only after 5 days), and may not appear at all. With a cold, a debilitating cough, sore throat when swallowing and a runny nose are noted.
- Red eyes, itching and watery eyes . The picture of the flu is complemented by red eyes, severe weakness, fever, and bursting blood vessels in the nose. And in severe forms, even convulsions, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, and lack of air are possible.
When you have a cold, your eyes do not turn red or water, and if this happens, it is more likely to indicate a bacterial infection.