The article was checked by gastroenterologist and endoscopist Kondrashova E.A. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, the cause of abdominal pain will be quickly identified and successful treatment will be carried out. At your service are qualified doctors - consultants of various profiles, surgeons and gastroenterologists on a single base; modern examination technologies and expert diagnostic equipment (endoscopy, endo-ultrasound, CT and MRI, all laboratory diagnostics, etc.). An individual and comprehensive approach to each patient ensures high efficiency of conservative and surgical treatment of the entire spectrum of diseases accompanied by abdominal pain.
The localization of abdominal pain does not always directly indicate a diseased organ. Pain in many diseases of the digestive system can spread to other areas of the abdomen.
Acute abdominal pain that leaves the patient in distress requires quick decisions because it may indicate an “abdominal catastrophe,” a condition requiring immediate surgical intervention.
Pathological causes of bloating
There are a large number of causes that lead to bloating. They can be divided depending on the system involved in the pathological process. However, they may differ depending on age and gender, since in females the cause of bloating is often diseases of the pelvic organs.
Hard belly in women
In addition to the problems of a hard abdomen, characteristic of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, the condition can develop due to gynecological diseases. Problems with the digestive tract include:
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Stressful impact.
- Inflammatory process in the peritoneum.
Among the gynecological problems leading to the appearance of a hard abdomen are:
- Initial stages of pregnancy. Immediately after fertilization, the level of progesterone in the body increases. It leads to a slowdown in intestinal motility, as well as a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Impaired implantation of the fertilized egg may not manifest itself clinically until the integrity of the fallopian tube or ovary is disrupted. The disease occurs suddenly and is accompanied by the appearance of a board-shaped abdomen, as well as sharp pain. When bleeding occurs, hemodynamic disturbances occur with a drop in blood pressure, as well as the appearance of cold sticky sweat and impaired consciousness.
- Ovarian apoplexy or disruption of the integrity of the cyst. Sexual intercourse, heavy physical work, and sports can provoke sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which quickly spreads to other parts. In this case, the patient’s abdomen becomes hard and the condition gradually worsens.
During pregnancy
The appearance of a hard belly during pregnancy may indicate various reasons, these include not only problems with digestion, but also problems with the organs of the reproductive system.
Problems with the intestines, accompanied by bloating and the appearance of a hard abdomen, may indicate a violation of its motility caused by excess production of progesterone. In later stages, problems are associated with an increase in the size of the uterus and problems with the movement of intestinal contents through its sections.
What types of discomfort in the lower abdomen are there?
There are a variety of organs located in the lower abdomen. These are the intestines, uterus, ovaries, bladder and so on. Unpleasant sensations in this area can occur both due to natural physiological reasons and as a result of the development of various diseases and pathologies.
Some unpleasant manifestations may be diagnostic criteria that can be used to suggest a particular diagnosis. There are several main types of such sensations:
- heaviness;
- feeling of fullness;
- Blunt pain;
- acute pain;
- cutting pain;
- feeling of fullness;
- feeling of stiffness and tension.
Unpleasant sensations can be localized on the right, left and center. Sometimes the pain is wandering and radiates to the groin, lower back, legs and other parts of the body.
It is also important whether the pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by additional symptoms. These include:
- temperature;
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain during urination;
- difficulty with bowel movements;
- severe diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- discharge from the genitals;
- menstrual irregularities.
Any additional symptoms should be reported to the doctor during the examination. Based on this data, he will be able to differentiate the diagnosis, prescribe examinations and select treatment.
The lower abdomen is hard, what could it be?
There are a large number of reasons that lead to the appearance of a hard belly. Among them, there are two main groups: physiological and pathological. Physiological conditions include overstrain of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall after playing sports or prolonged laughter, as well as crying. In women, the stomach may become hard in the first days of the menstrual cycle.
Among the pathological conditions, it is necessary to highlight the main ones. These include:
The main reasons for the feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen
Unpleasant sensations can be based on both natural and pathological processes. In women, heaviness in the lower abdomen is often associated with the menstrual cycle or pregnancy. Why is this happening?
- Unpleasant sensations and heaviness can occur during ovulation, when the follicle bursts and the egg is released from it. The pain in this case is dull and localized in the area of the ovaries.
- On the eve of menstruation, hormonal activity and spasms of the uterine muscles can lead to unpleasant and painful sensations.
- During pregnancy, heaviness and pain can occur for two reasons: during implantation of the embryo and due to the growth of the uterus.
However, most often the feeling of fullness and heaviness is associated with one or another pathology. Most often, pain in the lower abdomen is associated with the following diseases:
| Cause | Description |
| dysmenorrhea | pain may occur several days before menstruation; polycystic disease, in which pain is localized in the ovary area and may be accompanied by menstrual irregularities |
| endometriosis | the endometrium grows causing discomfort in the lower abdomen and is accompanied by discharge |
| inflammation of the bladder and ureters | accompanied by nagging pain, frequent urge to urinate and pain associated with it |
| inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs | discharge and other symptoms are also recorded |
| malignant and benign neoplasms | may be accompanied by weight loss, fever and increased sweating |
| constipation | the accumulation of feces in the rectum can cause pain, a feeling of fullness and discomfort |
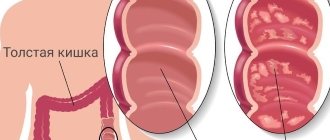
| inflammatory and parasitic processes in the intestines | pain can be caused both by the source of inflammation itself and by stool disorders and increased gas formation |
| colic in the intestines | spasm causes severe acute pain of various localizations |
| perforation processes in the intestines | intestinal contents enter the abdominal cavity and cause pain, inflammation and even life-threatening |
| inflammation of appendicitis | accompanied by severe pain, nausea, vomiting and fever |
| adhesions in the intestines | occur against the background of abdominal surgery and inflammatory processes |
In some cases, heaviness in the abdomen may be associated with overeating. Discomfort occurs during long feasts or long periods of hunger, when a person does not feel full and eats until pain appears.
It is very difficult to determine the cause of pain on your own, so you should definitely consult a doctor to understand what is causing the unpleasant symptoms.
Cherepenko Lyudmila Vikentievna
doctor - therapist • doctor - cardiologist
If other symptoms are added to the unpleasant sensations, we advise you to consult with our doctors to find the cause of the disease and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Online consultation
First aid
First aid for the appearance of a hard abdomen is carried out only after identifying the possible cause or provoking factors. If symptoms develop due to overeating, it is necessary to provide the patient with rest and use drugs that replace natural pancreatic hormones, as well as enterosorbents. If possible, it is recommended to have a bowel movement, as this will make you feel better.
During menstruation, it is allowed to use medications that have an analgesic or anti-inflammatory effect. First aid for pathological causes of a hard abdomen includes:
- Providing the patient with complete rest and taking a comfortable position that relieves pain.
- Limit the use of medicines, food, and water. This can lead not only to a deterioration in well-being, but also to difficulty in further diagnosis.
- Calling an ambulance.
- Freeing the stomach from constricting clothing.
- Applying a heating pad with ice or any cold object to the area of greatest pain. This will reduce possible blood loss and also slow down the growth of the pathogenic form with a decrease in the severity of pain.
Grodno Regional Children's Clinical Hospital
Details Published January 31, 2022
A gastric bezoar (stomach stone) is a foreign body that forms in the stomach after repeated ingestion of indigestible substances (hair, coarse plant fibers, etc.).
Reasons for the formation of bezoars:
- Violation of food culture. Poor chewing of coarse, fibrous heavy foods, swallowing fruit seeds
- Stomach diseases. Insufficient secretion of hydrochloric acid, slow evacuation of contents into the duodenum, excessive proliferation of Candida fungi
- Mental disorders . Neuroses, trichotillomania (pulling out and eating one's own hair), schizophrenia, mental retardation can cause uncontrolled absorption of inedible substances (plasticine, glue, hair) in large quantities.
- Stomach operations. Previous surgical interventions (gastric resection, vagotomy) contribute to a decrease in secretory function, digestive disorders, and the accumulation of indigestible products.
The mechanism of bezoar formation: a foreign body, entering the body with food or as a result of bad habits, is not digested for various reasons and is stored in the stomach. With repeated use, the substrate increases in size. The action of gastric juice enzymes causes compaction and hardening of the foreign body. As a result, a bezoar is formed, which grows and can fill the entire volume of the organ.
Classification:
Bezoars can have different composition and consistency (loose, dense, hard).
Depending on the origin, the following types of gastric calculi are distinguished:
- Phytobezoars . They make up up to 70% of all bezoars. Formed by eating the skins, seeds, peels of berries and fruits (persimmons, cherries, grapes, figs, etc.). The stones have different consistencies, a foul odor, and are dark green or brown in color.
- Trichobezoars . They are formed when hair regularly enters the stomach. More often they occur in neurosis-like conditions and mental disorders with an irresistible urge to bite off hair.
- Stibobesoars . Formed by frequent consumption of fatty foods of animal origin (lard, lamb). Once in the stomach, food is transformed and compacted to form fatty stones.
- Shellacobesoars . They occur when using inedible products of chemical origin (varnish, paint) as food. When entering the stomach, substances interact with water and precipitate.
- Stones of embryonic origin . Formed during the stage of intrauterine development. They are dermoid cysts or gastric teratoma.
- Lactobezoars . They are formed in newborns, especially premature children, who are fed with an artificial mixture with a high content of lactose and casein.
There are rare types of stomach stones:
Pyxobesoars are formed by consuming resin or pitch.
Hemobezoars are formed during prolonged ingestion of blood in patients with nasal and esophageal bleeding, portal hypertension.
Drug-induced bezoars can occur when taking poorly soluble and insoluble drugs (aluminum hydroxide, activated carbon).
Symptoms:
The rate of formation of gastric stones is different, ranging from several days to tens of years.
If the size of the stone is small, there are no symptoms of the disease.
As the bezoar increases, painful sensations appear in the epigastric region , a feeling of heaviness in the stomach that is not associated with food intake. Patients note rapid satiety with a small amount of food, nausea, vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, loss of appetite and body weight . Frequent belching occurs .
Subsequently, the pain increases. a feeling of a foreign body in the abdomen , which can change location. In people of asthenic physique, a dense formation in the epigastric region is sometimes palpated.
Diagnostics:
- 1. Fibrogastroscopy (main diagnostic method)
- 2. To diagnose the disease, an additional ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
Treatment
Treatment of the disease depends on the type, consistency, composition of the stone and concomitant pathology. Conservative treatment methods are effective for bezoars of soft and medium consistency, often of plant origin. Warm alkaline solutions based on soda, mineral water, and proteolytic enzymes are prescribed orally. Patients are advised to follow a gentle diet with limited fruits, meat and fatty foods. Stones of low density and relatively small sizes are removed endoscopically . When performing fibrogastroscopy, depending on the size and density, the bezoar is either completely removed or mechanically fragmented, and then, if possible, removed from the stomach. If it is technically impossible to perform this manipulation, then surgical treatment - laparotomy (incision of the abdominal wall), gastrotomy (incision of the stomach wall) and removal of the tumor from the stomach.
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease and late diagnosis can lead to a number of serious complications:
Prolonged stay of a bezoar in the stomach leads to the formation of bedsores of the organ wall. Local blood circulation is disrupted, ischemia and necrosis develop with the formation of ulcerations. Erosion and gastric ulcers can lead to perforation of the muscle layer and the occurrence of peritonitis and sepsis. A rare complication is intestinal obstruction. When a bezoar stone enters the small intestine and blocks the intestinal lumen, obstructive intestinal obstruction develops.
Diagnostics and prevention
The diagnosis is based on an external examination and conversation with the patient. The doctor finds out the main complaints, their dynamics, as well as the conditions under which they arise. It is important to clarify your medical history about previous illnesses and medications taken. The skin is examined, the abdomen is palpated, and blood pressure is measured. Based on the data obtained, additional research methods are prescribed, which include:
- A general clinical analysis of blood and urine, if possible, examines feces for dysbacteriosis or hidden blood, as well as worm eggs.
- Study of gastric juice. Abdominal pain can develop due to impaired digestive function caused by a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice and dysbiosis.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
- X-ray.
- FGDS.
- Colonoscopy.
If there is a marked deterioration in health and difficulties in making a diagnosis, diagnostic laparoscopy and laparotomy are performed.
The main preventive measures include:
- Maintaining an active lifestyle.
- Following a diet with limited consumption of foods containing simple carbohydrates, as well as fatty, spicy and smoked foods.
- Elimination of overeating.
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Compliance with recommendations for the treatment and prevention of chronic, previously identified diseases.
- Regular diagnostics of the body.
Treatment of diseases manifested by abdominal pain
Based on the diagnostic results, the consultant doctor clarifies the diagnosis and develops a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include:
- drug therapy,
- dietary food,
- modern techniques, for example, hemocorrection for autoimmune pathologies (autoimmune hepatitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis),
- surgical care of any volume, including minimally invasive endoscopic, laparoscopic surgical operations, etc.
If you are worried about abdominal pain, contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. Competent specialists will give you an accurate diagnosis and provide effective treatment within the optimal time frame.
You can see prices for services